Anode
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
List the 4 functions of the anode assembly
serves as the target surface for the high-speed electrons from the cathode
the source of the x-ray photons
conducts the high voltage from the cathode
serves as the primary thermal conductor
What are the two types of anodes?
stationary
rotating
What type of anode is a block of tungsten imbedded in the 45 degree angled end of a copper rod?
stationary anode
A stationary anode is about how much surface area and where is it found?
about 1.5 cm x 1 cm
only found in dental equipment and old x-ray units
Which anode type provides a greater surface area?
rotating anode
Which anode type dissipates heat better?
rotating anode
________ anode = 4mm² (surface area)
________ anode = 1835 mm²
stationary
rotating
What anode is used in most modern x-ray units?
rotating anode
What is the composition of the rotating anode disk?
5 to 13 cm in diameter
made of molybdenum
What is the composition of the target focal track (rotating anode)?
tungsten-rhenium alloy
What is the composition of the anode disk backing (rotating anode)?
molybdenum or graphite
List 3 advantages of tungsten as target material
high melting point (tungsten = 3370 C)
high atomic number (tungsten = 74)
heat-conducting ability
What is the area of electron interaction called? (what else is it called?)
the target area (focus, focal point, focal spot, or focal track)
What is the area where x-rays are created?
the target area
The _______ focal spot is the physical area of the focal track that is impacted by the electrons.
actual
The _______ focal spot is the area of the focal spot that is projected out of tube toward the patient.
effective
What is the effective focal spot controlled by?
the size of the actual focal spot (length of the filament) and the anode target angle
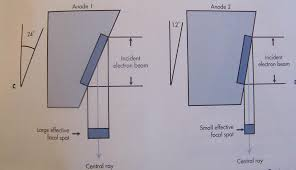
(Line Focus Principle)
When the target is angled (less than 45 degrees) the effective focal spot is _____ than the actual focal spot.
smaller
The smaller the angle, the _____ the effective focal spot.
smaller
What do anode angles range from?
What is the most common?
7 to 17 degrees
12 degrees
Because of the geometry of the angled anode target, the radiation intensity is greater on the ______ side.
cathode
How much can the intensity of the x-ray beam vary from anode to cathode?
45%
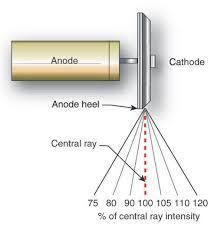
What is outside the glass envelope and consist of series of electromagnets that rotate the rotor?
stator
What is inside the glass envelope that revolves at 3,400 RPM?
rotor
A high speed rotor revolves at _____ RPM.
10,000