psychology exam 5
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Development psychologists
Study how behavior and mental processes change over the life span
Cross-sectional designs
measuring people from different age groups at the same time
Prone to cohort effects (people who grew up in one period of time may differ from people who grew up in a different period of time)
Longitudinal designs
measuring the same individuals at different points in time
Problems with attrition (people dropping out the study)
Gene-environmental interaction
Gene —> environment —> gene (loop)
Ways to make babies smarter
Stimulating environment?
The “Mozart effect” is short-term and due to arousal
No products that can make babies smarter
Books on parenting
Confusing genetic and environmental influences
e.g., angry dad --> angry baby
What did Piaget think
thought that children were “little scientists” trying to figure out the world
Assimilation
absorbing new information into one’s understanding of the world (without revising one’s overall understanding)
Accommodation
revising one’s understanding of the world to fit with new information
Object permanence
understanding that objects continue to exist even when they are out of view
Children fail such tasks at the sensorimotor stage
Conservation
understanding that transforming the physical presentation of a substance (or number of objects) does not change its amount
Children fail such task at the preoperational stage
Self
Children can recognize themselves in the mirror at around 18 months
Mirror self-recognition test
Sex differences
Differences beyond socialization
David Reimer
Hormones affect the brain/mind
Toy preferences
Differences due to socialization
Reinforcement of sex-stereotypical behavior
Social
Bowlby’s attachment styles
The strange situation procedure
Secure attachment
distressed when mom leaves, happy when she returns
Insecure-avoidant attachment
no distress when mom leaves, little reaction when she returns
Insecure-anxious attachment
distressed when mom leaves, ambivalent about her return
Theory of mind
the ability to reason about what other people know or believe
The false-belief task
Kohlberg’s levels of moral development
Postconventional
Conventional
Preconventional
Postconventional
focus on internal principles
Conventional
focus on societal values
Preconventional
focus on rewards and punishments
Fluid intelligence
the capacity of learning new ways of solving problems
Crystallized intelligence
accumulated knowledge acquired over time
Cognitive functioning and aging
As people become older adults, they tend to increase in crystallized intelligence but decrease in fluid intelligence
Abnormality
depends on cultural context, not all abnormalities are bad
Distress
some distress is caused by unpleasant events, some disorders may not consistently cause stress
Impairment
not all impairments are due to disorders
DSM (1st edition 1952)
Current edition: DSM-5
Potential dangers in using diagnostic labels:
Labels create preconceptions that affect our thoughts and behavior
People often have inaccurate and unkind beliefs about people with psychological disorders
Media influences
Believing that those with psychological disorders are dangerous
Benefits of using diagnostic labels:
Enables professionals to efficiently communicate about cases
Helps to identify proper courses of treatment
Anxiety disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder
Panic disorder
Phobias
Post-traumatic stress disorder
Obsessive-compulsive disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder
Core features:
Continually tense and uneasy – even in the absence of any specific anxiety-provoking stimulus
Excessive anxiety occurring most days and lasting at least 6 months
Disrupts normal functioning (social relationships, ability to work, etc.)
Panic disorder
Panic attacks – characterized by sudden onset of fear of disaster or losing control, strong physical reaction (racing heart, sweating, breathing problems, dizziness, etc.)
Intense worry about when the next attack will happen
Avoidance of places where attacks have occurred in the past
Panic attacks
characterized by sudden onset of fear of disaster or losing control, strong physical reaction (racing heart, sweating, breathing problems, dizziness, etc.)
Phobias
Excessive or irrational fear of a specific type of object or situation (e.g., spiders, small spaces, flying)
Reactions are uncontrollable
In some cases, phobias can result from a traumatic incident
Post-traumatic stress disorder
Results from experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event (e.g., war, abuse, natural disaster)
Characterized by flashbacks (reliving traumatic episode), avoiding reminders of the traumatic event, and hyperarousal (being on “edge”)
Obsessive-compulsive disorders
Obsessive thoughts or urges that are unwanted, persistent, and stress-inducing
e.g., concerns about cleanliness or order
Compulsions
repetitive behaviors or thoughts that are driven by obsessions
e.g., hand washing, checking, counting
Mood disorders
Major depressive disorder
Bipolar disorder
Major depressive disorder
Affects 16% of Americans
Can be detrimental to social relationships
Depressed people may not be reinforced by seeking pleasurable activities (so they may stop trying)
Depressed people may process negative info more than positive info
Symptoms of major depressive disorder (DSM-5)
Depressed mood
Loss of interest or pleasure
Change in weight or appetite
Insomnia or hypersomnia
Psychomotor retardation or agitation
Loss of energy or fatigue
Feelings of worthlessness or guilt
Impaired concentration or decisiveness
Thoughts of death or suicidal ideation (or attempt)
Bipolar disorder
Alternating between depression and mania
Mania is characterized by euphoria, grandiose self-esteem, and hyperactivity
Diathesis-stress model
many psychological disorders may be caused by a genetic predisposition (diathesis) and stress that acts as a trigger
Diametrical disorders of the social brain (Crespi & Badcock’s theory)
Autism-spectrum disorders
Low social cognition
Mechanistic thinking
Psychotic-spectrum disorders (e.g., schizophrenia)
Very high social cognition
Mentalistic thinking
Suicide
More than 30,000 people die by suicide in US each year (11th leading cause of death)
People coming out of depression are MORE likely to attempt suicide
Increased initiative
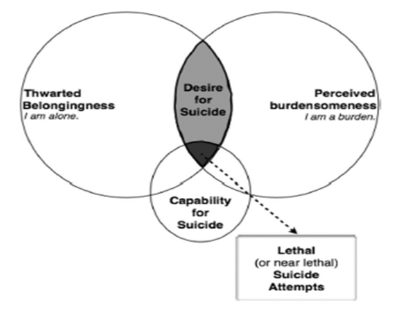
Interpersonal theory of suicide Thomas Joiner
Three factors:
Thwarted belongingness
Not feeling connected to others
Perceived burdensomeness
Feeling that others would be better off if one were dead
Capability for suicide
Lack of fear of death or pain, overcoming self-preservation instincts
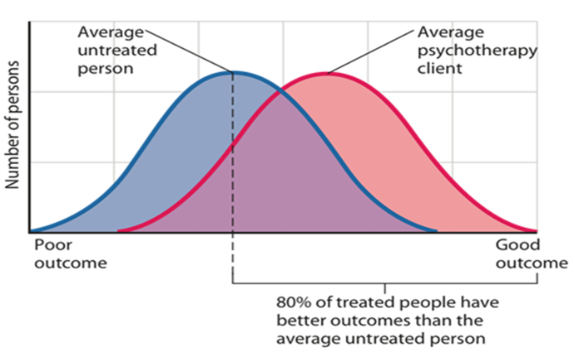
Psychotherapy
Psychological intervention designed to help people resolve emotional, behavioral, and interpersonal problems and improve the quality of their lives
Many types of providers (both professionals and non-professionals)
There are over 500 types (some based on evidence and some not)
The “Dodo bird” verdict
the idea that all forms of psychotherapy are roughly equal in effectiveness
Some meta-analyses suggest the major categories of therapy (psychodynamic, cognitive-behavioral, etc.) are similar in effectiveness
Some evidence that certain forms of therapy can be harmful (e.g., “reliving” traumatic episodes can be bad for those with PTSD)
Characteristics of the therapist can sometimes be more important than the type of therapy in determining effectiveness
Good therapists are warm and direct, they get feedback from clients, etc.
Carl Rogers’s three conditions
Genuineness (or authenticity)
Unconditional positive regard
Empathic understanding
Cognitive-behavioral therapies (CBT)
Attempt to replace irrational thoughts and maladaptive behaviors
Shaping behaviors
e.g., systematic desensitization (having clients relax while being exposed to feared stimuli in a stepwise manner)
Shaping cognitions
e.g., rational emotive behavior therapy (REBT)
People respond to the same events in very different ways
People's beliefs determine whether they will respond in desirable or undesirable ways
Therapists help clients to dispute irrational beliefs and encourage rational/effective beliefs
The ABCs of rational emotive behavior therapy (REBT)

Third wave therapies
Focus on awareness of all aspects of mind, beliefs, etc.
Urge clients to accept all of their thoughts (but still recognize irrational beliefs)
Often employ mindfulness mediation
Psychopharmacotherapy
the use of medications to treat psychological problems
few comments:
Scientists don’t know how many of these meds work
There are no optimal levels of neurotransmitters
Changes in the brain occur from both psychotherapy and psychopharmacology
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) - commonly referred to as “shock treatments”
–It can effectively treat severe depression, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia (typically 6-10 treatments)
–Only used when all other treatment fail
–Patients receive a muscle relaxer and are anesthetized during the procedure
“Attrition” refers to _______.
–A. the fact that people who grew up in one time period may differ from those who grew up in a different one
–B. revising one’s view of the world to fit with new info
–C. people dropping out of a longitudinal study
–D. the stigma of psychological disorders
–C. people dropping out of a longitudinal study
According to the interpersonal theory of suicide, which factor(s) lead to the desire for suicide?
•A. thwarted belongingness
•B. perceived burdensomeness
•C. capability for suicide
•D. A and B
•E. A, B, and C
E. A, B, and C
The overall number of disorders contained in the DSM __________ over time.
–A. stays the same
–B. has been increasing
–C. has been decreasing
B. has been increasing
Suppose someone were to avoid stepping on cracks in the sidewalk out of fear for their families safety. This behavior would be most indicative of ________.
–A. PTSD
–B. Generalize Anxiety Disorder
–C. Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
–D. Bipolar Disorder
C. Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
Which of the following criteria are most often used to identify psychologically disordered behavior?
–A. distress
–B. impairment
–C. abnormality
–D. all of the above
–E. only A and B
E. only A and B
Which task is used as a measure of children’s capacity for theory of mind?
–A. the strange situation procedure
–B. conservation tasks
–C. object permanence tasks
–D. the false-belief task
D. the false-belief task
According to Kohlberg, people who focus on societal values operate at which level of moral development?
–A. preconventional
–B. conventional
–C. postconventional
–D. none of the above
B. conventional
Which of the following psychologists focused most on characteristics of the therapist as being central to psychotherapy?
–A. Kohlberg
–B. Piaget
–C. Joiner
–D. Rogers
D. Rogers