Mendelian genetics principles EXPANDED (DONE) Week 10
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
EXAM #3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
The result from Gregor mendel’s remarkable crossing (mating) experiments form the basis of genetic science.
True
Which model system did Gregor Mendel select to facilitate his investigation of heredity?
Pea
A species that researchers intentionally choose to facilitate the research process is known as a—
model system
Due to spindle (M phase) checkpoint failure, which error can occur during meiosis l or meiosis ll that results in aneuploid gametes?
Nondisjunction
A recessive, loss of function, mutation on the X chromosome causes a dominant phenotype in males because males have—
1 X chromosome
The homozygous female parent horse produces white hair, and the homozygous male parent horse produces dark brown hair. This heterozygous colt produces light brown hair. This is an example of—
incomplete dominance
The mutated allele that causes cystic fibrosis causes digestive problems, ling damage, thick mucous, and increases the risk of infection. This mutated allele is—
Pleiotropic
Why is the mutated allele that causes sickle cell diseases “Pleiotropic”?
single gene mutations produces multiple effects on the body
define pleiotropic
single gene that influences multiple, seemingly unrelated phenotypic traits
What is the source of new alleles in a population?
Mutation
How do populations of an animal species, which inhabit different regions, benefit from having different allele for many genes?
Adaptation to local environmental conditions
In most animal, fungal, plant, and protistan populations, most genes typically have—
> 3 alleles
All the F1 offspring produced from the testcross experiment express the dominant phenotype. What is the unknown genotype of the parent of interest?
Homozygous dominant (PP)
A trait is unexpressed in the phenotype of the previous generation. This trait is expressed in the phenotype of the next generation. This trait is—
Recessive
A mutation that causes a muscle disorder in humans is not in the nuclear genome. This mutation must be in a gene in the—
Mitochondrion
In your cells, which organelles contain genes?
Mitochondrion & Nucleus
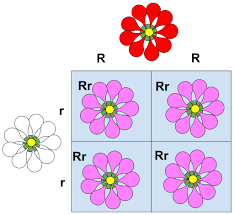
In some heterozygotes, what is incomplete dominance?
Neither allele is fully dominant, resulting in blended phenotypes in offspring
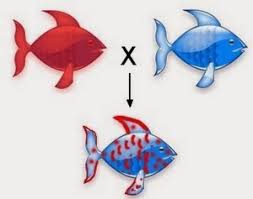
In some heterozygotes, what is co-dominace?
Both alleles of parents genes are expressed
Do safe blood transfusions require a knowledge of the co-dominance between the “A” allele & “B'‘ allele of the ABO gene?
Yes, its essential for determining which blood types are compatible
Which organelle(s) is the basis of cytoplasmic inheritance in humans?
Mitochondria
Which organelle(s) is the basis of cytoplasmic inheritance in plants?
chloroplasts and mitochondria
Why are some genetic disorders inherited only from the female parent?
Mitochondria is inherited from the mothers egg not the fathers sperm
Do mothers always transmit mitochondria genome coded traits to all children?
Yes, mitochondria traits are inherited from mothers egg never the fathers sperm
A new mutation that increases yield in tomatoes does not occur in genes in the nucleus or mitochondrion. In which organelle genome must this mutation occur?
Chloroplast
A mutation that contributes to a human muscular disorder was discovered.This mutation does not occur in the nucleus. Where must this mutation occur?
Mitochondria
What is polygenic inheritance?
regulation of one trait by many genes
What is an example of polygenic inheritances in humans?
two brothers like skin tone genotype
Describe how melanocyte cells determine skin tone, eye color, and hair color?
melanocyte cells produce and distribute the pigments melanin
Does a recessive mutation on the X chromosome causes a dominant phenotype or recessive phenotype in males?
dominant phenotype
Are males hemizygous for genes on the X chromosome?
Yes, having only one copy of a gene instead of two (XY)
In the human population,most genes of many alleles. What are two sources of new alleles in a population?
Mutation and genetic recomination
In the human population,most genes of many alleles. How do populations benefit from genetic variation?
enhances adaptability, survival, and long-term evolution potential, helping species exist longer in a changing world.
The red blood cells of heterozygotes with the A alle & B allele at the ABO gene express both glycoprotein A & glycoprotein B on their surface. This is an example of-
Co-dominance