CHEM-312 Quiz 2 (NO IUPAC post-lab)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
The mobile phase of GC is a ____________
A) gas, usually Oxygen
B) gas, usually helium
C) Liquid usually methanol
D) Liquid different solvents
B
Different types of GC columns are (Note: More than one answer)
A) Packed columns
B)Capillary columns
C) Slurry columns
D) Solid phase columns
A and B
What type of GC column can separate milligram quantities of materials
A) Packed columns
B) capillary columns
C) Slurry columns
D) Solid phase columns
A
What type of GC column works best with microgram quantities or less
A) Packed columns
B) capillary columns
C) Slurry columns
D) Solid phase columns
B
What type of column has better separating power
A) capillary columns
B) Slurry columns
C) Packed columns
D) Solid phase columns
A
The equilibria between adsorbed and free states in GC depends on each molecule's ______
(Note: Multiple Answer Question)
A) size (London forces)
B) polarity
C) ability to hydrogen bond
all of them
Which statement is correct
A) Molecules spending more time absorbed to the stationary phase will be carried through the column as rapidly as those that are weakly bound and free.
B) Molecules spending more time absorbed to the stationary phase will not be carried through the column as rapidly as those that are weakly bound and free.
B
In GC chromatogram peak areas representing the _______ of each individual component passing through the detector.
A) Boiling point
B) polarity
C) Amount
C
True or False:
GC chromatogram can be used to quantify the amount of each component in a mixture.
True
Which ones are NOT one of the types of detectors that most GC instruments use (Note: Multiple Answer)
A) TCD
B) DDT
C) ECD
D) FID
E) TLC
F) MS
B and E
Rank in order of increasing Rt on nonpolar GC column (1 is the lowest Rt, 5 is the highest Rt).
Methyl cyclohexane 101
Pentane 36
Octane 126
2,3-dimethyl octane 165
Heptane 98
1: pentane
2: heptane
3: methyl cyclohexane
4: octane
5: 2,3-dimethyl octane
Rank in order of increasing Rt on DEGS GC column (DEGS is fairly polar)
1 is shortest Rt and 4 is the longest Rt
Boiling Point
propionic acid 141
2-hexanol 140
isoamyl acetate 142
3,4-dimethylheptane 140
1: 3,4-dimethylheptane
2: isoamyl acetate
3: 2-hexanol
4: propionic acid
Rank in order of increasing Rt values on GC (with non-polar column).1 is shortest Rt and 4 is longest Rt
2-hydroxymethylcyclohexanol
hydroxymethylcyclohexane
methyl acetate
methylcyclohexane
1: methyl acetate
2: methylcyclohexane
3: hydroxymethylcyclohexane
4: 2-hydroxymethylcyclohexanol
Rank molecules in order of increasing Rf values on TLC.
1 is lowest Rf (moves the slowest) and 4 is the highest Rf (moves the fastest)
methyl acetate
methylcyclohexane
hydroxymethylcyclohexane
2-hydroxymethylcyclohexanol
1: 2-hydroxymethylcyclohexanol
2: hydroxymethylcyclohexane
3: methyl acetate
4: methylcyclohexane
The time it takes for a compound to exit the GC column after it is injected is _______
A) retention factor
B) retardation time
C) retardation factor
D) retention time
D
Which peak represents the compound that travels through the GC instrument
a) in the least amount of time? b) Which peak has the shortest Rt ? c) Which peak has the the longest Rt?
1) E,E, A 2) A,A,E 3) A, B, C 4) E, D, A
B
Suppose there are three colorless liquids- A, B, and C. Their relative boiling temperatures are B > A > C. The three component mixture is injected into a GC (non-polar column) whose oven temperature is held constant at 120ºC. Which chromatogram below best represents the order in which the three liquids exit the GC instrument?
A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4
C
A mixture of three liquid hydrocarbons was injected into a GC (non-polar column) at Toven= 95ºC. The resulting chromatogram is below.
a) Which compound is the most volatile?
b) Which compound most likely has the highest boiling point?
1) C, A 2) A,C 3)C,B 4) A, B
B
When a reaction is complete, it is necessary to do a _____________, that is, separate and purify the desired product from the mixture of byproducts and residual starting material.
A) liquid-liquid extraction
B) Solid-liquid extraction
C) workup
D) recrystallization
C
Organic products are often separated from inorganic substances in a reaction mixture by liquid/liquid extraction with an ____________ solvent
A) organic
B) inorganic
A
Which statement is correct?
A)ne large-scale extraction is more effective than several small-scale extractions
B) Several small-scale extractions are more effective than one large-scale extraction
B
The solvent used for extraction (in liquid/liquid extraction) should
A) Dissolve the substance to be extracted at high temperatures but not dissolve it atroom temperature. Should have low boiling point.
B) Should have high boiling point. Should not be highly flammable or toxic
C) Should not react with the solute or the other solvent. Should not be miscible withwater
D) all the above
C
To break emulsion
Note: this question is multiple answer (choose more than one option)
A) Centrifugation works very well
B) Making the aqueous layer highly ionic will help
C) Shake the mixture vigorously helps to break emulsion
D) Once emulsion is formed you can't break it
A and B
Drierite is
A) A specially prepared form of calcium sulfate, it is a fast and effective drying agent
B) Pellets of calcium chloride that clumps together when excess water is present
C) Finely powdered form of Magnesium sulfate a fast and fairly drying agent
D) It's a general name for any drying agent
A
Why do you cool down Tea extract in ice to below 40°C before adding dichloromethane
A) to decrease solubility of caffeine in dichloromethane
B) to prevent evaporation of dichloromethane
C) to increase solubility of caffeine in dichloromethane
B
What method should be used in the microscaleprocedure to purify the extracted caffeine?
A) recrystallization
B) sublimation
C) Column chromatography
B
When mixing organic and aqueous layers in separatory funnel you should
A) Shake extremely vigorously to make sure all caffeine is extracted to organic layer
B) Do not shake it so vigorously to prevent emulsion formation
B
Why did we add Na2CO3 to boiling water for extracting caffeine in the first step?NOTE: this question is multiple answer
A) To make sure acidic substances like tannins remain water soluble
B) Keep solution basic to leave caffeine in free base form
C) To decrease solubility of caffeine in CH2Cl2
D) Keep solution basic to leave caffeine in its salt form
A and B
what drying agent did you use to dry your caffeine extract in CH2Cl2
A) CaCl2
B) CaSO4
C) MgSO4
D) drierite
A
What compound(s) does the aqueous layer contain? And What compound(s) does the organic layer contain?
A) Tannins, sodium carbonate, and water in organic layer. Caffeine, dichloromethane in
aqueous layer
B) Sodium carbonate, and water in organic layer. Caffeine, Tannins, dichloromethane in
aqueous layer
C) Sodium carbonate, and water in aqueous layer. Caffeine, Tannins, dichloromethane in
organic layer
D) Tannins, sodium carbonate, and water in aqueous layer. Caffeine, dichloromethane in
organic layer
D
which functional group does not exist in caffeine
A) Amine
B) amide
C) ester
D) alkene
C
When did you stop adding drying agent?
A) when pellets stopped clumping together
B) when we couldn't see two layers
C) when solution color started to change
A
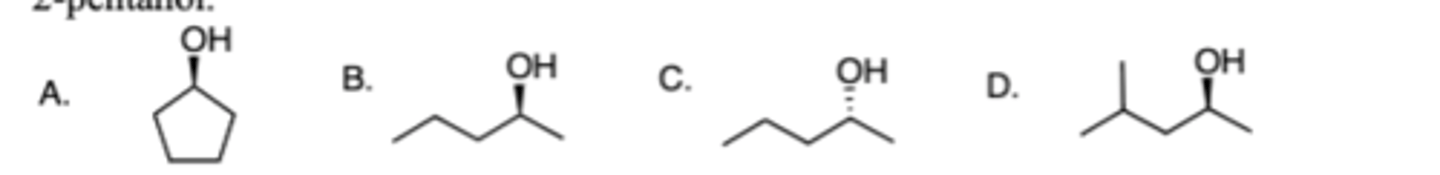
Which of the following is the correct structure for a compound with the IUPAC name (R)-
2-pentanol.
C
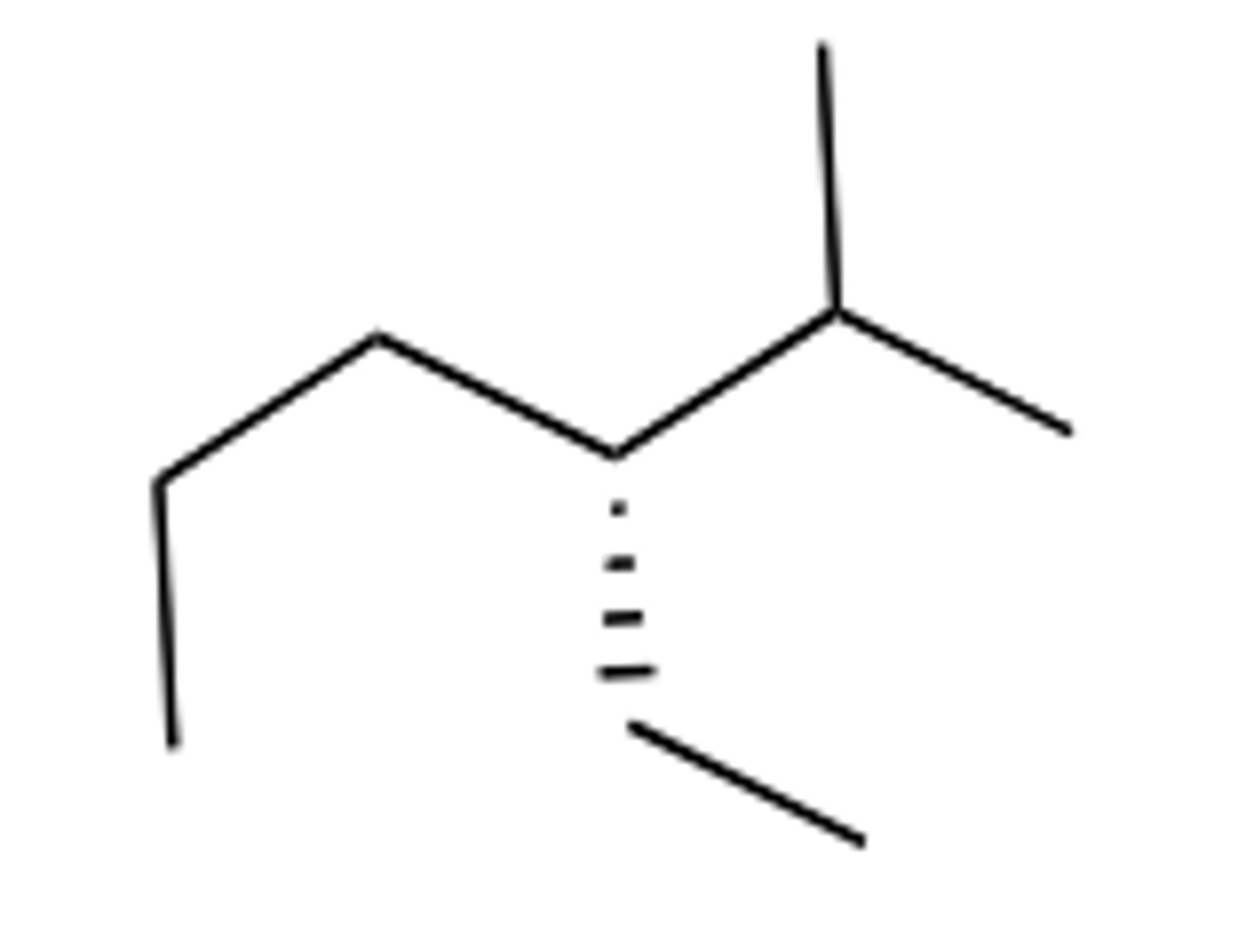
Which of the following is the correct structure for a compound with the IUPAC name (S)-
3-methylheptane.
B

Which of the following is the correct IUPAC name for the following structure?
A. (S)-3-ethyl-2-methylhexane
B. (R)-3-ethyl-2-methylhexane
C. (S)-3-ethyl-2-methylpentane
D. (R)-3-ethyl-2-methylpentane
B
If a sample of carvone gives observed rotation of 0 and the specific rotaion of pure R-
carvone is -61, which enantiomer is the unknown sample?
A. R
B. S
C. Racemic
C
What is the specific rotation of pure S-carvone if a sample of R-carvone of 85%ee has
observed rotation of -54?
A. -61
B. 64
C. 0
D. 61
B
What is the % of the R enantiomer in a sample of carvone that has observed rotation of 30,
specific rotation of R-carvone is -61.
A. 25.5%
B. 51%
C. 49%
D. 74.5%
A
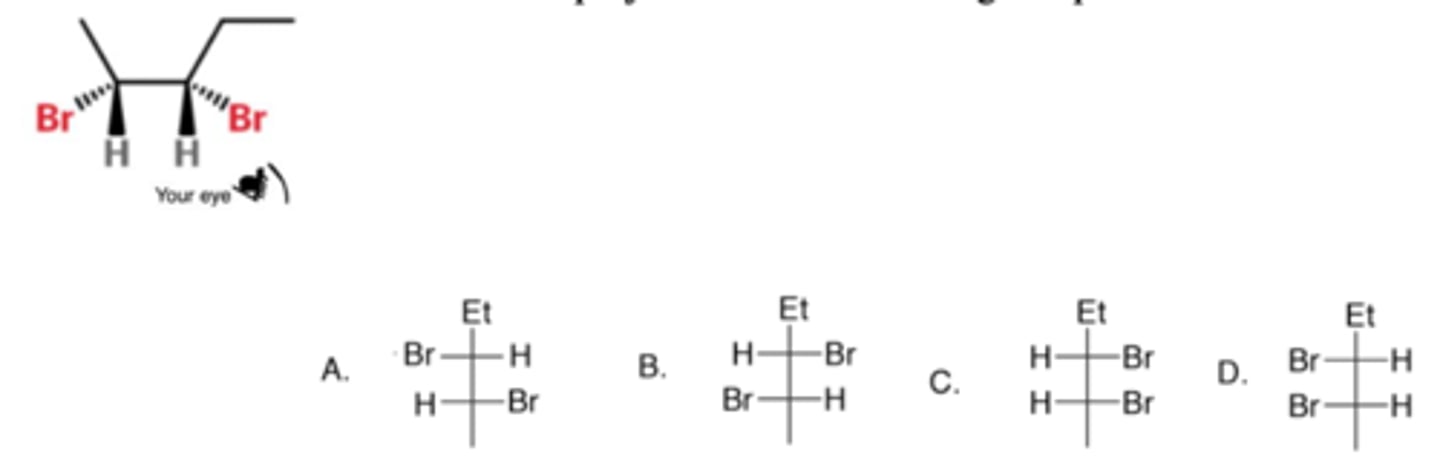
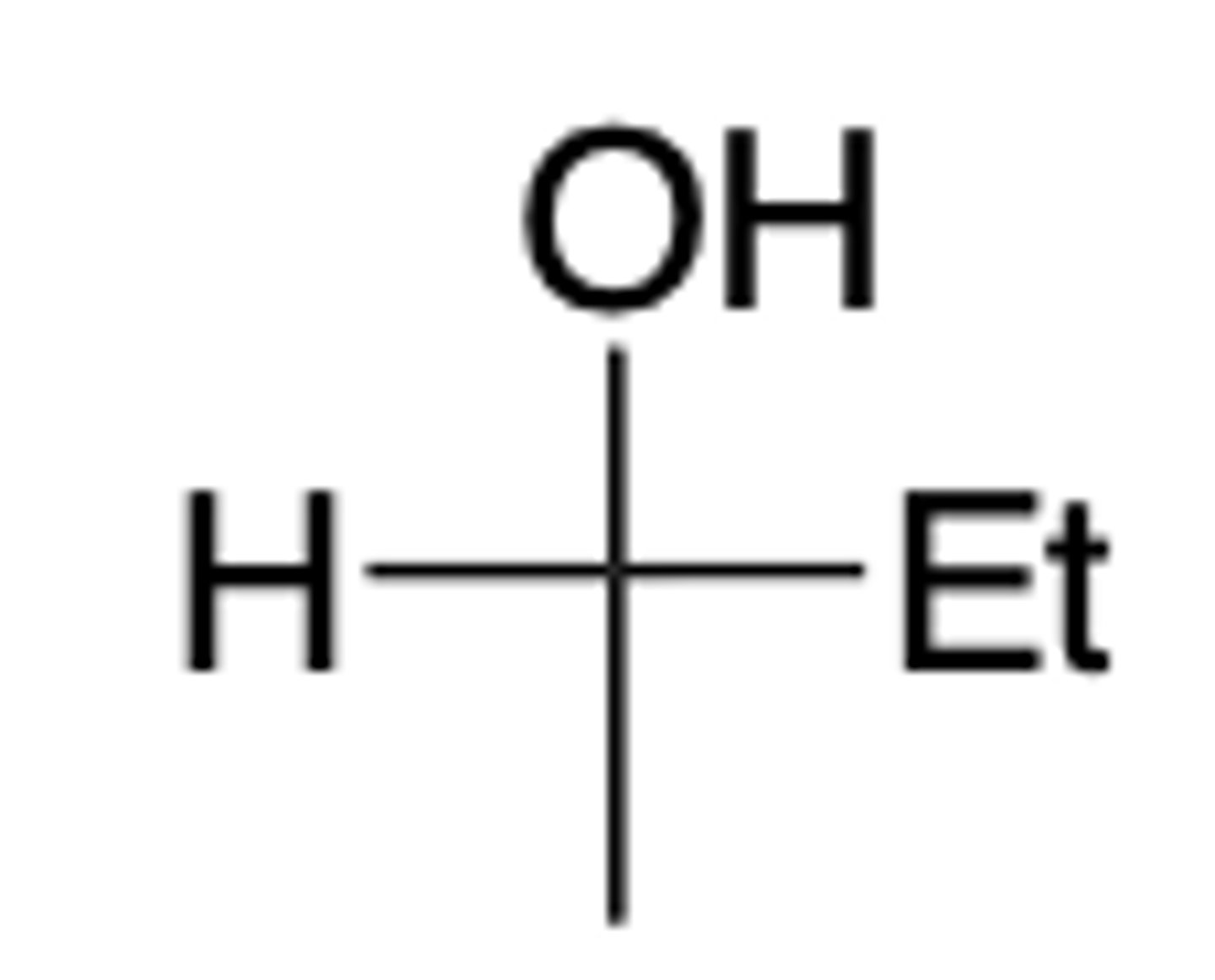
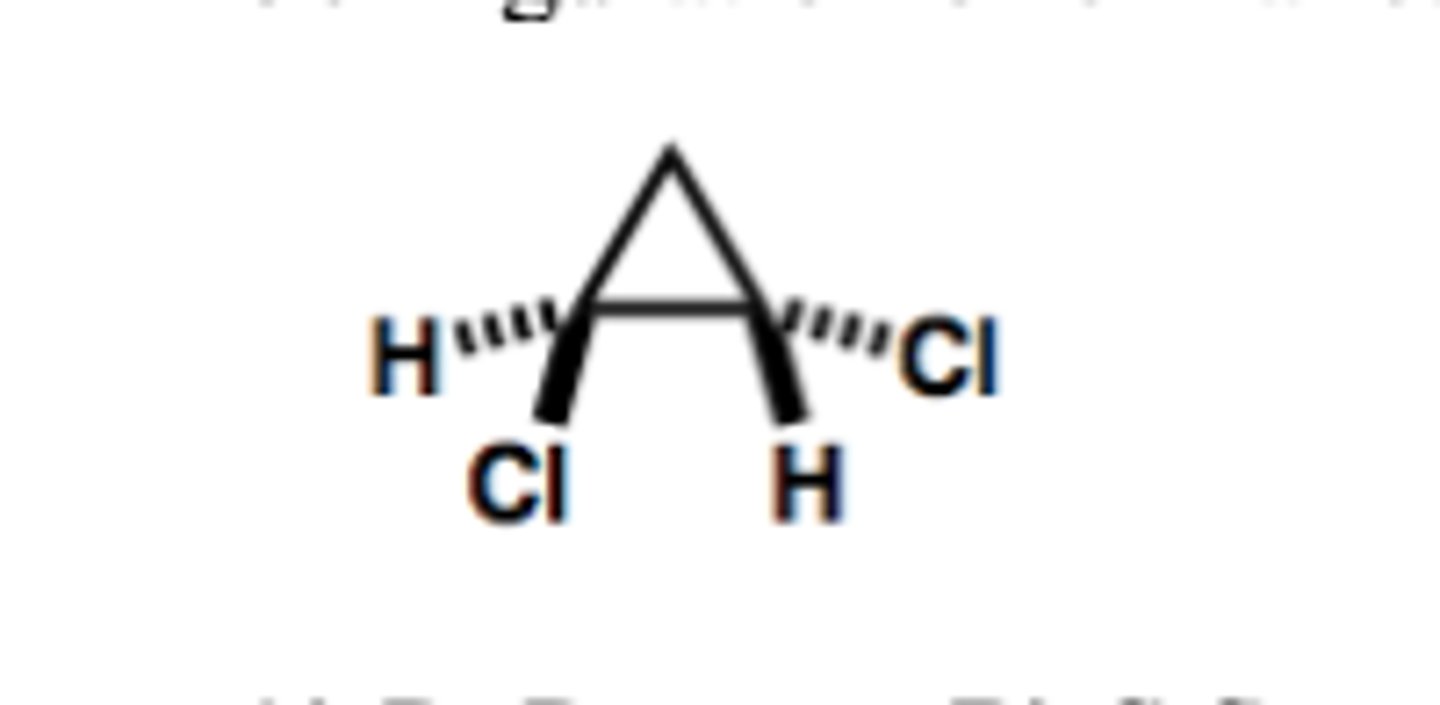
Which one is the correct Fischer projection of the following compound?
C
What is the relationship between the following two molecules?
A

Which of the following is the IUPAC name for the following compound.
A. (S)-2-pentanol
B. (S)-2-butanol
C. (R)-2-pentanol
D. (R)-2-butanol
B
Determine the configuration of the chiral carbon in the following molecule.
A) R
B) S
A
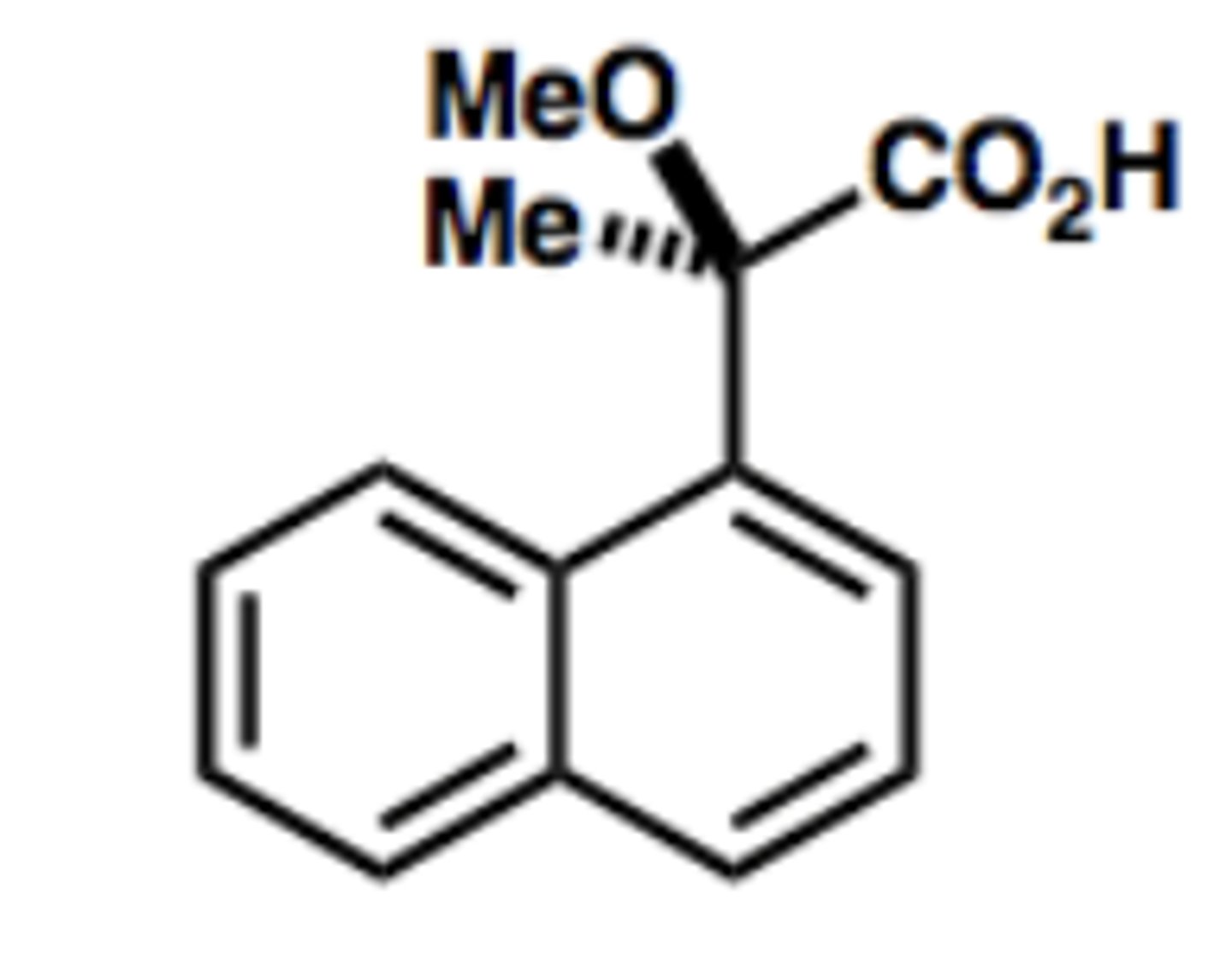
Determine the configuration of each chiral carbon in the following molecule (left to right).
A) R, R
B) S,S
C) R, S
D) S, R
B
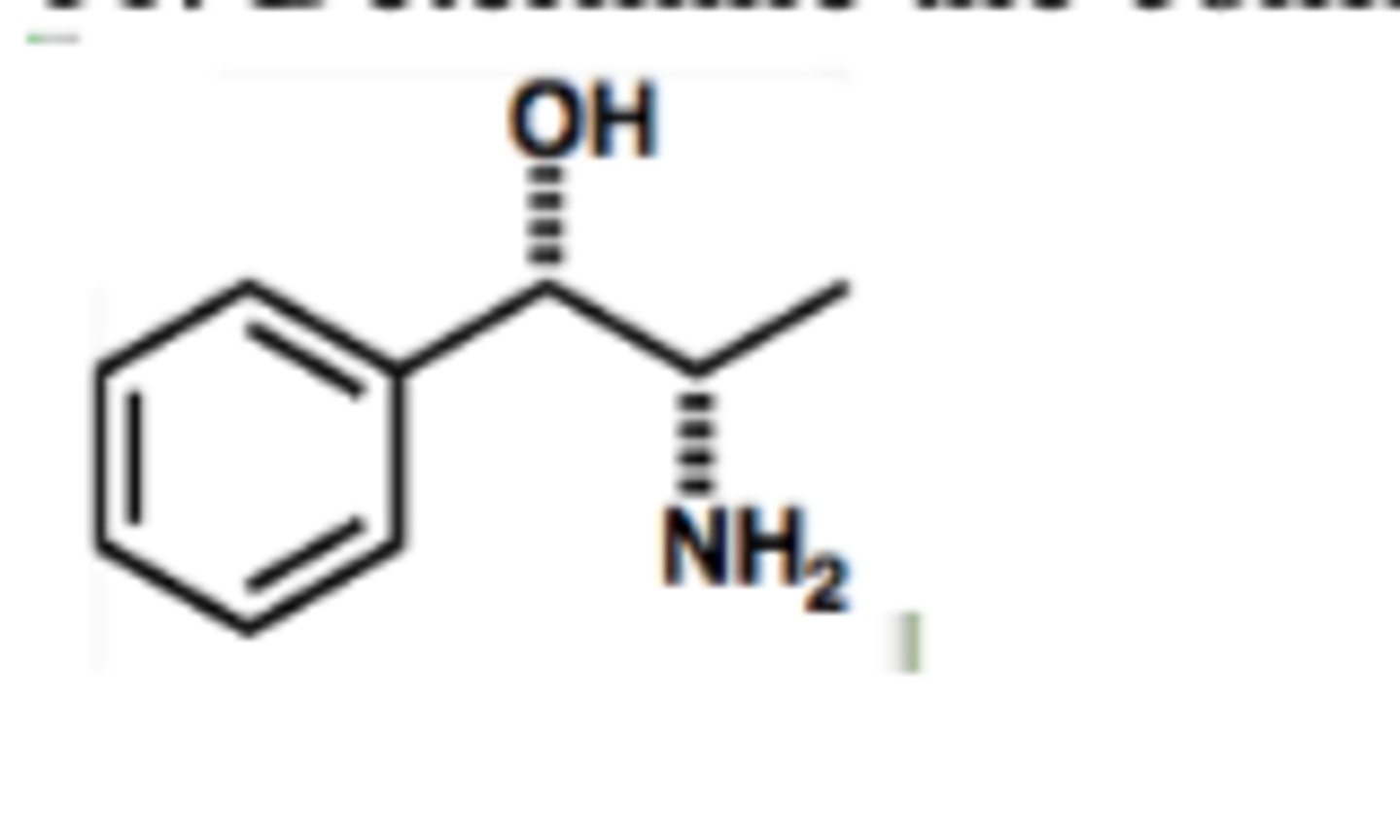
Determine the configuration of each chiral carbon in the following molecule.
Configuration of chiral carbons from left to the right are:
A) R, R
B) S,S
C) R, S
D) S, R
C
Use the following data to generate a graph of Sample Concentration (g/mL) on the x-axis
vs. optical rotation in degrees on the y-axis (in excel). Which graph (A,B, C, D) is similar
to the graph that you generated?
Observed Rotation of blank (°) =0
C
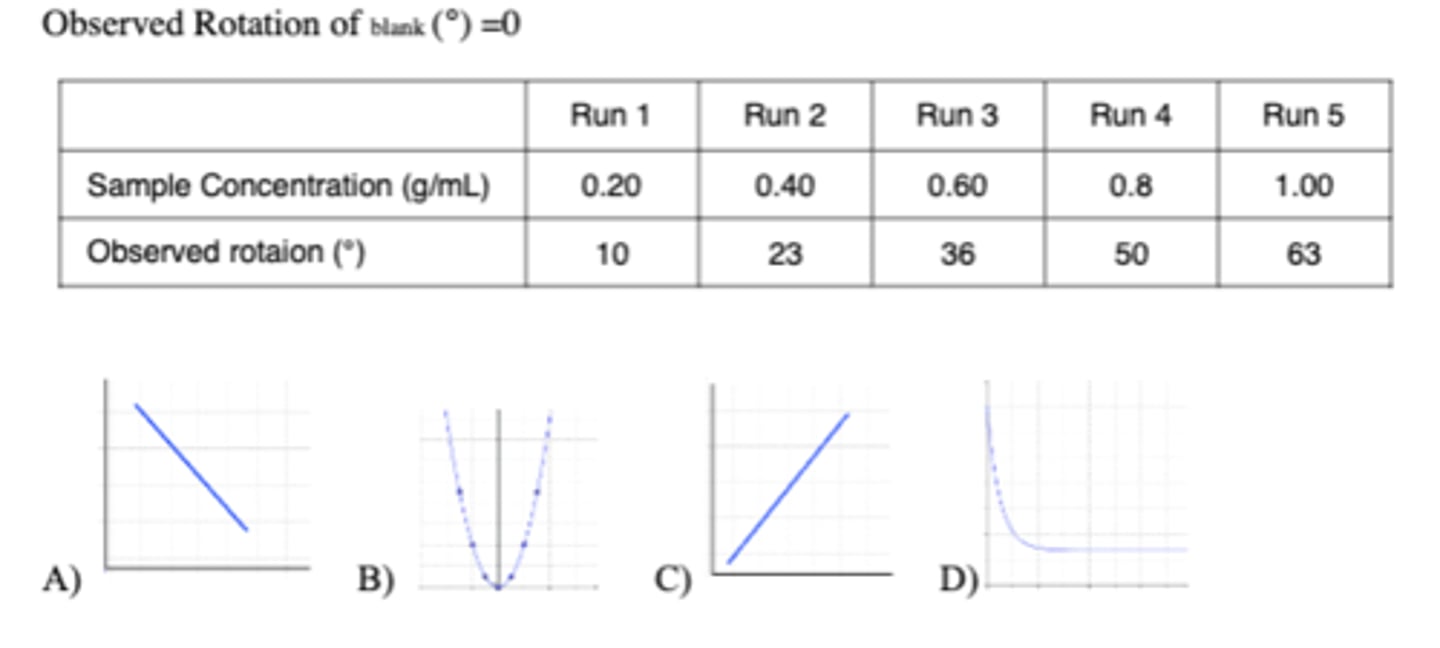
Using the graph generated in question 13, determine the relationship between sample
concentration and optical rotation.
A) linear
B) non-linear
C) exponential
A
Use the graph information in question 13 and identify the unknown
(Hint: calculate specific rotation [α])
A) Sucrose
B) Glucose
C) Fructose
D) galactose
A