PSYC 1 - Exam #1 Study Guide (Chapters 1 - 4)
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
Professor's Email
greg.feist@sjsu.edu
Professor's Office Hours
Tuesday & Thursday, 12-1pm
Professor's Office Location
DMH 313
Course Webpage
Canvas
Classroom Protocol
1. Attendance is strongly recommended with careful note taking
2. Be considerate of others and the instructor if you must show up late or leave early
3. Laptops are allowed only on the outer two sections
4. Cellphones are not allowed at any time
5. Engage in professional communication especially in emails
Penalty for not completing Research Participation requirement
You lose 6% of your grade (55 points)
Only form of extra credit
By completing all 13 chapters of the homework assignments, the 14th chapter is extra credit
Policy on bathroom breaks during exams
No bathroom breaks allowed during exams
Late work penalty
Assignments turned in after the deadline result in losing 3-4 points immediately and
additionally losing 3-4 points per day
Make-up exams
No makeup exams unless you have a valid medical excuse
Electronics Policy
- No cellphones allowed at any time
- Laptops are allowed only on the outer two sections of the classroom
University Policy on Academic Integrity
Requires honesty in all academic coursework
Exam #1 Date
September 18
Research Participation Hour Date
October 1
Writing Assignment #1 Date
October 2
Exam #2 Date
October 30
Writing Assignment #2 Date
November 13
Research Participation Hours and/or Alternative Assignment Date
December 4
Final Exam Date
December 16
Policy on Changing Final Exam Date due to 3 or more other exams in a day
If you have 3 finals in one day, let one instructor know 3 weeks in advance and provide evidence from your syllabus as proof
Is the mind adaptive and evolved
Yes
Where do the roots of psychology lie
In Philosophy and Physiology & Medicine
What is Mind-Body Dualism
The view that the mind (non-physical) and the body (physical) exist as separate entities
Tabula rasa
The notion that individual human beings are born "blank" and their identity is defined entirely by events after birth
Natural Selection
Feedback process where nature favors one design over another,
depending if it has an impact on reproduction
Scientific Method
a critical thinking process for experimentation that is used to explore observations and answer questions
Max Weber
A German political economist and sociologist who is considered one of the principal architect of modern social science
Gustav Fechner
A German philosopher, physicist, and experimental psychologist. An early pioneer in experimental psychology and founder of psychophysics
Charles Darwin
An English Natural scientist who laid down a framework for the theory of evolution
Weber-Fechner Law
States that the change in a stimulus that is just barely noticeable is a constant ratio of the original stimulus
Historical Schools of Thought
1. Evolutionary Theory
2. Structuralism
3. Functionalism
4. Gestalt
5. Behaviorism
6. Psychoanalysis
7. Cognitive Revolution
8. Drug Treatment
9. Evolutionary Psychology
10. Neuroscience
Evolutionary Theory
Based on natural selection, it is the process by which organisms change over time as a result of changes in heritable physical or behavioral traits
Structuralism
The methodology that elements of human culture must be understood by way of their relationship to a larger, overarching system or structure. It works to uncover the structures that underlie all the things that humans do, think, perceive, and feel
Functionalism
a school of thought, pioneered by William James, that focuses on the purpose and function of mental processes and behaviors rather than just their structure
Gestalt
means form, shape, or pattern
Behaviorism
psychology is only a true science if only examining observable behavior, no influence by ideas, thoughts, feelings, or motives
Psychoanalysis
A clinically based approach to understanding and treating psychological disorders; assumes that the unconscious mind is the most powerful force behind thought and behavior
Cognitive Revolution
The roughly twenty year period during the 1950's and 1960's when cognitivism became the dominant approach to psychology
Drug Treatment
for controlling pain if endorphins, thoughts, and feelings are not enough
Evolutionary Psychology
A theoretical approach to psychology that attempts to explain useful mental and psychological traits as the result of evolution and natural selection
Neuroscience
The study of how the nervous system develops, its structure, what it does, and its impact on behavior and cognitive (thinking) functions
Major Subdisciplines in Psychology
1. Cognitive
2. Developmental
3. Social
4. Clinical
5. Personality
6. Industrial
7. Education
8. Health
9. Biopsychology (Behavioral Neuroscience)
Cognitive Psychology
How we perceive, remember, and think
E.g., what causes memory loss?
Developmental Psychology
Studies the way thought, feeling, and behavior develop through the lifespan (from infancy to death)
E.g., can children remember experiences from their first year of life?
Social Psychology
how real or imagined presence of others influence how we feel, think, or do
E.g., when and why do people behave aggressively?
Clinical Psychology
diagnoses and treats mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders
E.g., what causes depression?
Personality Psychology
studies uniqueness of individuals
E.g., what are the underlying factors of personality
Industrial/Organizational Psychology
Examines the behavior of people in organizations & attempts to help solve organizational problems.
E.g., what motivates workers to do their jobs efficiently?
Education Psychology
Examines psychological processes in learning and applies psychological knowledge in educational settings.
E.g., why do some children have trouble learning to read?
Health Psychology
Examines the psychological factors involved in health and disease.
E.g., are certain personality types less vulnerable to disease?
Biopsychology (Behavioral Neuroscience) Psychology
Investigates the physical basis of psychological phenomena. Seeks to understand the mind through understanding the electrical and chemical activity of the nervous system.
E.g., how are memories stored in the brain?
Steps of the Scientifc Method/Research Process
(O-P-T-I-C) Observe, Predict, Test, Interpret, and Communicate
Empirical
based on thoughts and observation/experience
Scientific Attitude
Being honest, thinking critically, respecting evidence, and questioning authority
Pseudo-science
- Claims to be a science
- Lacks cumulative progress
- Lack of skepticism
- Vague explanations for how conclusions were reached
- Loose and distorted logic
Hypothesis
a specific, informed, and testable prediction of the outcome of a particular set of conditions in a research design
Variable
Anything that changes or varies
Independent Variable
What you are manipulating; an attribute that is measured by the experimenter while other aspects
of the study are held constant
Dependent Variable
What you are measuring; the outcome, response, or attribute that changes as a consequence of
variation in the independent variable
Naturalistic/Field Study Design
Describe: What is X?
Correlation Design
Determine relationships: Is X related to Y?
Correlation Relationship
Relationships do not equal causation
Correlation Coefficients
- If one variable increases, what happens to the other variable?
- Ranges between -1.0 to +1.0
- Closer to 0 = Less of a relationship
- Closer to -1/+1 = Better the relationship
Experiment Design
Determine cause and effect: Does X cause Y?
- Random assignment of participants to control and experimental groups
- Experimental control: Manipulation of independent variable
- Outcome variable: Dependent Variable
Validity and Reliability
A test is valid if it measures what it is supposed to measure. It is consistent if repeated outcomes of the test is the same.
What do you do once you have the data?
1. Organize and summarize: Averages and variability
2. Draw conclusions using statistics to rule out chance as an explanation: Use statistics and probability to rule out that findings were due to chance
Principles of Evolution
1. All receiving structures and forms change (usually but not always
gradually) over long periods of time
2. Evolution is "change over time infrequency which particular genes
occur within a breeding species"
3. Genetic changes create new structures
Four species of humans (homo-)
1. Homo Habilis (2.4 million - 1.5 million years ago)
2. Homo erectus (1.6 million - 100,000 years ago)
3. Home neanderthalensis (75,000 years ago)
4. Homo sapiens sapiens (Us, modern humans)
Structure of the DNA
1. Cell
2. Nucleus
3. Chromosome
4. Histones (Coils of DNA)
5. Gene
6. AT-CG base pairs
Cell
The smallest structural and functional unit of an organism
Nucleus
Contains the majority of a cell's genetic material
Chromosome
A threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus, carrying genetic information in the form of genes.
Histones
DNA tightly coiled many times around proteins that support the structure of chromosomes
Gene
A unit of heredity that is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristic of the offspring
AT-CG base pairs
Main ingredients of DNA.
- A: Adenine
- G: Guanine
- T: Thymine
- C: Cytosine
Monogenic transmission (Single-gene)
The heredity passing on of traits determined by a single gene
Polygenic transmission
The process by which many genes interact to create a single characteristic
Indirect effect of genes on behavior
Genes have very little direct effect on a person's behavior
General process from genes to behavior
Genes => Proteins => Physiological systems => Behavior
Genome
All the genetic information in DNA
Phenotype
The set of observable characteristics of an individual
E.g., Heigh, eye color, hair color
Heritability
How much of the variation seen in a certain trait within a population can be attributed to genetic variation, as opposed to environment
E.g., twin adoption studies which compare pairs of fraternal and identical twins
Epigenetics
Genetic influence is not permanently determined at birth. What we do and experience turns on/off our genetics
Glial cells (myelin)
Cells of the CNS that facilitates neural transmission, provides structural support, and holds neurons in place and provide them with nourishment
Neurons
Nerve cells that process and transmit information throughout the nervous system
Three kinds of neurons
1. Sensory Neurons
2. Motor Neurons
3. Interneurons
Sensory Neurons
Sensory neurons receive incoming sensory information from the sense organs (eyes, ears, skin, tongue, and nose)
Motor Neurons
Take commands from the brain and carry them to the muscles of the body. Intentional or unintentional, each time you move any muscle in your body, motor neurons are at work
Interneurons
Communicate only with other neurons.
Most common kind of neuron in the brain
Interneurons which outnumbers the other two types by at least 10 to 1
Three major principles of neuroscience
1. Neurons are the building blocks of the nervous system
2. Information travels within a neuron in the form of an electrical signal by active potentials
3. Information transmitted between neurons by means of chemicals called neurotransmitters
Anatomy of a neuron
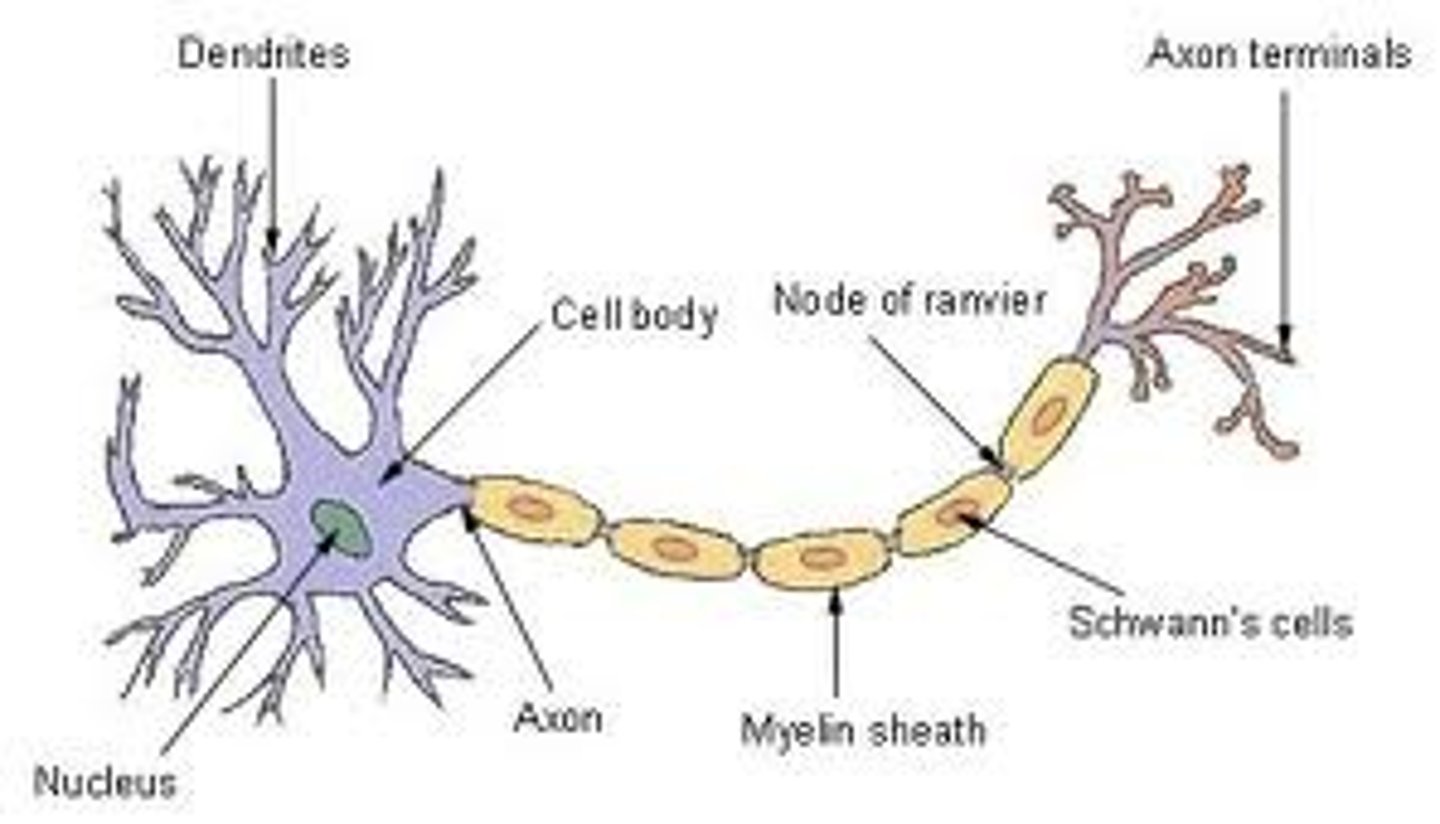
Soma
Also known as the cell body, it contains a nucleus and other components needed for cell maintenance and function
Axon
A long rod/projection that transmits electrical impulses towards the adjacent neuron
Dendrites
Finger-like projections that receive incoming messages from other neurons
Synapse
A gap/junction between the axon and the adjacent neuron
Terminal button
Located in each synapse at the end of an axon, it contains tiny sacs of neurotransmitters. When electrical impulses reaches the terminal button, it releases neurotransmitters into the gap between neurons
Neurotransmitters
Information transmitted between neurons
Synaptic Cleft
Gap between neurons
Resting potential of a neuron
Inactive; the difference in electrical charge between the inside and outside of the axon when the neuron is at rest
- More negative charge inside membrane due mostly to negatively charged anions A-