Life cycle of RBCS and recycling of hemoglobin components
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
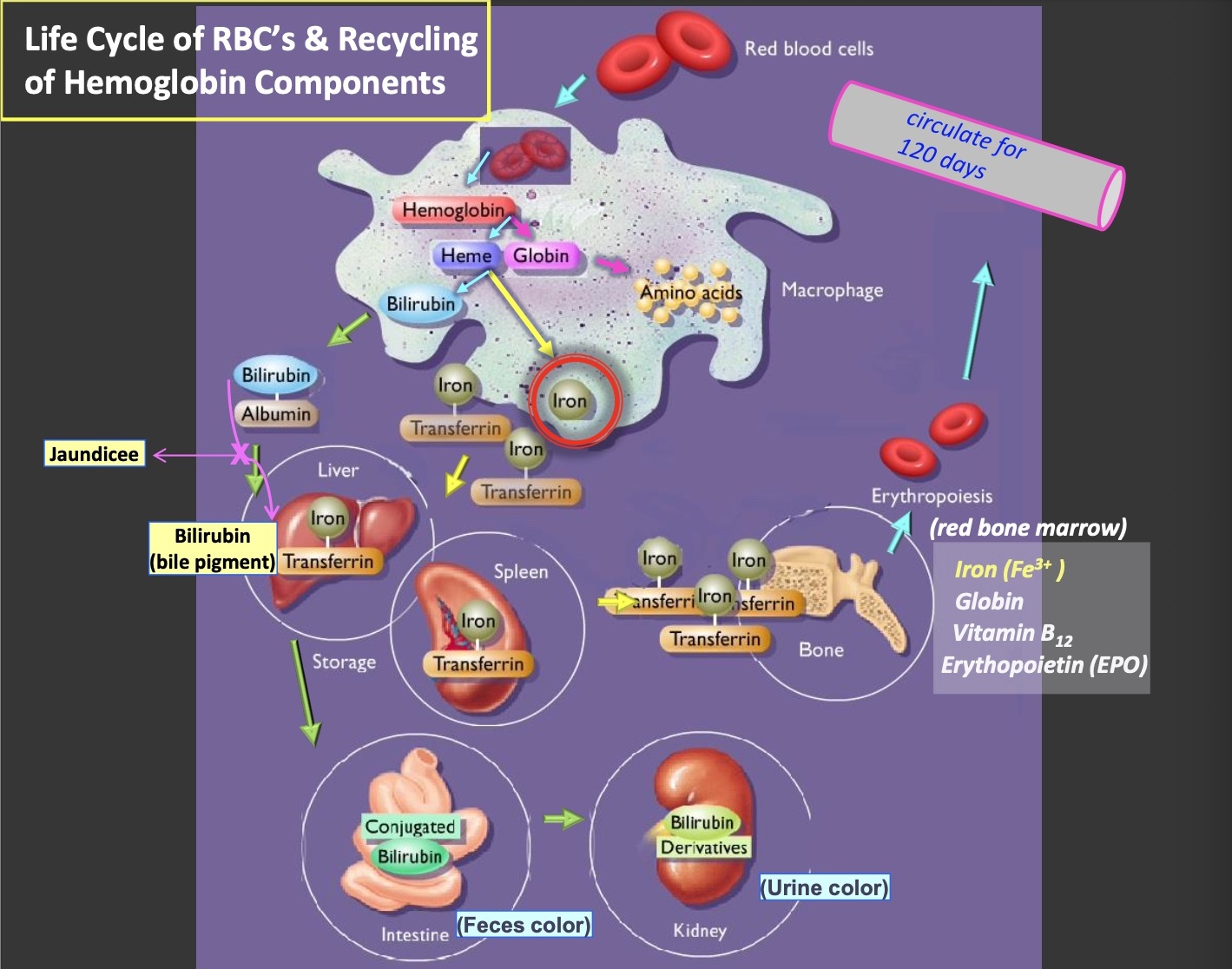
Life cycle of RBCS and recycling of hemoglobin components
Iron (Fe+3) (1)
transported in blood attached to transferrin protein
iron (Fe+3) (2)
stored in liver , muscle, or spleen
stored in liver , muscle, or spleen
iron is stored by attaching protein ferritin and Hemosiderin protein
Iron (Fe+3) (3)
being used for hemoglobin synthesis in bone marrow
Biliverdin (green) converted to bilirubin (yellow)
bilirubin secreted by liver to bile
bilirubin secreted by liver to bile (1)
converted to Urobilinogen then Stercobilin (brown pigment in feces) by bacteria of large intestine
bilirubin secreted by liver to bile (2)
if reabsorbed from intestines into blood is converted to a yellow pigment, urobilin and excreted in urine
polycythemia
an excess of RBCs
polycythemia primary (cause)
Cancer of the erythropoietic (RBC-producing) cells in red bone marrow
polycythemia primary (rbc count)
more than 11 million RBCs/ nanoLiters or hematocrit 80%
polycythemia secondary (cause)
Dehydration, emphysema, high alttiude, or physical conditioning
polycythecemia secondary (rbc coubt)
8million/nanoliters
dangers of polycythemia
INCREASE blood volume, blood pressure, viscosity
Dangers of polycythemia can lead to
embolism, stoke, or heart failure
anemia
not enough RBC’s or defect of RBC’S HB
anemia symptoms
O2- carrying capacity of blood decreases which causes lack of O2 for ATP and heat protection then leads to fatigue, cold intolerance, and paleness
anemia causes
nutritional, bleeding, hereditary and radiation toxin
anemia dangers (1)
tissue O2 decreases then leads to hypoxia
anemia dangers (2)
blood osmolarity decreases then leads to edema
anemia dangers (3)
blood viscosity decreases then leads to heart rate pressure increase (even cardiac arrest)
anemia leads to (1)
kidney failure or insufficient EPO
anemia leads to (2)
iron (FE2+) deficiency anemia
pernicious anemia
short of vitamin b12 folic acids (poor nutrition) or intrinsic factor (stomach problems)
vitamin b12 and folic acids
RBC proliferation in red bone marrow; intrinsic factor help b12 absorption
hereditary hemoglobin defects (1)
sickle cell anemia (mostly among african descent)
hereditary hemoglobin defects (2)
change in hemoglobin chain (6th amino acid) results in its low o2- binding capacity
hereditary hemoglobin defects (3)
malaria parasites die in this type of RBC (selection)
hereditary hemoglobin defects (4)
cells are rigid and sticky , often block small vessels and cause intense pain; can lead to kidney or heart failure, stroke, etc
hemorrhagic anemia
bleeding (ulcers)
hemolytic (lysis) anemia
defects in cell membranes cause RBC rupture
aplastic anemia
destruction of bone marrow (radiation/toxins)
plastic
grow