Unit 3 Learning Catalytics
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
One of the buffers that contribute to pH stability in human blood is carbonic acid (H2CO3). Carbonic acid is a weak acid that, when placed in an aqueous solution, dissociates into a bicarbonate ion (HCO3-) and a hydrogen ion (H+), as noted below.

If the pH of blood increases, one would expect _____.
decrease in the concentration of HCO3- and an increase in the concentration of H+
an increase in the concentration of H2CO3 and a decrease in the concentration of HCO3-
decrease in the concentration of H2CO3 and an increase in the concentration of HCO3-
an increase in the concentration of HCO3- and a decrease in the concentration of OH-
decrease in the concentration of H2CO3 and an increase in the concentration of HCO3-
Based on your knowledge of the polarity of water molecules, the solute molecule depicted here is most likely _____.
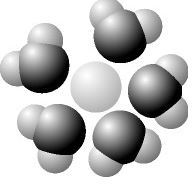
nonpolar
positively charged
without charge
negatively charged
postively charged
Identical heat lamps are arranged to shine on two identical containers, one containing water and one methanol (wood alcohol), so that each liquid absorbs the same amount of energy minute by minute. The covalent bonds of methanol molecules are nonpolar, so there are no hydrogen bonds among methanol molecules. Which of the following graphs correctly describes what will happen to the temperature of the water and the methanol?
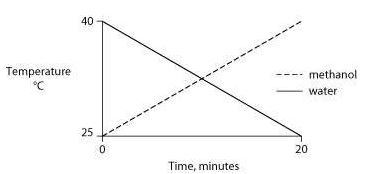
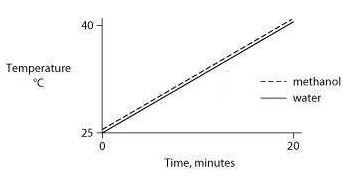
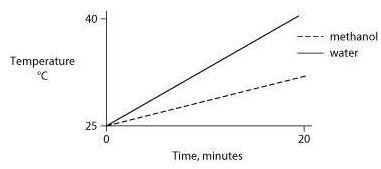
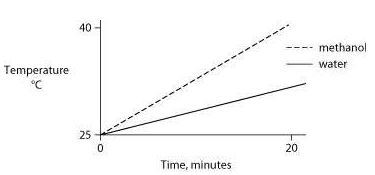

One idea to mitigate the effects of burning fossil fuels on atmospheric CO2 concentrations is to pipe liquid CO2 into the ocean at depths of 2500 feet or greater. At the high pressures at such depths, CO2 is heavier than water. What potential effects might result from implementing such a scheme?
increased carbonate concentrations in the deep waters
increased growth of corals from a change in the carbonate–bicarbonate equilibrium
no effect because carbon dioxide is not soluble in water
increased acidity and decreased carbonate concentrations in the deep waters
increased acidity and decreased carbonate concentrations in the deep waters
Which of the following statements about bulk flow are correct?
I) Bulk flow is driven primarily by pressure potential.
II) Bulk flow depends on a difference in pressure potential at the source and sink.
III) Bulk flow depends on the force of gravity on a column of water.
IV) Bulk flow may be the result of either positive or negative pressure potential.
I, II, and IV
and III
I, II, III, and IV
II and III
I, II, and IV
Arrange the following five events in an order that explains the mass flow of materials in the phloem.
1. Water diffuses into the sieve tubes.
2. Leaf cells produce sugar by photosynthesis.
3. Solutes are actively transported into sieve tubes.
4. Sugar is transported from cell to cell in the leaf.
5. Sugar moves down the stem.
1, 2, 3, 4, 5
2, 4, 3, 1, 5
4, 2, 1, 3, 5
2, 4, 1, 3, 5
2, 4, 3, 1, 5
Which of the following observations provides the strongest evidence against root pressure being the principal mechanism of water transport in the xylem?
Not all soils have high concentrations of ions.
Root pressure requires movement of water into the xylem from surrounding cells in the roots.
Over long distances, the force of root pressure is not enough to overcome the force of gravity.
There is no water potential gradient between roots and shoots.
Over long distances, the force of root pressure is not enough to overcome the force of gravity.
One is most likely to see guttation in small plants when the ____.
transpiration rates are high
root pressure exceeds transpiration pull
the preceding evening was hot, windy, and dry
roots are not absorbing minerals from the soil
root pressure exceeds transpiration pull
Photosynthesis ceases when leaves wilt, mainly because ____.
the chlorophyll in wilting leaves is degraded
flaccid mesophyll cells are incapable of photosynthesis
stomata close, preventing carbon dioxide from entering the leaf
accumulation of carbon dioxide in the leaf inhibits enzymes
stomata close, preventing carbon dioxide from entering the leaf
Water flows into the source end of a sieve tube because ____.
sucrose has been actively transported into the sieve tube, making it hypertonic
water pressure outside the sieve tube forces in water
the companion cell of a sieve tube actively pumps in water
sucrose has been transported out of the sieve tube by active transport
sucrose has been actively transported into the sieve tube, making it hypertonic
The necropsy (postmortem analysis) of a freshwater fish that died after being placed accidentally in saltwater would likely show that _____.
loss of water by osmosis from cells in vital organs resulted in cell death and organ failure
the kidneys were not able to keep up with the water removal necessary in this hyperosmotic environment, creating an irrevocable loss of homeostasis
the gills became encrusted with salt, resulting in inadequate gas exchange and a resulting asphyxiation
high amounts of salt had diffused into the fish's cells, causing them to swell and lyse
loss of water by osmosis from cells in vital organs resulted in cell death and organ failure
If ATP production in a human kidney was suddenly halted, urine production would
decrease, and the urine would be hypoosmotic compared to plasma
increase, and the urine would be isoosmotic compared to plasma
increase, and the urine would be hyperosmotic compared to plasma
decrease, and the urine would be isoosmotic compared to plasma
increase, and the urine would be isoosmotic compared to plasma