Evidence based EXAM 1
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
cohort study
A type of OBSERVATIONAL/longitudinal study that follows a group of people over time to assess the effects of certain exposures or interventions on specific outcomes.
randomized control trial
An experimental study design where participants are RANDOMLY ASSIGNED to TREATMENT, either the intervention or a placebo, enabling comparison of outcomes between groups.
ecological study
A type of observational study that examines the relationships between exposure and outcome at the POPULATION or group level rather than individual level.
case control study
A form of OBSERVATIONAL study that compares individuals WITH a specific condition (cases) to those WITHOUT it (controls) to identify potential risk factors or causes.
case-report
A detailed report of the symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of an INDIVIDUAL patient, often used to highlight unusual or novel cases in clinical practice.
case series
A research study that collects and analyzes data from a GROUP of patients with a similar diagnosis or condition over a specific time period, providing insights into clinical trends and outcomes.
systematic review and meta-analysis
A COMPREHENSIVE survey of EXISTING studies on a specific topic, evaluating and summarizing findings, often combined with statistical analysis to derive a pooled estimate of effect.
narrative review
A type of literature review that summarizes and discusses findings from various studies on a specific topic without using a systematic approach, focusing on broad insights rather than quantitative analysis.
all or none study
ALL patients died BEFORE treatment was available, and SOME SURVIVE after; or SOME died BEFORE treatment was available, and NONE DIE after
yes (smoking)
what would 1 be labeled as
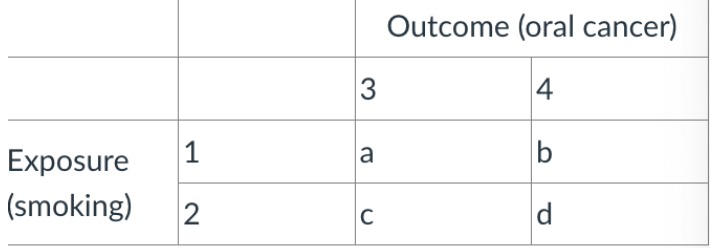
total number with oral cancer
what would the total of column 3 represent?
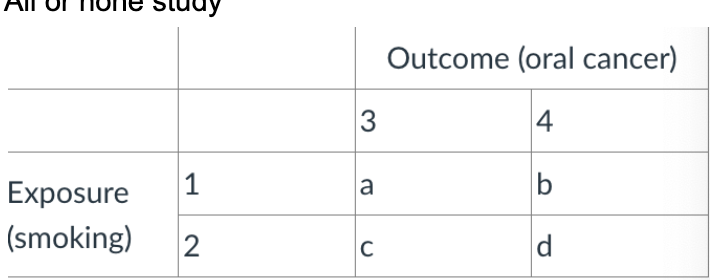
ab/cd
how would odds ratio be calculated from this table?
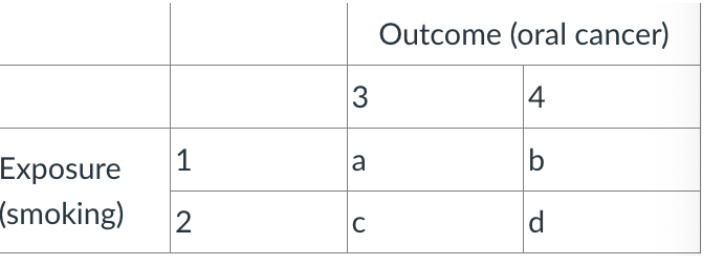
greater than 1
what odds ratio indicates statistical significance
95% confidence interval that goes below 1 (ex: 0.7-2.0)
What would make an odds ratio greater than 1 NOT significant
true end point
clinical outcome that accurately reflects TANGIBLE patient BENEFIT, such as how patient FEELS, FUNCTIONS, or SURVIVES
surrogate endpoint
a clinical outcome that is often measured earlier, that may PREDICT the EFFECT of a treatment but does not directly measure patient outcomes.
heuristics
enabling someone to discover or learn something for themselves
dunning-kruger effect
occurs when a persons LACK of knowledge or skill in a subject leads them to OVERESTIMATE their own competence.
anchoring bias
a cognitive bias that occurs when information and data that support initial impressions are prioritized, even when the first impressions are wrong
confirmation bias
the tendency to search for, interpret, and remember information that confirms one's preexisting beliefs.
surrogate
what type of endpoint would INCREASED bone DENSITY be?
true
what type of endpoint would DECREASED bone FRACTURE be?
intent to trrat population
The group of patients in a clinical trial who are included in the analysis based on the treatment they were assigned, REGARDLESS of whether they completed the treatment or adhered to the protocol.
intent-to-treat (ITT) analysis
gold standard analysis for randomized control trials
per-protocal population
The group of patients in a clinical trial who COMPLETE the study as originally planned, ADHERING to the assigned treatment protocols.
probability/risk
likelihood of an event happening
odds
likelihood of an event happening over the event not happening
relative risk
ratio of risk between two groups
number needed to treat
number of patient to treat to prervent one additional bad outcome, 1/risk differrence
exposure is beneficial
what does a odds ratio between 0 and 1 indicate
selection bias
bias resulting from the way i which study participants are selected from population of interest
misclassification bias
bias resulting from the way in which study participants are classified with respect to exposure or outcome
meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
what is the most trustworthy source of evidence in research
mendelian randomization
a method of using measured variation in genes of known function to examine casual effect of modifiable exposure on disease in observational studies
sensitivity
test’s ability to designate an individual WITH disease as POSITIVE (TRUE POSITIVE)
specificity
test’s ability to designate an individual WITHOUT disease as NEGATIVE (TURE NEGATIVE).
lead-time bias
occurs when a disease is detected by a screening at an earlier time that it would have been based on clinical appearance
length-time bias
an overestimation of survival duration due to relative excess of cases detected that are slowly progressing, leading to a misleadingly favorable prognosis.
stage migration bias
changes in criteria for assigning stages of disease over time, which can result in apparent improvements in survival rates without actual changes in the natural course of the disease.
linear no-threshold model
screening that has been shown to cause more harm than good, ex: low-dose radiation exposure, as there is no safe dose level below which no harm occurs.
preventative medicine
practice of recommending HEALTHY people adopt a lifestyle change or intervention to prevent disease and promote overall health. based on HIGH level evidence
curative medicine
practice of recommending intervention to symptomatic patient who seek care, can be based on LOW level evidence
animal studies and in-vitro (not in living being)
what are the least reliable studies
true
are unplanned visit/hospitalizations considered true or surrogate endpoint?
surrogate
would a decrease in number of ulcers over time be a true or surrogate endpoint
true
would reduction in patient pain be a true or surrogate endpoint
surrogate
would a reduction in oral lichen planus erosive area be a true or surrogate endpoint
surrogate
would lesion size reduction be surrogate or true endpoint
true
would pain intensity scored by patient be a true or surrogate endpoint
surrogate
would recurrence of lesion diagnosed by a medical professional be a true or surrogate endpoint.
surrogate
would the clinical response of a lesion be a true or surrogate endpoint
true
would a self-evaluation of symptoms by patient be a true or surrogate endpoint