🧫 Canovas Lecture 2
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Polymorphisms in Genes
Definition
Polymorphisms = variations in DNA sequence between individuals
Location
Can occur within a gene (coding or regulatory regions) or outside genes
Effect
Some polymorphisms change how a gene works
Others have no effect and are used as markers
Use in QTL
Polymorphisms help identify genetic differences linked to traits
QTL Detection: Marker Genotyping
Genotyping
Genotype individuals at the marker locus to see which alleles they carry
Visualization
Develop a method to visualize DNA sequence
Use primer and enzyme combinations to target the sequence with polymorphisms
DNA is cleaved into fragments of different molecular weights to see differences
Challenge
Increase the number of loci tested while reducing cost per genotype
Genotyping by PCR
DNA Sequence Differences
Restriction endonuclease = enzyme that cuts DNA at a specific sequence
Differences in DNA sequences are coded as alleles
Process
PCR amplifies the DNA region of interest to see which alleles an individual has

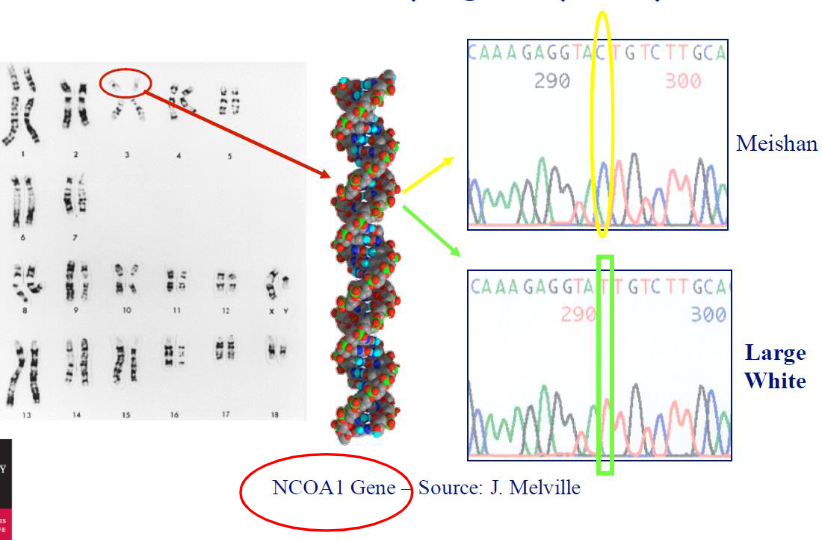
Genotyping by Sequencing Specific Genes/Markers
Purpose
Identify polymorphisms = differences in DNA sequence between individuals
Schematic
Shows how DNA from a specific gene or marker is sequenced to detect polymorphisms
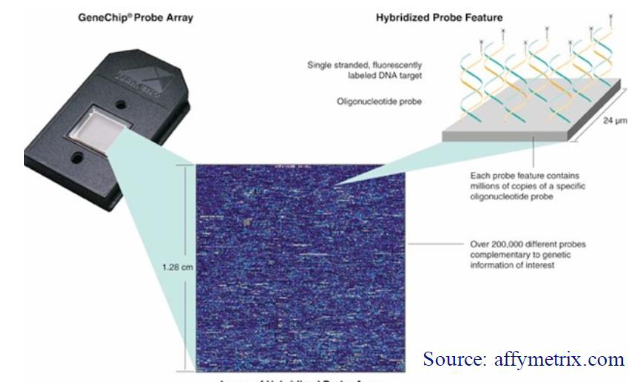
Genotyping by High Density Marker Panels
High Density Marker Panels
Use many markers = 50,000, 100,000, 500,000, or 1,000,000
Anonymous Marker Approach
Markers are "unimportant" polymorphisms used to locate QTL
Process
Photo-etch a glass slide, build Velcro-like tags
Tags "grab" matching animal DNA
Grabbed DNA lights up spots = shows genotype
Genotyping by Whole Genome Sequencing
Purpose
Genotype individuals by reading the entire DNA sequence of their genome
Sequence Example
Shows a section of DNA from an individual
Nucleotides (A, T, C, G) represent the genetic code
Process
Use a genome sequencer to read all DNA
Every nucleotide is detected to find polymorphisms and determine genotype
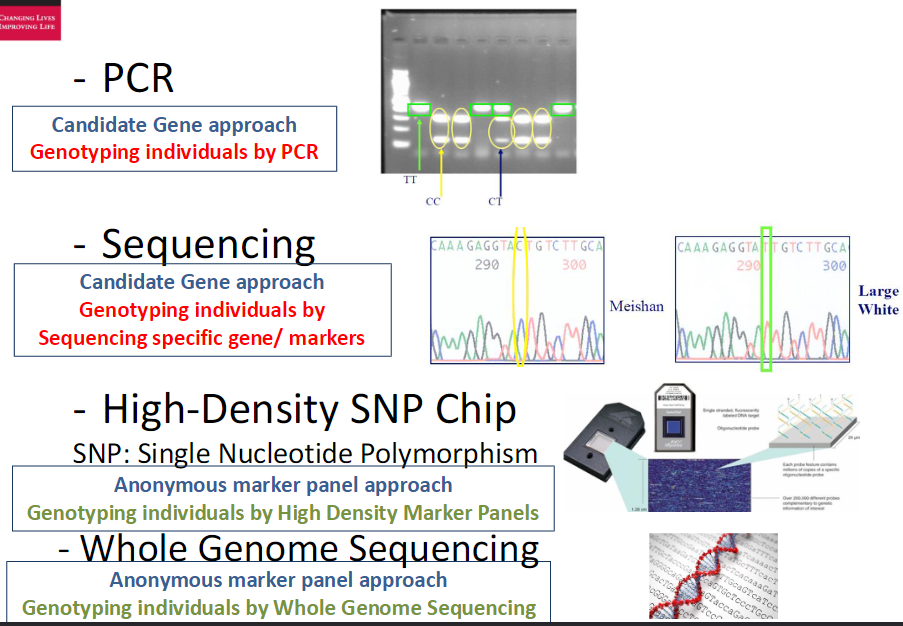
Summary of Genotyping Methods 1. Candidate Gene Approach and 2. Anonymous Marker Panel Approach
PCR
Candidate Gene approach = genotype individuals by PCR
Target specific gene and identify polymorphisms
Sequencing
Candidate Gene approach = sequence specific genes or markers
Whole Genome Sequencing = sequence entire genome
High-Density SNP Chip
Anonymous marker panel approach = genotype individuals by High Density Marker Panels
SNP = Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
Summary
Candidate Gene approach → PCR or Sequencing specific genes/markers
Anonymous marker panel approach → High Density Marker Panels or Whole Genome Sequencing