Exam One
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What are the three unexplainable phenomena from classical mechanics?
Quantized energies, Photoelectric Effect, and Electron Diffraction
What was the purpose of the Black Body Radiation Experiment?
As you heat an object like a metal, the color changes to white hot. As a result the temperature increases and the object is emitting radiation, which are different frequencies.
What is visible light?
THe form of electromagnetic radiation, which is a wave that travels through a vacuum at a constant speed.
What is the speed of light?
2.99792558 × 10^8 m*s^-1
How is an electromagnetic wave expressed?
Two perpendicular waves an electric and a magnetic wave
What is wavelength (λ)?
The distance between two consecutive wave maxima (m)
What is the Period (T) of a wave?
The time it takes to travel from one maxima to the next (sec)
What is the Frequency (𝓋) of a wave?
The number of cycles per second (Hz or s^-1)
What is wavenumber (ṽ) of a wave?
TH einverse of wavelength (cm^-1)
What is the visible range of light?
400 - 700 nm
What can a microwave wave do to a molecule?
Cause rotational movement in a polar molecule
What can infrared waves do to a molecule?
Cause bending vibration; if the bent shape of the molecule is polar
What can visible waves do to a molecule?
Excite the electrons; done if the molecule is colored in the world
What can ultraviolet waves do to a molecule?
Can break chemical bonds
When thinking about Black Body radiation, what happens as the temperature is increased?
The energy spectral density increase and the max spectral energy density shifts to a smaller wavelength.
What is spectral energy density?
The relative amount of energy per unit volume of a wave
What is the ultraviolet catastrophe discovered in research of Black body radiation?
There is a point at the start of the ultra violet range where the Rayleigh-Jeans equation does not match experimental results.
What is Plank’s model of vibrational energy?
Evib = 0, h𝓋, 2h𝓋, 3h𝓋, 4h𝓋, …
What is the jkey takeaway of black body radiation using oscillators?
Energy is quantized
The second experiment done to discover quantum chemistry was about heat capacity for solids. What is heat capacity?
The amount of energy needed to increase a unit mass of a substance by 1 K.
In gases is Cp or Cv larger, where the subscript denotes the variable held constant?
Cp was larger and the difference equalled the gas constant, R>
In solids what is the relation of Cp and Cv?
They are essentially the same.
In classical physics, an atom can move in 3 directions and vibrate (which accounts for 2 directions). The average energy equals what for 1 mole of a substance?
Eavg = 3kT or 3RT
What does Cv,m equal based on classical mechanics?
3R.
What is the problem with the gas constant relation?
The relation Cp,m = 3R works for high temperatures but a low temperatures it is horribly inaccurate, meaning there needs to be a solution found.
Einstein tried to solve the classical physics problem of Heat Capacity at low temperatures, however, his theory is not perfect, why is it not?
It fails to accurately predict heat capacity at very low temperatures due to limitations in its assumptions and the simplifications made for the behavior of solid materials. Most oscillators do not get energy at such a low temperature making the assumption cause deviation, and he made the crude approximation that all moleucle made the same frequency which does not hold true for all materials, leading to inaccuracies in predictions.
What is spectroscopy?
Shine a light at a sample and see what happens.
How doe we understand atomic molecular spectra now?
The enrgy of an atom or molecule can only have discrete values.
When an atom or molecule jumps between two energy levels, the energy difference — the energy that is released or absorbed — is also confined to discrete values
The frequency of radiation is a function of the energy difference: discrete change in energy means discrete v (frequency)
What was the ∆E equation that resutlsed from spectroscopy?
∆E = hv, where h = 6.626 × 10-34 J•s
If there is only a small energy difference between states of the electron then …
The energy has a large wave and a small frequency and vice versa if there is a large energy difference, the wave is short and the frequency is high.
What is the photoelectric effect?
The photoelectric effect is the phenomenon where electrons are emitted from a material when it absorbs light energy. This effect demonstrates that light can behave as both a wave and a particle, supporting the concept of quantized energy levels.
To determine that intensity of light does not matter as a result of the photoelectric effect, what three things were determined?
If the UV frequency is below a threshold value, then no electrons are ejected
If the frequency is above a threshold photoelectrons appear
The kinetic energy of ejected electrons varies with frequency.
How cna the photoelectric effect be understood?
By treating radiation as a stream of photons of energy, hv, where a photon can collide with an electron and eject if hv > ɸ.
What is ɸ in the photoelectric effect?
ɸ represents the work function, which is the minimum energy required to eject an electron from a material.
What is the equation for kinetic energy in the photoelectric effect?
½ me v2 = hv - ɸ; which means the kinetic energy of a photoelectron varies linearly with frequency (v) and we can determine h from the slope.
What is wave particle duality?
Wave-particle duality is the concept in quantum mechanics that describes how all particles exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties. This principle is fundamental to understanding phenomena such as light behavior and the behavior of electrons.
What was the Davisson-Germer Experiment?
demonstrated the wave nature of electrons by showing electron diffraction patterns, confirming the principles of wave-particle duality. This experiment helped validate de Broglie's hypothesis regarding the dual nature of matter.
Why was a crystal used in the Davisson-Germer experiment to diffract electrons?
A crystal was used in the Davisson-Germer experiment to create a regular array of atoms, which allowed for the diffraction of electrons, demonstrating their wave-like behavior.
What is the deBrolie relation”?
A particle that has a linear momentum of p = mv can also be treated as a matter wave with a wavelength λ = h/p. Where y = sin(2πx/λ)
What is the first key feature of quantum mechanics?
Atoms and molecules cannot have any energy at all — they can only take up discrete, quantized energy.
What is the second key feature of quantum mechanics?
both light and matter behave as particles and as waves at the same time
What is the third key feature of quantum mechanics?
microscopic objects do not have a definite trajectory — we cannot exactly tell where they are and where they are heading at any time, t.
When thinking in terms of classical mechanics as particle has …
a definte trajectory at a time, t, and it can be found at a precise location with a precise velovity. However a wave does not have a precise location.
When thinking of a quantum particle, the particles has…
no trajectory. It is spread through space like a wave. Meaning all that we can say about the particles location and velocity is contained in the wave function, Ψ
What is a wave function look like?
A fuzzy trajectory of a particle, that is obtained through Schrödinger’s Equation.
What is the wave function?
A mathematical description of the quantum state of a particle, encapsulating probabilities of its position and momentum.
If you do not account for the nuclei moving in a wave function model how many variables are there in the wavefunction of water?
30 variables, looking at the x,y, and z position of each electron.
If you do account for the nuclei moving in a wave function model how many variables are there in the wavefunction of water?
There are 39 variables representing the positions of each electron in three-dimensional space and the vibrational motion of each nuclei. This includes the x, y, and z coordinates of each electron along with additional vibrational degrees of freedom for the nuclei.
What is a Hamiltonian Operator?
The Hamiltonian operator is a central concept in quantum mechanics, representing the total energy of a system, including both kinetic and potential energy. It plays a crucial role in determining the evolution of the wave function over time.
What is the equation of the Hamiltonian Operator?
.
What is the general form of an Eigenvalue Equation?
(Operator)(Function) = (Constant Value)(Function)
What is the goal of the hamiltonian operator?
To find the eigenvalues (energies) and their corresponding eigenfunctions of the hamiltonian operator
What does the hamiltonian operator prove?
That the de Brolie equation λ = h/p is valid
What is the Born Interpretation?
It states that the square of the wave function's amplitude gives the probability density of finding a particle in a given state.
What is probability density?
Probability density is a measure of the likelihood of finding a particle in a specific position or state, typically represented as the square of the wave function's amplitude in quantum mechanics.
How is a wavefunction normalized?
A wavefunction is normalized when its total probability density over all space equals one, ensuring that the particle is found somewhere in that space.
If the wavenumber is not normalized and the equation does not equal zero or infinity, but is a finite integer, what is the next step?
To make it normalized, by dividing the wavefunction by the square root of its integral over all space.
When solving the time-independent Schrödinger equation ĤΨ = EΨ, we
know Ĥ, look for E and Ψ
The function Ψ(x) = sin(Ax) satisfies the one dimensional Schrödinger equation (-ħ2/(2m) * d2Ψ/dx2 = E Ψ
E = ħ^2 A^2 / (2m)
The acceptable wavefunctions for a particle in a box of length L correspond (inside the box) to standing waves with wavelengths
2L, L, 2L/3, L/2, …
Which formula gives the average location <ẋ> of a particle in the box 0≤x≤L described by the wavefunction, Ψn(x) = Nsin(nπx/L)
<ẋ> = N²∫0L x sin(nπx/L)dx
What is the average location <ẋ> of a particle in the box 0≤x≤L, described by the wavefunction Ψn(x) = Nsin(nπx/L)
<ẋ> = L/2
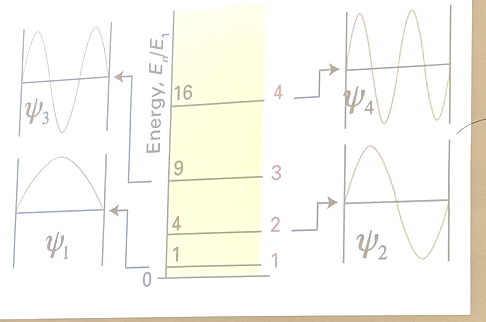
The figure below shows the 4 lowest energy wavefunctions Ψ1, Ψ2, Ψ3, Ψ4 for a particle in a one dimensional box. Which wavefunctions give the max probability density at the very center of the box.
Ψ1, Ψ3