Cellular Bio - Energetics
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Appetite & Satiety
(Cellular Bio - Energetics)
Control of food intake is a complex process
Two competing behavioral states
Appetite - hunger
Satiety - feeling full/satisfied
What are the two hypothalamic centers?
(Cellular Bio - Energetics)
Feeding center: Tonically activate (active when hungry)
Satiety center: Inhibits feeding center (you’re not hungry)
What is the glucostatic theory?
(Cellular Bio - Energetics)
The satiety center has neurons called glucostats that rapidly absorb blood glucose after a meal
Hypothesis: Glucose uptake causes the satiety center to send inhibitory signals to the hunger center and thus suppresses appetite
What is the lipostatic theory?
(Cellular Bio - Energetics)
Body fat content is maintained for homeostasis
When energy balance is positive, fat increases
Leptin release (from fat cells)
Leptin feeds back to the brain to decrease energy storage
Don’t need anymore energy - enough is stored
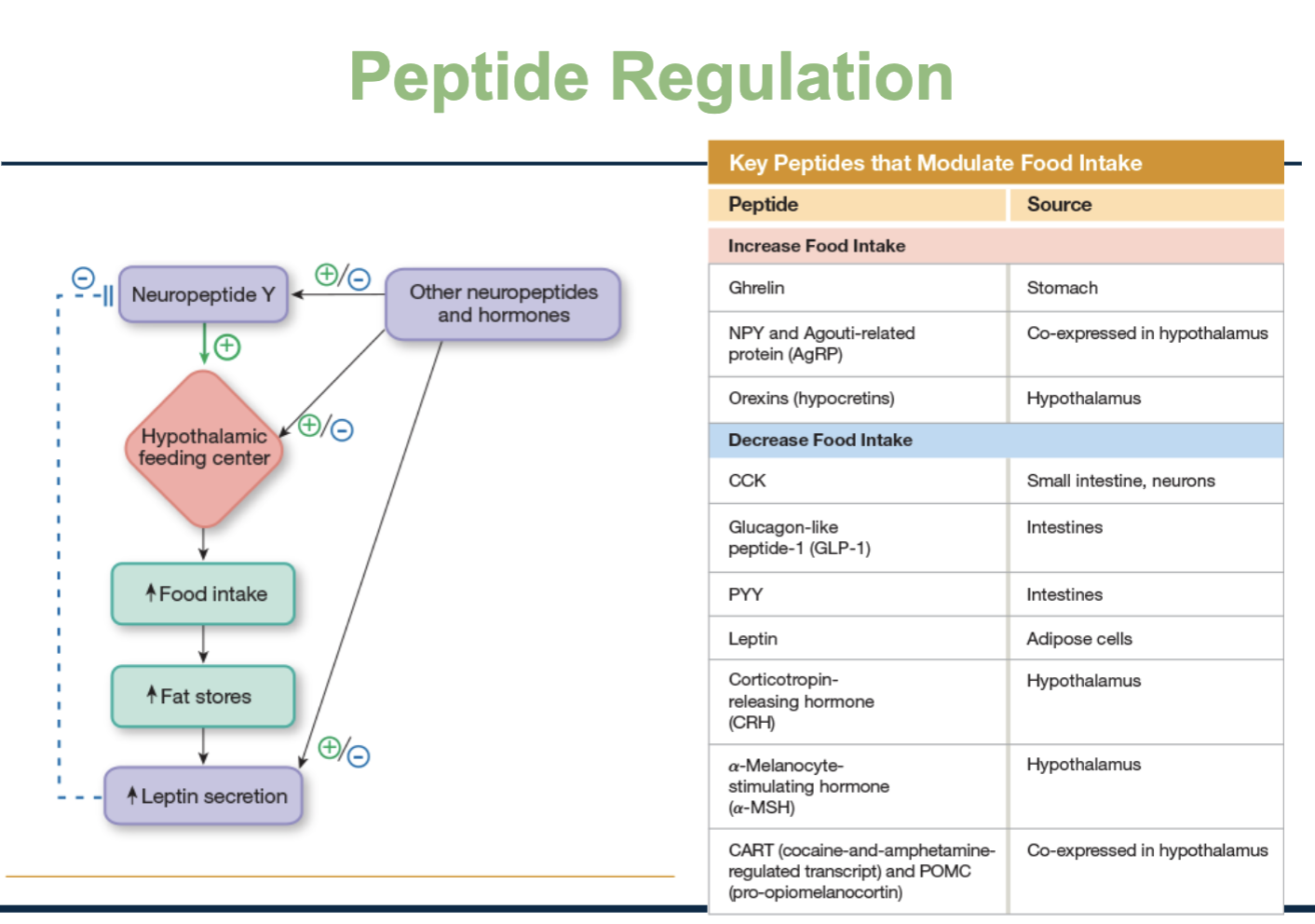
Explain the process of peptide regulation.
(Cellular Bio - Energetics)
Neuropeptide Y: Hunger-stimulating peptide made in the hypothalamus, which activates the hypothalamic feeding center
When the feeding center is activated
↑ Food intake
↑ Fat stores
↑ Leptin secretion (leptin comes from fat cells)
Leptin then feeds back to the brain and:
Inhibits NPY
Suppresses the feeding center
Part of a negative feedback loop
↑ Fat, ↑ Leptin, less hunger/eat less
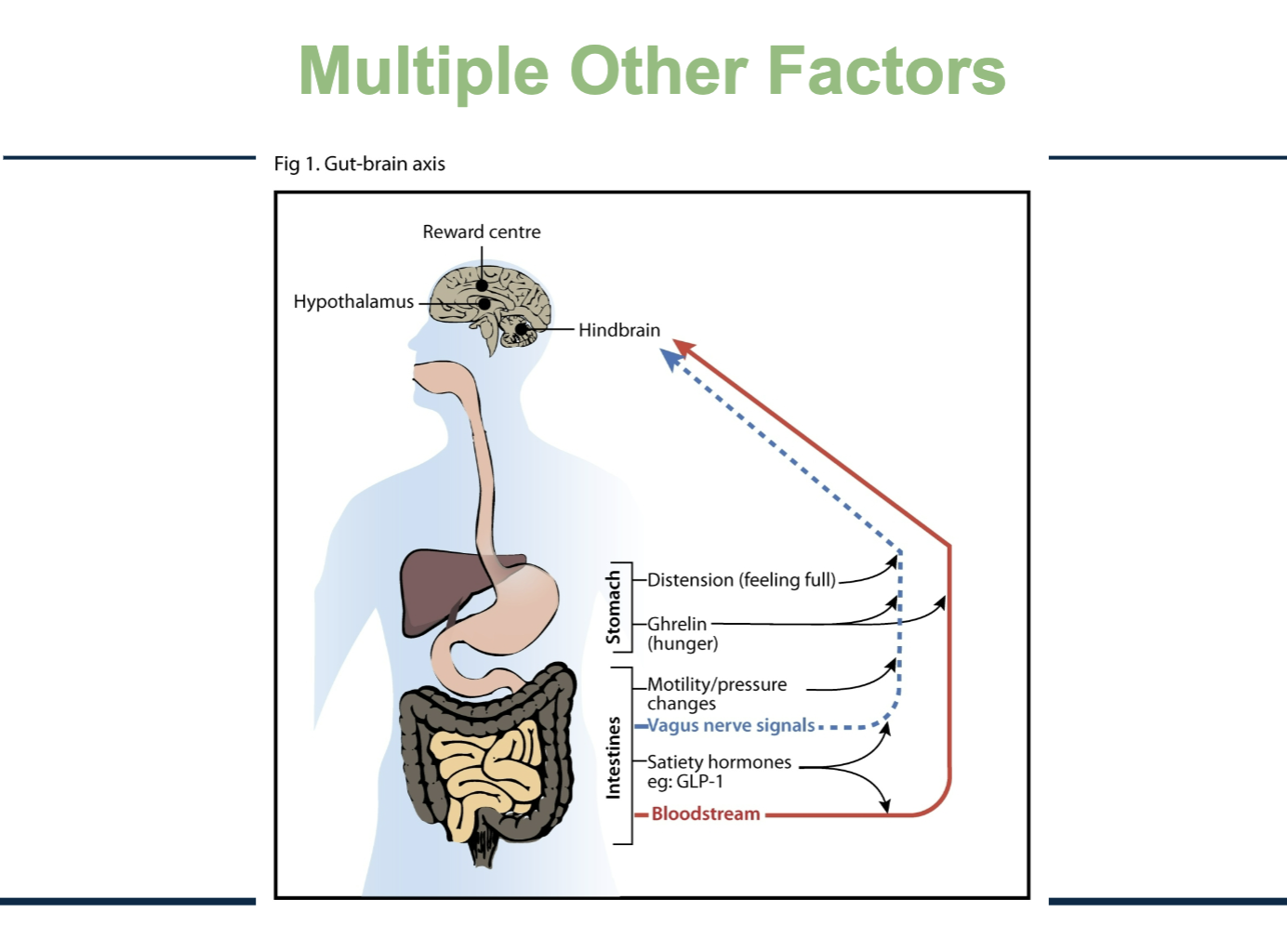
How does the gut communicate with the brain to regulate hunger and satiety?
KEY TAKEAWAY: Food intake isn’t regulated by just one hormone or one brain center. It’s influenced by mechanical signals, nerves, hormones, and reward pathways all at once.
Nerve signals (blue dashed line – vagus nerve)
Stomach distension (stretching when you eat → “I’m full”)
Changes in gut movement/pressure
These travel quickly to the hindbrain and hypothalamus.Ghrelin from the stomach - induce hunger
Hormones in the bloodstream (red line)
Ghrelin from the stomach → signals hunger
Satiety hormones like GLP-1 from intestines → signal fullness
These circulate in blood and act on the brain.
The brain areas involved:
Hypothalamus – homeostatic control (energy balance)
Hindbrain – basic feeding control
Reward center – pleasure/motivation to eat
How do we do work?
Eating!
First law of thermodynamics (conservation of energy)
Change in energy = Energy intake - Energy Output
Energy Intake = Diet
Energy Output = Work + Heat
Work: Transport, Mechanical, Chemical
How do we intake energy?
Through food (energy)!
Direct calorimetry'
Fat - 9 kcal/g
Protein 4 kcal/g
CHO (carbohydrate) - 4 kcal/g
Energy of Absorption
Digestive Waste
Energy Output
By mass balance: Output = Intake - Heat
Indirect calorimetry
Oxygen consumption
CO2 production
Respiratory Quotient (indicates what fuel source is being used)
1 - CHO
0.8 - Protein
0.7 - Fat
6 kcal/L O2 (RQ = 1)
Metabolic Rate - L O2/day x kcal/L O2
What are the factors that contribute to the basal metabolic rate?
Age and sex
Lean Body Mass
Hormones
Genetics
Activity/diet level
Thermic effect of eating
How often you eat
How much heat is released from digestion
How is glucose (from blood or glycogen) converted into usable energy?
Through the process of glycolysis!
Fed state
Occurs in cytoplasm
Glucose enters the cell and becomes G6P
This glucose comes from blood glucose or glycogen (stored glucose)
Glucose goes through glycolysis to become pyruvate
Anaerobic pathway: becomes lactate
Aerobic pathway: enters mitochondria
Explain the steps of aerobic metabolism
Takes place in the mitochondria (aerobic metabolism)
Pyruvate → Acetyl-CoA
Fatty acids are broken down by beta oxidation → Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA enters citric acid cycle
Produces CO2 and high energy electrons from NADH and FADH2
Electrons → ETC → lots of ATP + H2O
Excess acetyl-CoA in liver → ketone bodies
How does the body make glucose during fasting?
Through gluconeogenesis (fasting state)!
Occurs in liver & kidney
Lactate, amino acids → pyruvate
Pyruvate + amino acids + glycerol → G6P → Glucose (liver/kidney(
Maintains blood glucose when intake is low
How many net ATP are produced through anaerobic metabolism?
2 ATP
How many net ATP are produced through aerobic metabolism?
30-32 ATP
(26-28 from ETC)
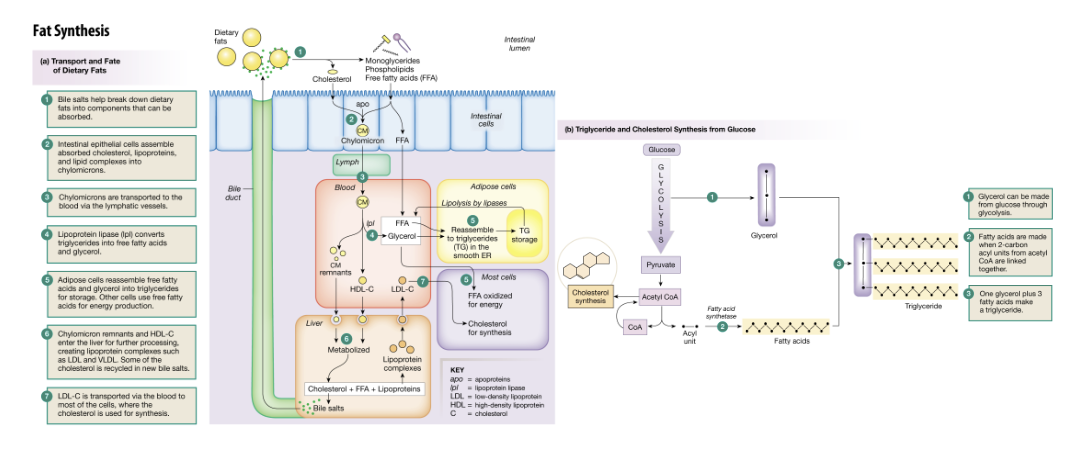
Explain the process of lipid anabolism
Fat synthesis consists of two parts:
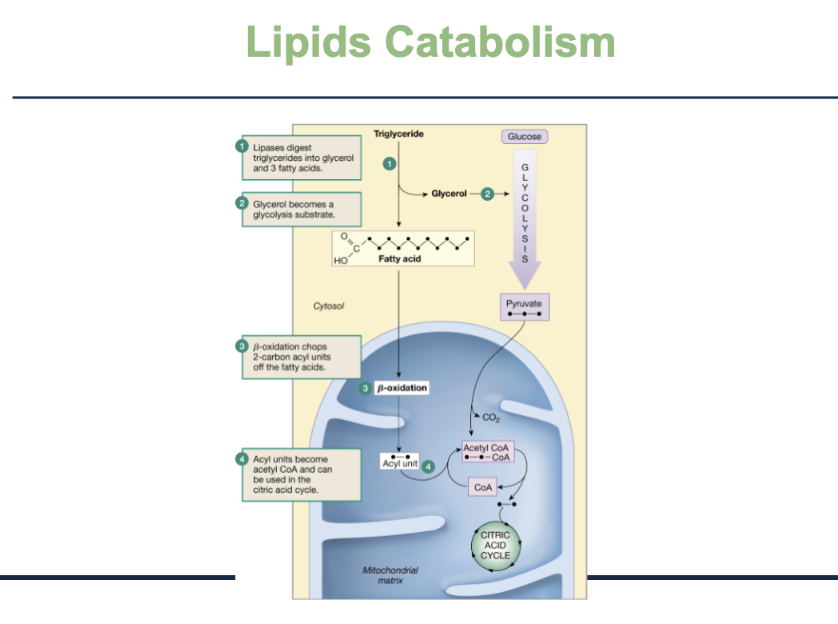
Explain the process of lipid catabolism.
Triglycerides are broken down
Enzymes called lipases split a triglyceride into:
1 glycerol
3 fatty acids
Glycerol enters glycolysis
Glycerol becomes pyruvate and is used to make ATP
Fatty acids enter the mitochondria
Inside, they undergo β-oxidation
This process chops fatty acids into 2-carbon units
2-carbon units → Acetyl-CoA
Each unit becomes acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle
→ produces CO₂, high-energy electrons
→ feeds the ETC to make lots of ATP
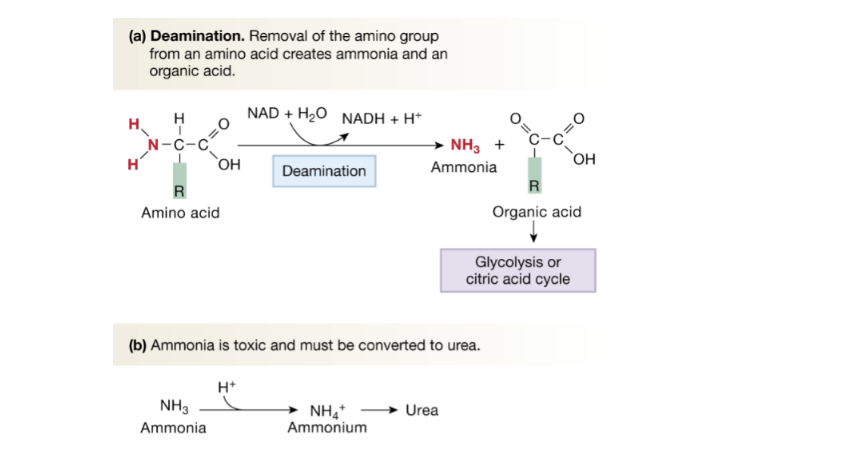
What happens to amino acids during deamination, and why must ammonia be converted to urea?
Deamination: Amino group from an amino acid is removed to produce ammonia and an organic acid, which then enters glycolysis or the citric acid cycle
Ammonia is toxic, which is why it is converted to urea
What is the fed state?
Absorptive
Energy absorbed and stored
Ingested molecules (from food)
Used in energy
Used in synthesis
Stored
Anabolism - builds complex molecules required for bodily processes
What is the fasted stated?
Energy used
Catabolism - breaks down nutrients/molecules for energy
What are the three fates of ingested biomolecules?
Energy to do mechanical work
Synthesis for growth and maintenance
Storage as glycogen and fat
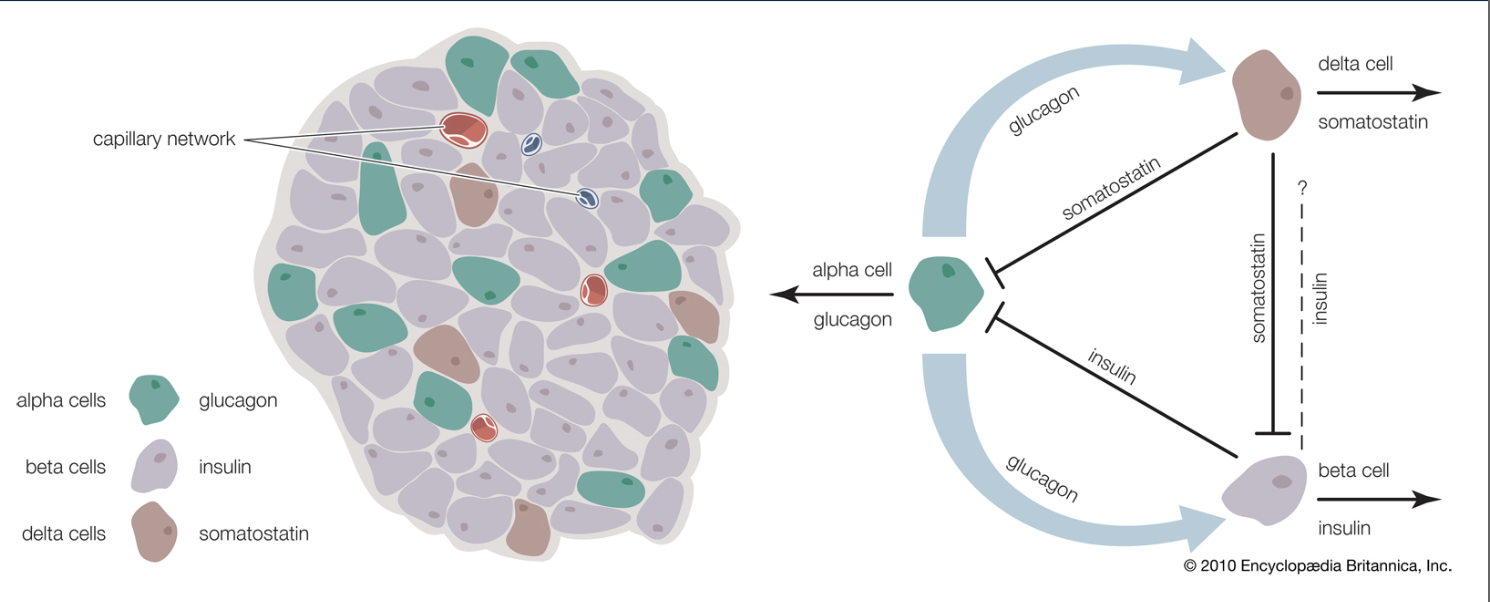
How do alpha, beta, and delta cells in the pancreatic islets (cluster of cells) interact to regulate blood glucose?
Alpha cells (green) → secrete glucagon
Beta cells (purple) → secrete insulin
Delta cells (brown) → secrete somatostatin
Note: F cell produces pancreatic polypeptide
Beta cells predominate (60-80%)
Cells linked by tight junctions
Regulated entry of small molecules
Blood flows from beta to alpha and delta cells (BAD)
Beta cell is primary glucose center
Diagram:
Beta cells → Insulin
Lowers blood glucose
Inhibits alpha cells (↓ glucagon release)
Alpha cells → glucagon
Raises blood glucose
Stimulates beta cells → ↑ insulin release
Stimulate delta cells → ↑ somatostatin
Delta cells → somatostatin
Alpha cells → ↓ glucagon, ↓ blood glucose
Beta cells → ↓ insulin, ↑ blood glucose
What is the function of glucagon?
Source: alpha cell (pancreas)
Target Tissues: Liver (adipose, skeletal muscle)
Action: Promotes glycogenolysis (breaking down stored glycogen into glucose-1-phosphate and glucose in the liver and muscles) and gluconeogenesis in the liver
What is the function of insulin?
Source: beta cell (pancreas)
Target Tissues: Liver (adipose, skeletal muscle)
Action: Promotes uptake of glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids from blood into cells for storage as glycogen, protein, and triglyceride
What is the function of somatostatin?
Source: Delta cell (pancreas), GI tract, hypothalamus
Target tissues: Other islet cells, GI tract, brain, and pituitary gland
Action:
↓ release of insulin and glucagon
↓ GI tract motility
↓ growth hormone secretion
What is the function of ephinephrine?
Source: Adrenal medulla
Target tissues: Many
Action:
Promotes glycogenolysis in liver, lipolytic vis hormone-sens. Lipase
What is the function of cortisol?
Source: Adrenal cortex
Target tissues: Many
Action: Antagonizes insulin action
Think of it being like a court (its arguing against insulin)
What is the function of GLP?
Source: Ileum
Target tissues: Pancreas, stomach, brain, heart
Action:
↑ beta cell mass and insulin secretion
Delays gastric emptying
↓ food intake and glucagon secretion
What is the function of leptin?
Source: Adipoctyes
Target tissues: CNS (basomedial hypothalamus)
Action:
Signals adequacy of energy stores (doesn’t need anymore)
↓ food intake
What is glycogenesis?
The process of synthesizing glycogen (stores glucose)
What is glycogenolysis?
The process of breaking down glycogen to release glucose
What is gluconeogenesis?
The process of synthesizing glucose
What is glycolysis?
The process of utilizing glucose metabolically
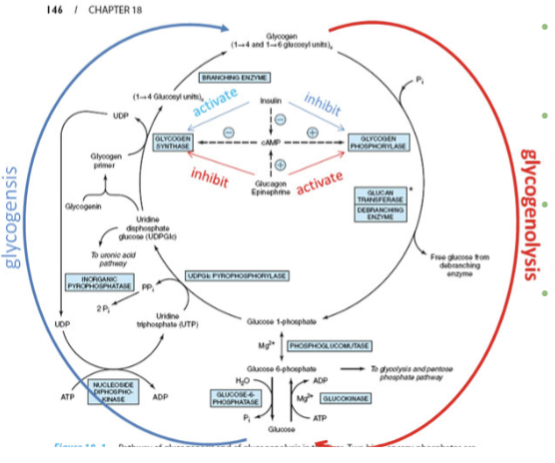
Explain the glucose–glycogen metabolic see-saw.
When one process is running, the other isn’t
Fed state (high blood glucose, insulin present)
→ The body wants to store glucose (so u need a large concentration of glycogen)
→ Glycogenesis is activated
→ Glycogenolysis is inhibitedFasting or stress (low blood glucose, glucagon/epinephrine present)
→ The body wants to release glucose
→ Glycogenolysis is activated
→ Glycogenesis is inhibited
At the enzyme level:
Glycogen synthase = makes glycogen
Activated by insulin
Inhibited by glucagon/epinephrine (via cAMP, phosphorylation) → has stored enough glycogen
Glycogen phosphorylase = breaks down glycogen
Activated by glucagon/epinephrine
Inhibited by insulin
Hormones control this “see-saw” through signaling pathways (cAMP, phosphorylation) so the cell never wastes energy building and breaking glycogen at the same time.
How is glucagon and insulin balanced?
Fed state:
Insulin dominates
↑ Glucose oxidation
↑ Glycogen synthesis
↑ Fat synthesis
↑ Protein Synthesis
Fasted State:
Glucagon dominates
↑ Glycogeneolysis
↑ Gluconeogenesis
↑ Ketogenesis
Before meal:
↑ Glucagon
↓ Glucose
↓ Insulin
After meal:
↓ Glucagon
↑ Glucose
↑ Insulin
Describe how insulin functions in the fed state.
How does insulin function in adipose and resting skeletal muscle (both fasted and fed state)?
Fasted state:
No insulin - no GLUT4 transporters in the membrane
Fed state:
Insulin signals the cell to insert GLUT4 transporters into the membrane, allowing glucose to enter the cell
Insulin binds to the receptor
Signal transduction cascade - GLUT4 transporters are produced
Exocytosis (transporter fuses with membrane)
Glucose enters the cell via the transporter
How does insulin function in liver hepatocytes (both fasted and fed state)?
Fasted state:
The hepatocyte makes glucose and transports it out into the blood, using GLUT2 transporters
Low insulin (doesn’t bind to receptor)
High concentration of glucose (inside cell)→ glycogen stores and gluconeogenesis
Fed state:
The glucose concentration gradient reverses and glucose enters the hepatocyte
Hexokinase-mediated conversion of glucose to G6P keeps intracellular [glucose] low
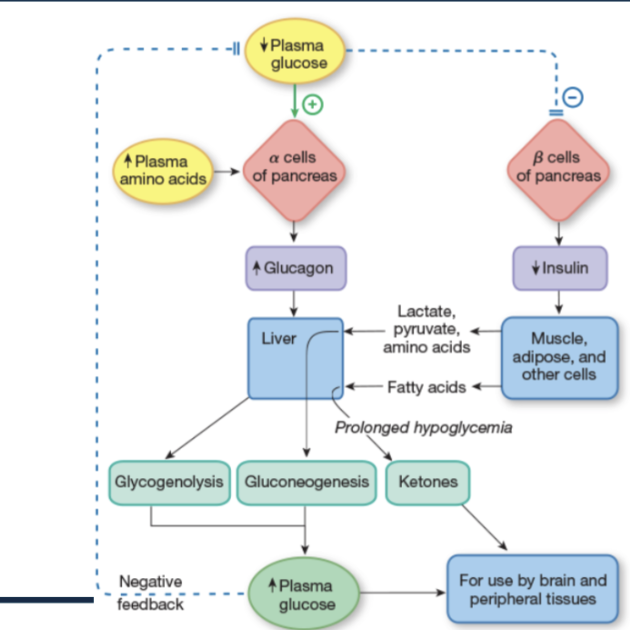
How does the body regulate blood glucose in the fasted state using glucagon?
↓ Plasma glucose
Low glucose stimulates α cells in the pancreas
At the same time, low glucose inhibits β cells, so insulin decreases (not enough plasma glucose to uptake)
α cells release glucagon (↑ glucagon) + ↑ plasma amino acids
Glucagon’s main target is the liver.
Glucagon acts on the liver to raise blood glucose:
↑ Glycogenolysis – liver breaks down glycogen → releases glucose
↑ Gluconeogenesis – liver makes new glucose from:
Lactate
Pyruvate
Amino acids
During prolonged fasting:
Liver produces ketones from fatty acids
Other tissues help supply fuel:
Muscle, adipose, and other cells release:
Amino acids
Lactate/pyruvate
Fatty acids
These go to the liver to support gluconeogenesis and ketone production.
Result:
Liver releases glucose into the blood → ↑ plasma glucose
Brain and peripheral tissues now have fuel
Rising glucose provides negative feedback, reducing further glucagon release
What are the pharmacologic properties of insulin?
Protein metabolism
↑ Transport amino acids into cells
↑ Protein synthesis
Positive nitrogen Balance
Diabetes - low insulin → ↑ aa, ↑ FFA (ketosis), ↓ protein synthesis, ↑ glycogenolysis, ↑ glucose
What is the fate of CHO?
Absorbed as: Glucose primarily; also fructose and galactose
Fed-state Metabolism:
Used immediately for energy through aerobic pathways (glycolysis and citric acid cycle)
Stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles (glycogenesis)
Excess converted to fat and strored in adipose tissue (lipogenesis)
Fasted-state Metabolism:
Glycogen polymers are broken down (glycogenolysis) to glucose in the liver and kidneys or to G6P for use in glycolysis
What is the fate of proteins?
Absorbed as: Amino acids, primarily plus some small peptides
Fed-state Metabolism:
Most amino acids go to tissues for protein synthesis
If needed for energy, amino acids converted in liver to intermediates for aerobic metabolism (deamination)
Excess is converted to fat and stored in adipose tissue (lipogenesis)
Fasted-state Metabolism:
Proteins broken down into amino acids
Amino acids deaminated in liver for ATP production or used to make glucose (gluconeogenesis)
What is the fate of fats?
Absorbed as: Fatty acids, triglycerides, and cholesterol
Fed-state Metabolism:
Stored as triglycerides primarily in the liver and adipose tissue (lipogenesis)
Cholesterol used for steroid synthesis or as a membrane component
Fatty acid used for lipoprotein and eicosanoid synthesis
Fasted-state Metabolism:
Trigylcerides broken down into fatty acids and glycerol (lipolysis)
Fatty acids used for ATP production through aerobic pathways (beta oxidation)
How does metabolism work?
All chemical reactions that take place in an organism
Catabolism - breaking down molecules
Anabolism - building complex molecules
Kilocalories are measures of energy released from or stored in chemical bonds
Primary source of energy for cellular reactions is adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
How do cells regulate their metabolic pathways?
Controlling enzyme concentrations
Producing modulators that change reaction rates
- Feedback inhibition
Using different enzymes to catalyze reversible reactions
Compartmentalizing enzymes within organelles
Maintaining optimum ratio of ATP to ADP
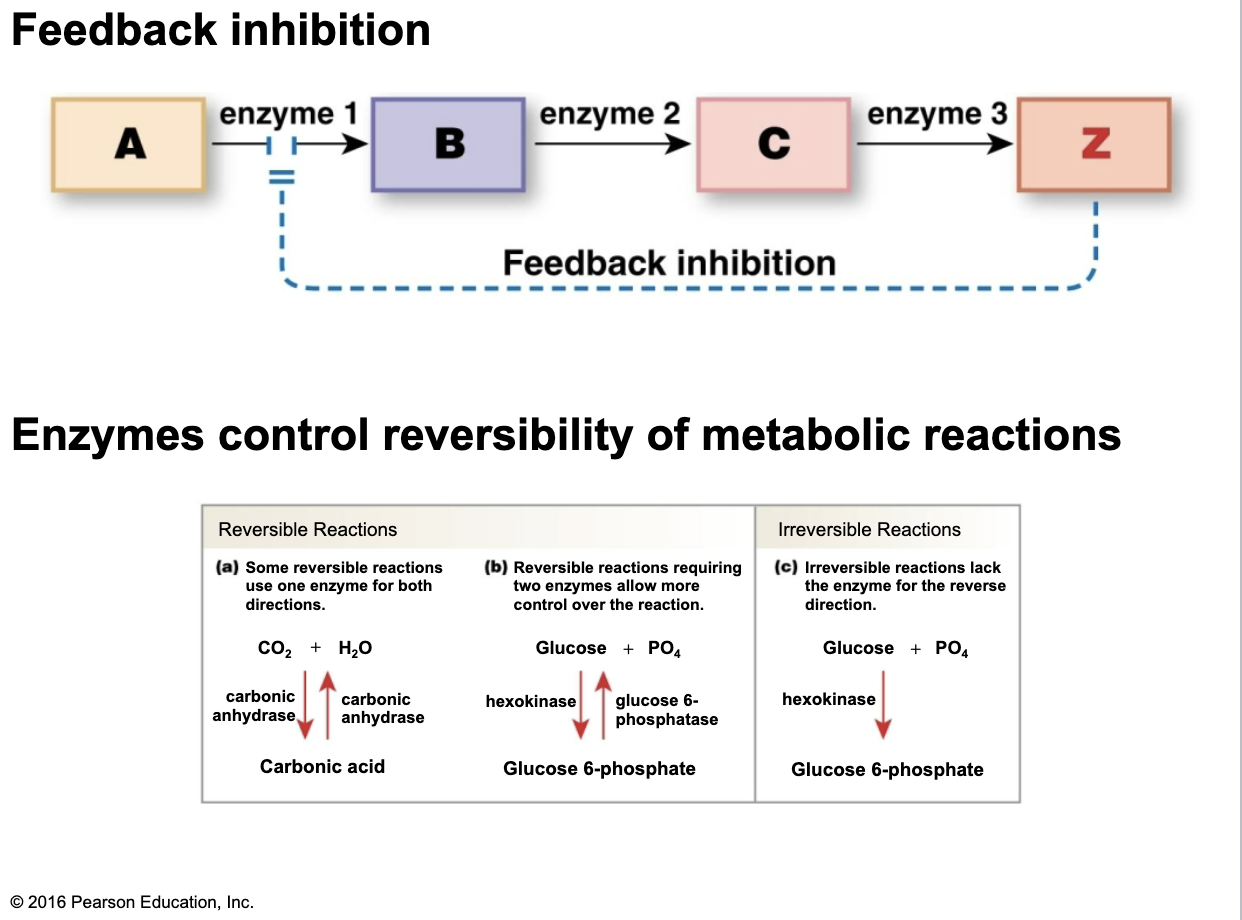
How do enzymes participate in feedback inhibition?
Control reversibility of metabolic reactions
What are the different types of work?
Chemical work: Making and breaking of chemical bonds
Transport work:
Moving ions, molecules, and larger particles
Useful for creating concentration gradients
Mechanical Work
Moving organelles, changing cell shape, beating flagella and cillia
Contracting muscles
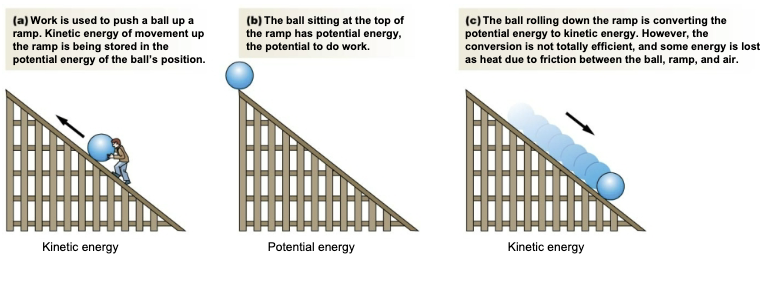
What are the two forms of energy?
Kinetic Energy:
Energy of motion
Work involves movement
Potential energy:
Stored energy
In concentration gradients and chemical bonds
Must be converted to kinetic energy to perform work
Transformation efficiency
What are the two laws of thermodynamics?
First Law of thermodynamics: Total amount of energy in the universe is constant
Second Law of thermodynamics: Processes move from state of order to randomness or disorder (entropy)
Chemical reactions
Bioenergetics is the study of energy flow through biological systems
Chemical reactions
Reactants become products
Reaction rate
Free energy
Activation energy
Net free energy change of the reaction
Exergonic vs endergonic reactions
Coupled reactions (energy from 1st reaction can be used in the second)
Reversible vs irreversible reactions
Enzymes
Speed up the rate of chemical reactions
Catalysts
Reactants are called substrates
Mostly proteins
Isozymes
Catalyze same reaction, but under different conditions
Diagnostic enzymes (act differently in each environment)
May be activated, inactivated, or modulated
Coenzymes → (e.g., vitamins)
Chemical modulators → temp and pH
Enzymes lower the activation energy of reactions
What are the categories of enzymatic reactions?
Oxidation-reduction reactions
Hydrolysis-dehydration reactions
Addition-subtraction-exchange reactions
Ligation reactions
How is heat production, gain, and loss balanced?
By body temperature!
Humans are homothermic temperature regulated within narrow range
Heat input = heat output
Heat input
Internal heat production
External heat input (radiation and conduction)
Heat output
Radiant heat loss
Conductive heat loss (can touch temp)
Convective heat loss (feel change in temp)
Evaporative heat loss (sweating/cooled)
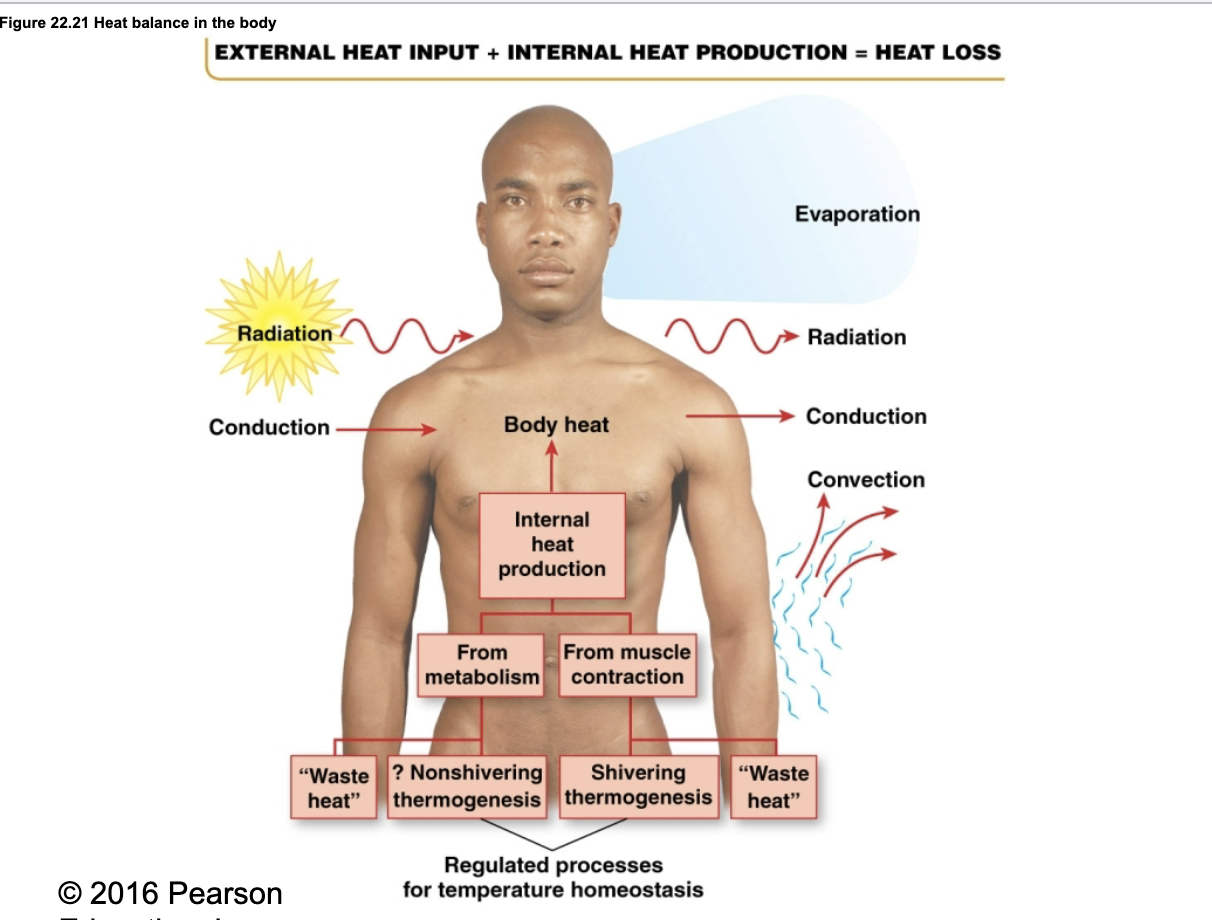
How does the body maintain heat balance to regulate body temperature?
External heat input + internal heat production = heat loss
Heat Gain:
External heat input
From the environment via radiation and conduction
Internal heat production
From metabolism (“waste heat”)
From muscle contraction
Shivering thermogenesis (in cold)
Nonshivering thermogenesis
Above are regulated processes for temp homeostasis
Heat Loss:
Radiation
Conduction
Convection
Evaporation
When you’re cold:
Heat production ↑ (shivering, metabolism)
Heat loss ↓
When you’re hot:
Heat loss ↑ (sweating, vasodilation)
Heat production ↓
What are the hypothalamic responses to increased vs decreased body temperature?
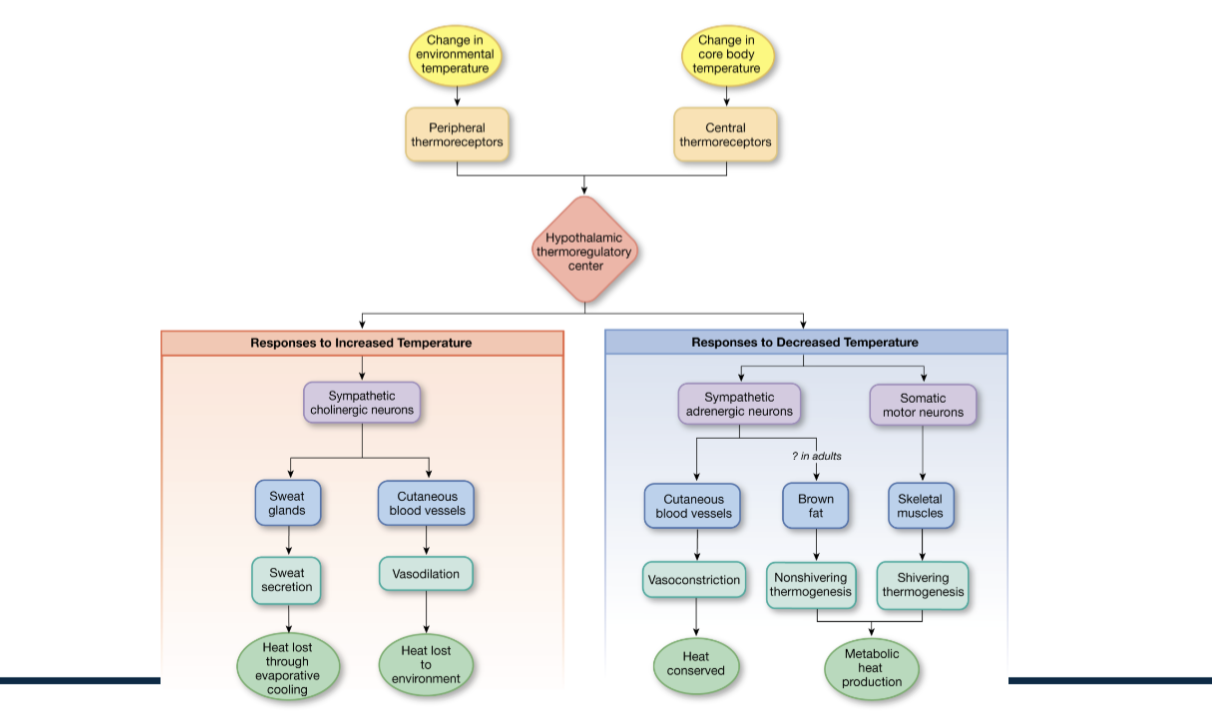
Explain how temperature is regulated through homeostasis.
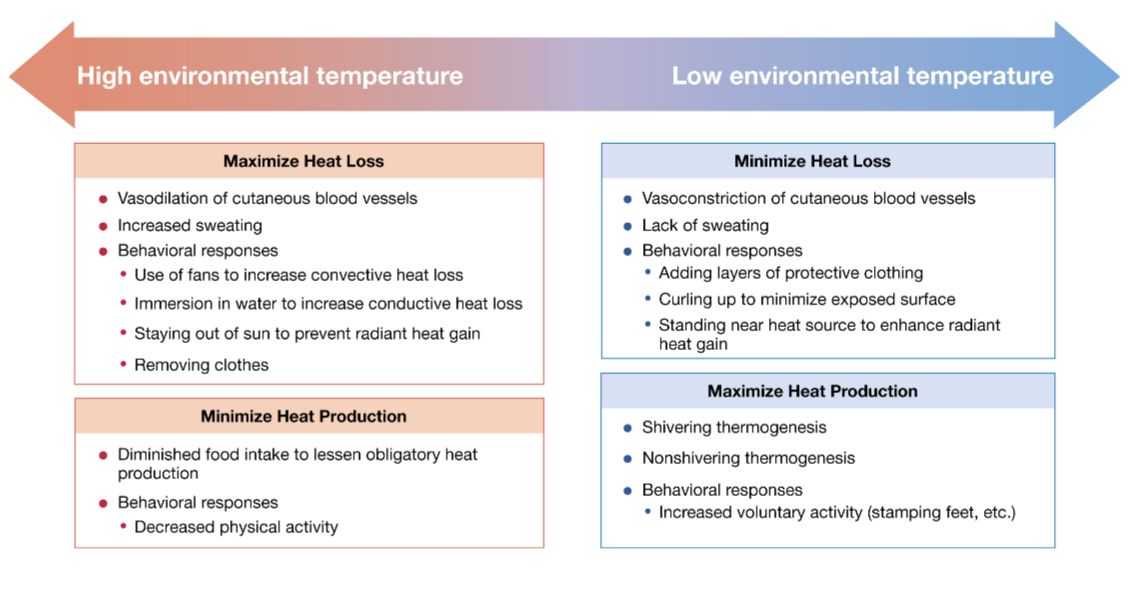
How can body’s thermostat be reset?
Physiological regulation
Circadian rhythm, menstrual cycle variations, postmenopausal hot flashes, fever
Fever is immune response to pyrogens
Pathological conditions
Hyperthermia
Heat exhaustion
Heat stroke
Malignant hyperthermia
Hypothermia