2.1 AB WASTES PROPERTIES
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
AGRICULTURAL WASTES
non-product outputs of production and processing of agricultural products that may contain material that can benefit man but whose economic values are less than the cost of collection, transportation, and processing for beneficial use.
Manure
is composed of animal feces and urine and may contain livestock bedding, additional water, and waste feed
PHYSICAL, CHEMICAL, BIOLOGICAL
TYPES OF WASTE
PHYSICAL WASTE
Observable, quantifiable measurable, sensible
CHEMICAL WASTE
Chemical composition is change based on reaction.
BIOLOGICAL WASTE
Organic component, microbial activities
INTENSIVE PROPERTY
Properties that does not depend on the amount of matter in a sample. E.g.. Color, odor, and texture.
EXTENSIVE PROPERTIES
Properties do depend on sample size. E.g. volume, mass, size, weight, length.
COLOR
Grayish brown or yellowish indicates fresh manure. Within the passage of time, as putrefaction starts it begins to get black.
ODOR
Fresh sewage is not offensive. Within 3 to 4 hours, all oxygen present in the sewage gets exhausted and starts emitting offensive odor by hydrogen sulfide gas
TEMPERATURE
affects the biological activity of bacteria present in manure and it also affects the solubility of gases in liquid form.
BULK DENSITY
Mass of sample per unit volume
CONSISTENCY
Can be obtained based on moisture content
MC ≥ 96% - liquid
90% < MC < 96% - slurry
80% < MC < 90% - semi-liquid
MC ≤ 80% - solid
MOISTURE CONTENT
The part of waste material removed by evaporation and drying (%
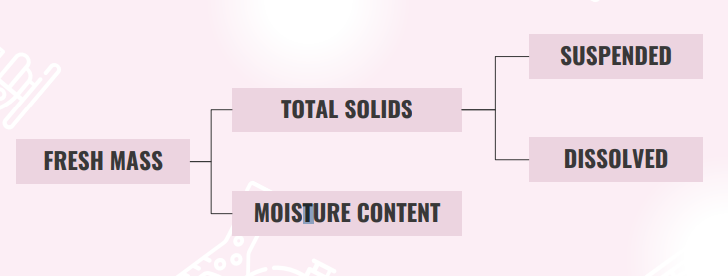
MASS COMPOSITION OF WASTE
TOTAL SOLIDS (TS)
All the matter that remains as residue upon evaporation at 103°C to 105°C.
TOTAL DISSOLVED SOLIDS (TDS)
Solid particles that can pass through a 2-micron filter. It include dissolved minerals and salts in the water.
TOTAL SUSPENDED SOLIDS (TSS)
These are larger particles (>2-micron). These are organic and inorganic materials such as sediment, algae, and other contaminants that affects the turbidity of wate
TDS DETERMINATION METHODS
GRAVIMETRIC METHOD
ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY
GRAVIMETRIC METHOD
Gravimetric means "by weighing". Total dissolved solids is weighed after water is boiled away
ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY
TDS meter measures how well the water conducts electricity. It then converts that to concentration of total dissolved solids
FIXED SOLIDS
These are the residue left in the vessel after a sample of solution has been ignited and heated to dryness at 550°C or greater.
VOLATILE SOLIDS
These are solids lost after ignition at 550°C or greater.

MASS COMPOSITION OF WASTE
ORGANIC MATTER
Compounds (commonly suspended solids) containing elements of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. It includes proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and oil.
NITROGEN
The total nitrogen includes ammonia (NH3), nitrite (NO2), nitrate (NH3) and organic nitrogen
PHOSPHORUS
The total phosphorus includes the elemental phosphorus and other soluble phosphorous compounds that leads to nutrient pollution to water together with nitrogen.
(BOD) Biochemical Oxygen Demand
(COD) Chemical Oxygen Demand
BIOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES
(BOD) Biochemical Oxygen Demand
The amount of oxygen required by microorganisms to break down organic waste at a certain temperature over a particular period of time
(COD) Chemical Oxygen Demand
Rapid laboratory procedure using chemical oxidants and heat to fully oxidize organic components of waste
BOD5
indicates the amount of oxygen which bacteria and other micro organisms consume in a water sample during the period of 5 days at a temperature of 20 °C to degrade the water contents aerobicall
is thus an indirect measure of the sum of all biodegradable organic substances in the water.
1-2 mg/L
Very Good: There will not be much organic matter present in the water supply.
3-5 mg/L
Fair: Moderately Clean
6-9 mg/L
Poor: Somewhat Polluted - Usually indicates that ,organic matter present and microorganisms are decomposing that waste.
100 mg/L or more
Very Poor: Very Polluted - Contains organic matter
BACTERIA
ALGAE
FUNGI
PROTOZOA
VIRUSES
COMMON MICROORGANISMS IN WASTE
BACTERIA
These includes living organisms present in wastes.
● Often unicellular ● Omnipresent ● Beneficial ● Pathogenic
Microorganisms are essential for treatment of waste in compost, biogas and lagoons.
PSYCHROPHILES MESOPHILES THERMOPHILES
TYPES OF BACTERIAL BASED ON OPERATIONAL TEMPERATURE
PSYCHROPHILES
grows best at low temperatures (-10°C – 20°C)
MESOPHILES
grows best in moderate temperature (20°C - 45°C)
THERMOPHILES
grows in extremely hot environments (32°C – 93°C)
PSEUDOMONA
SPHAEROTILUS
ZOOGLOEA
BDELLOVIBRIO
NITROSOMONAS
COLIFORM
NITROBACTER
ROTIFER
COMMON BACTERIA IN WASTEWATER
PSEUDOMONA
• Reduce Nitrate (NO3) to Nitrite (N2).
• Can be found in soil, marshes, water areas.
• Pathogenic
ZOOGLOEA
• Lower the BOD levels.
• Can be found in fresh waters (Polluted).
SPHAEROTILUS
• Helps to provide Nutrients and control DO concentration.
• Usually found water areas.
BDELLOVIBRIO
• Remove pathogens (Salmonella)
• Usually found in soil, sewage, and other terrestrial and aquatic habitats.
NITROSOMONAS
• Transform Ammonium (NH4) to Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2).
• Usually found in soil and water areas.
NITROBACTER
• Transform Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) to Nitrate (NO3)
• Usually found in soils, natural stones, fresh and salt water.
COLIFORM
• Commonly used as indicator potential presence of disease-causing bacteria in water/ pathogens.
• Usually found in soil, surface of water, and human skin.
• Some are harmless, some are pathogenic.
ROTIFER
• Grows when the of water has plenty of oxygen.
• It lowers the BOD levels, lowers the toxicity, and stabilizes the water system.
• Found in many types of water.
FUNGI
These are saprophytes which feeds and grows on dead organisms. It is important in decomposing organic matter to simple forms. Some fungi are single-celled, while others are multicellular. .
yeast
Single-celled fungi are called
hyphae (hypha)
Multicellular fungi have many — (singular: —), which are branching filaments.
ALGAE
It is a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms commonly classified as either microalgae or macroalgae.
It consumes nutrients in wastewater beneficial to oxidation ponds. For bodies of water, it may cause eutrophication which causes problems when decayed
PROTOZOA
a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. It includes paramecium, amoeba, and euglena.
Common species feed on bacteria so they help in the purification of treated waste water. Some of them are pathogenic.
VIRUSES
a major hazard to public health. Some viruses can live as long as 41 days in water and wastewater at 20 ºC. They cause lots of dangerous diseases.
Wastewater may contain adenovirus, HAV, HEV, poliovirus, and rotavirus.