Skin Integrity and Wound Care Essentials
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Skin
Largest organ, weighs ~12 lbs, ~15% TBW.
Acid Mantle
Skin's protective barrier, pH 4.5 - 5.5.
Vitamin D Synthesis
Requires sunlight for production in skin.
Thermoregulation
Body temperature control via sweating and goosebumps.
Epidermis
Top layer of skin, provides barrier protection.
Dermis
Inner layer of skin, contains collagen and blood vessels.
Collagen
Protein providing structure and strength to skin.
Hypodermis
Layer beneath skin, stores fat and insulates.
Pressure Injury
Damage to skin and underlying tissue from pressure.
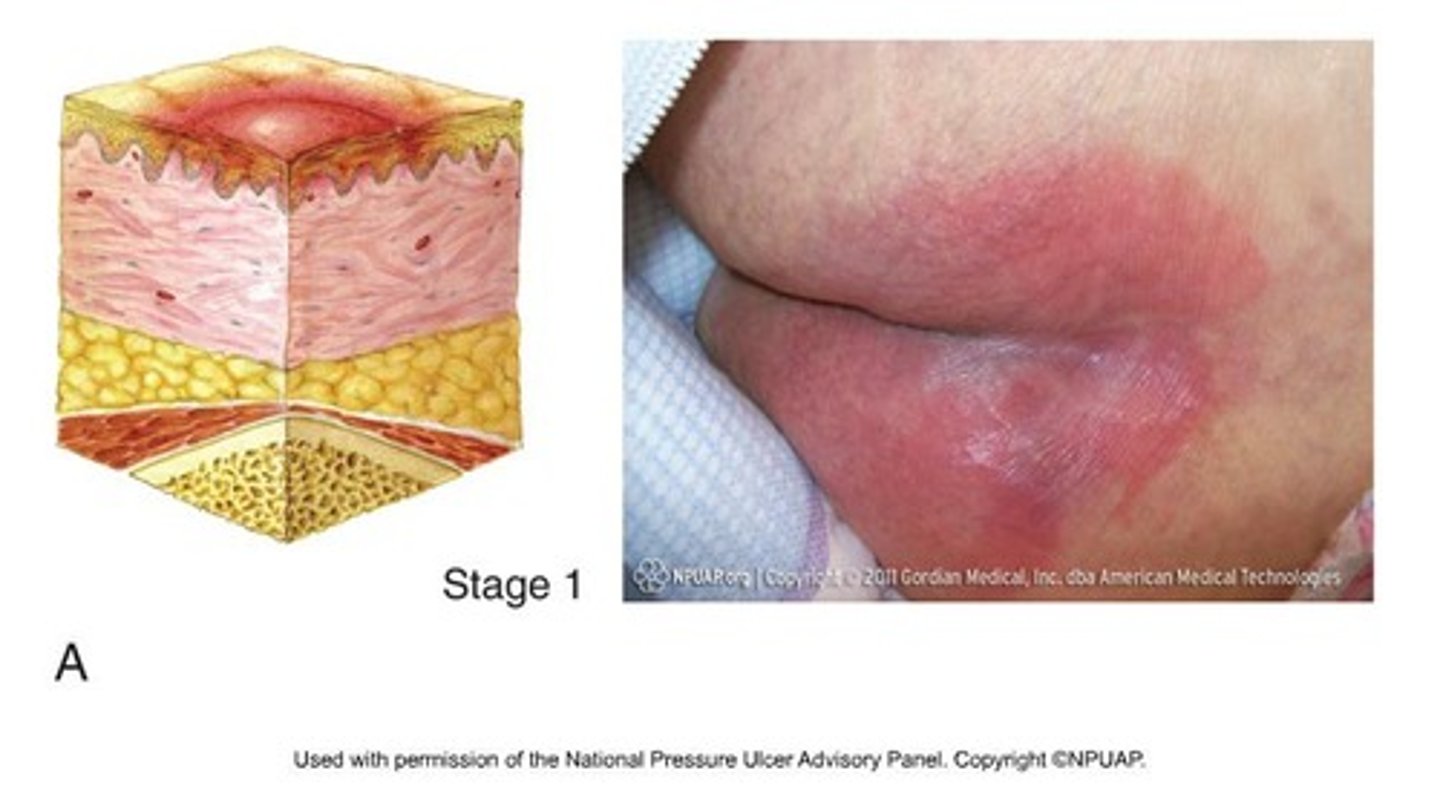
Stage 1 Pressure Injury
Intact skin with non-blanchable redness present.
Stage 2 Pressure Injury
Partial-thickness skin loss involving epidermis and dermis.
Stage 3 Pressure Injury
Full-thickness tissue loss, visible fat may be present.
Stage 4 Pressure Injury
Full-thickness loss with exposed muscle, tendon, or bone.
Unstageable Pressure Injury
Base obscured by slough, cannot determine stage.
Deep Tissue Pressure Injury (DTPI)
Maroon, non-blanchable intact skin or blood blister.
Risk Factors for Pressure Injuries
Includes impaired mobility, moisture, poor nutrition, age.
Wound Healing Complications
Includes hemorrhage, infection, dehiscence, and evisceration.
Delayed Wound Healing
Caused by anemia, malnutrition, smoking, and infection.
Medical Adhesive Injury
Skin damage from medical adhesive use.
Medical Device Injury
Pressure injury caused by medical devices.
Wound Care Best Practices
Frequent repositioning and meticulous skin care essential.
Partial-thickness wound repair
Involves inflammatory response and epithelial migration.
Full-thickness wound repair
Includes hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling.
Wound healing assessment
Conducted on admission and with condition changes.
POA documentation
Must be recorded within 24 hours of admission.
Wound bed description
Includes sutures, granulation, and maceration assessment.
Wound culture procedure
Clean with NS; avoid pus or dead tissue.
Levine Quantitative Swab Technique
Method for accurate wound culture sampling.
Braden Scale
Tool for assessing pressure injury risk.
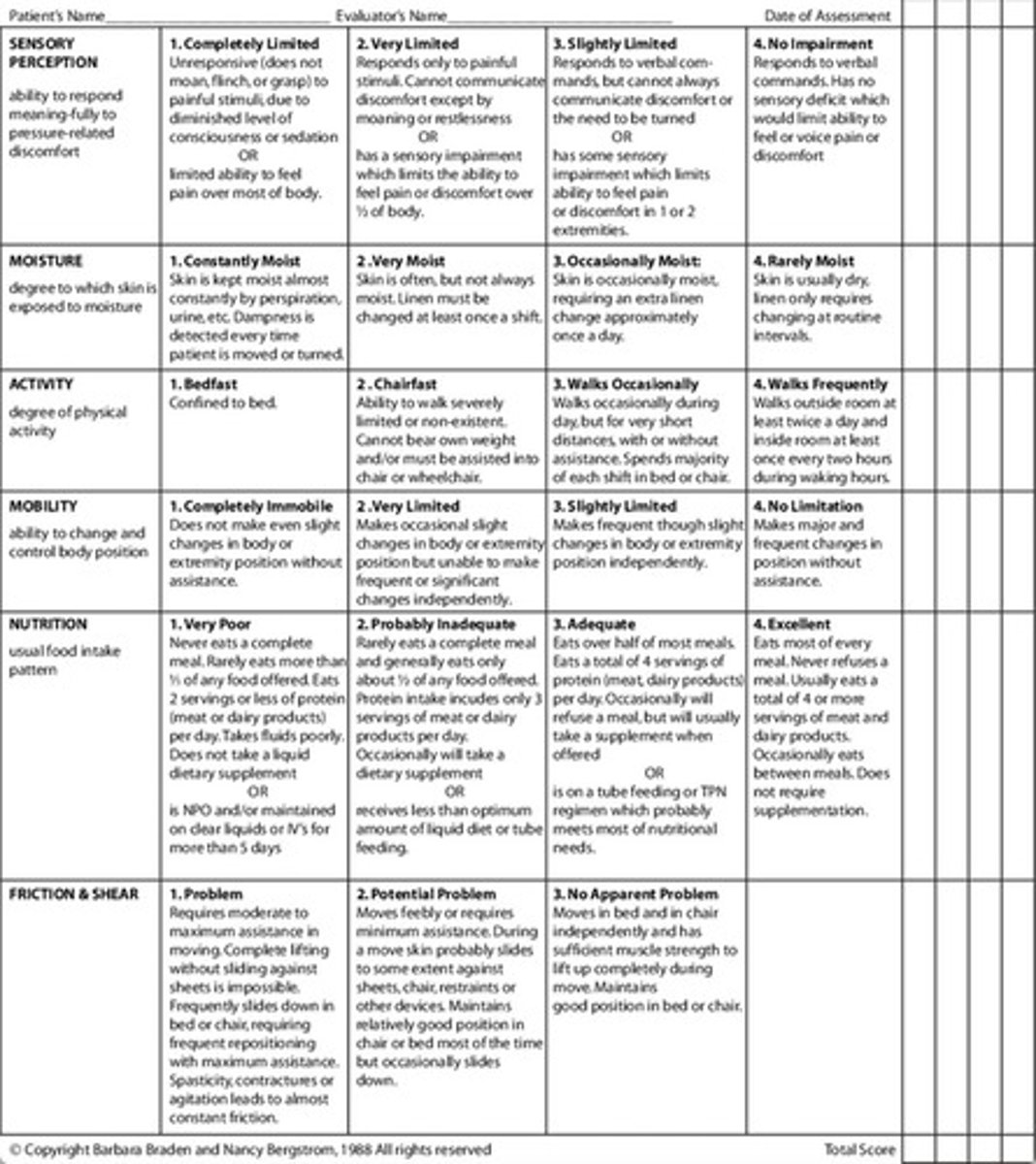
Braden scoring mild
Score of 15-18 indicates mild risk.
Braden scoring moderate
Score of 13-14 indicates moderate risk.
Braden scoring high
Score of 10-12 indicates high risk.
Braden scoring severe
Score of 9 or less indicates severe risk.
Nursing diagnoses for wounds
Includes impaired healing and skin integrity issues.
Nursing process planning
Interventions based on risk assessment and patient goals.
Q2H turn schedule
Reposition patients every two hours to prevent pressure.
Dressing change preparation
Evaluate pain and administer analgesics beforehand.
Dressing change procedure
Carefully clean and manipulate dressings to minimize pain.
Wound packing materials
Includes packing strips, gauze, and alginates.
Negative-pressure wound therapy
Technique to promote healing in complex wounds.
Dressing securement methods
Use tape, bandnet, or roll gauze for dressing.
Patient education
Involves teaching about wound care and prevention.
Nursing process evaluation
Assess if wound healing is progressing positively.
Wound response evaluation
Assess measurements, drainage, inflammation, and pain.
Moisture management
Aim for moist wounds, avoid extremes of wet/dry.
Signs of infection
Indicators include fever, drainage, and redness.
Healing potential factors
Malnutrition, perfusion, care adherence, and motivation.
Primary intention healing
Edges approximated with sutures, glue, or staples.
Wound infection indication
Purulent drainage from the incision site.
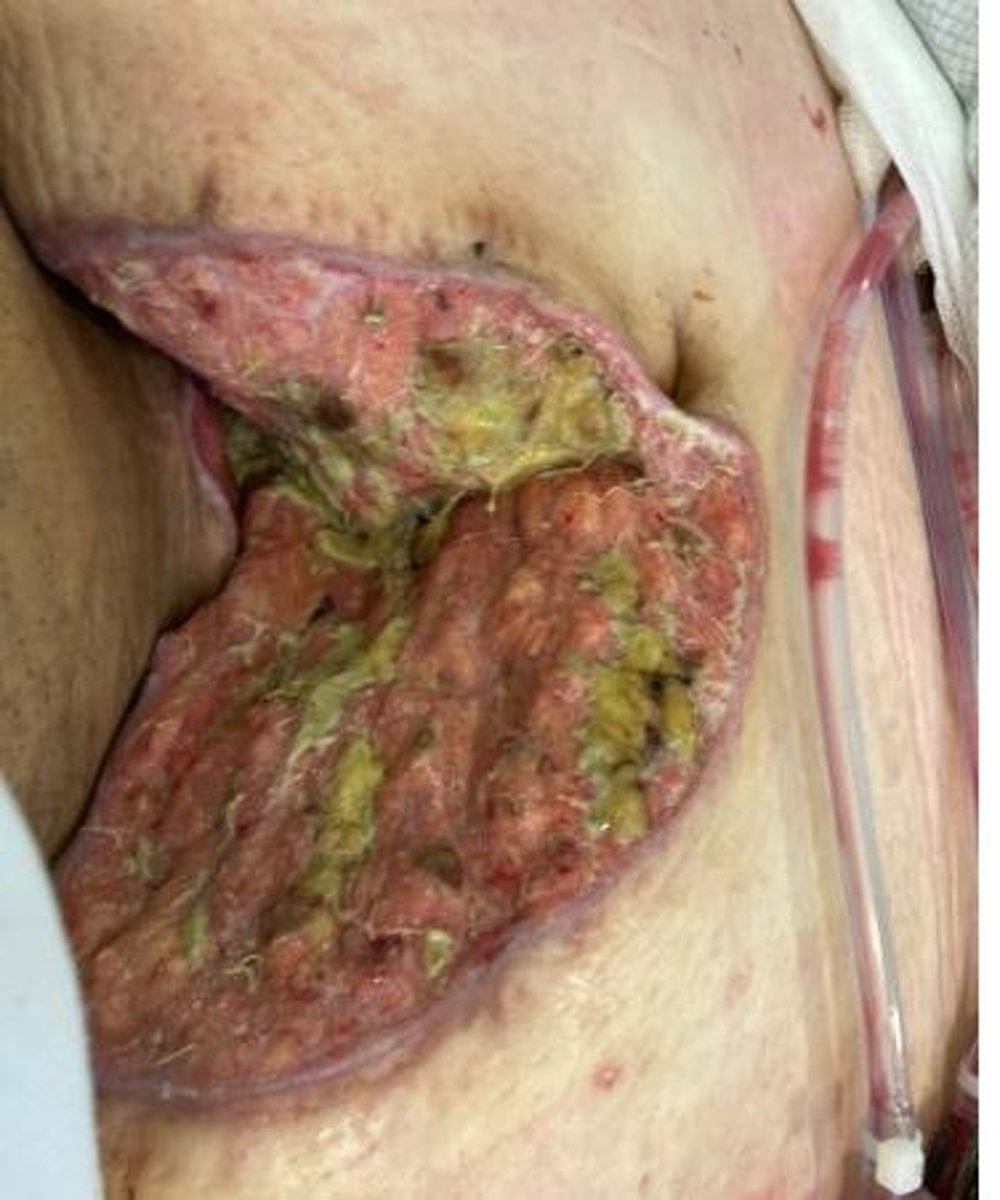
Surgical drains
Devices placed to remove fluid post-surgery.
Drain site care
Clean from insertion site outward to prevent infection.
Cleansing intervals
Clean drain sites at ordered intervals and as needed.
Skin protection
Keep dressings clean, dry, and intact.
Ostomy definition
Surgical opening in abdomen for waste exit.
Stoma
Opening formed for stool or urine exit.
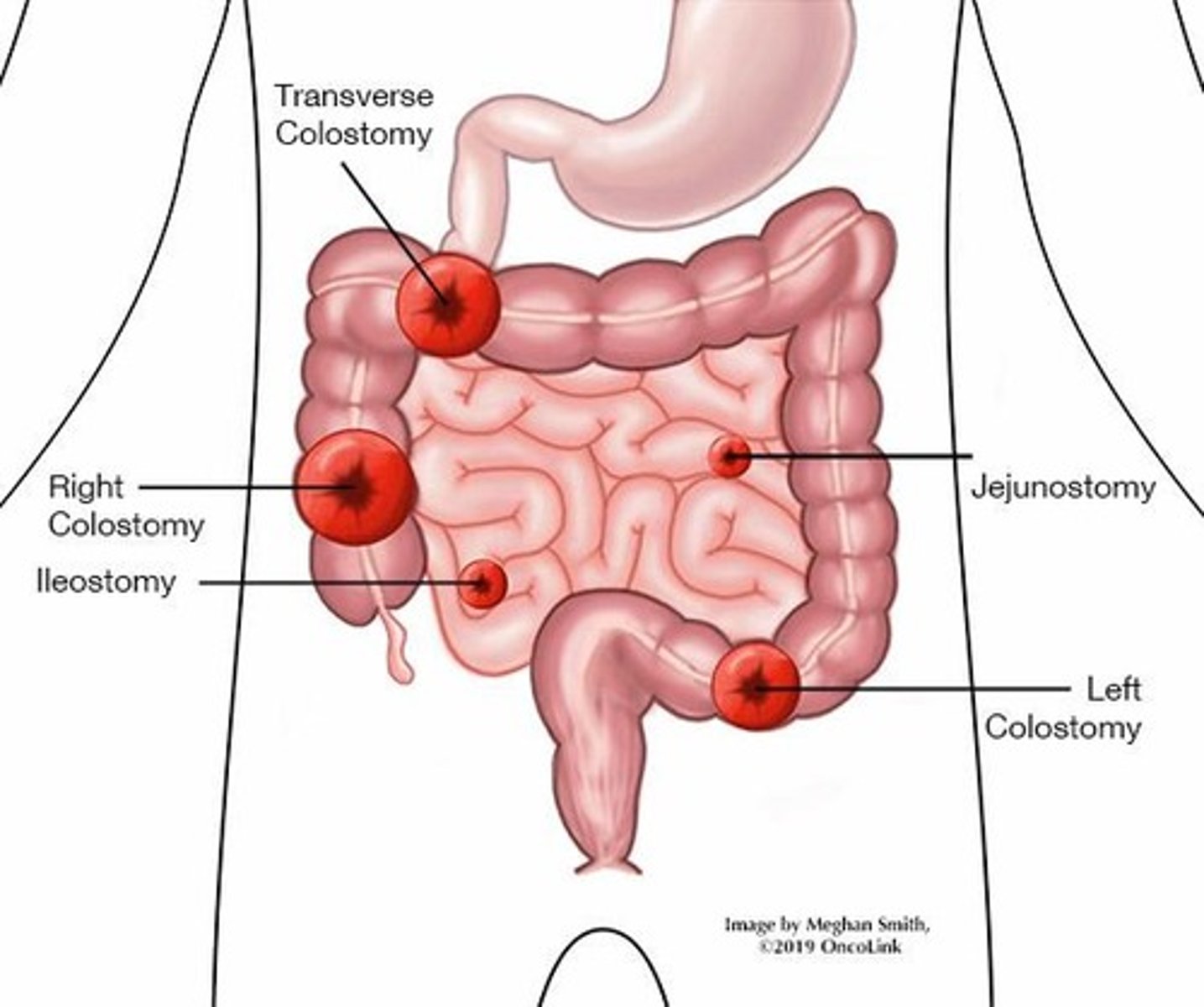
Bowel diversions
Includes jejunostomy, ileostomy, colostomy types.
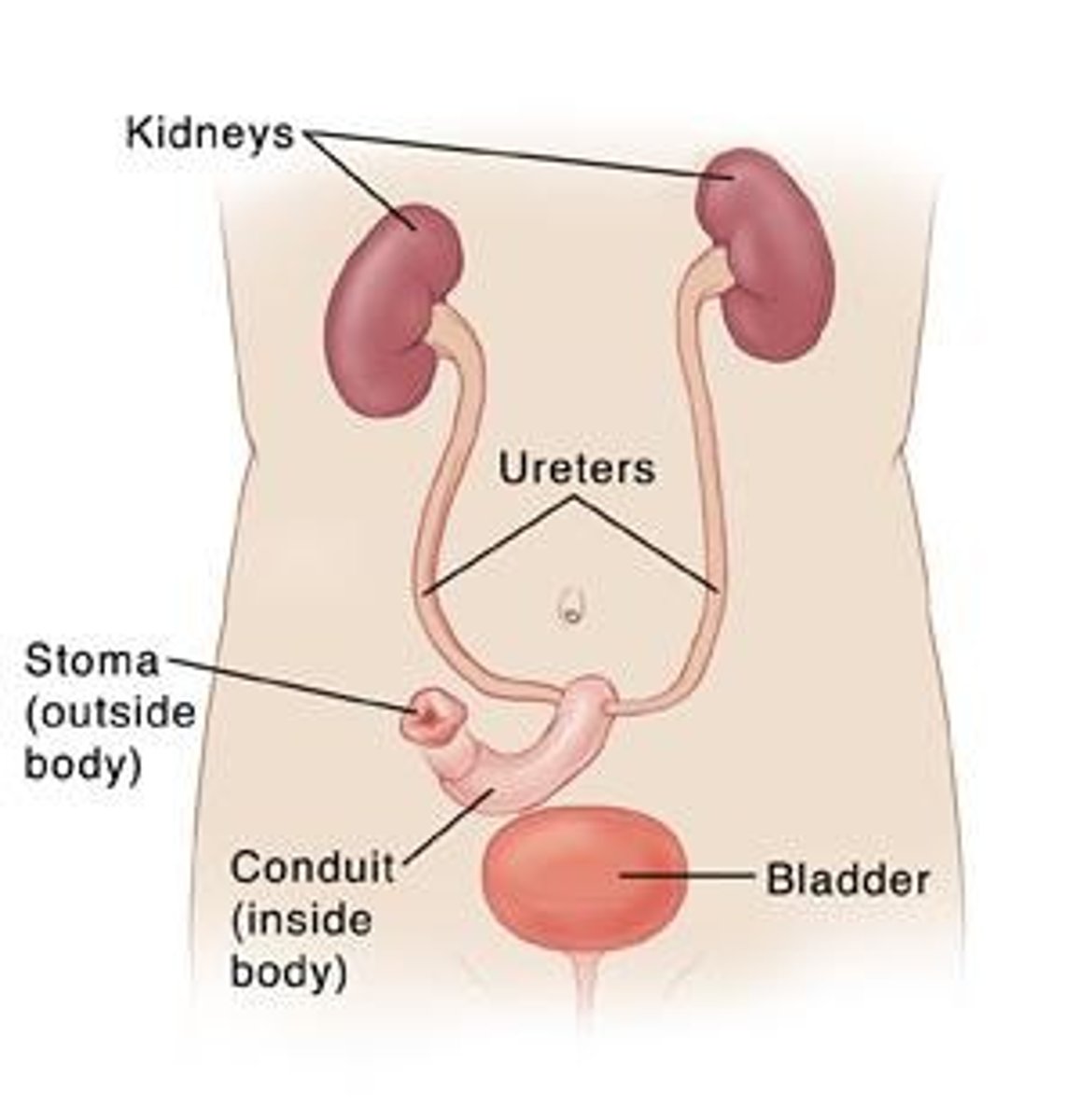
Bladder diversions
Includes vesicostomy and ileal conduit types.
Compassion in ostomy care
Show empathy and maintain professionalism with patients.
Ostomy odor management
Deodorants available to manage odor issues.
Nursing interventions
Actions taken to address patient care needs.
NPWT
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy for wound management.
Leak assessment
Determine leak location in NPWT dressing.
Drain output monitoring
Note location, type, and amount of drain output.
Heat and cold implementation
Requires MD order; assess tolerance factors.
Overexposure assessment
Evaluate effects of prolonged heat or cold exposure.
Leak Assessment
Identify incision leak location due to moisture.
Stoma Paste
Used to seal skin creases around stomas.
Transparent Film
Drape applied to check for skin seal.
MARSI
Medical Adhesive Related Skin Injury risk.
Specialty Bed Decision Tree
Guides selection of appropriate mattress surfaces.
Q 2 Hours Repositioning
Turn patients every two hours post-op.
Float Heels
Technique to prevent pressure injuries on heels.
Nutritional Support
Encourage hydration and good nutrition for skin health.
Barrier Cream
Protects skin from incontinence-related damage.
Skin Assessment in Dark Skin
Assess color, temperature, and tenderness changes.
Chronic Tissue Damage
Consider in skin folds for wheelchair-bound patients.
Pale Pink Skin
Indicates potential skin loss in darker skin.
Gray/Lavender Skin
May indicate moisture or fungal rash.
Repositioning Frequency
Wheelchair-bound patients need repositioning every hour.
Incontinence Care
Essential to prevent skin breakdown in vulnerable patients.
Wheelchair Cushion
Recommended to redistribute pressure and prevent injuries.
ROM Exercises
Prevent contractures and improve patient mobility.
Device-Related Injuries
Caused by improper fitting of wheelchair frames.
Skin Integrity Maintenance
Essential for preventing pressure injuries.
Skin Care Bundle
Includes surface, movement, incontinence, and nutrition.