Chapter 30 - Plant Defense and Behavior
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Types of pathogens for plants
- Pathogens feed on living (biotropic) or dead (necrotropic) cells.
- Some rely on the living cells to reproduce (use the cells machinery to replicate DNA).
parasitic plants
tap into the host plant's tissue to retrieve water and minerals or sugars.
potato blight consequences
plants: death
humans:
- major economic and cultural consequences ("The Great Famine")
- demographic, political, cultural shifts
how does potato blight enter plant
1. finds gaps in cuticle (2 kinds)
2. opens gate
3. breaks it down
spreads inside plant using existing transport tissues
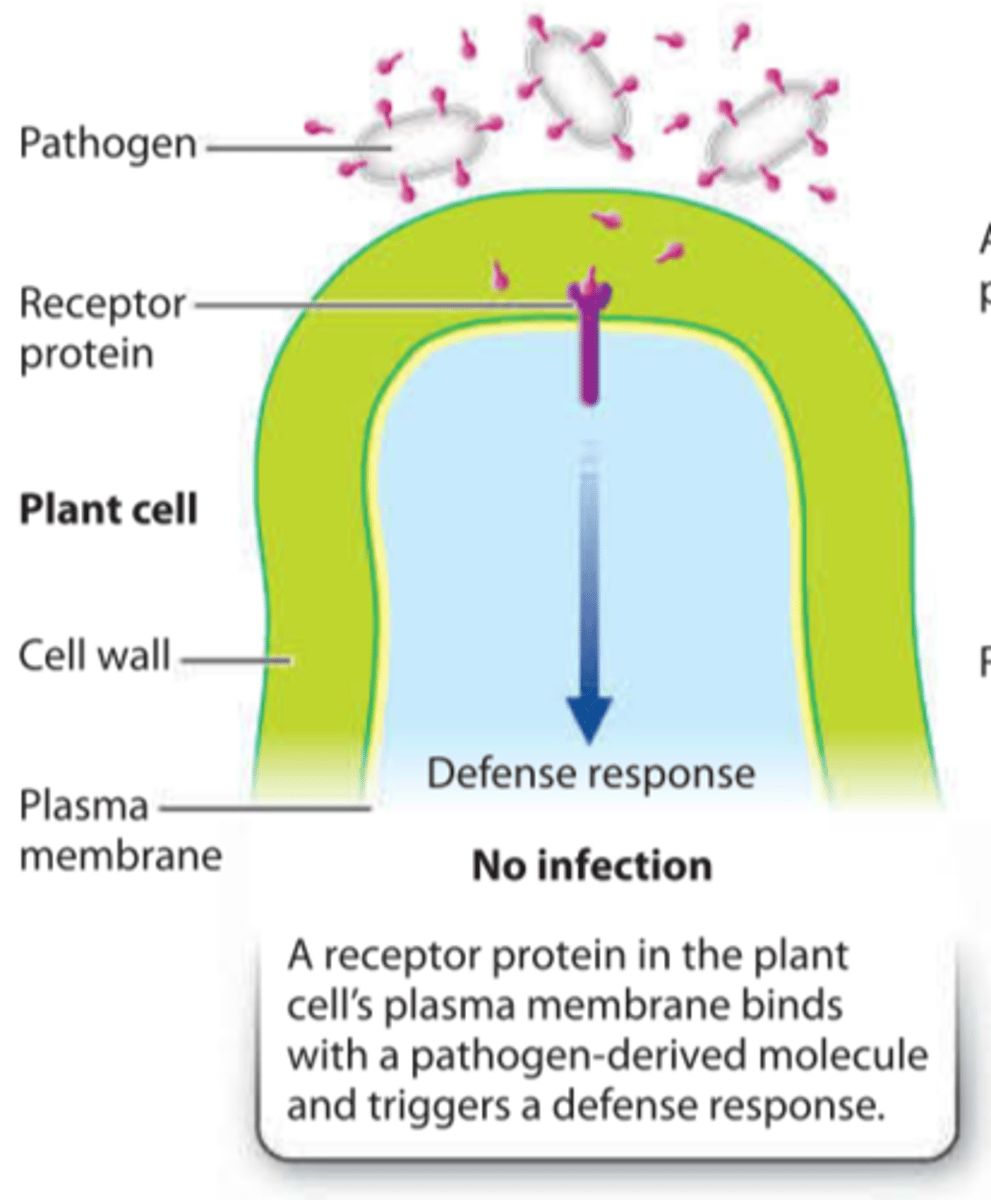
basal immune system
consists of receptors located on the plasma membrane which recognize highly conserved molecules generated by broad classes of pathogens
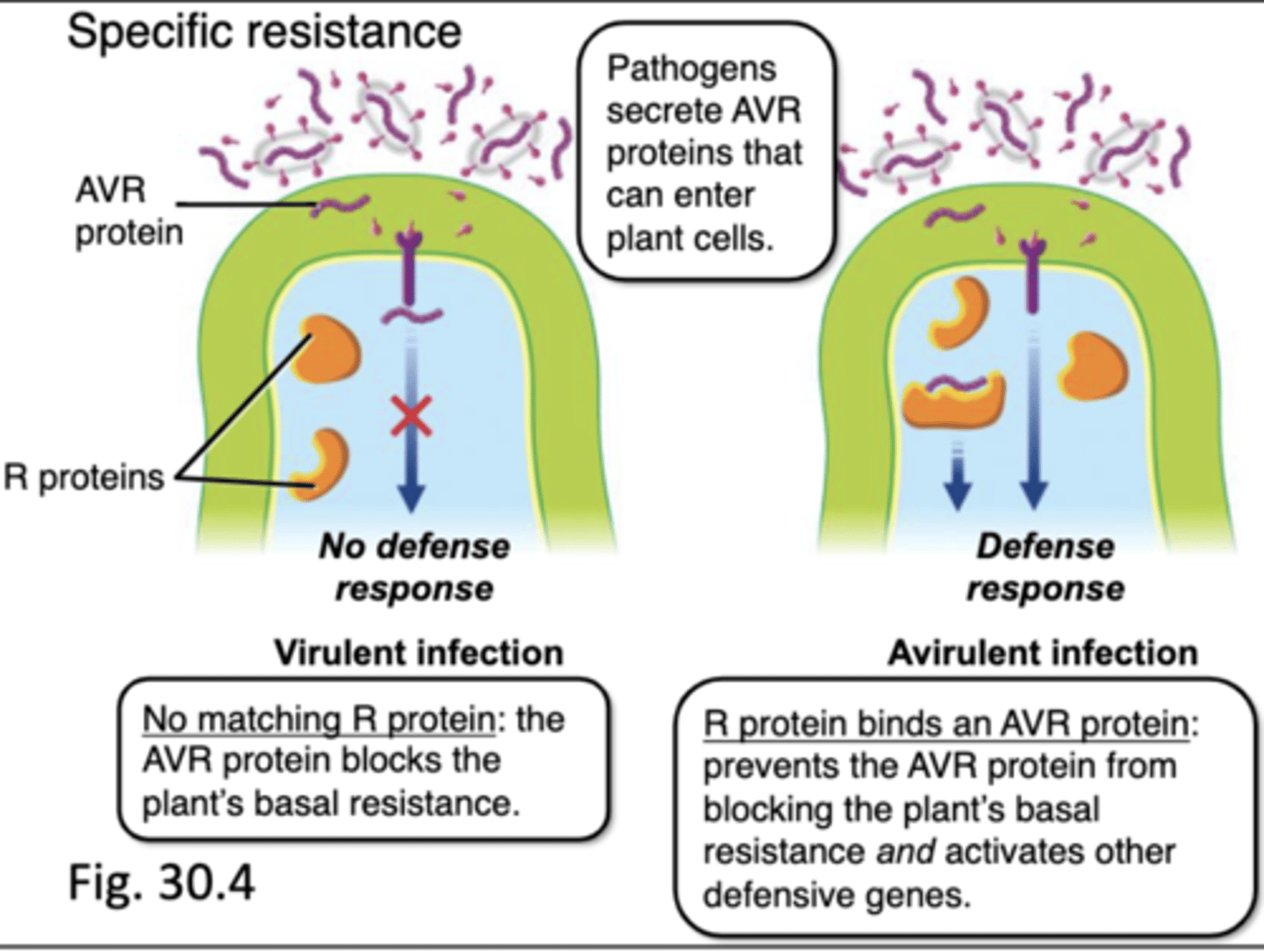
specific immune system
when an R protein binds with an AVR protein, it prevents the AVR protein from blocking plant's basal resistance and directly activates defensive genes
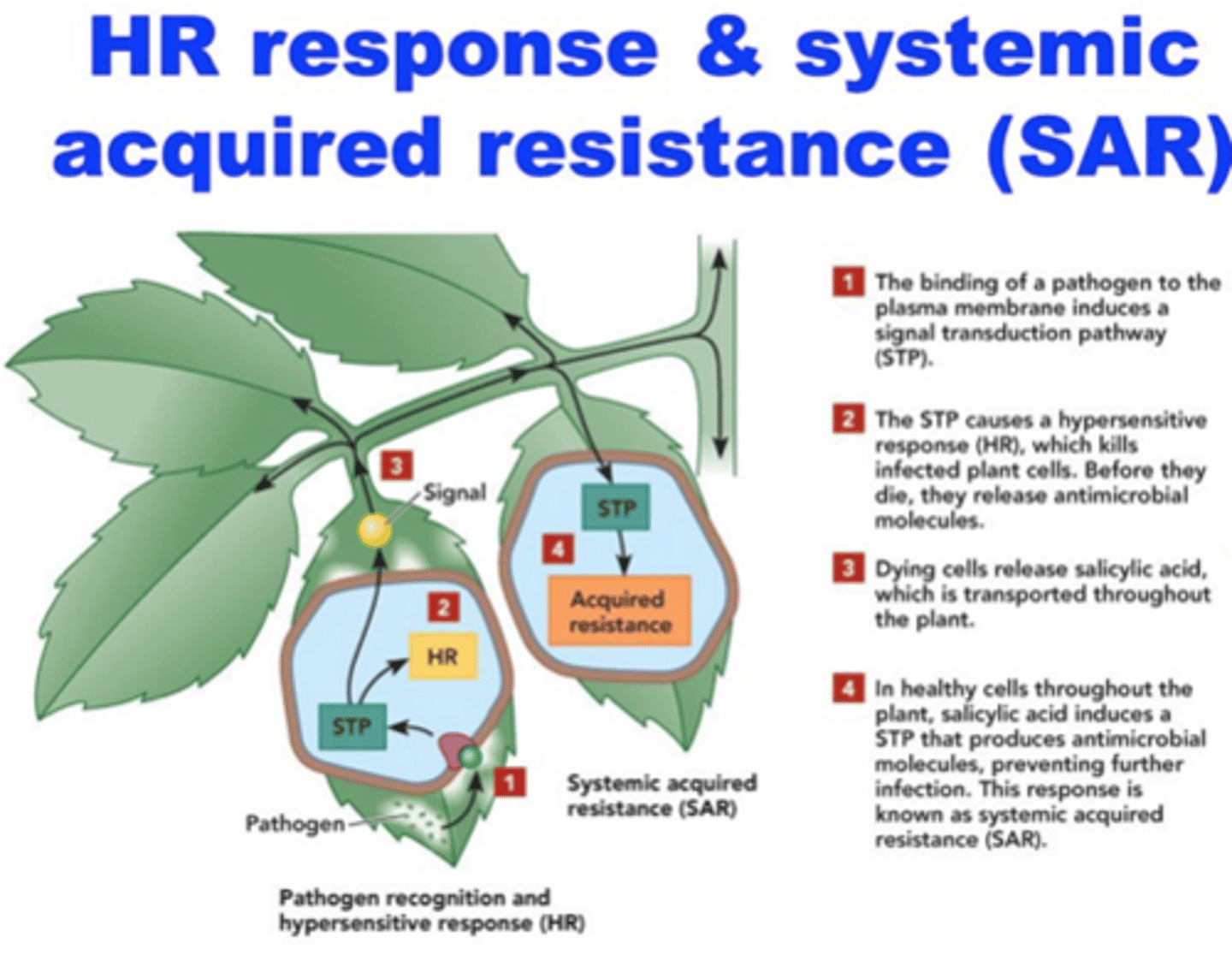
Hypersensitve Response
layer of dead cells around infected area (containment) caused by upping production of reactive oxygen species by the leaf!
physical response to pathogen
closing stomata, cell wall strengthening, xylem plugging
chemical response to pathogen
antimicrobial
vascular wilt disease
Plant cuts off all nutrients going to the infected area (plugs the xylem)
- sometimes leads to plant suicide
- death of individual but survival of population
systemic acquired resistance
A defensive response in infected plants that helps protect healthy tissue from pathogenic invasion.
plant response to virus
1. Interfering with the virus' RNA
2. Cut the dsRNAUsing the fragments as bait to hybridize against complete RNA
3. Destroying the RNA.
4. siRNA move through plasmodesmata, alerting other cells of invasion.
Crown Gall disease
Some bacteria acquired the ability to insert some of its genome into the plant's own genome and triggering a behavior by the plant cell.
It infects roots and stems and causes galls, by the proliferation of plant cells (triggered by hormones and synthesized by the infected plant cells).
alkaloids
potent plant chemicals that contain nitrogen
terpenes
- often volatile; spread easily, may serve as warning signals.
- may serve as an active defense mechanism, interfering by mimicking hormones with insect development (sometimes the best defense is pre-emptive attack!).
phenols
- Bind to proteins and reduce digestibility!
protein based chemical defenses
- some plants produce "novel" amino acids which are then integrated into the insect herbivores and interfere with function and growth of insect
- antidigestive proteins called protease inhibitors that bind to the active site of enzymes that break down proteins in the herbivore's digestive system.
ecological defenses
Recruiting biotic defenders, in particular ants.
1. provide nectar outside of flower
2. ants attracted and will consume every other insect/larvae they encounter while prospecting for nectar
3. removing ants leads to higher herbivory
symbiosis of ants and acacia
- These plants provide food and shelter to ants.
- Ants live in the plant and defend the plant
- Plants provides ant with food.
-ants may kill pollinators. but flower emit a chemical repelling the ants but not pollinators.
- co-evolution: these plant lack chemical defenses and now depend on the ants.
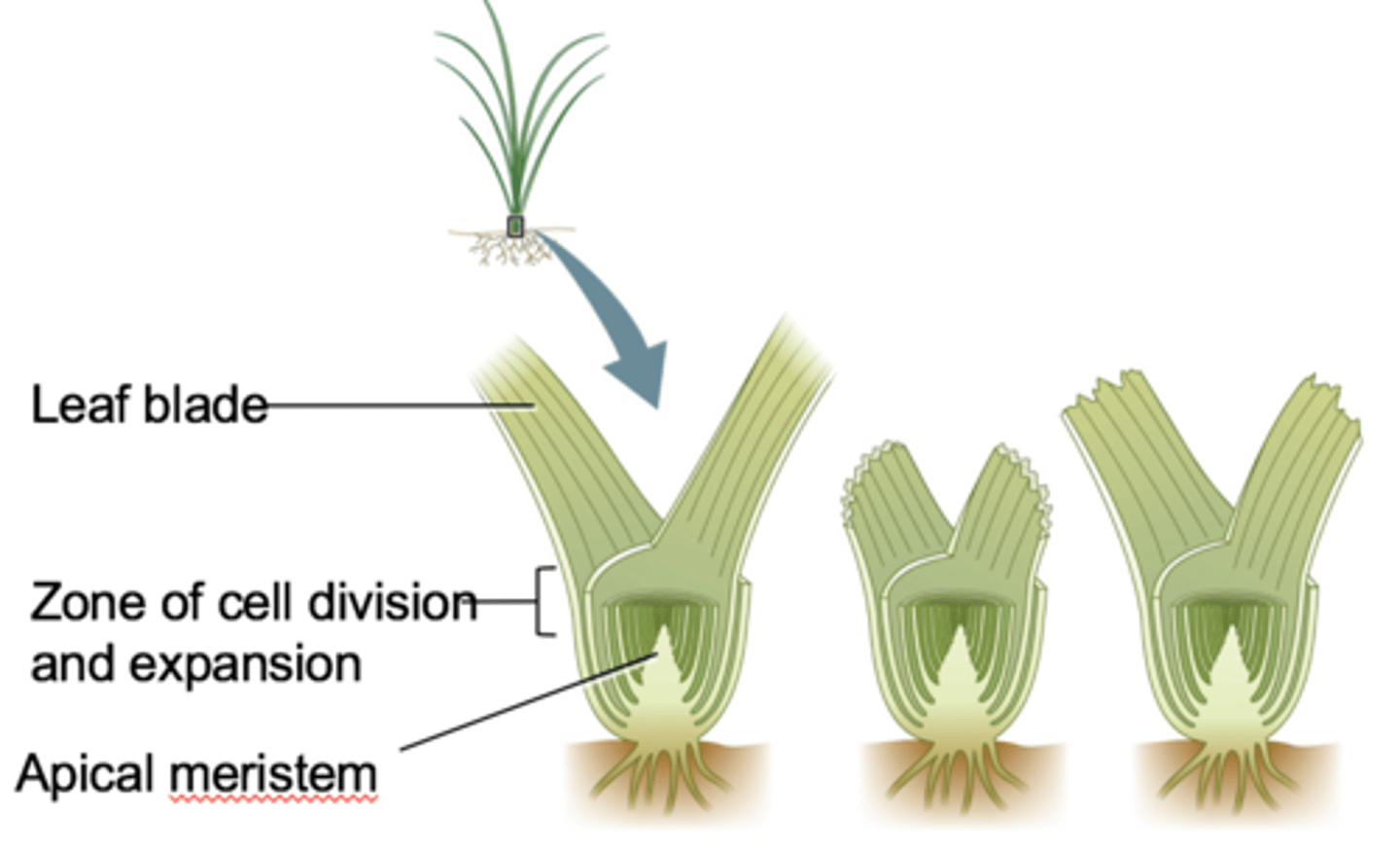
adaptation in grasses
Stems of grasses are short (apical meristems are close to the ground), leaves are tightly imbricated and leaves continue to grow from their base.
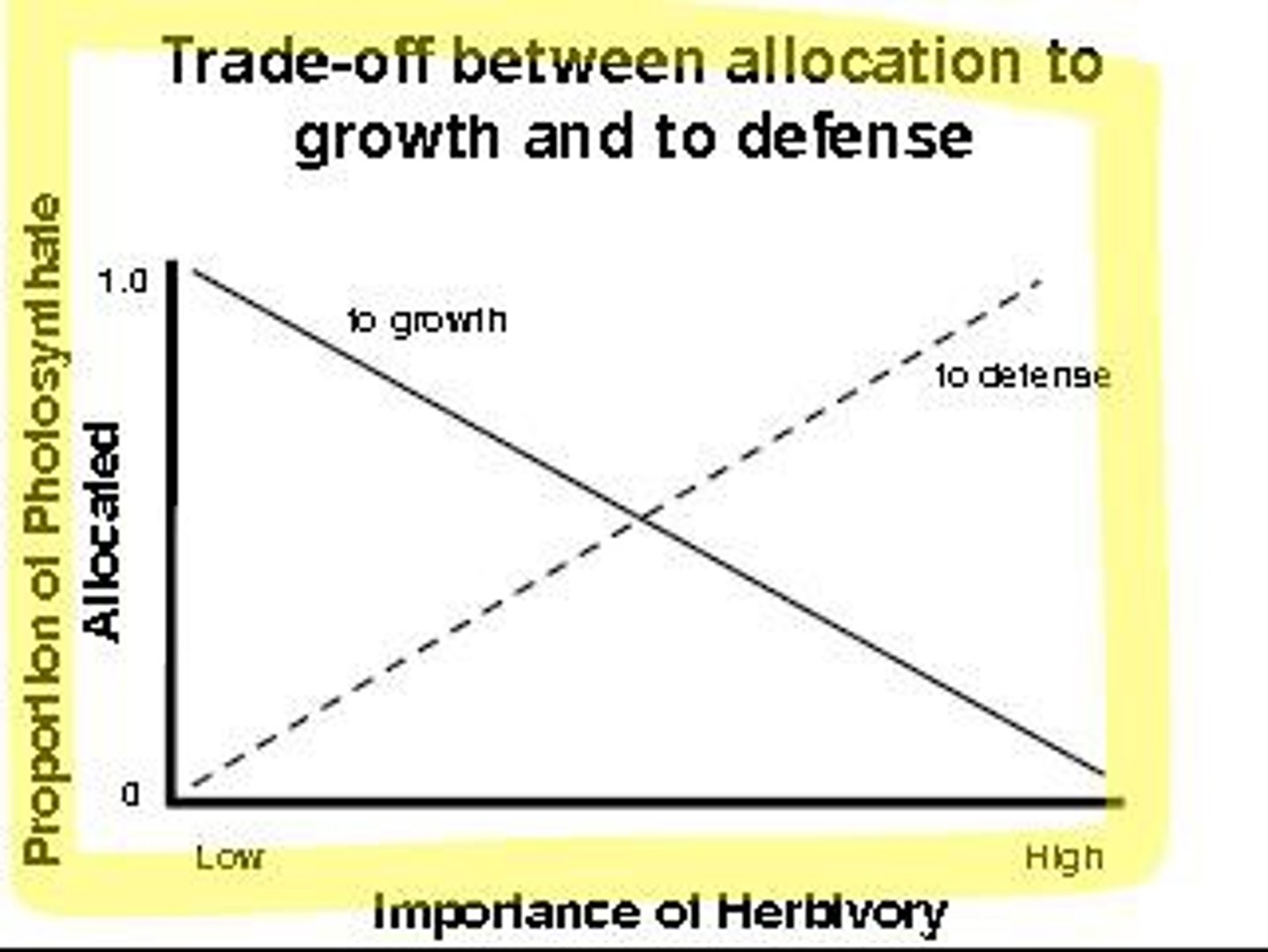
Growth and Defense Trade-off
-Growth rate may determine investment in plant defenses.
-Ability to grow fast, if for examples nutrients are abundant, may allow for fewer investments in plant chemical defenses.
-Plants that invest heavily in chemical defenses will grow more slowly since they allocate fewer resources to growth
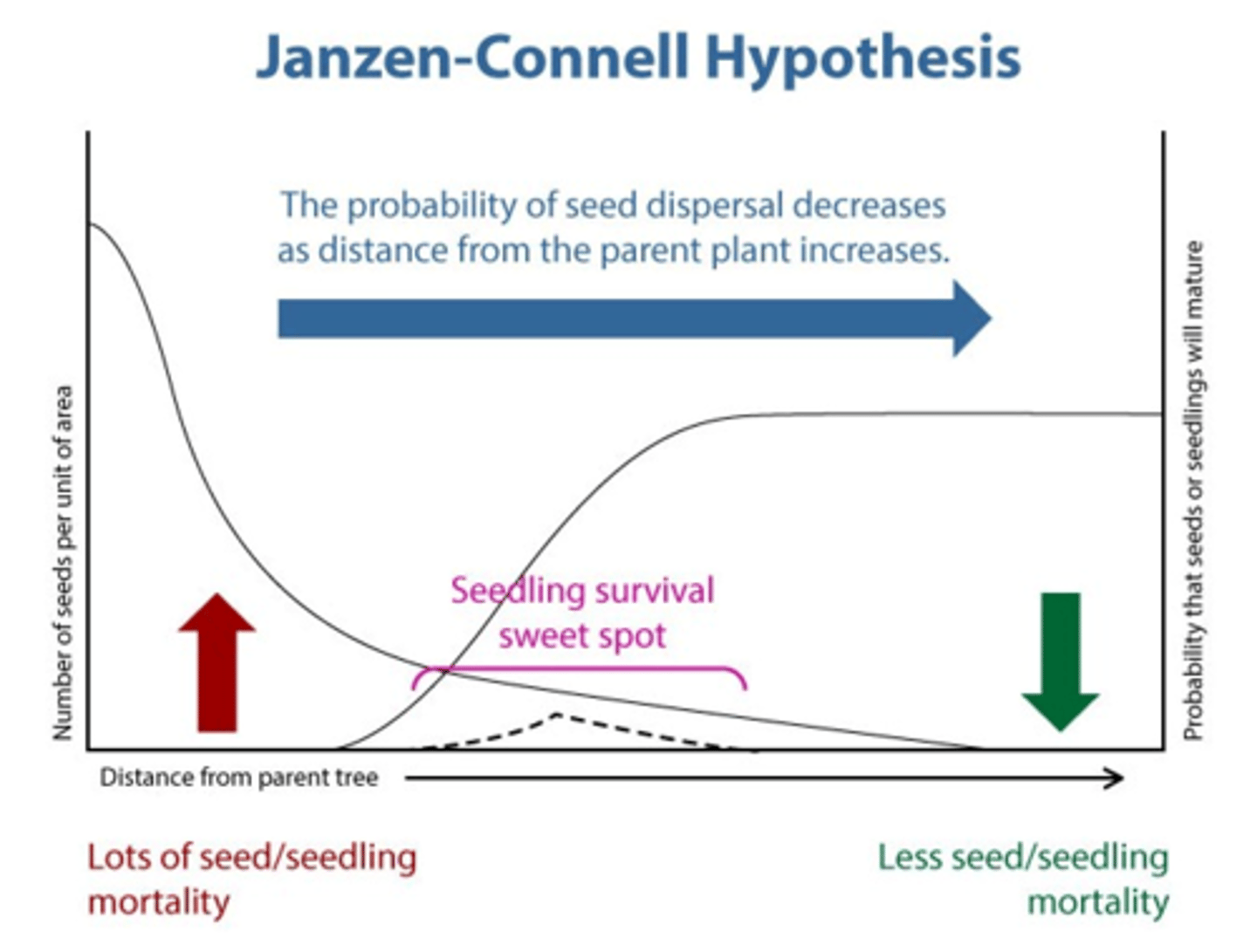
Janzen-Connell Hypothesis
- Vulnerability of a population to disease is dependent on the density of its individuals.
- Many, low-density species are more likely to survive than a few, high-density species.
- Dispersal of seeds is critical not simply to reduce competition between generations but also to reduce exposure of the offspring to pathogens.
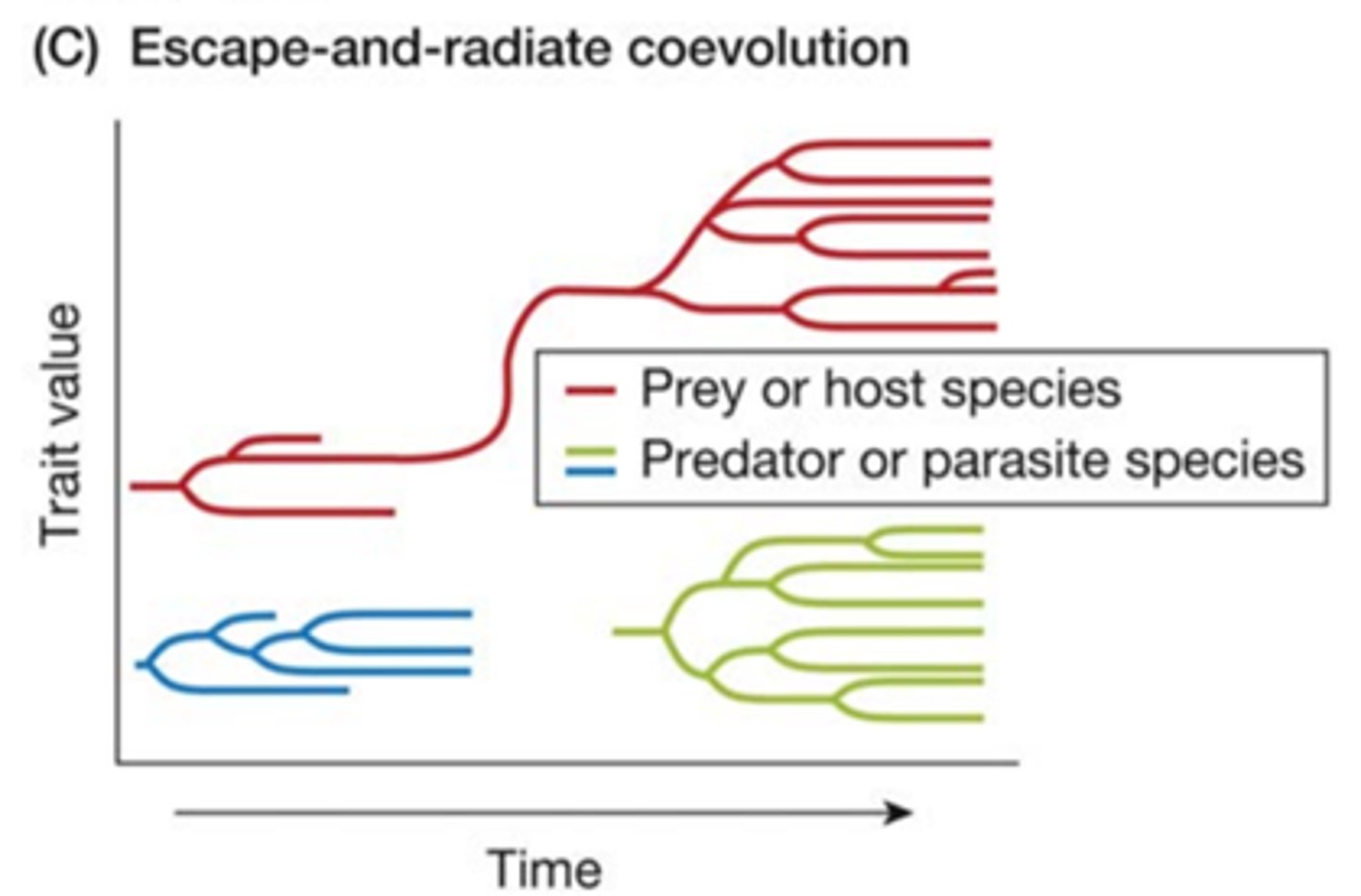
escape and radiate
a species evolves a defense against enemies and is thereby enabled to proliferate into a diverse clade
ways to protect crops from herbivores and prthogens
- Applying pesticides/herbicides
- Understanding the ecology of the farm
- Crop breeding