AP Psychology: Topic 4.1 - Attribution Theory and Person Perception, AP Psychology: Topic 4.2 - Attitude Formation and Attitude Change, AP Psychology: Topic 4.3 - Psychology of Social Situations, AP Psychology: Topic 4.4 - Psychodynamic and Humanisti…
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
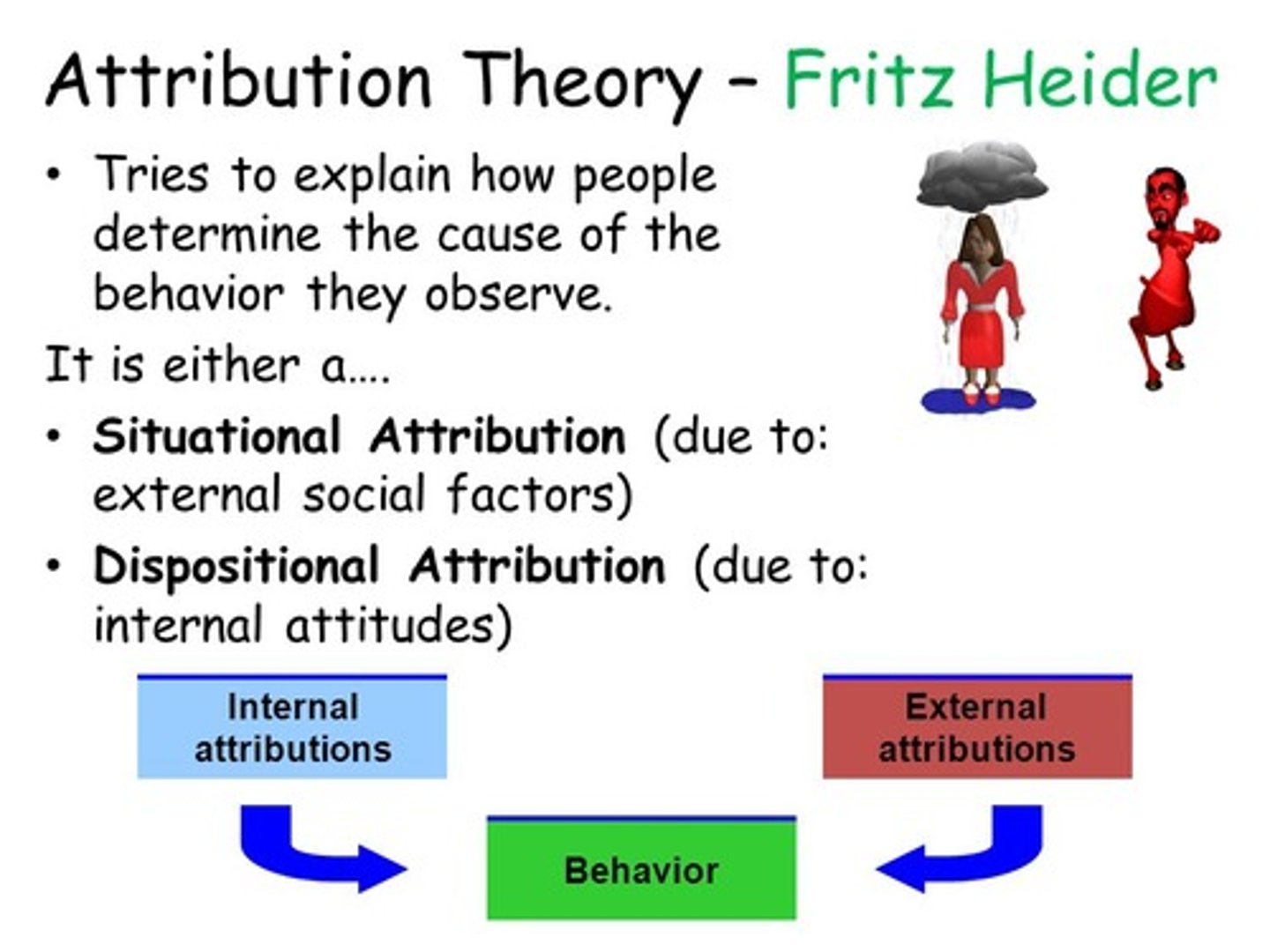
Attributions
refers to how individuals perceive the causes of everyday experience, as being either external to themselves or internal
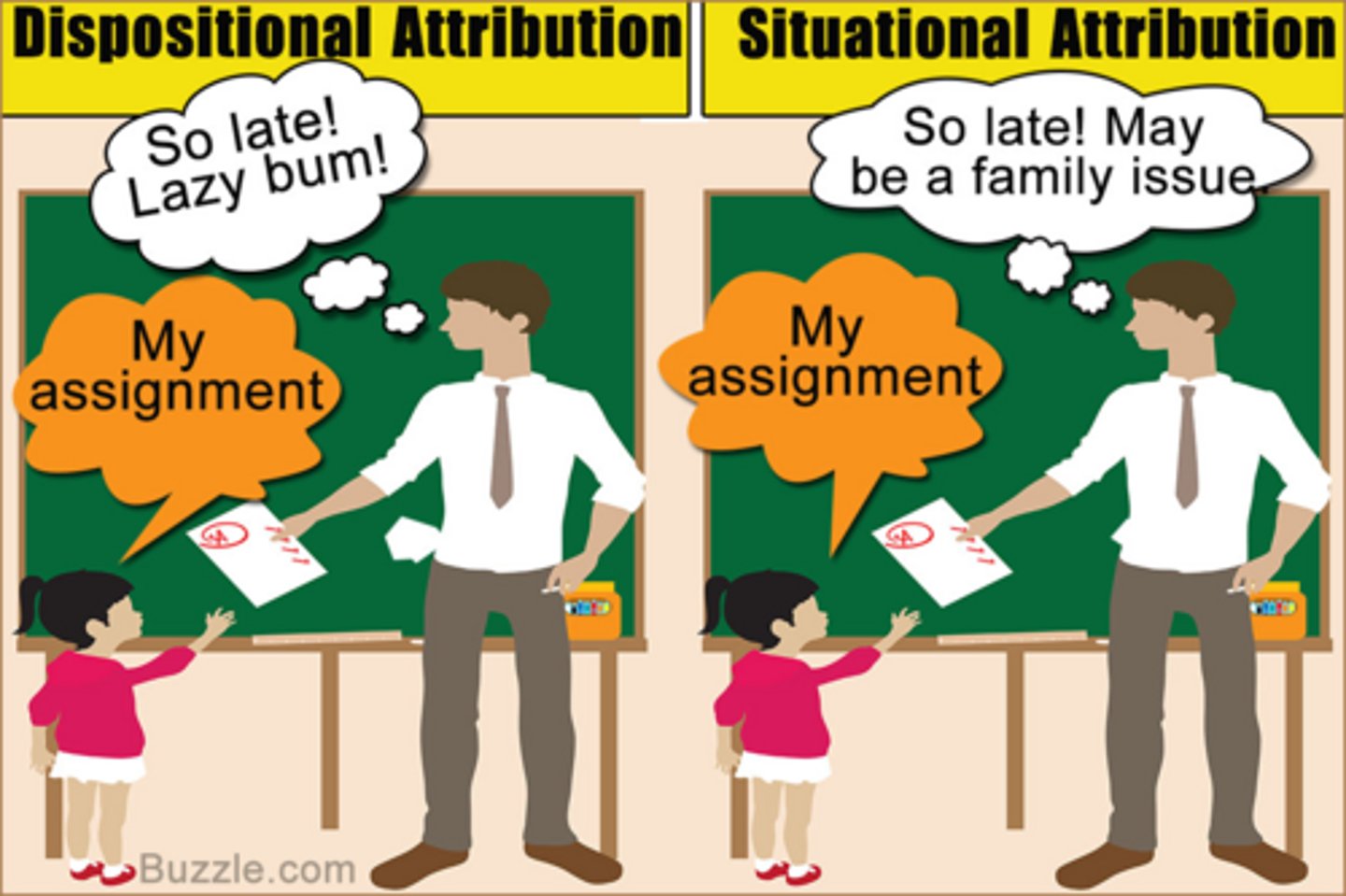
Dispositional attributions
refers to attributing someone's behavior to their personality or character

Situational attributions
when a person believes an event is caused by factors that are outside of themselves (external attribution)
Explanatory style
how people explain to themselves why they experience a particular event-- this can either be categorized as positive (optimistic) or negative (pessimistic)
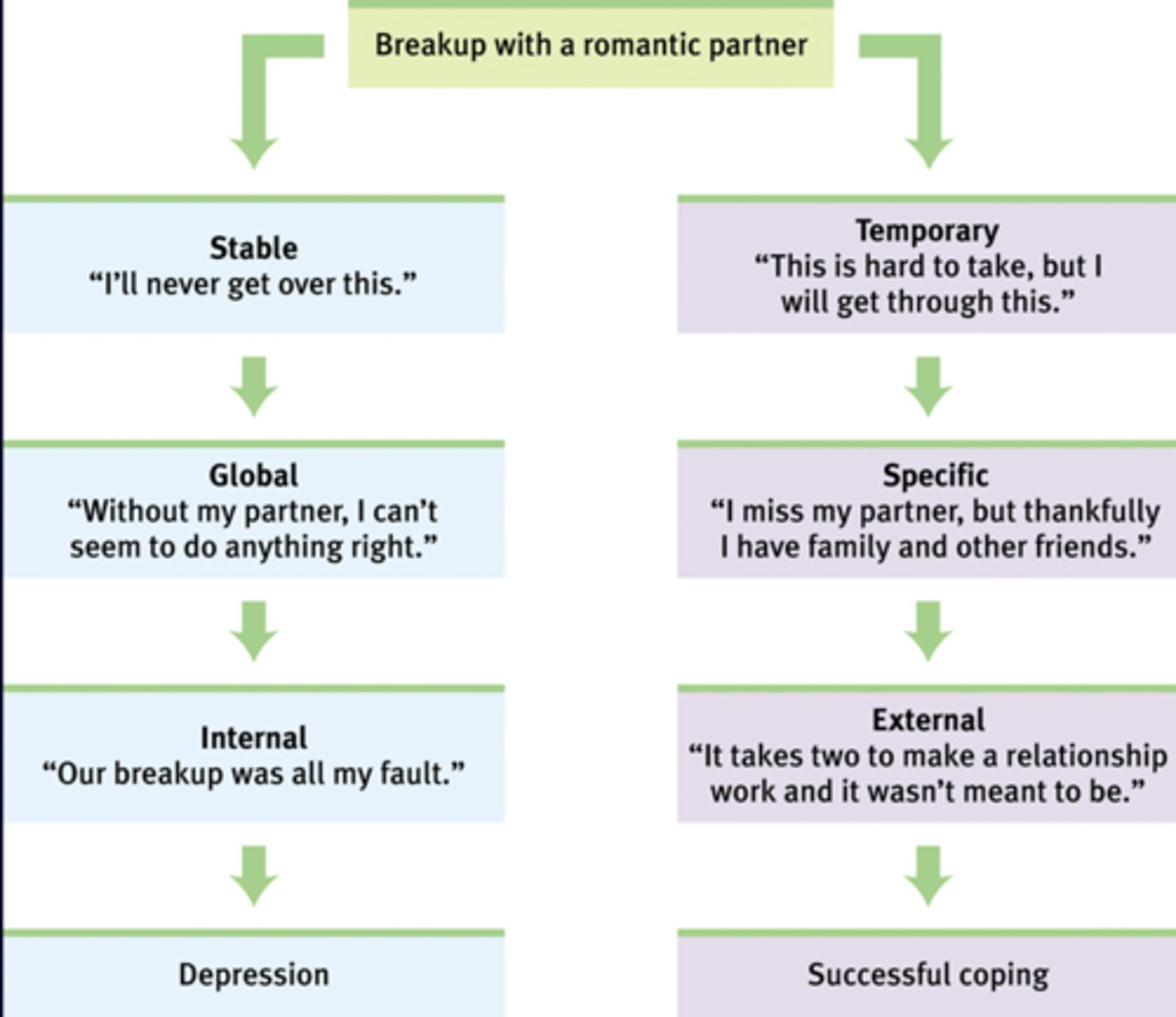
Optimistic explanatory style
the perspective that a challenging situation is temporary, there are aspects the person can control, and it's not their fault
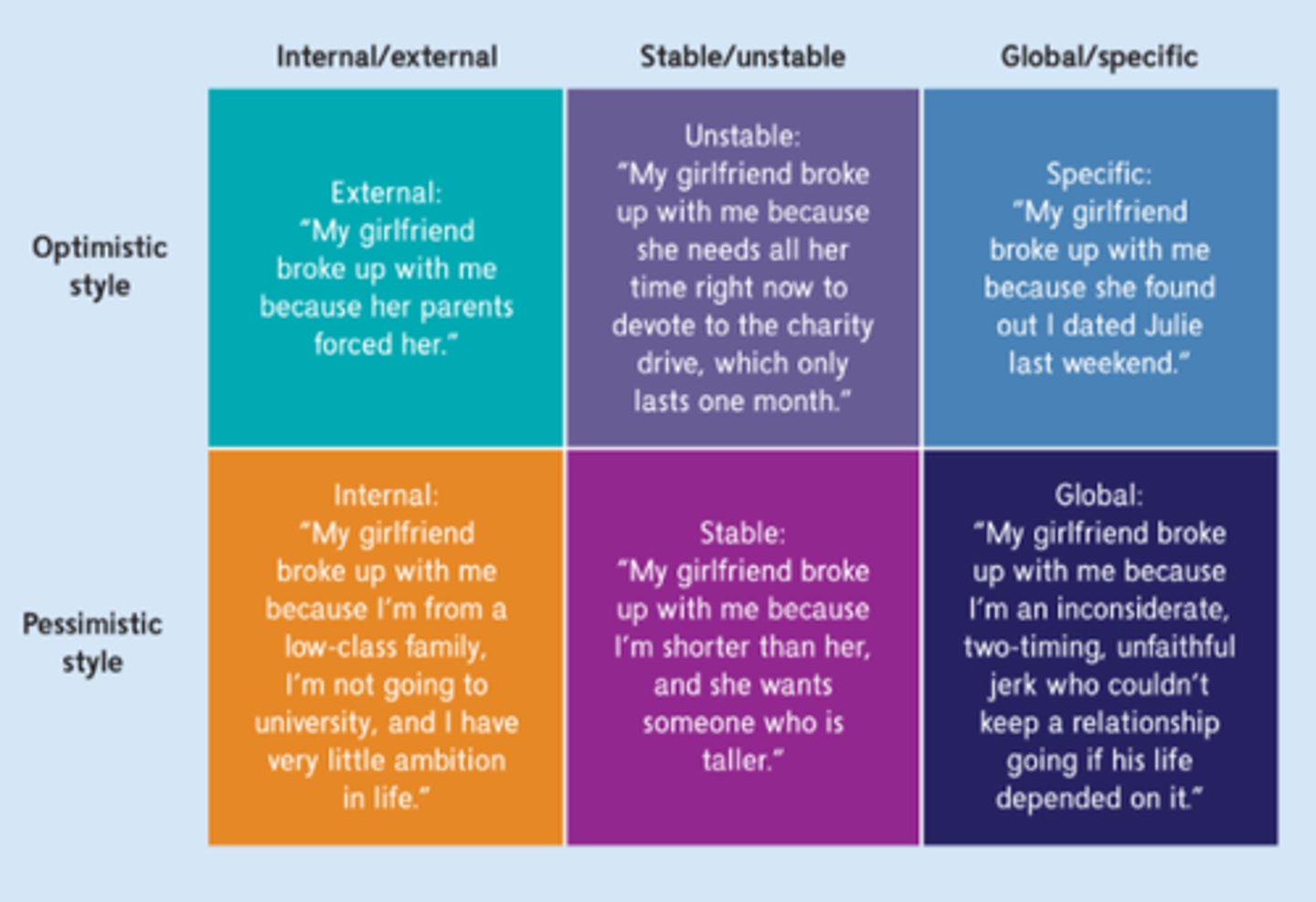
Pessimistic explanatory style
the tendency to explain bad events in a self-blaming manner, viewing the causes as global (affecting many aspects of life), stable (likely to happen again) and internal (caused by the self)

Fundamental attribution error
the tendency to overemphasize personal characteristics and ignore situational factors in judging others' behavior

Actor/observer bias
the tendency to attribute the behavior of others to internal causes, while attributing our own behavior to external causes

Self-serving bias
the tendency for people to take personal credit for success but blame failure on external factors

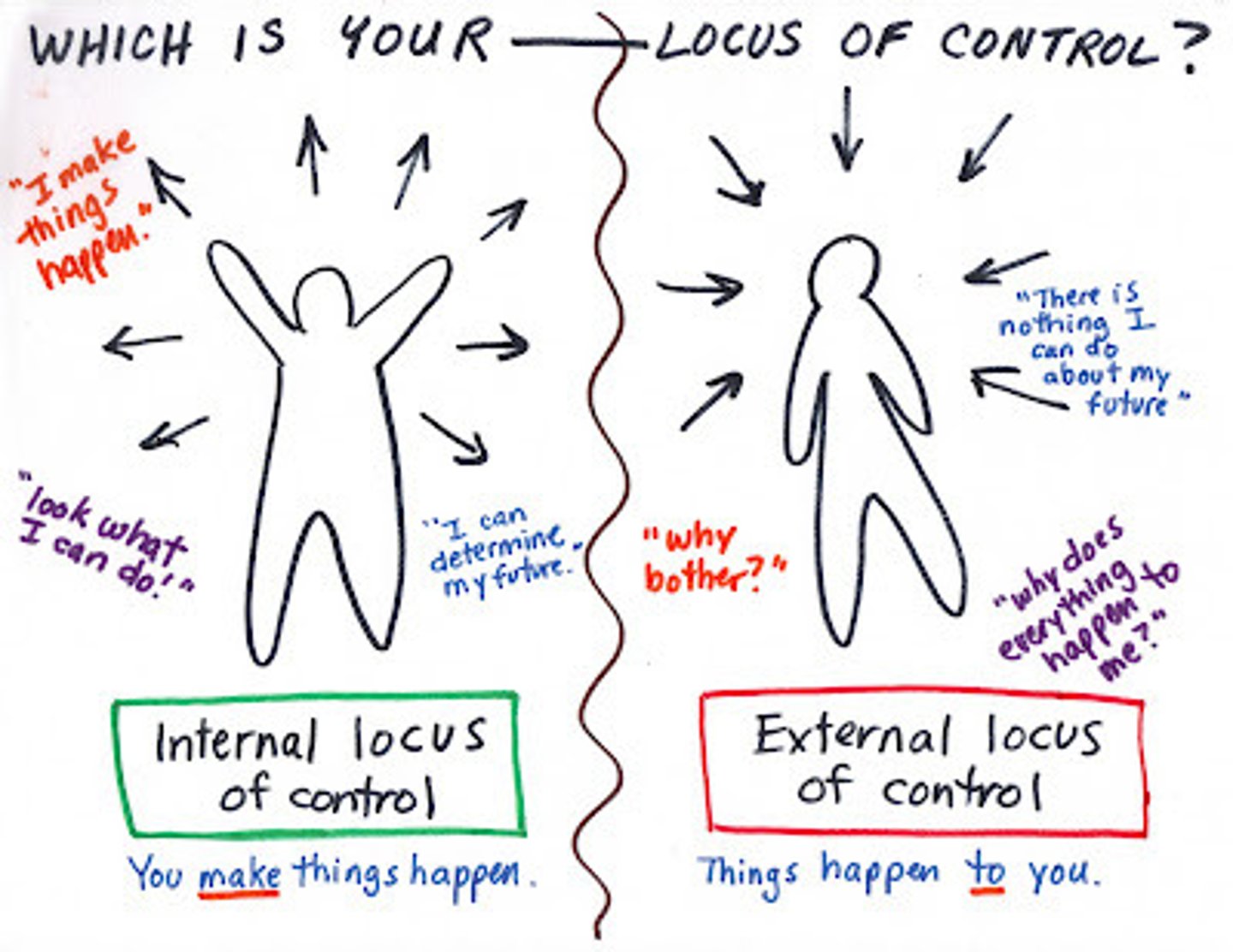
Internal locus of control
the belief that an individual has control over their own actions and outcomes in life

External locus of control
the perception that chance or outside forces beyond one's control determine their fate
Mere exposure effect
the tendency of people to like things or people they are exposed to more often rather than things they have only been exposed to a few times

Self-fulfilling prophecy
a prediction that motivates a person's behavior to cause itself to become true

Social comparison
when an individual evaluates their abilities and attitudes based on how they see themselves in comparison to others
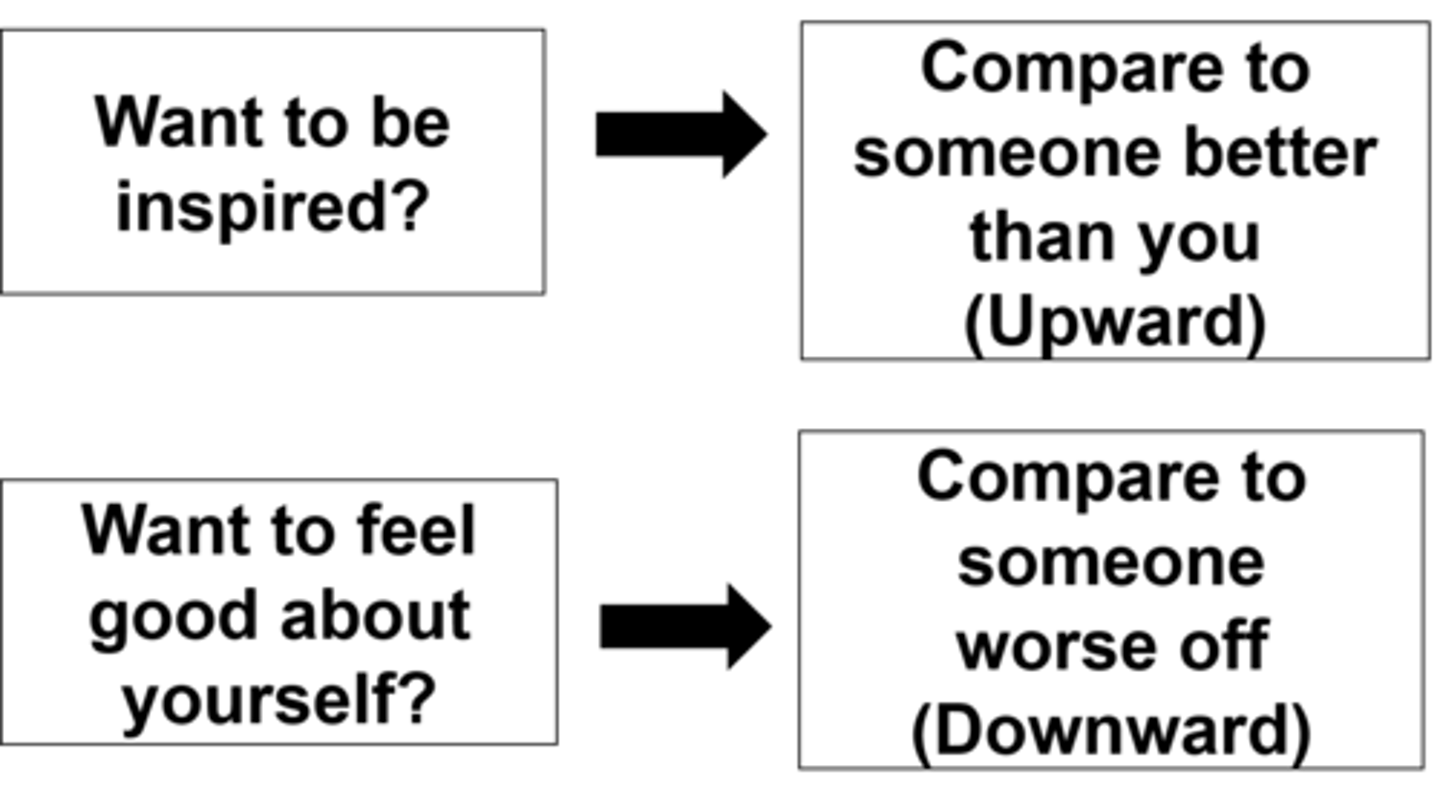
Upward social comparison
comparing oneself with someone who is perceived as being better in a particular area

Downward social comparison
comparing oneself with someone who is perceived as being worse in a particular area
Relative deprivation
A perception by an individual that they are not doing well (e.g., wealth, social status) in comparison to others

Stereotype
a widely held but fixed and oversimplified belief about a group of people or things

Prejudice
an unjustified judgment, opinion, or attitude directed toward certain people based on their membership in a particular group
Discrimination
unjustifiable negative behavior toward a group and its members

Implicit attitudes
attitudes that influence a person's feelings and behavior at an unconscious level
Ethnocentrism
the tendency to look at the world primarily from the perspective of one's own culture

Just-world phenomenon
the tendency for people to believe the world is just and that people get what they deserve and deserve what they get
Out-group homogeneity bias
the perception that individuals in an out-group are more similar (homogeneous) than they really are, as compared to members of one's in-group
In-group bias
the tendency to favor one's own group over other groups

Belief perseverance
the tendency to continue believing something even after the evidence supporting it has been contradicted

Confirmation bias
a tendency to search for information that supports one's preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence

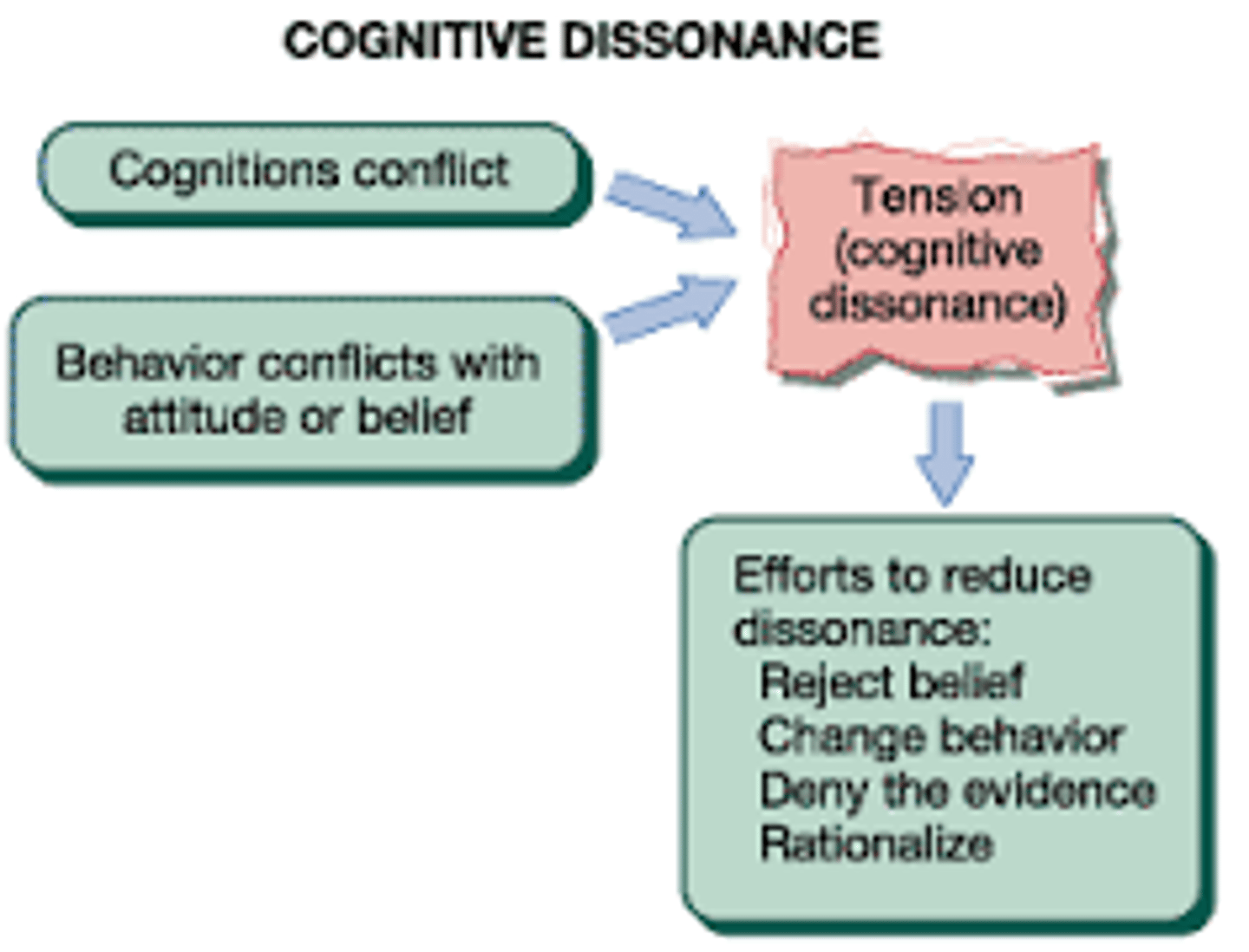
Cognitive dissonance
the discomfort a person feels when their beliefs are inconsistent with their actions
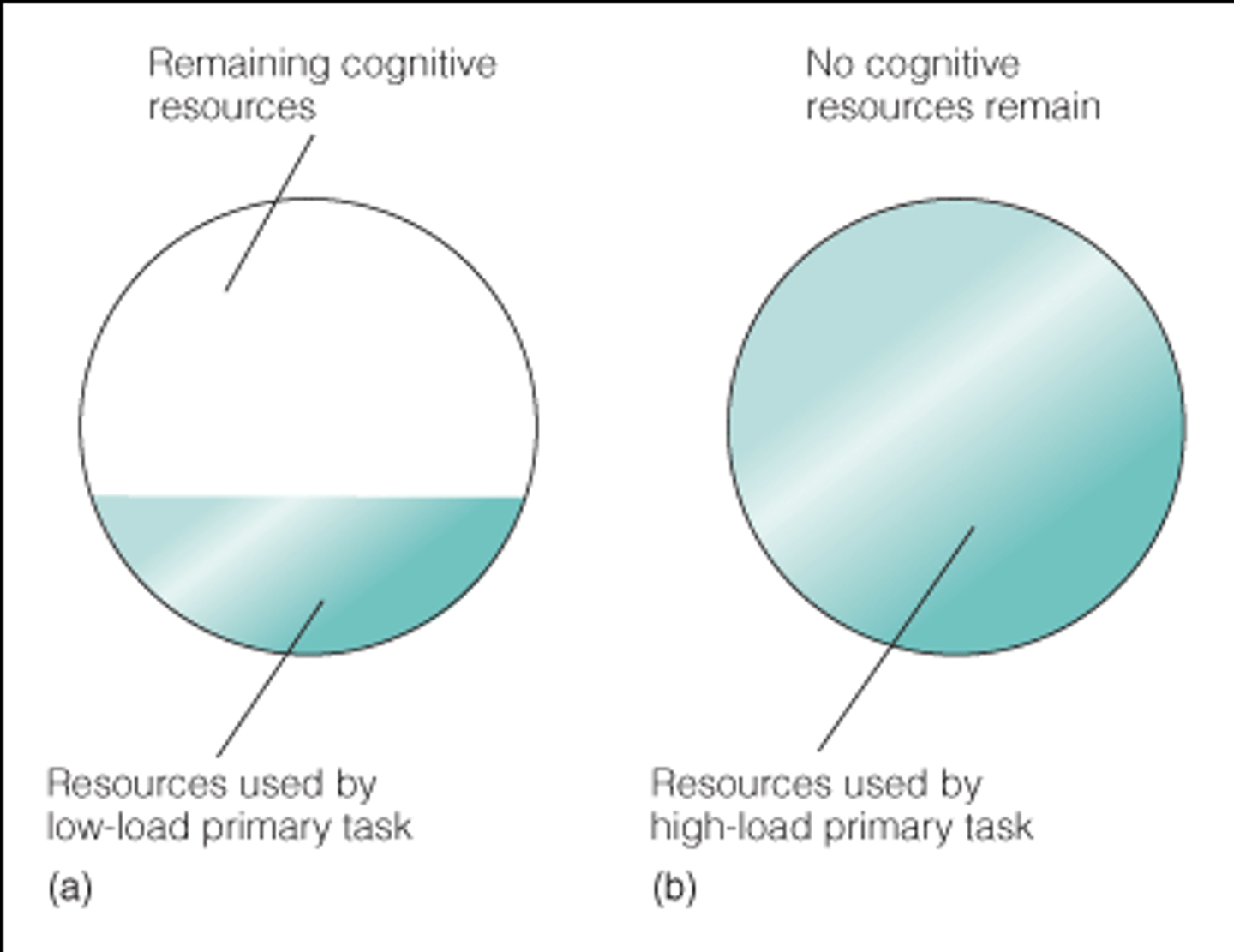
Cognitive load
the amount of information the working memory can process at any given time
Social norms
the unwritten rules and expectations that dictate how individuals should behave in a particular social group or society

Social influence theory
the idea that a person's behavior can be heavily influenced by the ideas and actions of others
Normative social influence
factors that influence a person to conform in order to be accepted and belong to a group

Informational social influence
when people conform because they believe the group is competent and has the correct information, particularly when the situation is ambiguous

Persuasion
strategies used to influence someone's attitudes, beliefs, behaviors, or decisions

Elaboration likelihood model (ELM)
analyzes the variables that cause long-term and short-term attitude changes to understand the effectiveness of persuasive messaging
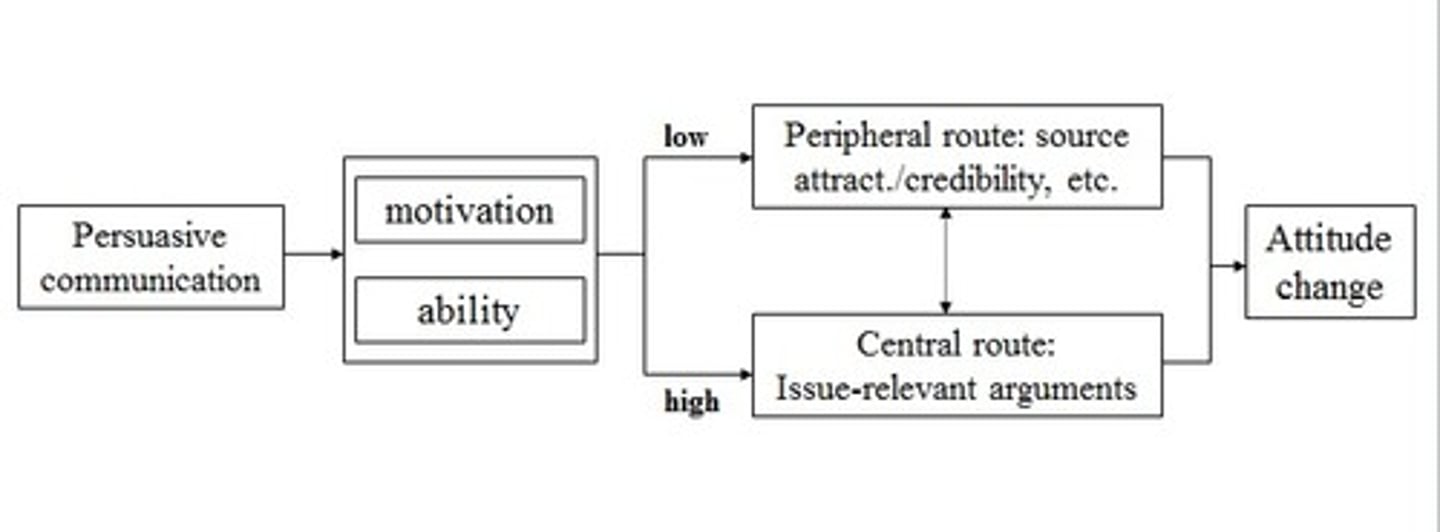
Central route
a method of persuasion that uses evidence and logical arguments to influence people, often resulting in a lasting attitude change

Peripheral route
focuses on factors other than the message itself because the recipient has little or no interest in the subject and/or has a lesser ability to process the message, often resulting in a temporary attitude change

Halo effect
the tendency to draw a general impression about an individual on the basis of a single characteristic
Foot-in-the-door technique
persuasive technique involving making a small request before making a bigger one

Door-in-the-face technique
persuasive technique involving making an unreasonably large request before making the small request the person is hoping to have granted

Conformity
adjusting one's behavior or thinking to coincide with a group standard

Obedience
a form of compliance that occurs when people follow direct commands, usually from someone in a position of authority

Individualism
giving priority to one's own goals over group goals and defining one's identity in terms of personal attributes rather than group identification

Collectivism
giving priority to the goals of a social group and defining one's identity accordingly

Multiculturalism
a situation in which distinct cultural groups in a society share equal value

Group polarization
when a group's decision making process results in a more extreme decision than its members would have made if deciding on their own

Groupthink
when members of a group conform to majority opinion to maintain group harmony rather than stating their own views

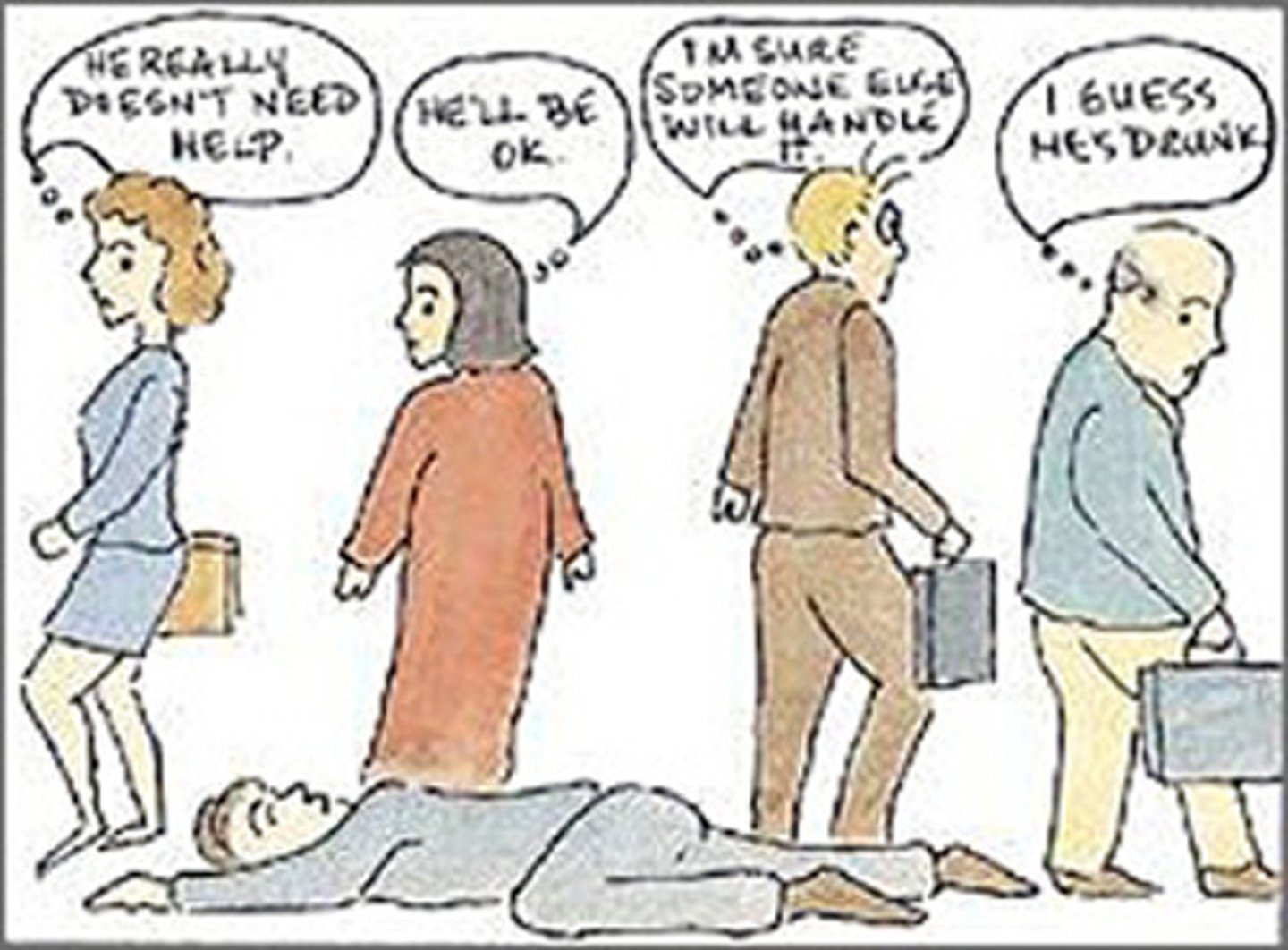
Diffusion of responsibility
the more onlookers there are, the less personal responsibility individuals will feel to take action

Social loafing
the tendency for people to put in less effort when working on a task as a group, compared to when working alone

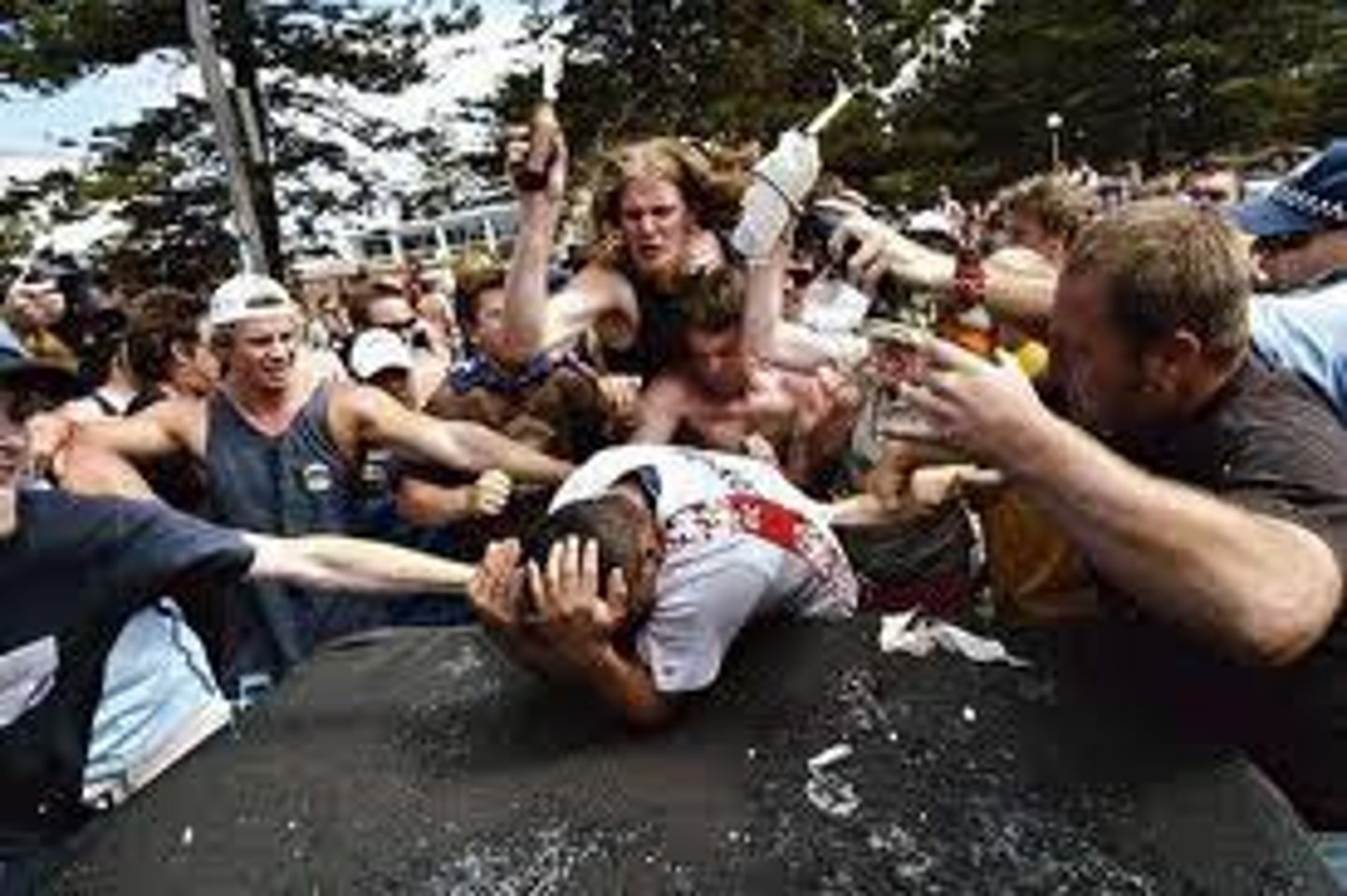
Deindividuation
when individuals lose self-awareness and self-restraint in group situations and engage in impulsive, deviant, and sometimes violent acts

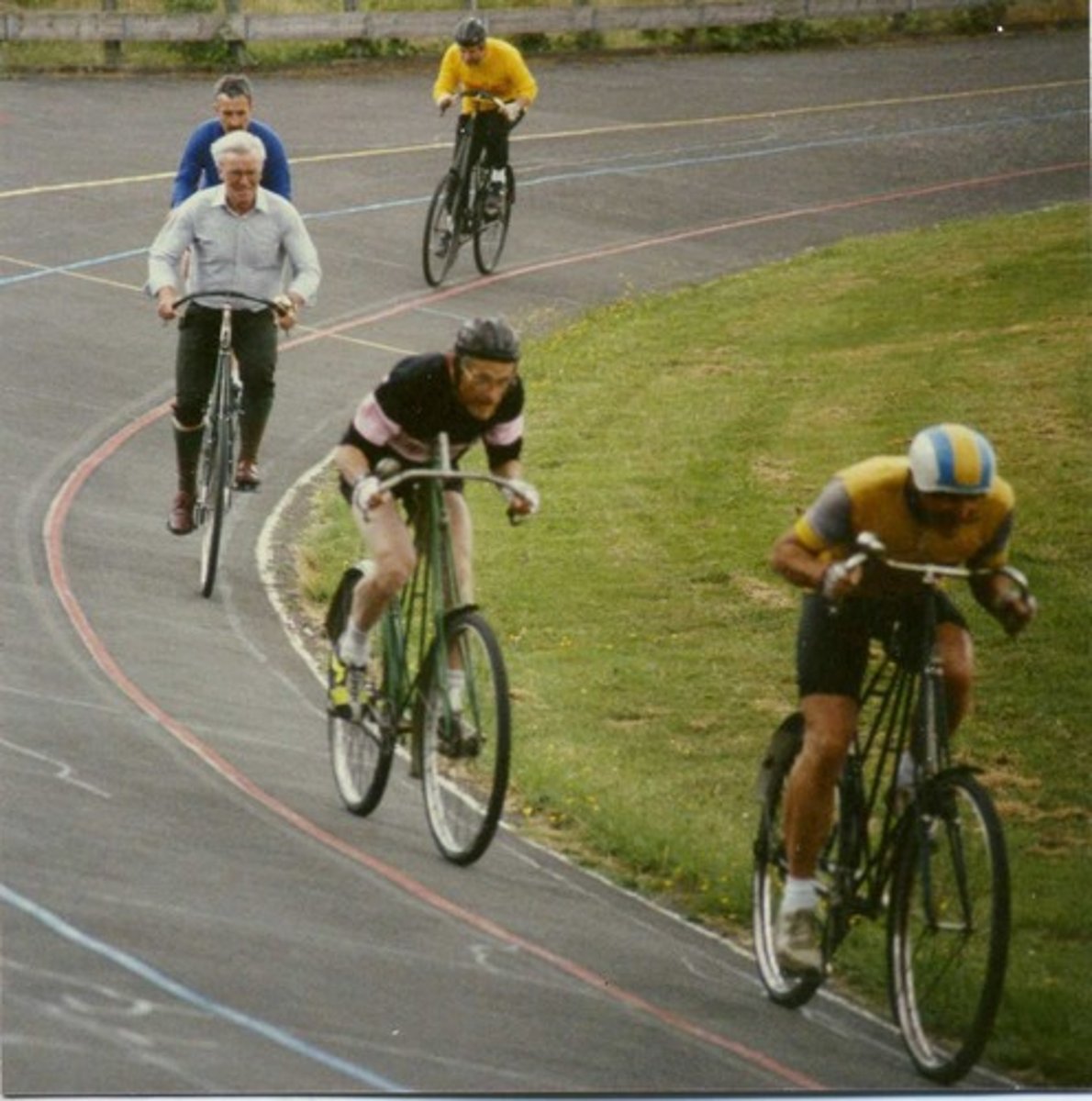
Social facilitation
a phenomenon where people show increased levels of effort and performance when in the presence of others

False consensus effect
the tendency to overestimate the extent to which others share one's own beliefs and behaviors

Superordinate goals
shared goals that override differences among people and require their cooperation

Social traps
decisions by individuals or groups that seem good and produce a short-term benefit, but that hurt society in the long run

Industrial-organizational (I/O) psychologists
researchers and practitioners who use the principles of social psychology to improve the workplace (e.g., job satisfaction, employee retention, productivity)

Burnout
a state of physical, emotional, and mental exhaustion created by long-term exposure to a stressful situation (e.g., a demanding job) and accompanied by lowered performance and motivation

Altruism
unselfish concern for the welfare of others

Prosocial behavior
positive, constructive, helpful behavior (the opposite of antisocial behavior)

Social debt
when people act in a prosocial way because they have been helped by others in the past (paying it forward) or by feeling responsible for the common good of society (doing my part)

Social reciprocity norm
the idea that a person is motivated to do good things because others have shown acts of kindness to them in the past

Social responsibility norm
an expectation that people will help those dependent upon them or those who need assistance even if doing so may not offer any visible reward

Bystander effect
the tendency for any given bystander to be less likely to give aid if other bystanders are present
Situational variables
factors in a particular context that can impact an individual's likelihood of helping another person

Attentional variables
elements of attention that can impact an individual's likelihood of helping another person

Psychodynamic theory
Freudian theory that unconscious forces determine behavior
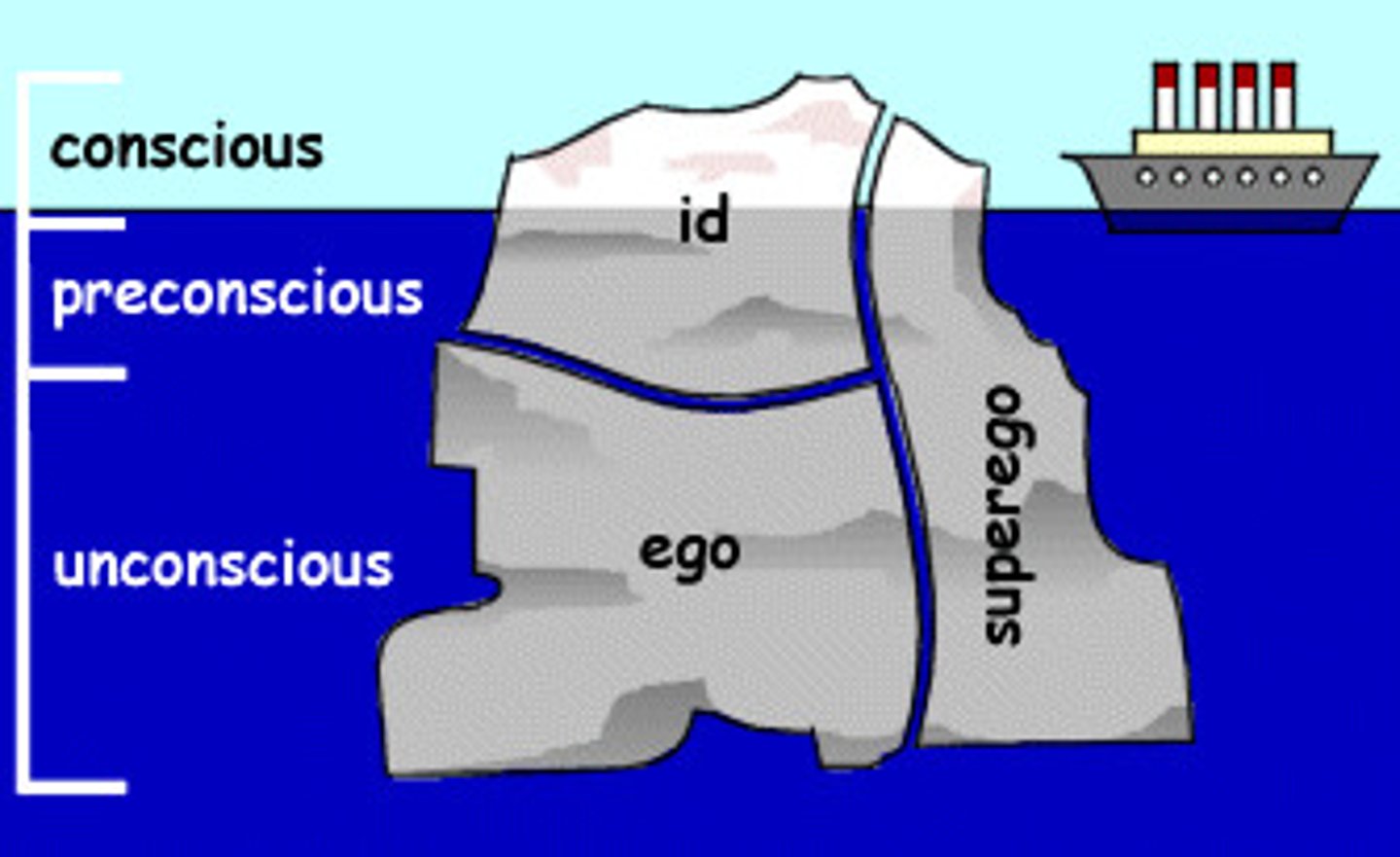
Unconscious processes
mental activities that occur outside of a person's awareness, such as thoughts, desires, and memories that are hidden from conscious thought
Ego defense mechanisms
things that protect the conscious mind from the anxiety that arises from unacceptable impulses

Denial
a defense mechanism by which people refuse to believe or even to perceive painful realities

Displacement
defense mechanism in which a person redirects a negative emotion from its original source to a less threatening recipient (e.g., a person angry at their boss may "take out" their anger on a family member)

Projection
a defense mechanism that directs things a person doesn't like about themself toward someone else (e.g., a cheating spouse suspects their partner is being unfaithful)

Rationalization
a defense mechanism in which people justify unwanted feelings with seemingly logical explanations (e.g., a student who is rejected from their dream college may say they are happy to attend a school that's less competitive and more welcoming)

Reaction formation
a defense mechanism in which a person expresses an exaggerated, opposite version of how they actually feel

Regression
a defense mechanism in which an anxious individual retreats to an earlier stage of development (e.g., a first grader reverts to thumb sucking because they have anxiety about school)

Repression
a defense mechanism in which anxiety-provoking thoughts and feelings are forced to the unconscious

Sublimation
when a person redirects unacceptable feelings into a socially acceptable activity (e.g. after being fired, a person puts more effort into caring for their family)

Projective tests
personality assessments that present ambiguous visual stimuli to a person and asks them to respond with whatever comes to mind

Preconscious mind
Freud's term for memories that are not presently at the level of awareness but can accessed
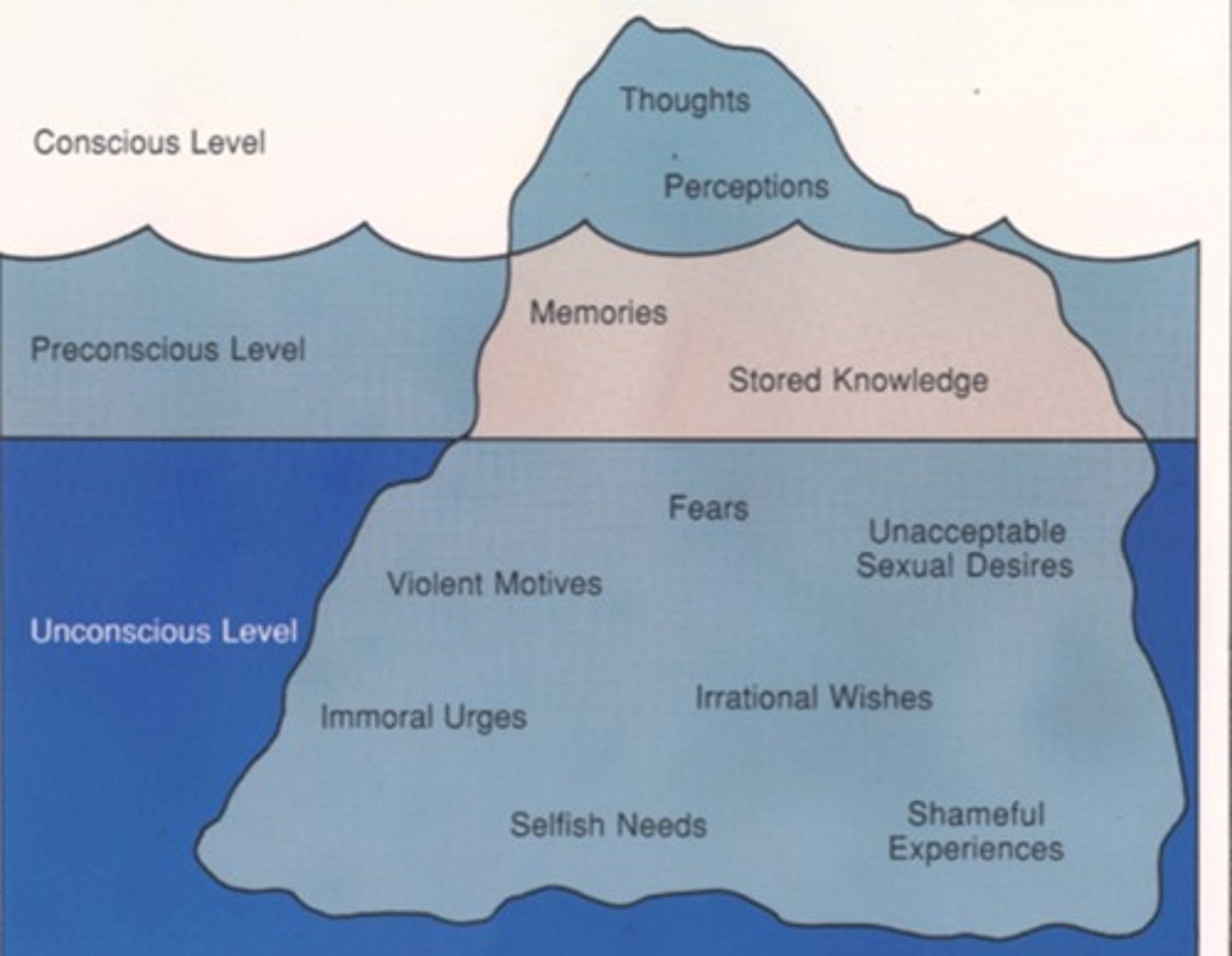
Unconscious mind
Freud's term for the thoughts, desires, and urges that are actively repressed from consciousness and that affect mental activity outside of active awareness

humanistic psychology
studies the whole person by looking at behavior through the eyes of the person doing the behaving with the goal of developing a healthy sense of self
Unconditional regard
a client-centered technique in which a therapist shows positive feelings and acceptance to the client, regardless of what the client says or does

Self-actualizing tendency
a desire that pushes a person to grow, to be creative, and to reach their full potential
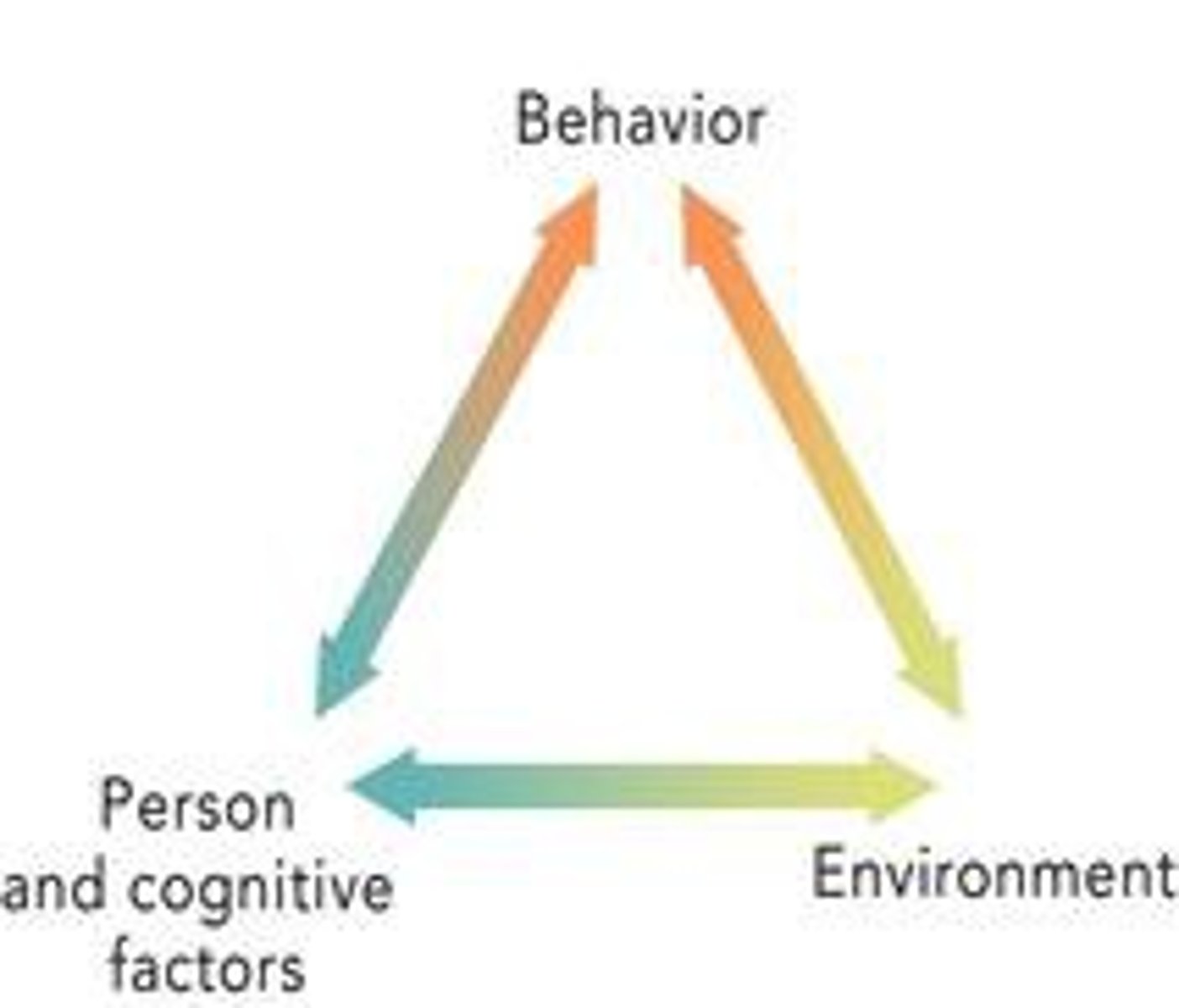
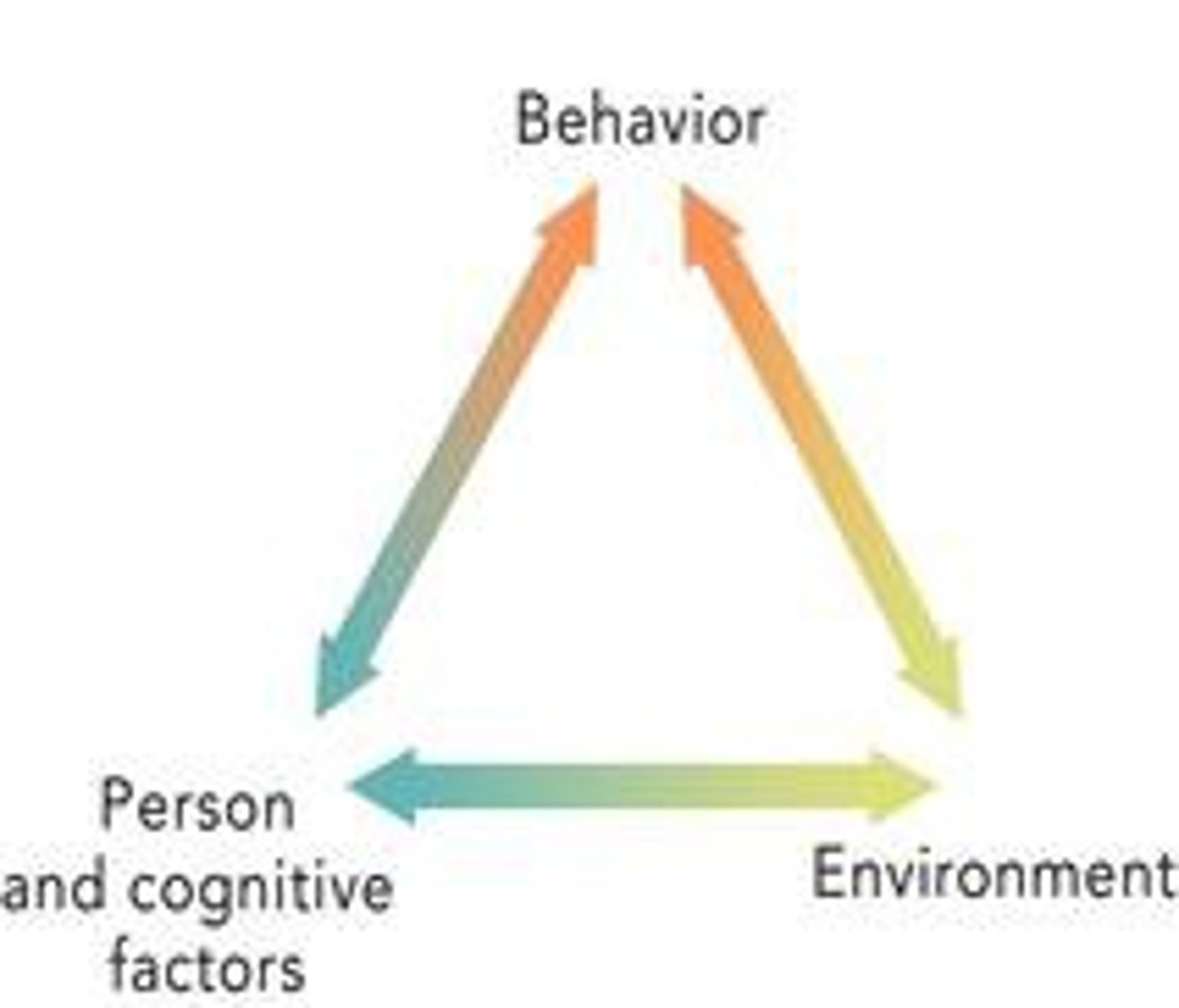
Social-cognitive theory
a psychological theory that emphasized the dynamic interaction between people (personal factors), their behavior, and their environments
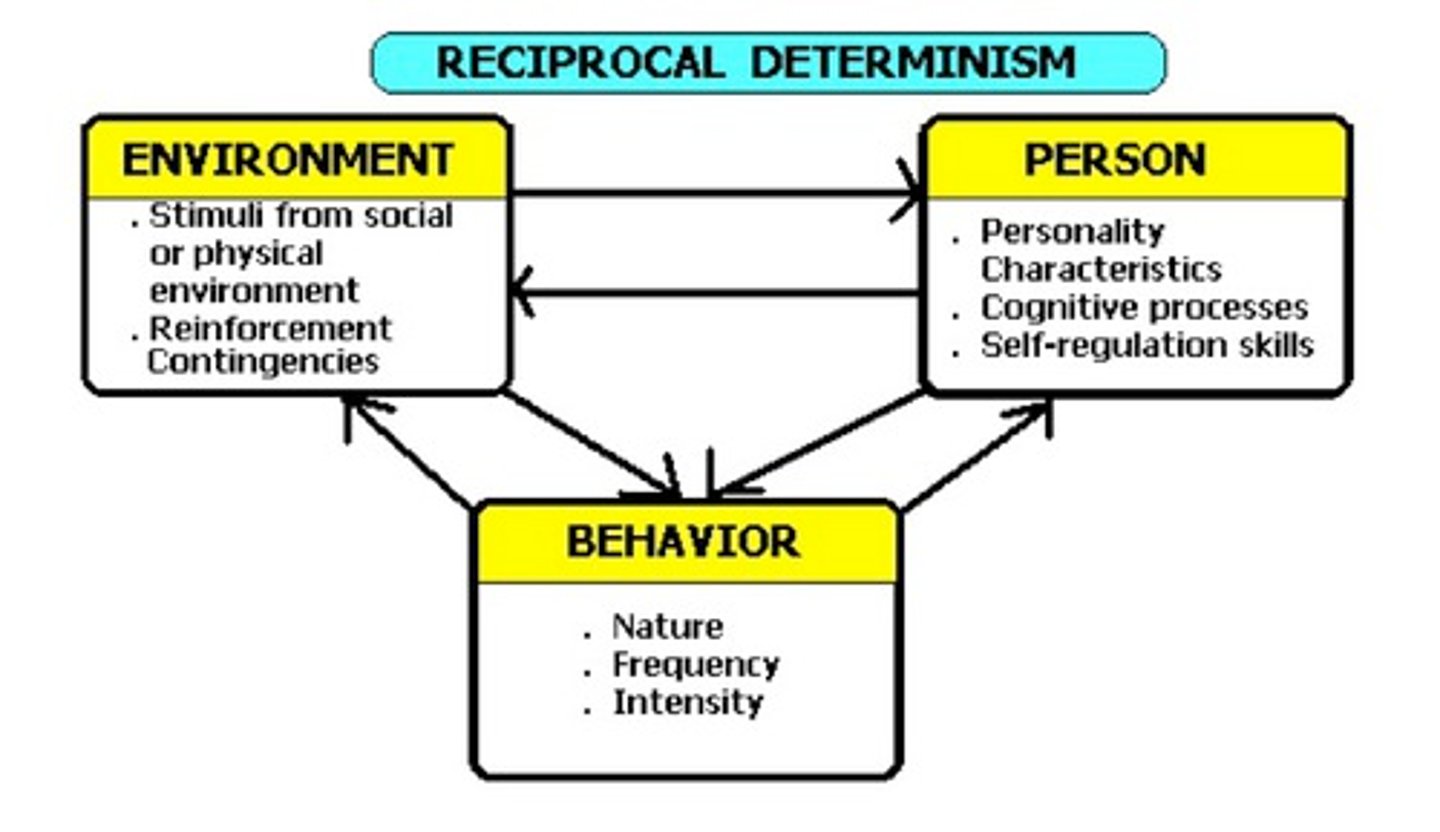
Reciprocal determinism
the idea that a person's behavior both influences and is influenced by personal factors and their social environment
Self-concept
the overall view a person has of themselves, including their beliefs, physical and mental attributes, and social interactions
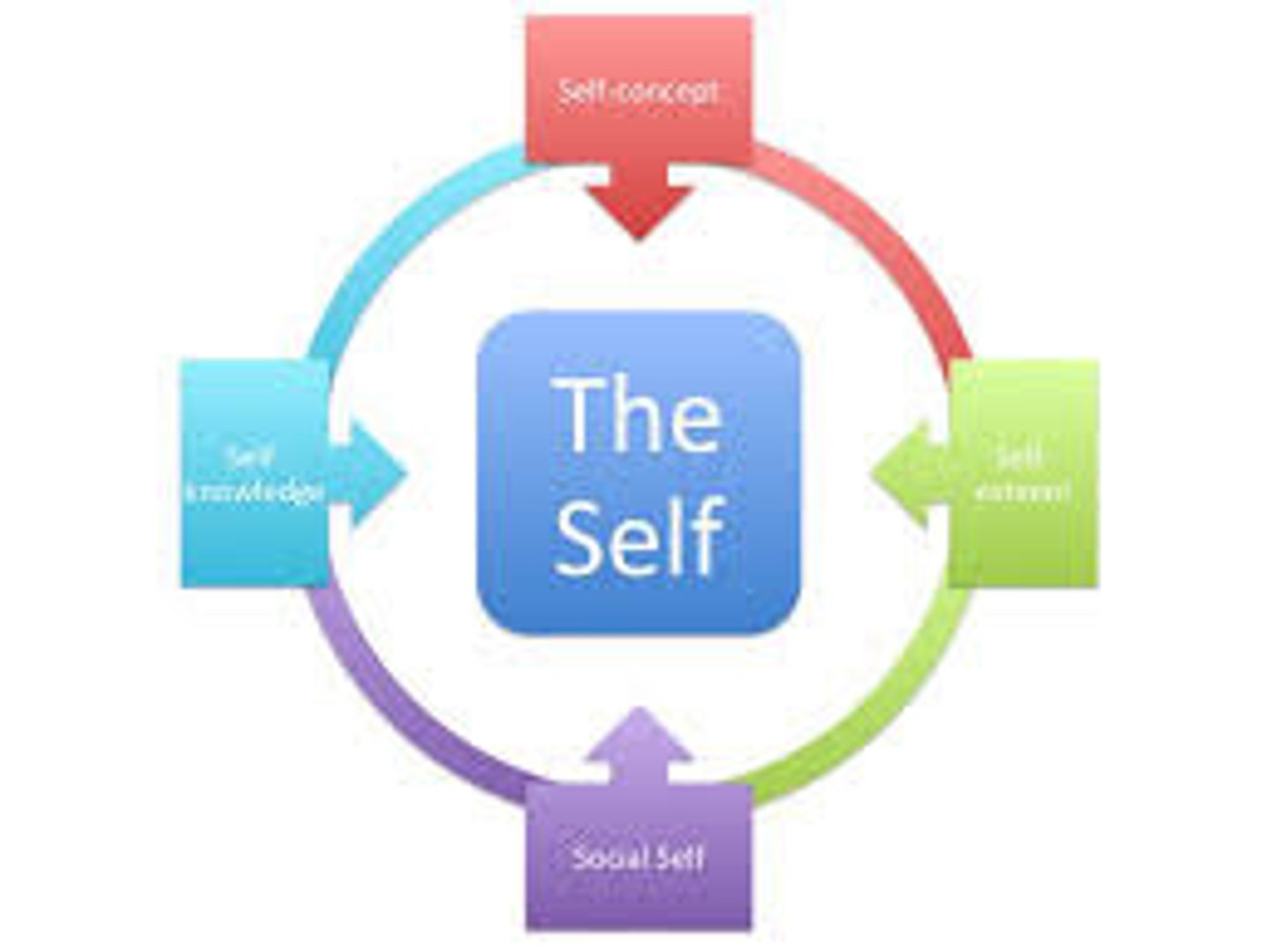
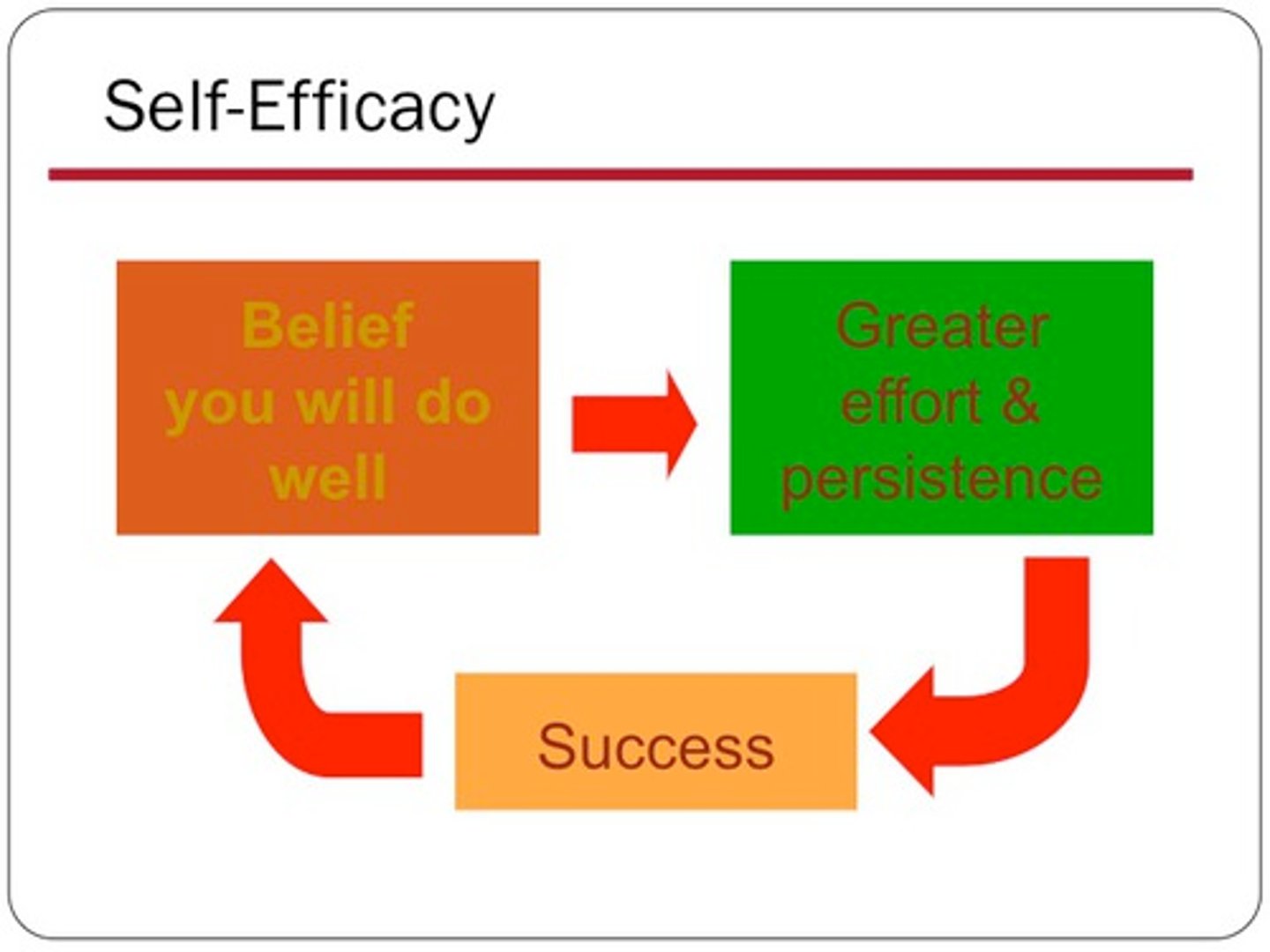
Self-efficacy
a person's belief in their ability to perform a task or reach a goal
Self-esteem
the degree of confidence and value a person has for themselves

Trait theories
categorizes and describes the characteristics that make up human personality in an effort to predict future behavior

Big Five theory
identifies five main characteristics that account for most individual differences in personality (agreeableness, extraversion, conscientiousness, openness to experience, and emotional stability (neuroticism))

Agreeableness
a person's concern for social harmony and their tendency to get along with others

Extraversion
describes people who are sociable, talkative, assertive, and active

Conscientiousness
describes a person's level of organization, persistence, and motivation to accomplish a goal

Openness to experience
describes how open-minded, imaginative, creative, and insightful a person is
Emotional Stability
the extent to which people feel secure and unworried and how likely they are to experience negative emotions under pressure

Personality inventories
an assessment tool (usually a questionnaire that measures and evaluates an individual's personality, such as traits, behaviors, and attitudes
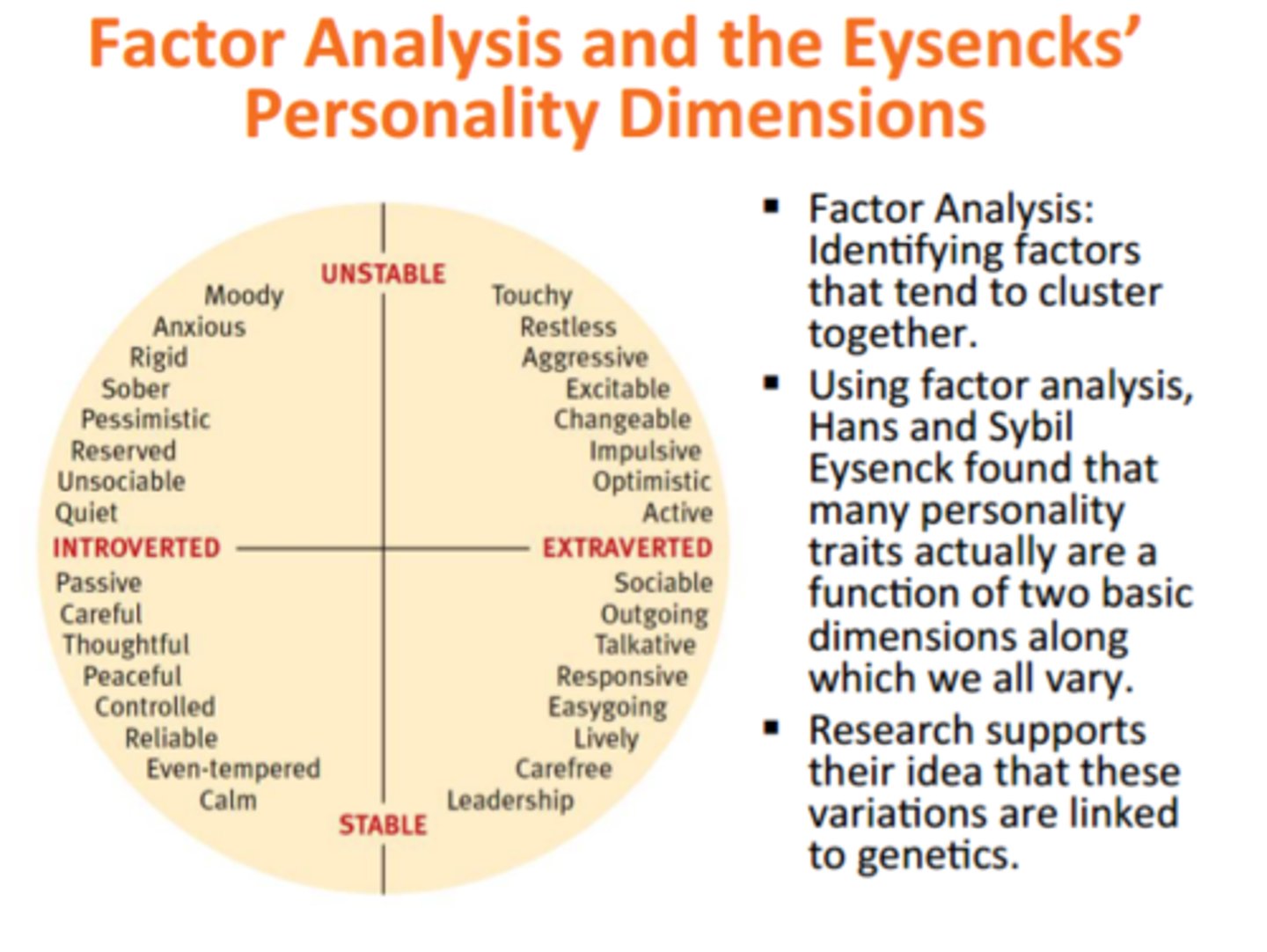
Factor analysis
a statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items on a personality test to identify things that help interpret a person's total score
Drive-reduction theory
states that motivation comes from biological needs or drives that cause people to act in ways that restore balance

Homeostasis
the tendency of the human body to seek balance, equilibrium, and stability
Arousal theory
people's tendency to maintain a balance of arousal and excitement to avoid boredom and apathy with each person having their own optimal level of arousal

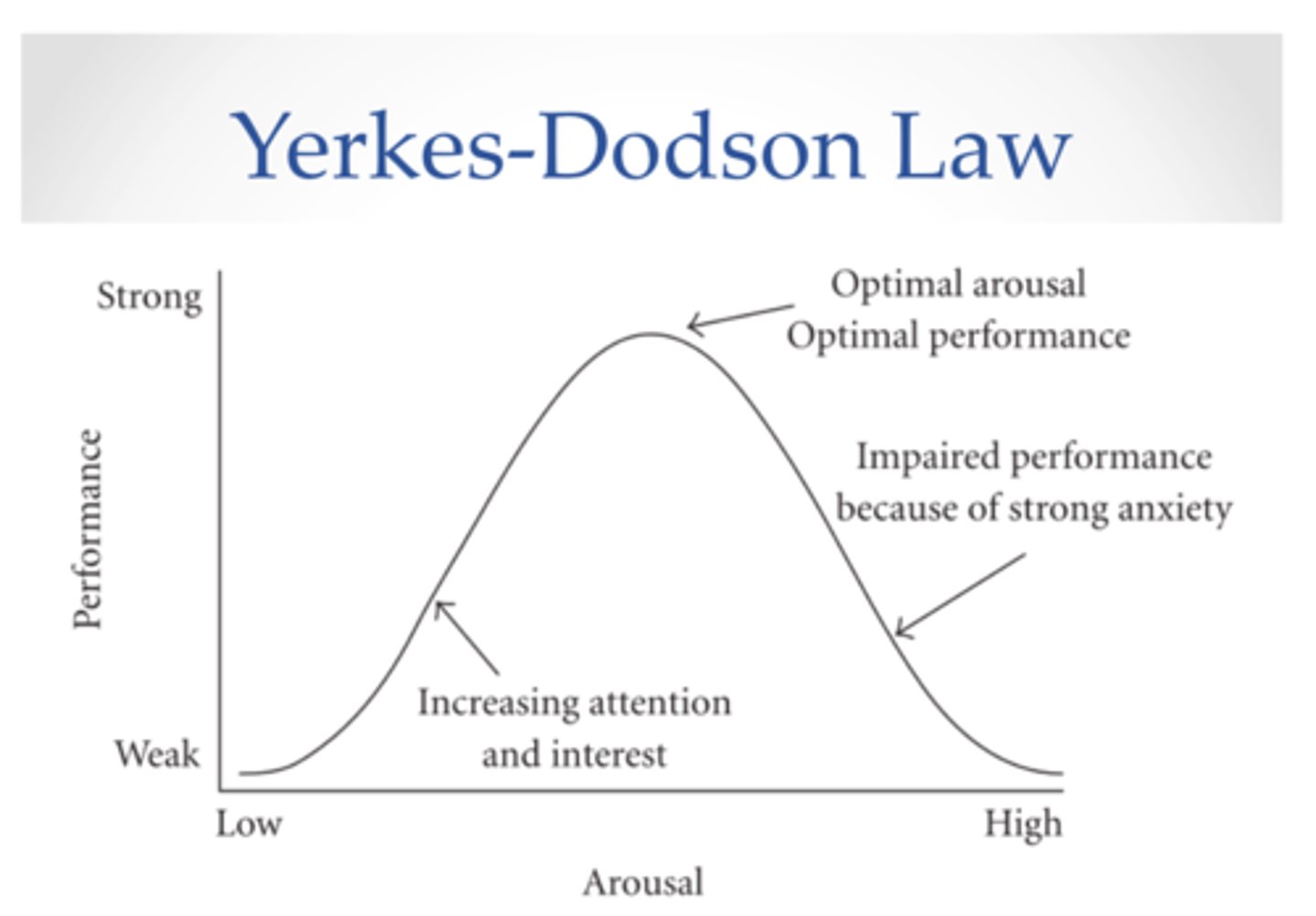
Optimal level of arousal
the psychological state where a person feels alert and engaged--but not stressed--and is able to perform at their best
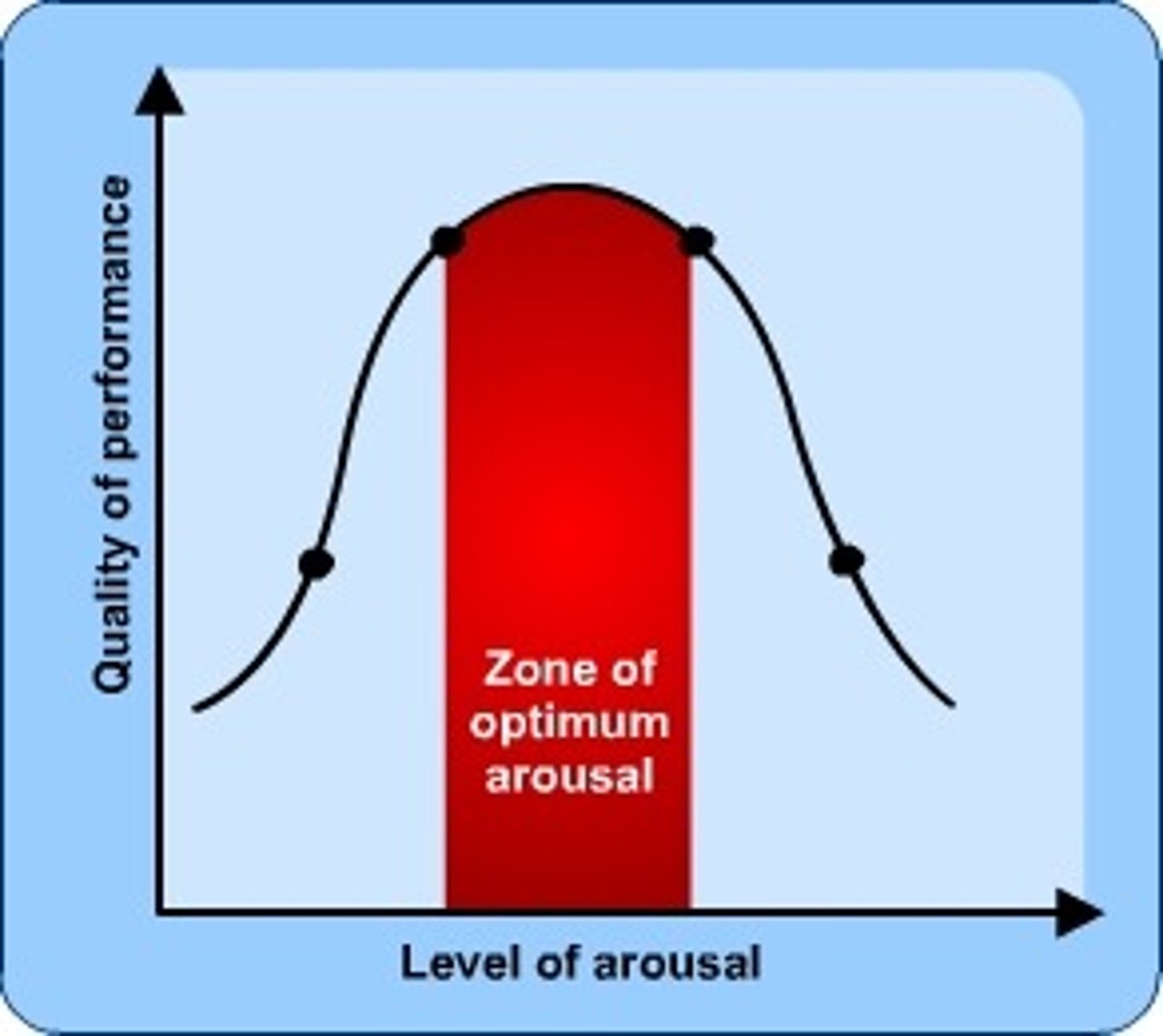
Yerkes-Dodson Law
states that performance improves with arousal, but only up to a certain point