ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIA | 6.1
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Electrolytes
substances that, when dissolved in a solvent (usually water), produce
ions that can conduct electric current.
Non-electrolytes
substances or solutes whose solutions contain molecules and thus do not conduct electricity.
strong electrolytes and weak
electrolytes.
Electrolytes can be classified into two main categories:
Strong electrolytes (e.g., strong acids and bases)
completely dissociate in water,
weak electrolytes (e.g., weak acids and bases)
do not completely dissociate in water.
two arrows
pointing in different directions indicate reversibility of the reaction
and the incompleteness of the dissociation.
Siemens per meter
(S/m) or Siemens per centimeter (S/cm)
Conductivity is a measure of how well solutions allow the flow of
electrical charges or ions through it. It is expressed in units of .
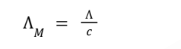
molar condctivity
where Λ
conductivity of the weak acid
c
concentration of the weak
acid in molarity.
fraction dissociation (α)
measure of the degree
to which the acid or base dissociates or ionizes in an aqueous solution.
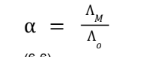
fraction dissociation (α) formula
Λo
limiting conductivity or the molar conductivity when the solution is
diluted infinitely.
Limiting conductivity
refers to the conductivity of an electrolyte when
it is completely dissociated into ions at an infinitely low concentration or dilution.