Marketing Test 2
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
SWOT
Strengths- internal capabilities that help us reach objectives
Weaknesses- internal limitations that inererfere w/company ability to reach objectives
opportunities- external factors that you can use to your own advantage
Threats- current and emerging external factors that may challenge company performance
Difference between strengths/weaknesses and oppourtunities/threats
Strengths and Weaknesses- 4 P’s (product, price, place, promotion) and relate to the brand and internal
Opportunities and Threats- PEST, related to the product category or industry and external
Communication and coordination device
external and internal members of marketing activities have the same goal
Criterion for decision making
objectives help in the evaluation of creative
Evaluation tool
determine if advertising was successful or not
Vanity Metrics
registered users, downloads, and raw page views.
Things that are easily manipulated and do not correlate to numbers that really matter: active users, engagement
Key performance indicator (KPI)
Indicates progress to intended result
ex: Restaurant KPI is the return rate
ex: clothing- fitting room conversion- how many people try on clothes
Top of Funnel (TOFU)
Goal is to generate interest/awareness, initiate customer journey
ex: social media and influencer marketing
Middle of Funnel (MOFU)
Nurture and guide to be a qualified customer
ex: online classes, white papers and research reports
Bottom of Funnel (BOFU)
convert potential customers to actual customers
ex: coupons and discount codes
SMART Objectives
Specific- should state exactly what should be achieved
Measurable- capable of being measured
Achievable- should be realistic given the circumstances
Relevant- should be relevant for those responsible for them
Time-bound- time frame in mind
EX; The marketing objective is to increase the customer retention for ABC by 30% within the third quarter of this year
STP
Segmentation- Dividing a market into smaller segments with distinct needs, characteristics, or behavior that might require separate marketing strategies or mixes.
Targeting- The process of evaluating each market segment’s attractiveness and selecting one or more segments to enter
Positioning- Arranging for a market offering to occupy a clear, distinctive, and desirable place relative to competing products in the minds of target consumers
Need for segmentation and targeting: Market Differences
-different needs and wants
-different characteristics
Need for segmentation and targeting: Limited resources
-marketing budget
-time/distribution/media
-human resource
Needs of segmentation and targeting: Marketing efficency
-intense competition
-minimum input, maximum output
Type of Marketing segmentation: geographical
divides the market in to different geographical units such as nations, regions, states, counties, or cities
A company needs to pay attention to geographical differences in needs and wants
Types of Marketing segmentation: Demographic Segmentation
Divide the market into groups based on variables such as age, gender, family size, income, occupation, etc
Types of marketing segmentation: psychographic segmentation
involves dividing your market into segments based upon different personality traits, values, attitudes, interests, and lifestyles of consumers
Types of marketing segmentation: Behavioral segmentation
divides buyers into groups based on their knowledge, attitudes, uses, or responses to a product
Targeting
The process of evaluating each market segment’s attractiveness and selecting one or more segments to enter
6 types of targeting
1) size of opportunity
2) segment size
3) level of competition
4) segment growth
5) match with corporate objectives
6) corporate resources
Target market vs Target audience
Target market- market segment that a company chooses to focus its marketing resource
Target audience- selected group within the target market that is primary focus of a specific marketing campaign
Buyer persona
A detailed and semi-functional representation of an ideal customer
Importance of positioning
needs for differentiation
-how do different brands of water stick out
Triad of Brand Distinction
Brand is the only, the first, or the best
My brand is (only, first, best) in (place), for a (group), or with a (feature)
Systematic weighted sum method (6+4)
1) identify consideration set- know who you are competing with (Hilton v Mariott)
2) Draw Salient attitudes- price, location, service, customer reviews
3) measure importance of each attribute
4) evaluate each brand with each attribute- are you satisfied with the price of hilton
5) analyze data
6) strategic applications
improve evaluations for our weaknesses
attack a weak point of the competitor
modify the consumers perceptions of the importance of a salient attitude
suggest a new salient attribute
Source based positioning (9)
philosophy- “we love to see you smile” -McDonalds
Product attribute- “chocolate that melts in your mouth, not your hand” -m&m
Benefit- “For life, -Volvo”
Value- “15 minutes can save you 15% or more….”
Brand personality- “Just do it”
User image/life-style- “Silly rabbit, trix are for kids”
Time, place, Occassion- redbull gives you wings
competition- “the most trusted name in news” -CNN
product class- “Brush like a dentist” -Oral B
Product
Includes services, events, locations, persons, places, organizations, ideas
consumer vs industrial products
consumer- bought by final customer for personal consumption- Lipton, Dove, Mayo- different uses for each person
industrial- bought for further processing or conducting a business- machines/parts
Brand
name, term, sign, symbol, design that identifies the product/service of one seller/group of sellers that differentiates them from competitors
Brand equity
differential effect that knowing the brand name has on customer response to the product or its marketing
loyalty
awareness
quality perception
image association
Brand heiarchy (3)
Corporate brand- Nintendo
Individual brand- nintendo switch
modifier (pet name)- nintendo switch lite
brand extension
when a company uses one of its established brand names on a new product or new product category
instead od saying “Coca-Cola water” its “Dasani”
Advantages of using existing brand name (8- know roughly)
Facilitate new product acceptance
Reduce risk perceived by customers
Reduce costs of introductory and follow-up marketing programs
Avoid cost of developing a new brand
Allow for packaging and labeling efficiencies
(If successful) Enhance the parent brand image
Bring new customers into brand franchise and increase market coverage
Revitalize the brand
Disadvantages of using existing brand names
Can confuse or frustrate consumers
Can encounter retailer resistance
Can fail and hurt parent brand image
Can succeed but cannibalize sales of parent brand
Can succeed but diminish identification with any one category
Can succeed but hurt the image of parent brand
Can dilute brand meaning
Can forgo the chance to develop a new brand
Customer experience (CX)
is a totality of cognitive, affective, sensory, and behavioral consumer responses during all stages of the consumption process including pre-purchase, consumption, and post-purchase stages
customer success
a business method ensuring customers achieve success: their desired outcomes while using your product or service.
customer support
reactive, short-term focus, resolves product issues, not a revenue center
Service marketing: Intangibility
Cannot be seen, heard, tasted, or smelled before purchase
Service marketing: Inseparability
services cannot be separated from their providers
ex: going to the hair salon for a haircut
service marketing: perishability
service cannot be stored for later sale or use
Service marketing: variability
quality of service depends on who provides them and when, where, how
Internet of Things (IOT)
interconnection via the internet of computing devices embedded in everyday objects, enabling them to send and receive data
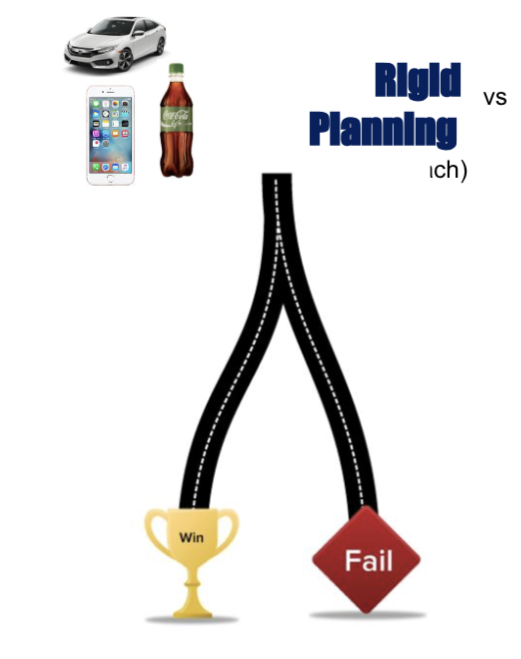
Rigid Planning
Traditional approach
Steps: 1) idea generation, 2) idea screening, 3) concept development and testing 4) test market, 5) commercialization
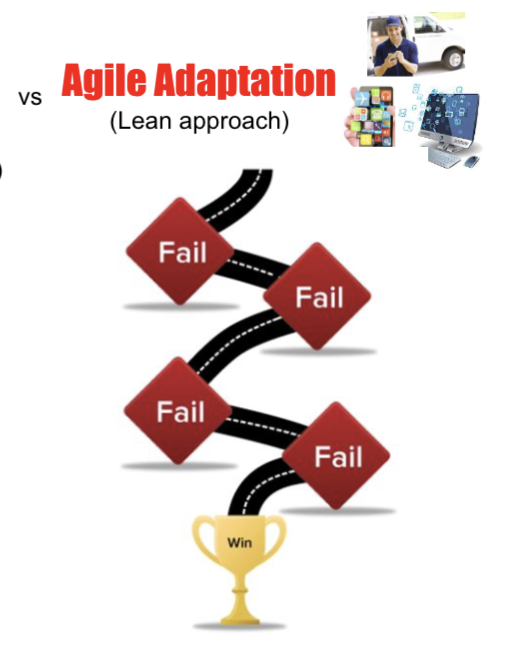
Agile Adaptation
Lean approach
When test market vs when firms may not test market in product development
When firms test market- new product, large investment, uncertainty or marketing program
When firms may not test market- simple line extension, copy of competitor product, low costs, management confidence
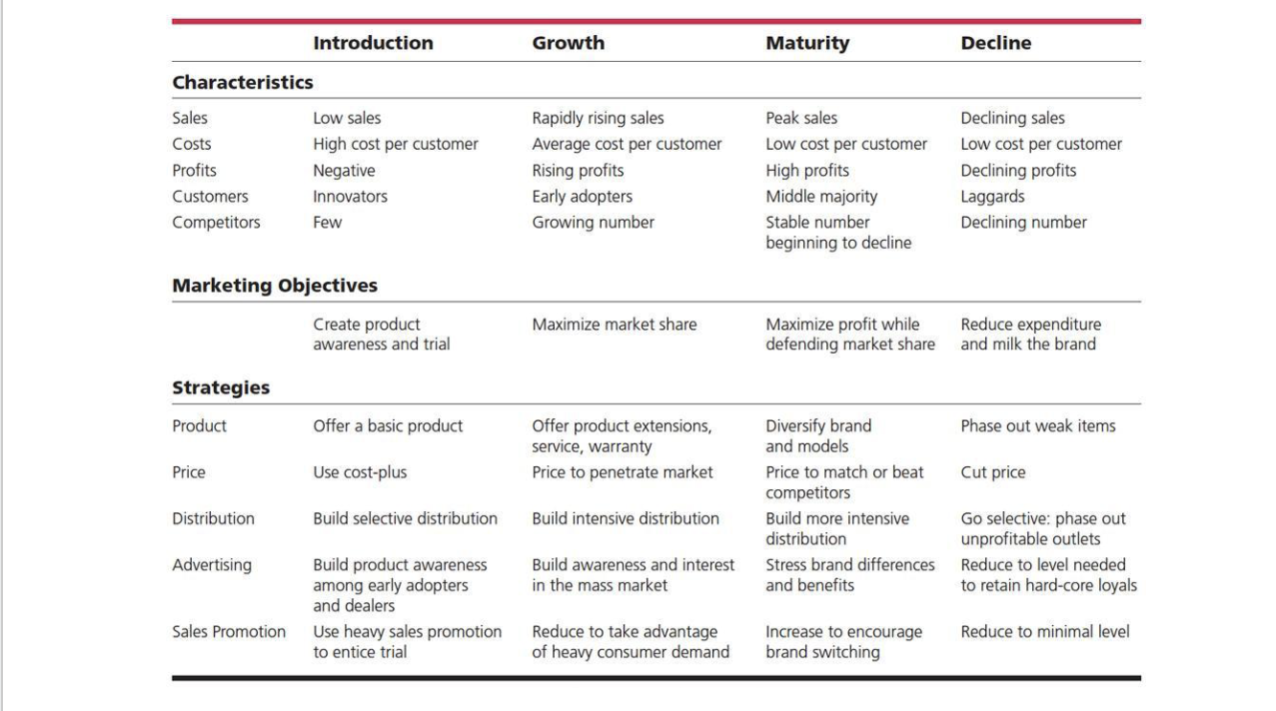
Product Life cycle (PLC)
5 stages/know graph
The process a product goes through from when it is first introduced into the market until it declines or is removed from the market
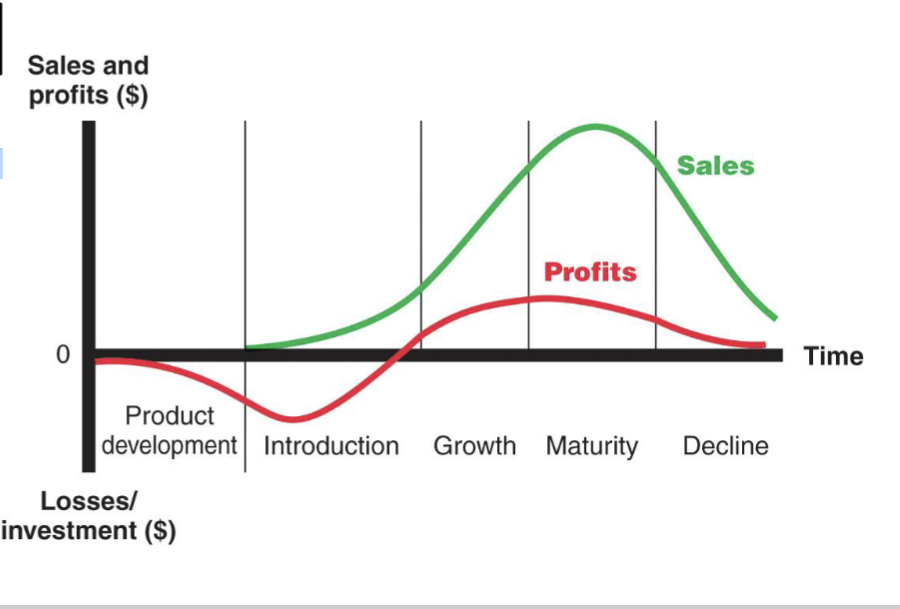
Characteristics, Marketing Objects, and strategies depending on each PLC
MVP
Minimum Value Product- product with just enough factors to gather validated learning about the product and its continued development
Ex: A startup wants to create a language learning app. Instead of building a full-fledged app with multiple languages, interactive games, speech recognition, and progress tracking, their MVP could be a basic web platform that offers simple vocabulary flashcards for just one language, like Spanish
Pivoting
Strategic shift in business model, target, audience, or marketing channels
if sales do better in Japan than the US, then shift to Japan
Tool-to-Network Shift
Business evolves from useful tool to a valuable network
instagram- originally for photo filters, and now social media
A/B Testing
method used to compare two versions of a webpage, email, ad, or marketing asset to determine which one performs better
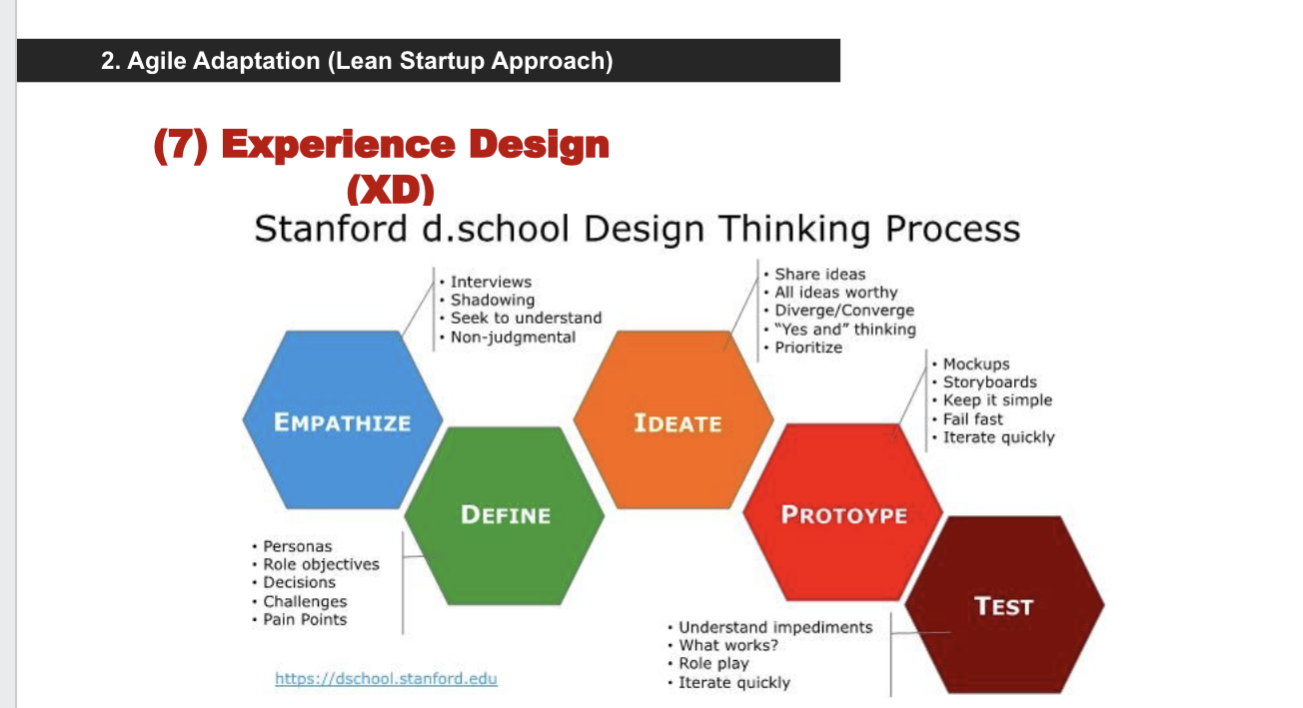
Experience design
create a frictionless experience for the customer anytime they interact w/ use a brand
change in a ketchup bottle