DENT Fun. I - Peptide & Steroid Hormones
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What are the 3 Classes of Hormones?
- Amino Acid-Derived
- Peptide
- Lipid-Derived
Hormones from the Hypothalamus
- Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH)
- Thyroid Releasing Hormone (TRH)
- Corticotropin Releasing Hormone (CRH)
- Dopamine/Prolactin Inhibiting Hormone (PIH)
- Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GHRH)
GHRH
Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone
- Released by the Hypothalamus
- Controls release of GH from the anterior pituitary
TRH
Thyroid-Releasing Hormone
- Targets the Anterior Pituitary for release of TSH
____ is a Small Peptide Hormone.
TRH
What is the primary structure of TRH?
Glu-His-Pro-NH2 x4
Tripeptide that is ~12 amino acids long
Hormones from the Pituitary
- Growth Hormone (GH)
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
- Prolactin
- ADH
- Oxytocin
ADH
Antidiuretic Hormone
- Upregulates aquaporin channels in the collecting ducts of nephrons, retaining water
- Released by Posterior Pituitary
Growth Hormone
Targets the Liver and Bone, increasing metabolism and bone growth
____ and ____ are both Large Protein Hormones.
Growth Hormone/Insulin
Small Peptide Hormones
Are at a low concentration and soluble enough to be transported unbound to any soluble carrier
Large Protein Hormones
Carried by soluble proteins that resemble the protein receptor the Hormone binds at its target
Where are Peptide Hormones taken after binding to their receptor?
The Lysosome to be broken down
Oligopeptides
12-20 amino acids
Polypeptides
20-40 amino acids
Alpha-Cells
Pancreatic cells that secrete Glucagon
Beta-Cells
Pancreatic cells that secrete Insulin
Delta-Cells
Pancreatic cells that secrete Somatostatin
Insulin
- 2 chains bound by 2 disulfide bonds; 1 of the chains has an intra-chain disulfide bond for a total of 3
- Facilitates the uptake of Glucose into cells via upregulation of Glucose transport proteins
- Glycogen Synthesis
- Lipogenesis
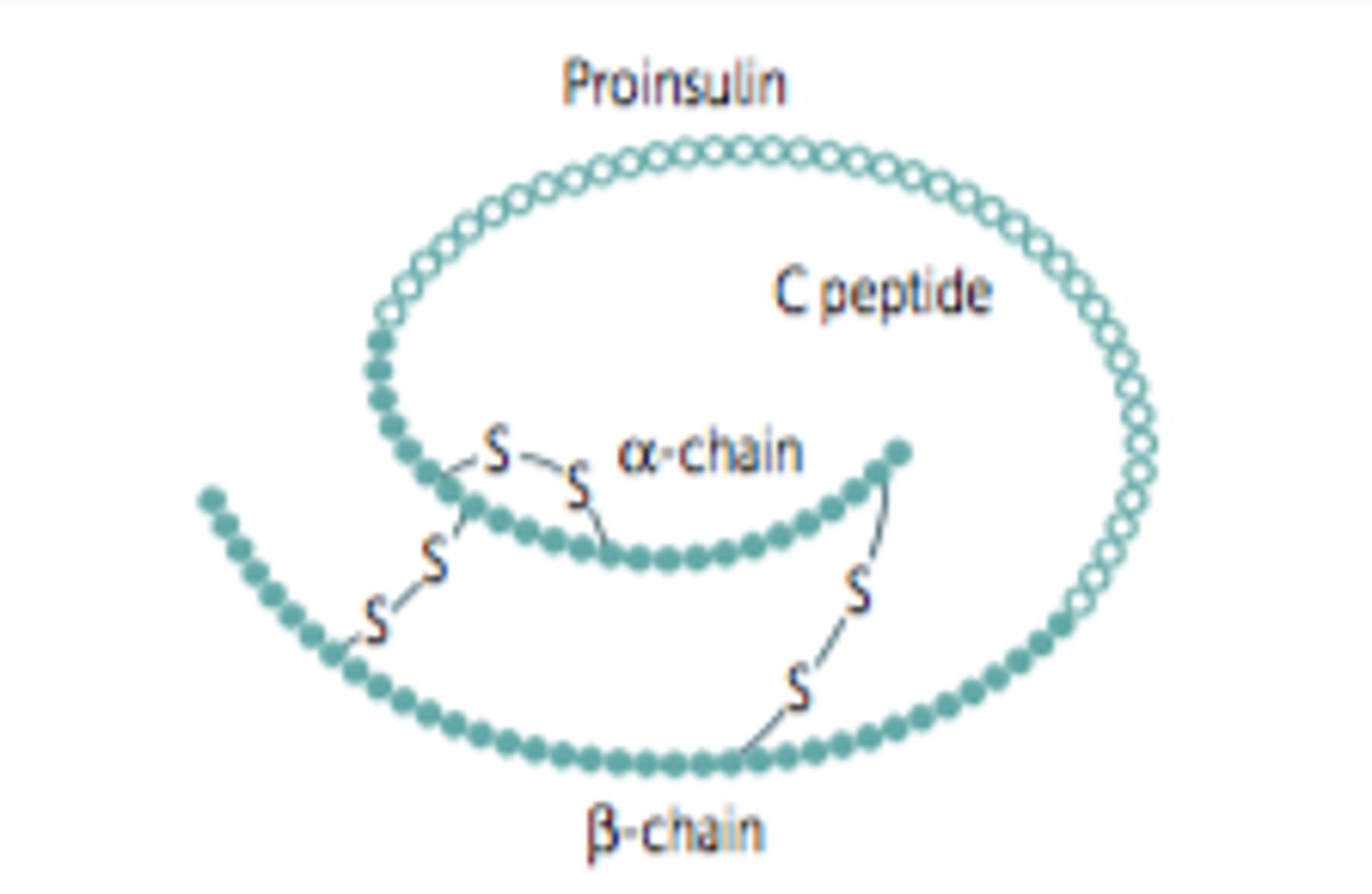
Insulin Synthesis
(1) Preproinsulin synthesis in RER
(2) Cleavage of presignal = Proinsulin
(3) Proinsulin is transported to the Golgi to be packaged
(4) Proinsulin cleavage = Insulin
(5) Exocytosis of Insulin via Ca2+
Insulin Receptor
- Protein composed of a tetra-peptide (2 Alpha + 2 Beta Subunits)
- When bound, activates Tyrosine Kinase inside the membrane
How does Insulin move Glucose into Cells?
(1) Insulin binds to receptor
(2) Signaling pathway triggers Glut4 to move to the plasma membrane
(3) Transporter fuses to membrane and will take up Glucose as long as Insulin keeps coming from Beta-Cells
What are the 2 subunits of a G-Protein?
- Beta-Gamma Subunit
- Alpha-Subunit
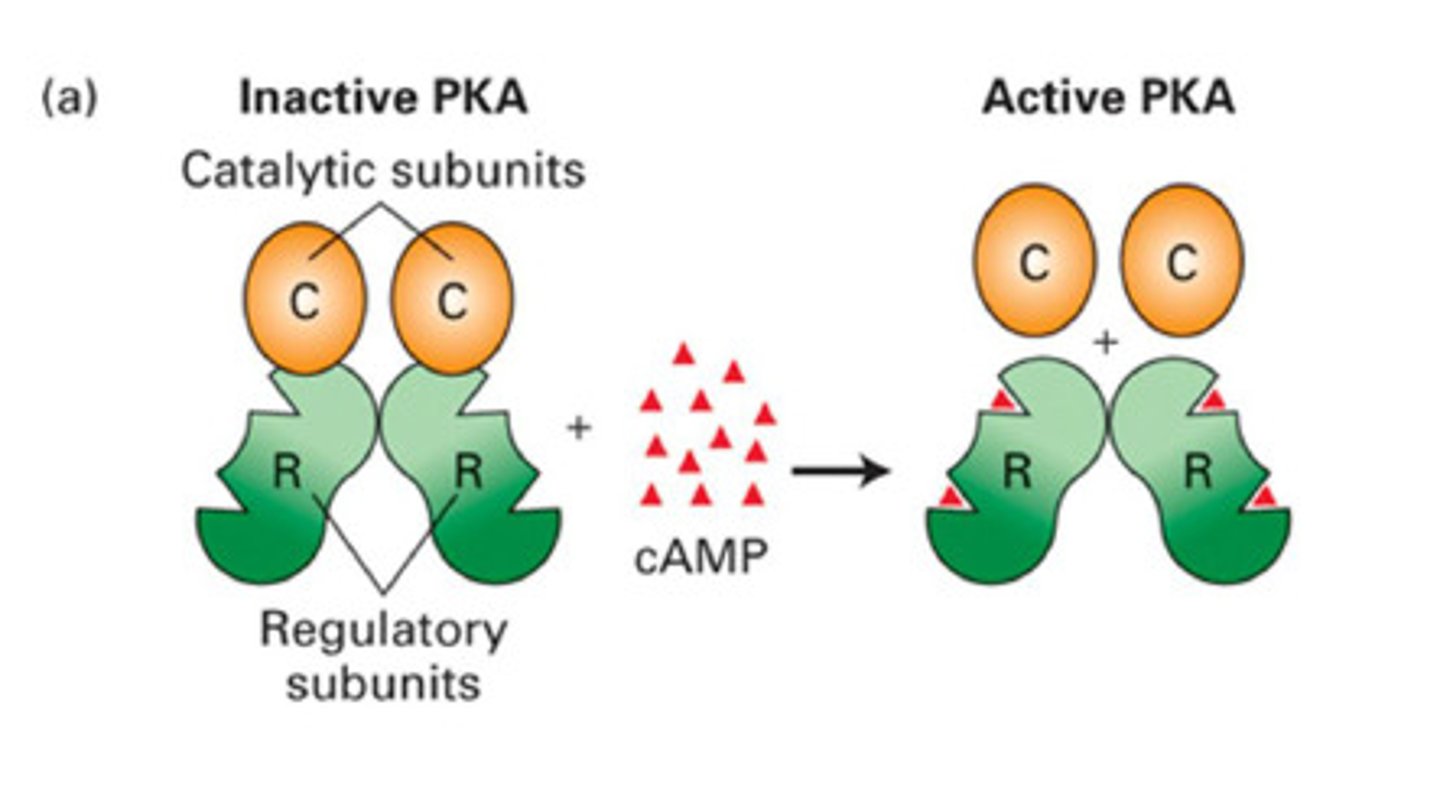
General cAMP Mechanism
(1) Stimulatory G-Protein is bound by external receptor
(2) Internal Alpha-Subunit replaces GDP with GTP, activating the subunit
(3) Active Alpha-Subunit turns Adenylyl Cyclase (AC) on
(4) AC converts ATP into cAMP
(5) GTPase on Alpha-Subunit hydrolyzes GTP into GDP, turning it off
G-Proteins can also be inhibitory (T/F)
True
Know G-Proteins at different tissues??
cAMP can be broken down before it enters a cascade. What enzyme breaks cAMP down?
cAMP Phosphodiesterase (PDE)
cAMP typically activates ____ in the first step of most cascades.
Protein Kinase A (PKA)
PKA
Tetrameric protein that, when stimulated by cAMP, dissociates into 3 subunits. 2 of these are active catalytic subunits.
Ca2+/Calmodulin Mechanism
(1) Hormone binds to cell membrane receptor
(2) Through G-Protein it a. opens cell membrane Ca2+ channels and b. releases Ca2+ from the ER
(3) Increased intracellular [Ca2+]
(4) Ca2+ binds to Calmodulin
(5) Ca2+ Calmodulin Complex produces physiologic response
Utilizes PKC instead of PKA
What 2 Hormones utilize the Ca2+/Calmodulin Mechanism?
- ADH
- TRH
Peptide Hormones
Hormones composed of short chains of <12 amino acids
- Polar
- Largely use G-Proteins via PKA or Ca2+-DAG Pathway
Peptide Hormones are synthesized as ____ or ____.
prehormones/preprohormones
Peptide Hormones are stored in ____.
membrane bound granules
What are the 3 types of Steroid Hormones?
- Glucocorticoids
- Mineralocorticoids
- Androgens/Estrogens
Glucocorticoids
Cause...
- Increased metabolism of carbs, lipids, and proteins
- Immunosuppressive Effects
Cortisol
Mineralocorticoids
Promote reabsorption of Na+ and excretion of K+ in the Kidneys, affecting TBV
Aldosterone
Androgens/Estrogens
Sex Hormones
Testosterone/Estrogen
Steroid Synthesis is stimulated by the ____.
Pituitary
What are the 3 major locations of Steroid Synthesis?
- Adrenal Gland
- Testes
- Ovaries
Steroids are made from ____ in the ____.
cholesterol/mitochondria
ACTH
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
- Stimulates the Adrenal Glands
Adrenal Cortex
Produces...
- Cortisol
- Aldosterone
- Androgens/Estrogen
Adrenal Medulla
Produces NE/E
Corticosteroids
P450 Enzymes
Enzymes responsible for the modification of the Cholesterol tail via mixed function oxidation, producing Steroid Hormones
What is needed for Cholesterol Modification?
- P450 Enzymes
- NADPH
- O2
Glucocorticoid Functions
[Cortisol]
- Increase [Glucose] via Gluconeogenesis
- Suppress immune System
- Aid in fat, protein, and carb metabolism
- Decrease bone formation
Cushings Syndrome
Condition caused by prolonged exposure to high [Cortisol]
- Bone Loss
- Muscle Wasting
Mineralocorticoid Function
[Aldosterone]
- Na+ retention/K+ excretion via Kidney reabsorption of at the distal tubules and collecting ducts; Causes increased water retention and an increase in BP
Conns Syndrome
Increased production of Aldosterone in the Adrenal Glands
Addison's Disease
Aldosterone Insufficiency
Androgens
[Testosterone]
- Growth of muscle mass and bone density
- Secondary male characteristics
Estrogen
- Metabolism
- Secondary female characteristics
- Decreased bone resorption
Steroids require ____.
carrier proteins
What are the 3 Carrier Proteins of Steroids?
- Transcortin
- SHBG
- Albumin
Transcortin
Corticosteroid and Cortisol binding globulin
SHBG
Sex Hormone Binding Globulin
- Glycoprotein that binds Testosterone and Estradiol
- Produced by the Liver, Brain, Uterus, and Vagina
Influence bioavailability of sex hormones, therefore, their effect on the body
Albumin
Binds both corticosteroids and sex hormones
Steroid Hormone Mechanism of Action
(1) Steroid binds receptor in Cell and releases the blocking protein
(2) Steroid-Receptor Complex enters nucleus and modifies transcription of genes
Some protein-hormone complexes bind enhancer regions. The enhancer regions must be able to reach the ____ to influence transcription.
promoter region
Steroid Hormones are derived from the ____ ring.
cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene
Peptide Hormones can be administered orally (T/F)
False; Steroid Hormones can though