Cardiovascular System
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
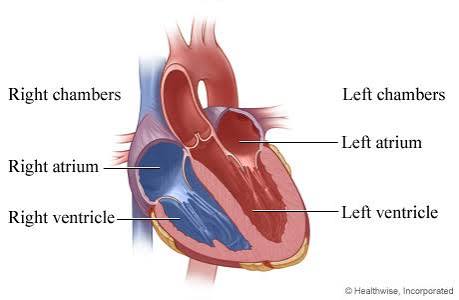
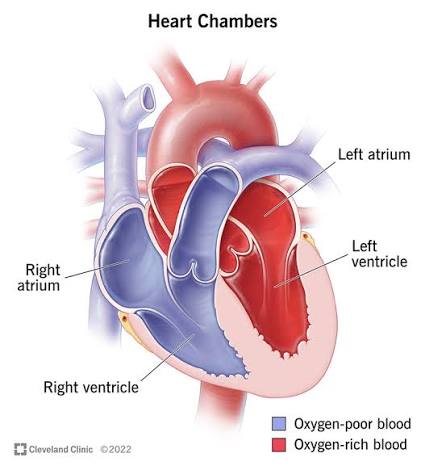
Q: What are the four chambers of the heart?
A: Right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle.
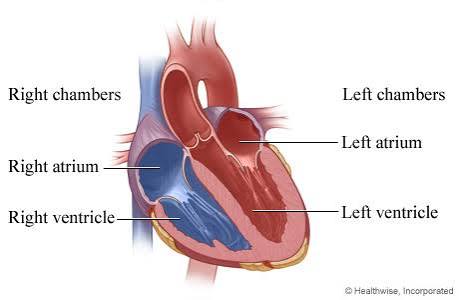
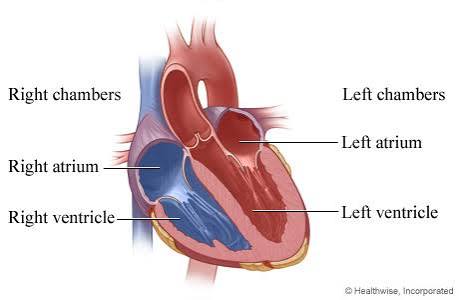
Q: What does the right atrium do?
A: Receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the vena cava.
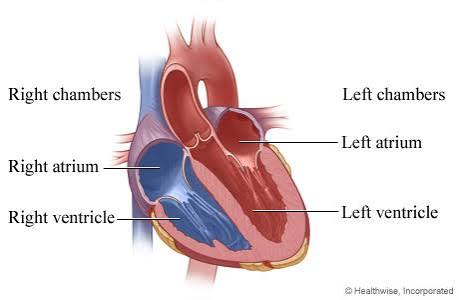
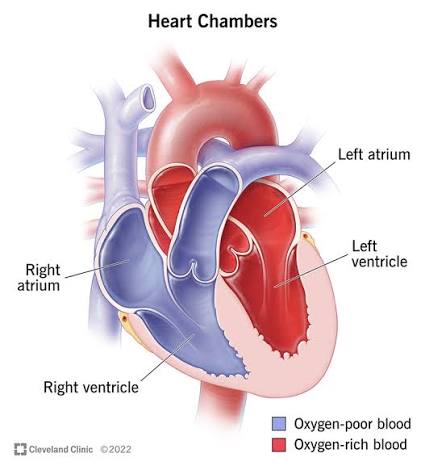
Q: What is the function of the right ventricle?
A: Pumps blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery.
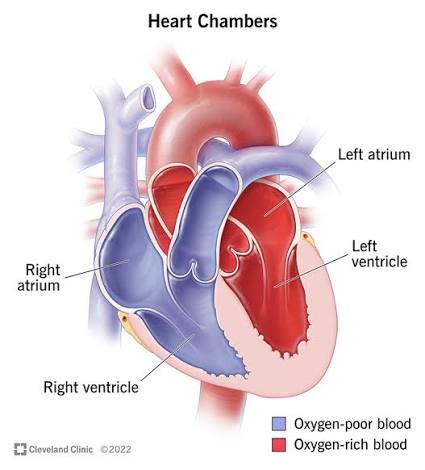
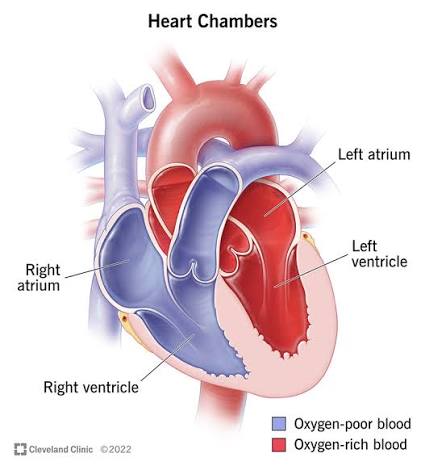
Q: What does the left atrium do?
A: Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins.
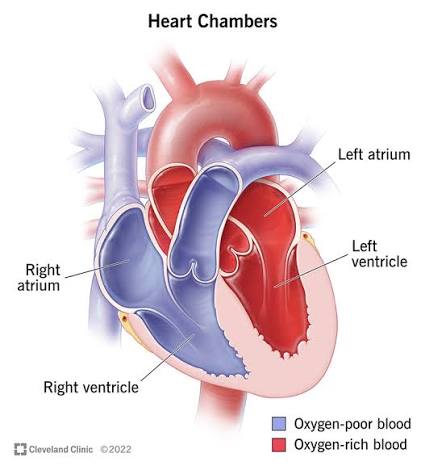
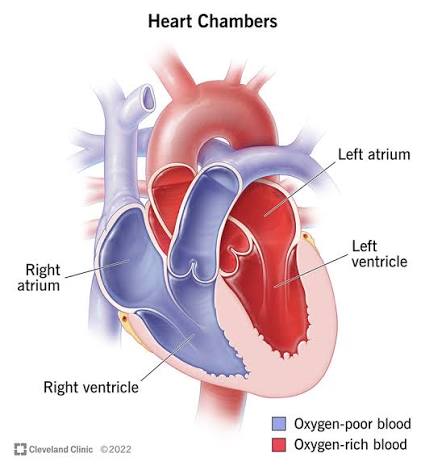
Q: Why does the left ventricle have thicker walls?
A: It must pump blood to the entire body, requiring more force.
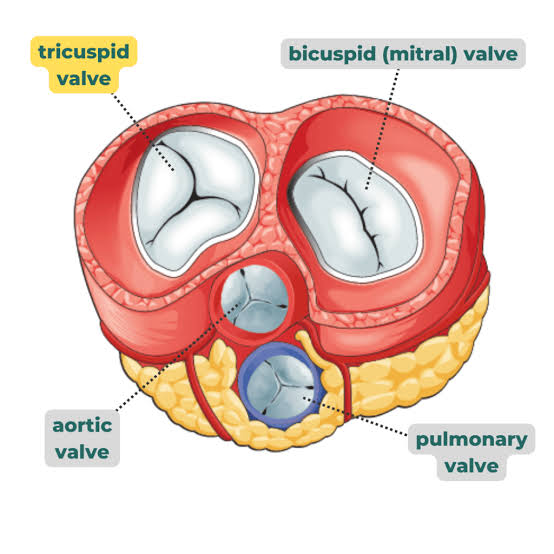
Where is the tricuspid valve located
A: Between the right atrium and right ventricle
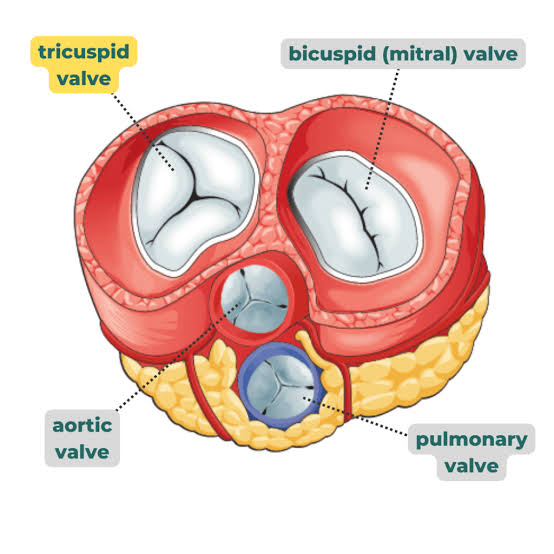
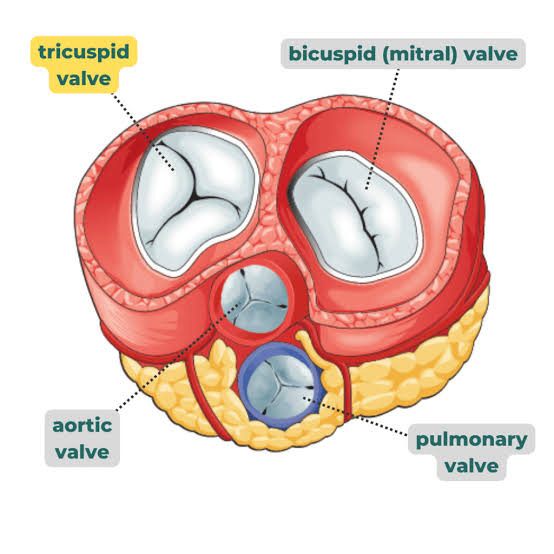
Q: Where is the bicuspid (mitral) valve located?
A: Between the left atrium and left ventricle.
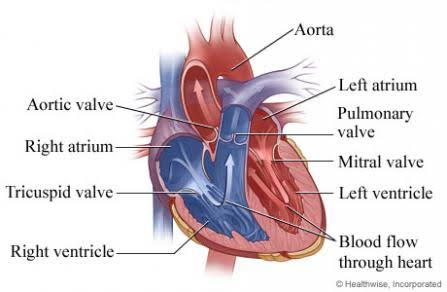
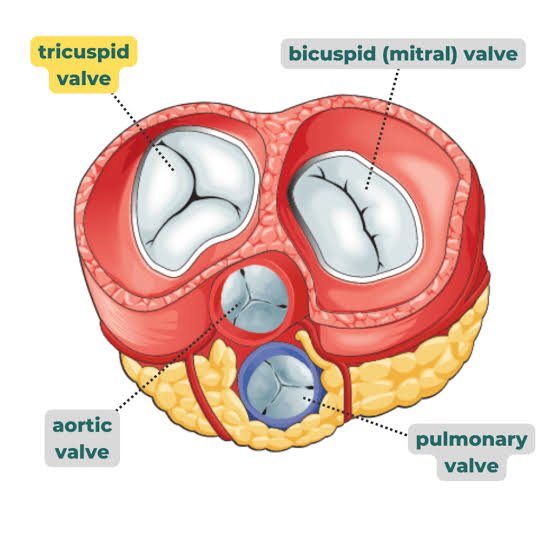
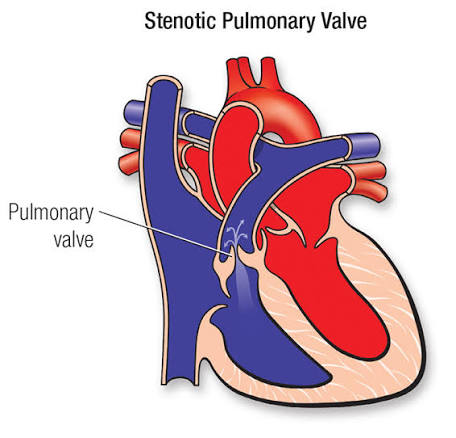
Q: What does the pulmonary valve do?
A: Controls blood flow between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery.
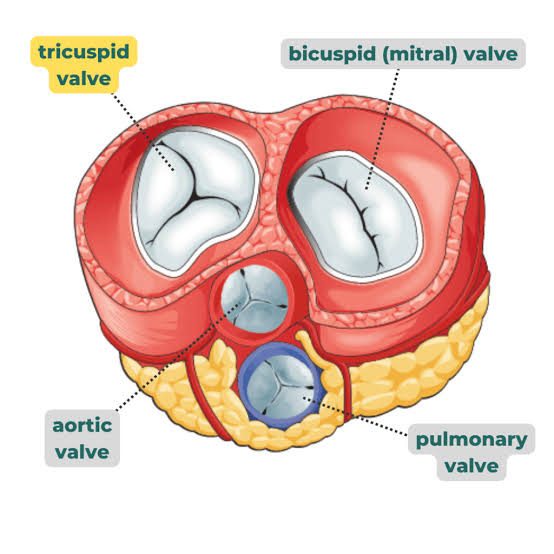
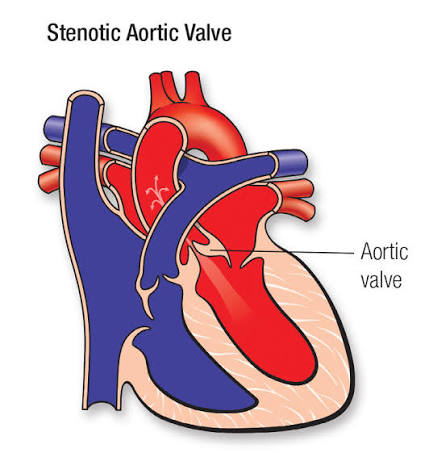
Q: What does the aortic valve do?
A: Controls blood flow between the left ventricle and aorta.
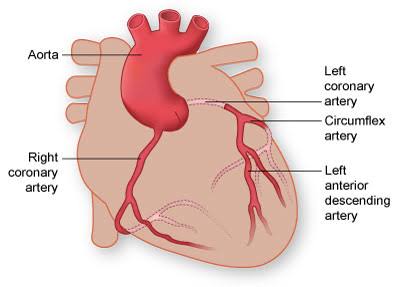
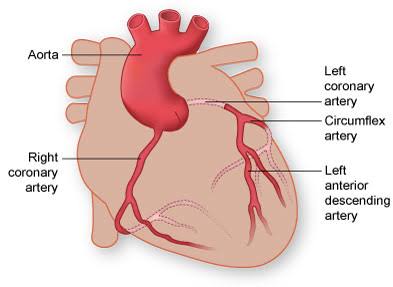
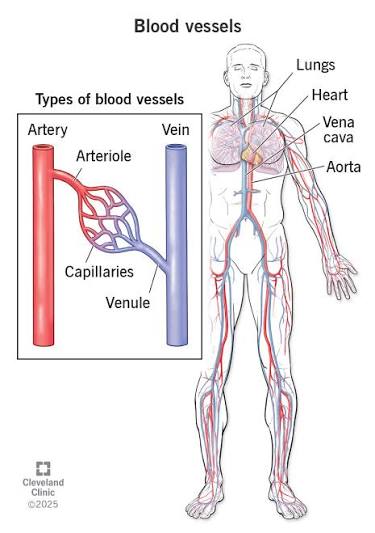
Q: What do arteries do?
A: Carry blood away from the heart under high pressure.
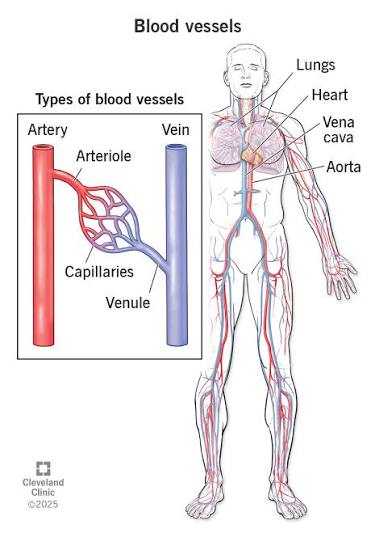
Q: What do veins do?
A: Return blood to the heart and contain valves to prevent backflow.
Q: What are capillaries?
A: Microscopic vessels where gas and nutrient exchange occurs.
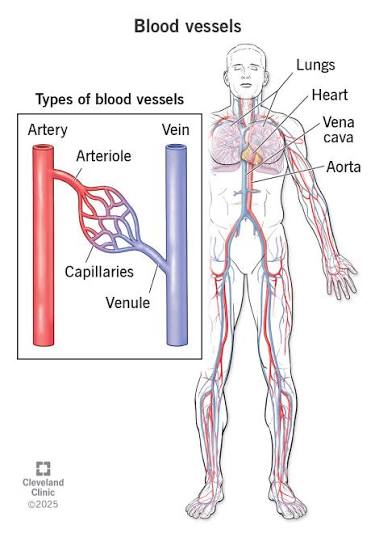
Q: What are arterioles and venules?
A: Smaller vessels that connect arteries and veins to capillaries.
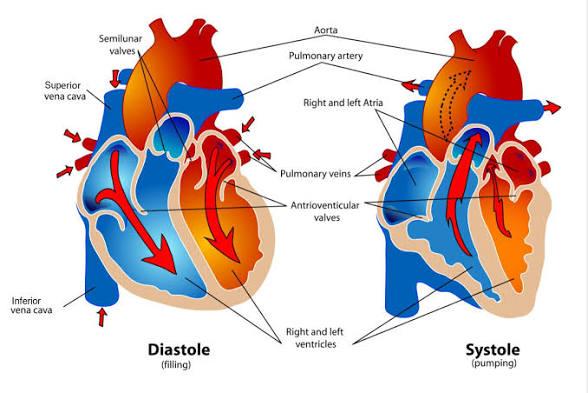
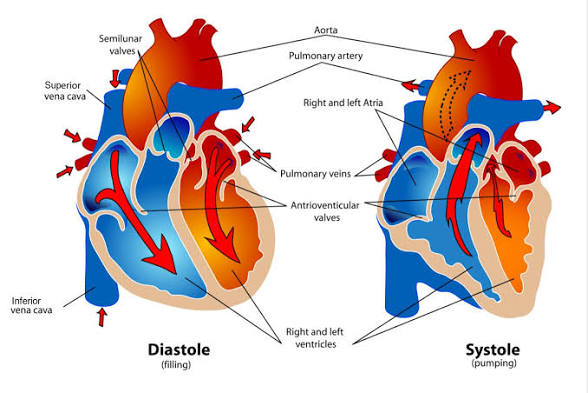
Q: What is systole?
A: The contraction phase when ventricles pump blood out.
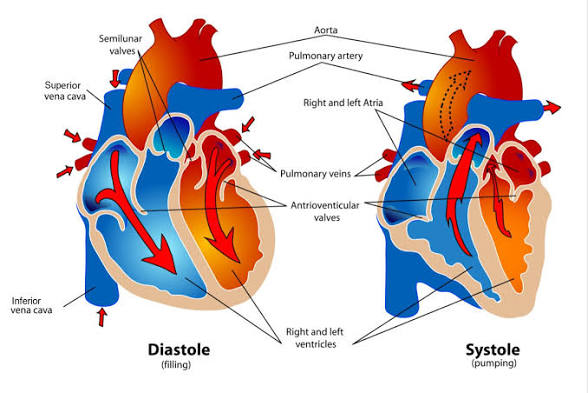
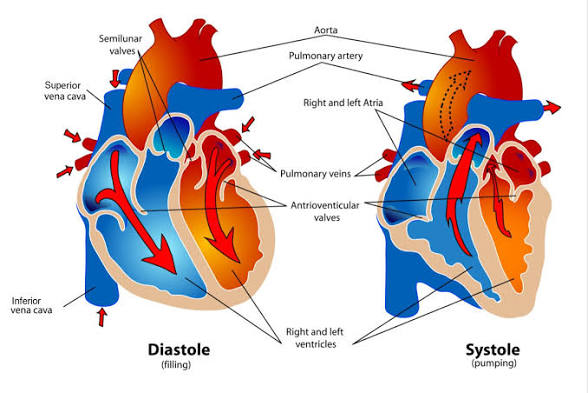
Q: What is diastole?
A: The relaxation phase when ventricles fill with blood.
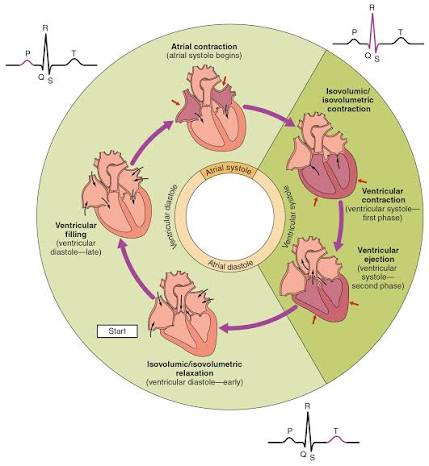
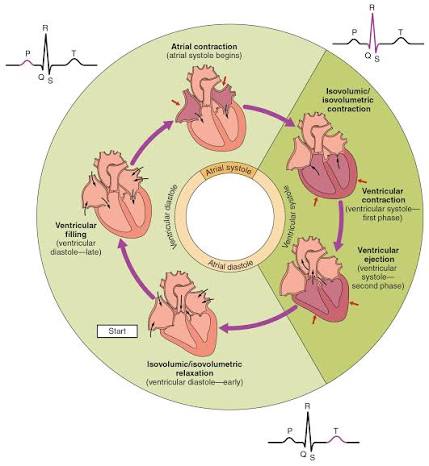
Q: How long does one complete cardiac cycle take at rest?
A: About 0.8 seconds.
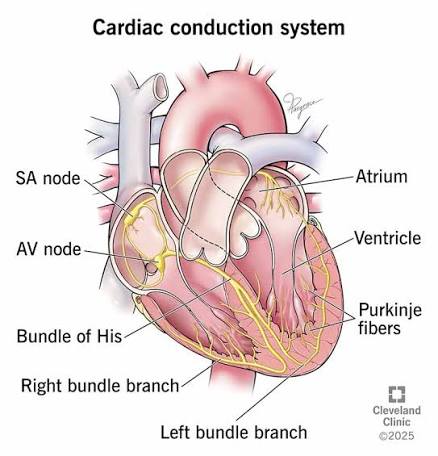
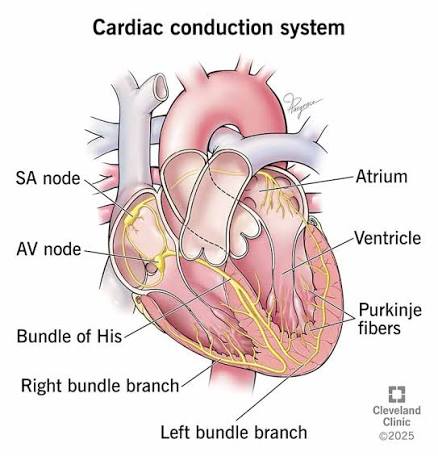
Q: What is the SA node?
A: The heart’s natural pacemaker located in the right atrium.
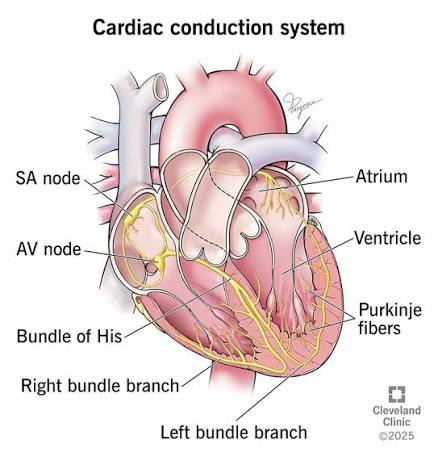
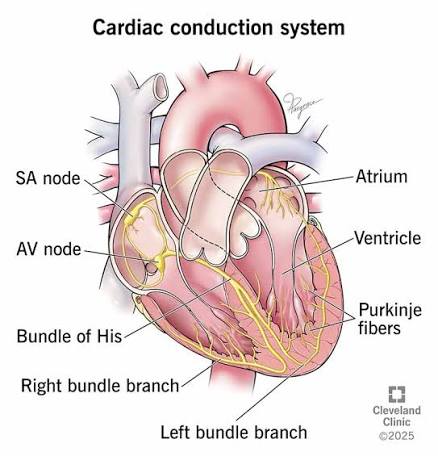
What is the AV node’s function?
A: Delays the signal between atria and ventricles
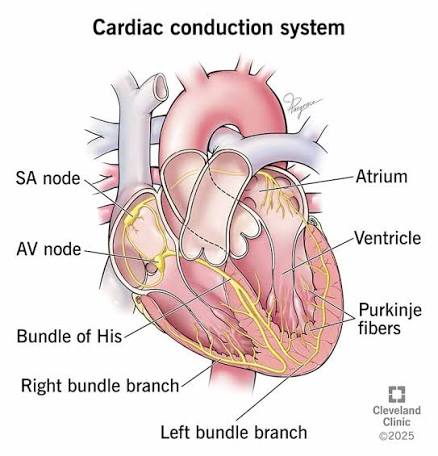
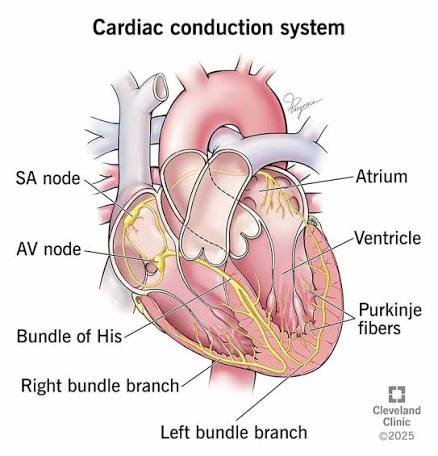
What do the Bundle of His and Purkinje fibers do?
A: Conduct electrical signals through the ventricles.
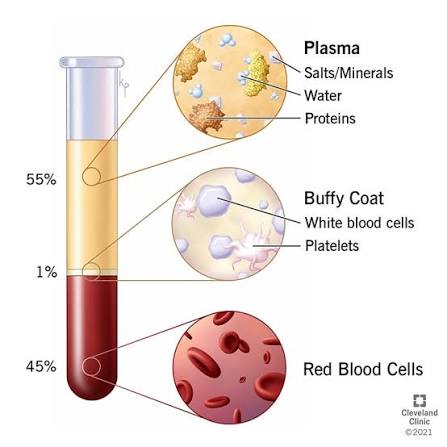
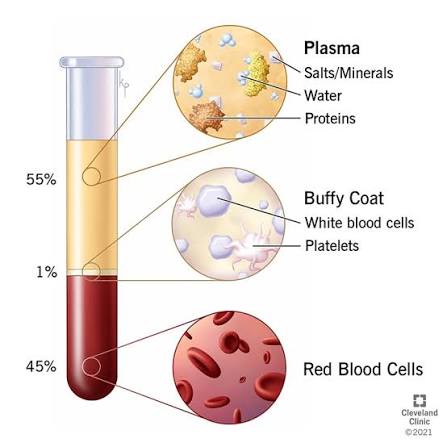
What makes up about 55% of blood volume?
A: Plasma — the liquid portion containing water, proteins, nutrients, and wastes.
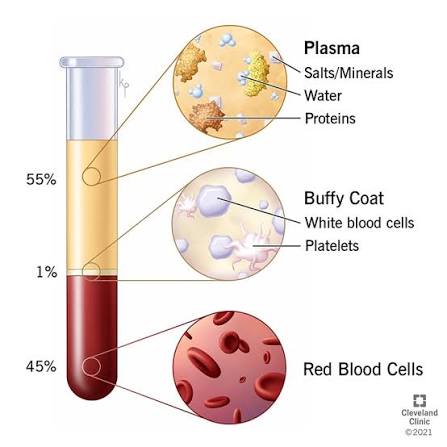
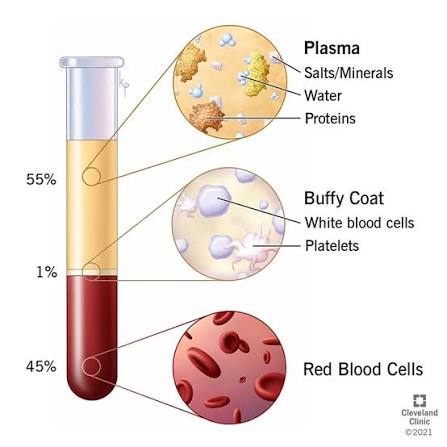
What are red blood cells responsible for?
Transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide using hemoglobin.(44%)
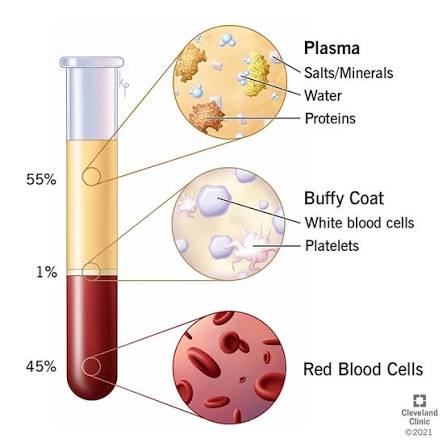
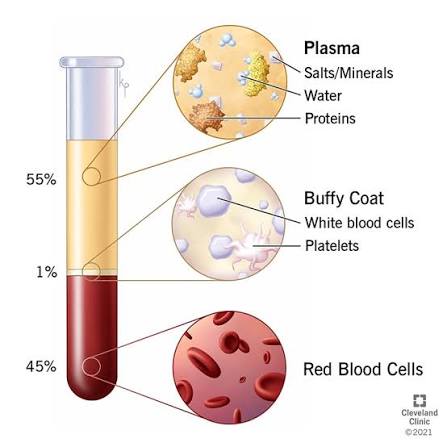
Q: What do white blood cells do?
A: Defend the body against pathogens.
Makes up (1%)
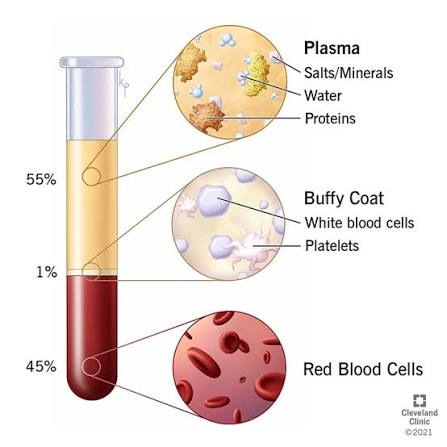
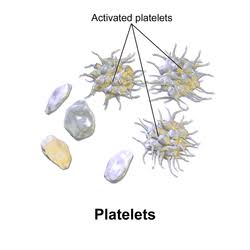
What are platelets?
A: Cell fragments that help with blood clotting.
Why do red blood cells lack a nucleus?
A: To maximize space for hemoglobin and oxygen transport.
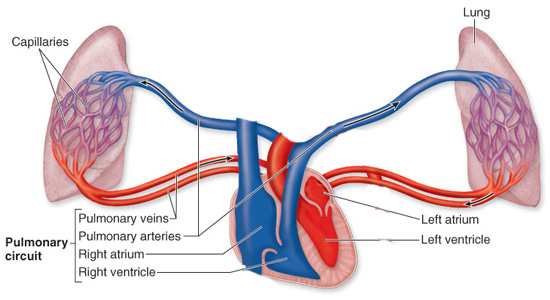
Q: What is pulmonary circulation?
A: Blood flow from the right heart to the lungs and back to the left heart for oxygenation.
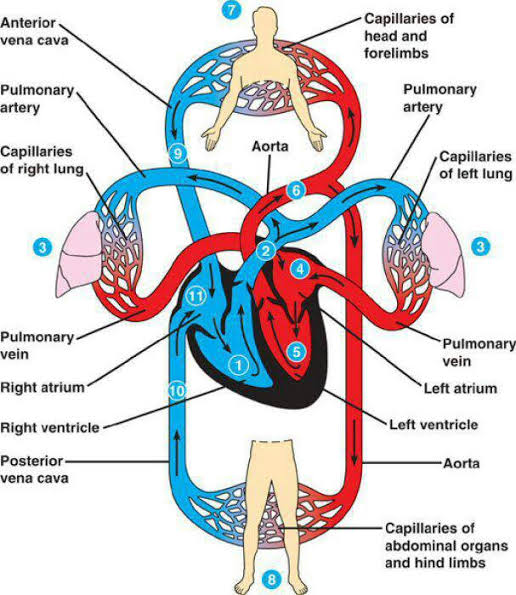
Q: What is systemic circulation?
A: Blood flow from the left heart to body tissues and back to the right heart.
Q: What is the hepatic portal system?
A: A route that carries blood from the intestines to the liver.
Q: What is coronary circulation?
A: The heart’s own blood supply.
Q: What is systolic pressure?
A: Maximum pressure during ventricular contraction.
Q: What is diastolic pressure?
A: Minimum pressure during ventricular relaxation.
Q: What is normal adult blood pressure?
A: About 120/80 mmHg.
Q: What factors affect blood pressure?
A: Cardiac output, blood volume, and vessel
Q: How does the body maintain cardiovascular homeostasis?
A: Through negative feedback loops that stabilize blood pressure and heart rate.
Q: What do baroreceptors detect?
A: Changes in blood pressure.
Q: What do chemoreceptors monitor?
A: Oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
Q: How does the autonomic nervous system regulate the heart?
A: Adjusts heart rate and vessel diameter based on body needs.
Q: What does sympathetic stimulation do?
A: Increases heart rate and contractility (fight-or-flight).
Q: What does parasympathetic stimulation do?
A: Decreases heart rate (rest-and-digest).
Q: Which hormones increase heart rate?
A: Epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Q: What other factors can affect heart rate?
A: Temperature and electrolyte balance.
Q: How does heart rate change during exercise?
A: It can increase from about 70 to over 180 beats per minute.
Q: What happens to stroke volume during exercise?
A: It increases due to stronger contractions.
Q: How does regular exercise improve cardiovascular health?
A: Strengthens the heart and improves circulation efficiency.
Q: What is hypertension?
A: Chronic high blood pressure that disrupts homeostasis.
Q: What is atherosclerosis?
A: Plaque buildup that narrows and stiffens blood vessels.
Q: What is heart failure?
A: The heart’s reduced ability to pump blood effectively.
Q: What are arrhythmias?
A: Irregular heartbeats that disrupt normal blood flow.
Q: How do lifestyle choices affect cardiovascular health?
A: Diet, exercise, and stress management help maintain homeostasis.
Q: What other factors can affect heart rate?