Legal studies wk 2 international law& institutions of internnational law
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What does international law regulate?
Relations between states and international institutions.
Define Private International Law.
Also called “conflict of laws,” it deals with cases within domestic systems involving foreign elements, determining which country’s law applies or which court should hear the case.
Define Public International Law
Governs relations between states and international bodies.
What is supranational law?
Law that transcends individual nations’ laws, binding them within certain regions (e.g. the EU), promoting cooperation and integration beyond borders.
What is sovereignty?
The authority of a state to govern itself without external interference.
What is “consent” in international law?
States agree voluntarily to be bound by treaties and rules.
What does “Pacta Sunt Servanda” mean?
States must keep and honour treaties they have signed, in good faith.
Define Customary International Law
Rules that become binding through long-standing and consistent practice accepted as law.
Define Treaties and Conventions
Written agreements between states that create binding legal obligations.
Define Diplomatic Immunity
Legal protection that prevents diplomats from being prosecuted or sued in their host country.
Define State Responsibility
States are legally responsible for breaches of international law and must make reparations
Why is international law necessary?
To prevent chaos, define state responsibilities, and ensure order in areas like human rights, trade, environment, and war.
What Does International Law Cover? name the areas
Human rights, disarmament, crime, refugees, migration, nationality, war conduct, environment, trade, and global commons like space and oceans
How Is International Law Different from Domestic Law?
Domestic law is hierarchical (law above individuals), while international law is horizontal—states are equal and must consent to be bound.
Key Domestic Law Features
Separate branches (legislature, executive, judiciary); vertical authority; law of subordination.
What is unique about the international legal system
No central authority; based on cooperation, consent, and mutual recognition between states
What are the sources of international law with eg for each
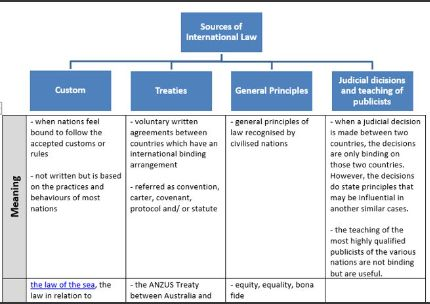
What are the sources of public international law
International conventions, custom,general pricniples of law , judicial decisons , writingof publicists
What are the key principles of international law in order

What is international law divided into, and define each term and what they do
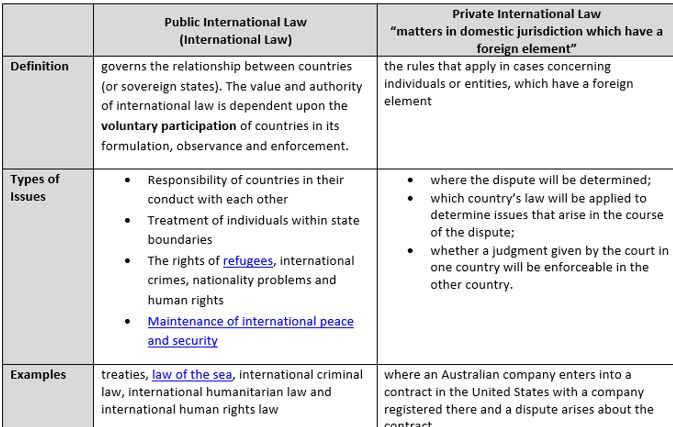
What does private international law cover

what does public international law cover

what does supranational law cover

What are the different types of international law?

What are the 5 organisation that develop apply and enforce international rules
United nations, international criminal coirt, world trade organnisation, interntional monetary funds, regional bodies
What is the UN
The main international organization for global cooperation, founded in 1945.
What does the UN do
A forum where all world nations can gather to discuss common problems and find shared solutions. It works to maintain international peace and security, promote human rights, and provide humanitarian aid.
What is Australias role in the UN
A founding member; advocates for international law, peacekeeping, and human rights; serves on UN bodies like the Security Council; and is a top financial contributor.
What is the International criinal court (ICC)
An independent international court located in The Hague
What does the International criminal court (ICC) do
Investigates and prosecutes individuals for the world's most serious crimes: genocide, war crimes, crimes against humanity, and the crime of aggression.
What is the international court of justice (ICJ)
The primary judicial organ of the United Nations.
What does the International court of justice (ICJ) do
Settles legal disputes between countries (contentious cases) and gives advisory opinions on legal questions from UN bodies. Its rulings in disputes are binding but enforcement relies on state cooperation.
What is the World trade organisation
WTO is the global international organization dealing with trade rules.
What does the world trade organisation do
The WTO facilitates and regulates international trade
What is the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and World bank
Two major international financial institutions.
What do the International Monetary Fund (IMF) & World Bank do
The IMF works to ensure global financial stability, provides policy advice, and gives emergency loans to countries. The World Bank focuses on long-term economic development and poverty reduction by providing funding and expertise for projects.