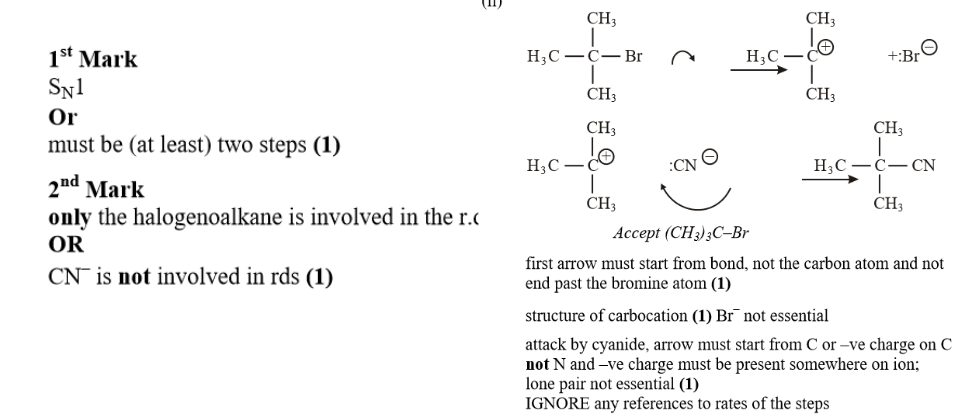
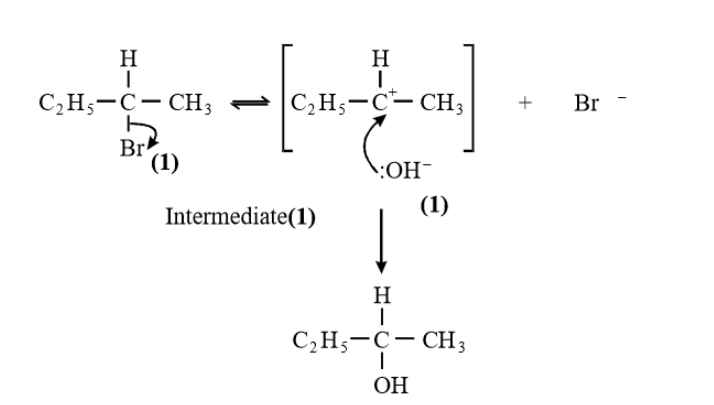
Kinetics II PMT
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Define the term rate of reaction
Change in concentration (of any reactant or product) per unit time. State what is being monitored (usually production of a product).
At a given instant, how could you calculate the rate of reaction?
Rate of reaction = change in concentration / change in time
How could you measure the rate of reaction experimentally (different methods)?
Use a colorimeter at suitable intervals if there is a colour change.
If gas is evolved, use a gas syringe to collect volume of gas evolved, or measure the change in mass of the reaction mixture.
Use titration to time how long it takes for the end-point to occur.
How can you determine the rate constant and rate expression for a reaction?
Only experimentally
What affects the value of the rate constant for a given reaction?
Temperature, nothing else
What is a generic rate expression and state what each term means.

Do species need to be in the chemical equation to be in the rate expression?
No - species in the chemical equation may be excluded and species not in the chemical equation e.g. catalysts, may be included.
Define the term order of a reaction with respect to a given product.
The power to which a species’ concentration is raised in the rate equation.
Define the term overall order of reaction.
The sum of the orders of reaction of all species in the rate expression e.g. x+y
How would you calculate the units of a rate constant?
Units of rate are moldm³s^(-1) and units of concentration are moldm^-³
Rearrange rate equation to get k=
Sub in units and cancel them out.
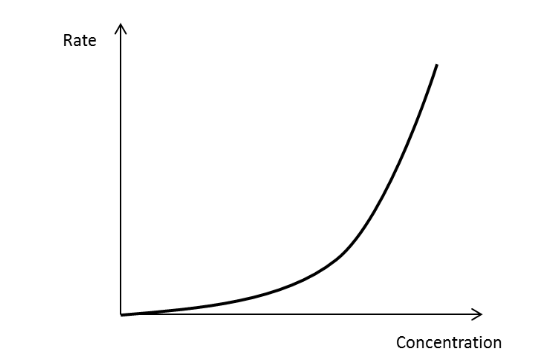
How would you draw a rate concentration graph?
Plot [A] against time, draw tangents at different values → draw secondary graph of rate against [A]
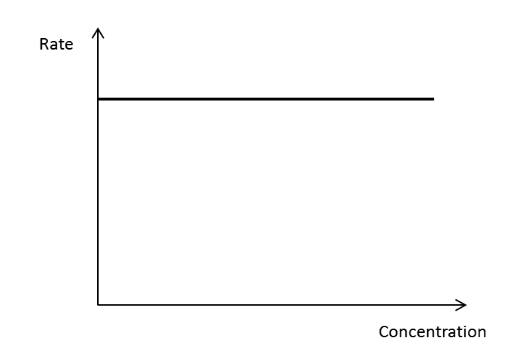
Draw a rate concentration graph for a zero order reactant
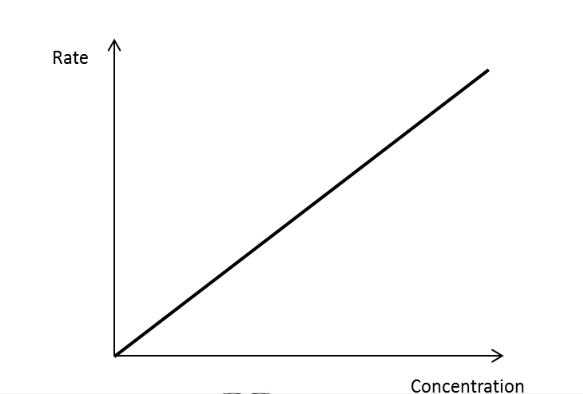
Draw a rate concentration graph for a first order reactant.
Draw a rate concentration graph from a second order reactant.
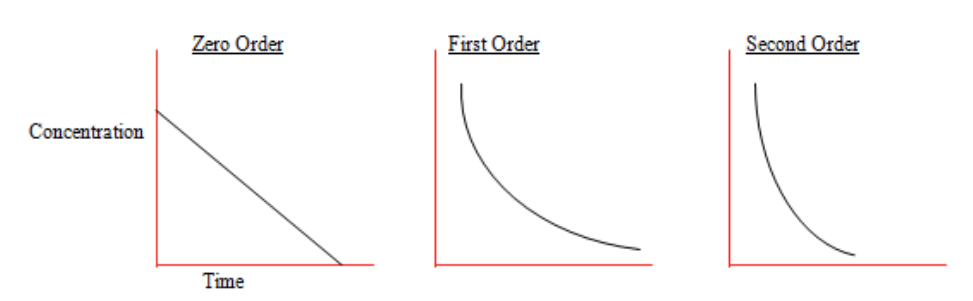
Draw the concentration time graphs for zero, first and second order reactants.
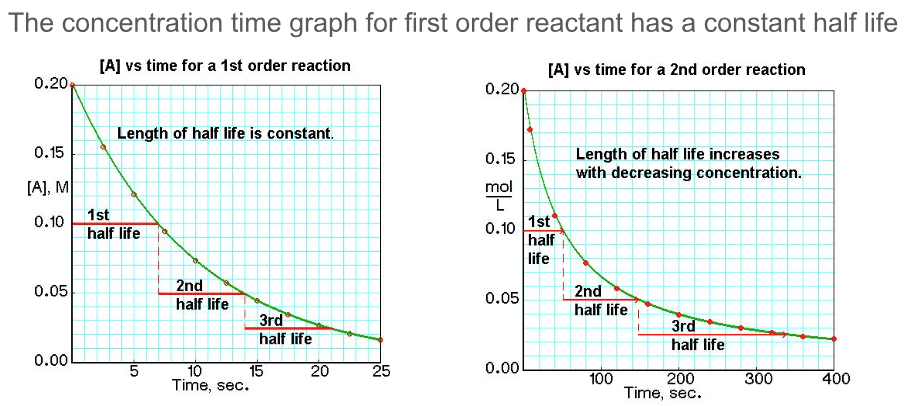
How can you tell the difference from first order and second order reactants from concentration time graphs?
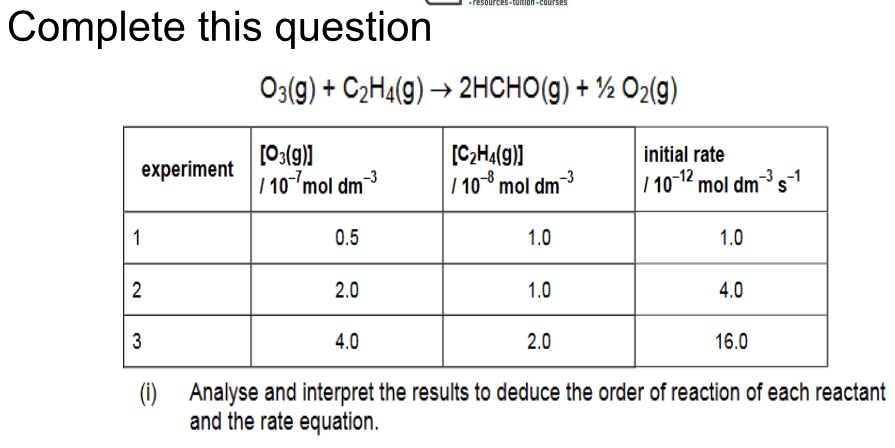
How could you find the rate expression using the initial rate method?
Do a series of experiments, during which you vary concentrations, so the concentration of just one reactant changes each time.
Plot a graph of concentration against time for each reactant and use a tangent at t=0 to find the initial rate of reaction.
Compare rates and concentrations between each experiment to find order of reactants and overall rate equation.
What must you add to react with the I2 as it is produced for an iodine clock reaction? (equation)

When does the starch turn a blue-back colour in an iodine clock reaction and why?
When all of the Na2S2O3 has been used up and so I2 is produced, which reacts with starch, leading to a blue-black colour.
How can you calculate the rate of reaction from the data from an iodine clock reaction?
Record time taken for colour change to occur. Use rate = 1/t. This is effectively the initial rate.
What is the effect of a 10K temperature increase on the rate of reaction, roughly?
Doubles rate of reaction
What is true of the half life of a first order reactant (concentration against time graph)?
Half life is constant

What is the Arrhenius equation? What does each term mean?

How can you convert the Arrhenius equation into a useful form for plotting a graph?

What is the rate-determining step?
The slowest step in a reaction mechanism, which determines the overall rate of reaction
How does the rate determining step link to the species involved in the rate expression?
Any species involved in the rate-determining step appears in the rate expression. Species only involved after the rate-determining step do not appear in the rate expression.