Gr 9 Science CPT
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Physical properties (qualitative and quantitative)
Qualitative observation = An observation of a substance that is not measured and does not have a numerical value
E.g. colour, odour, texture
Quantitative = Measured and has a numerical value
E.g temperature, height, mass
Physical properties (with our 5 senses)
State: how fast particles are moving // E.g solid liquid gas
Taste: the sensation of flavour // E.g bitter sweet sour
Texture: the visual and tactile quality of a surface // E.g smooth silky rough
Lustre: shininess or dullness // reflexive = high degree of lustre // E.g. mirror
Optical Clarity: the ability to allow light through // E.g. transparent translucent opaque
Hardness: ability to scratch or be scratched by another substance // E.g. diamonds
Electrical conductivity: the ability of a substance to allow current to pass through it
Malleability: the ability of a substance to be hammered into thin sheets // E.g. gold
Ductility: ability of a substance to be drawn (pulled) into a finer strand // Eg. metals
Flexibility/brittleness: how bendable something is // If not bendable = ridged // If bendable = elastic
Solubility: ability to dissolve into something else
Soluble: salt will dissolve in water
Insoluble: metal will not dissolve in water
Viscosity: the ability of a substance to resist flow
Slower pour = more viscous / faster pour = less viscous
Physical Change
Can usually be reversed
Is a change in which the composition of the substance remains unaltered and no new substances are produced
E.g. when ice melts into liquid or when paper is folded into an airplane
Chemical properties
A property of a substance that describes its ability to undergo changes to its composition to produce one or more new substances
Include how a substance interacts with other substances such as water oxygen or acids
Can only be observed when a chemical change occurs
E.g. Combustibility, ability to rust, ability to react with an acid or bases / water
Chemical change
Always result in the formation of one or more new substances
The original substance does not disappear
The components of the original substance are simply rearranged in the process of forming a new substance
Chemical Change Evidence
A change in colour: has formed a different colour than the original substance
A change in odour: formed a new detectable odour
Production of gas: new substance is produced in the form of gas
Bubbles are visible, not caused by heating
Change in temperature or light: energy is released (exothermic) or absorbed (endothermic) during a chemical change
E.g. photosynthesis vs cellular respiration
Formation of a precipitate: does not dissolve in the mixture and shows up as a solid called precipitate
Characteristic Physical Properties
A physical property that is unique to a substance and that can be used to identify it.
E.g. how a fingerprint is unique to an individual
It can be determined without changing the composition of the sample
Density: ratio of mass to volume, usually in g/㎤ and g/mL
D = m/V m = DV V = m/D
Melting point: solid to liquid // 0 degrees C
Freezing point: liquid to a solid // 0 degrees C
Boiling point: liquid to gas // 100 degrees C
Electric conductivity
Atomic Structure
The number of protons in the nucleus determines what the element number is (atomic number) of the element
Atom: p+ = e–
Ion: p+ ≠ e–
Mass #: p+ + n0
Standard Atomic Notation
Element symbol is located in the middle
Atomic number is on the bottom left (# of protons or # on the periodic table)
Mass number is on the top left (protons + neutrons)
Charge is on the top right (positive, negative, neutral)
Valence electrons are the amount of electrons on the outermost ring
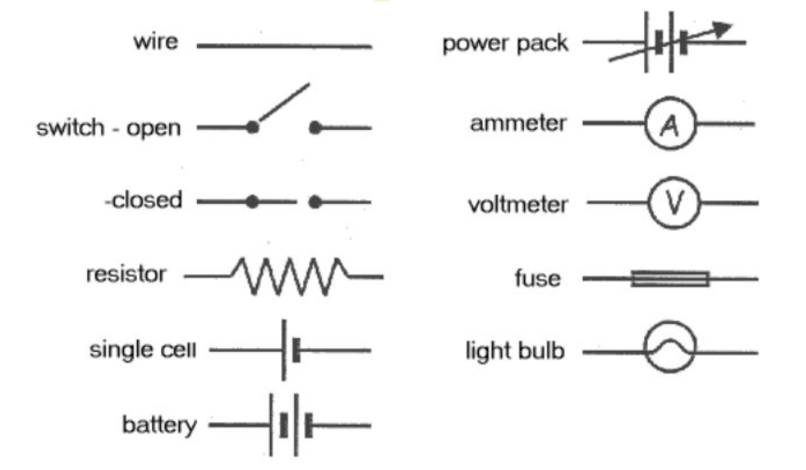
Electric circuits consist of
Energy Source: a device that provides electrons and causes the electrons to move // E.g. battery
Load: a device that transforms electrical energy into other forms of energy (light, heat and sound energy) // E.g. a light bulb, stove
Conducting Wires: a material that provides a pathway for electrons to flow from one component of the circuit to another E.g. copper wires
Switch: controls the flow of electrons by opening or closing the circuit
Switch off = circuit open = incomplete path for electrons
Switch on = circuit closed = complete path for electrons to flow
How to draw circuits
Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s Law: the straight line relationship among voltage and current.
R = V/I
Resistance (Ω) = Voltage / Current
Ohm found that the ratio/slope V/I was constant for a particular resistor
Kirchhoff’s law - series
All electrons must pass through all lamps
Current is the same through each load
The potential difference is divided up between all the loads
T = total
IT = I1 = I2 = I3…
VT = V1 + V2 + V3…
Kirchhoff’s law - parallel
Electrons have a choice of path
The current is different at each load
The potential difference is constant
IT = I1 + I2 + I3…
VT = V1 = V2 = V3…
Increase decrease Kirchhoff’s Law
Each time another load is added to a circuit in parallel, the total resistance of the circuit decreases
The electrons are able to move more freely
Since V is constance, if R decreases, I will then increase
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD)
a measure of how quickly oxygen is used by microorganisms
A high BOD means there are many organisms and oxygen is being used up very quickly
↑ pollution = ↑ microorganisms = ↑ BOD = ↓ oxygen levels
Eutrophication
excessive richness of nutrients in a lake or other body of water, frequently due to runoff from the land, which causes a dense growth of plant life and death of animal life from lack of oxygen
Algae blooms
During rainfalls, fertilizers can enter aquatic ecosystems
This leads to the growth of algae, called algae bloom
When algae grows, dies and decomposes in high volumes
The decomposition is caused by bacteria that use up oxygen
Bacteria decreases the level of dissolved oxygen in the aquatic ecosystem, killing fish that live there
Photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide + water —light→ glucose + oxygen
Light energy is absorbed by plants via chloroplasts and converted to sugar/usable energy
Organisms that perform photosynthesis create their own energy rich food using the sun
They are called producers (autotrophs)
On land: green plants
In water: microscopic organisms like algae
Cellular respiration
The sugar made in photosynthesis is then used by organisms to perform the complementary reaction cellular respiration
The products of photosynthesis are converted back into carbon dioxide, water, + ATP
ATP: usable energy for ourselves and all the cells in our body for activities
Apparent magnitude
The brightness of the star as it appears to us humans on Earth
Hippachus developed the idea of classifying stars by their brightness
1st magnitude stars are the brightest while 6th is the weakest (the smaller #, the brighter)
Absolute magnitude
The actual amount of light given off by a star at a standard distance
Standard distance: 33 lightyears from it
The sun’s absolute value is 4.8 from 33 LY away
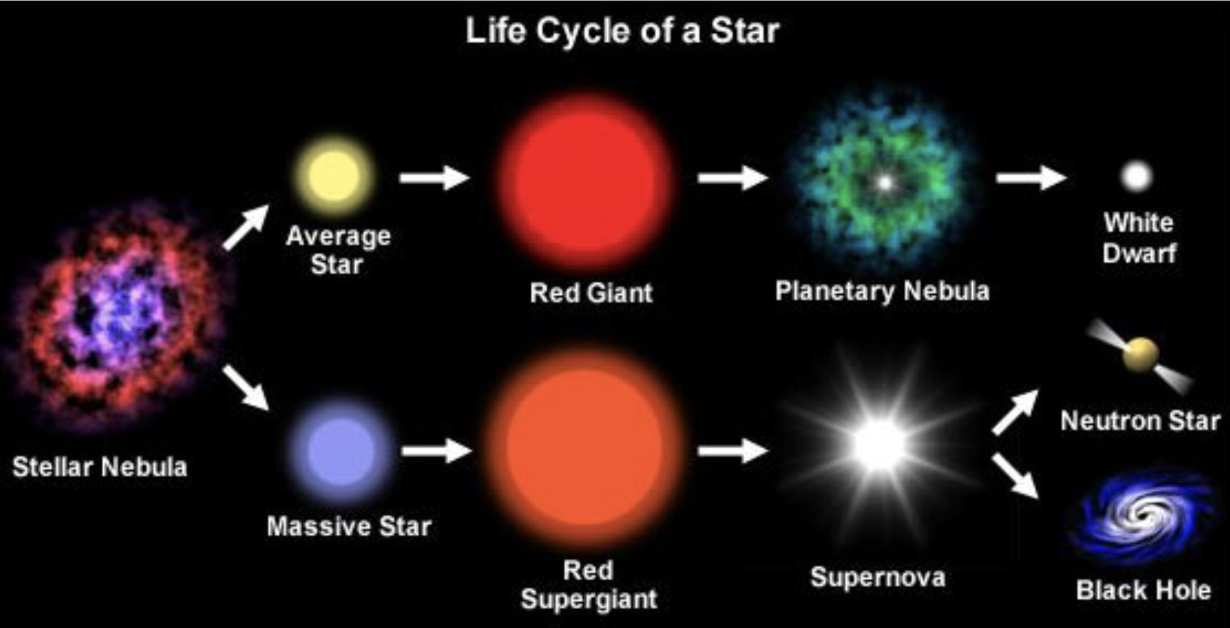
Categorizing Stars
Red Giants: large, bright, cool
White Dwarfs: small, dim, hot
Blue Supergiants: very large, brightest, hottest
Red Dwarfs: small, dim, cool
Life cycles of stars
Geocentric vs heliocentric models
Solar Eclipse
A solar eclipse: moon blocks the light from the Sun, except for the corona
Although the moon is 400 times smaller than the Sun, it is also 400 times closer to the earth than the Sun
Only possible during the new moon phase it occurs when we do not see the illuminated side of the moon
Only seen in the lunar shadow path (the specific area on Earth that the moobs shadow covers during the eclipse)
There can be partial solar eclipses and total solar eclipses
Lunar Eclipse
A lunar eclipse: when the Earth is between the Sun and the moon
The Earth casts a shadow on the moon, causing it to glow red or orange
A partial lunar eclipse: only part of the Moon passes through the shadow of Earth
A total lunar eclipse: the entire moon passes through the shadow of the Earth
Can be seen anywhere that the Moon is above the local horizon, so if the moon is up wherever you are, you will be able to see it
Tides
When the moon, the Sun and the Earth are aligned, spring tides occur
When the moon and the Sun are on perpendicular sides of the Earth, weaker, neap tides occur