Grade 10 Chemistry
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Periodic Table
Table listing all known elements. The elements are grouped according to their properties and in order of the number of protons in their nucleus.
Periods
Subdivisions of geological time. Periods are the rows of the periodic table.
Groups
Columns of the periodic table containing elements with similar properties.
Periodic Law
Statement made by Mendeleev that the elements with similar properties occur at regular intervals when all elements are listed in order of atomic mass.
Symbols
One (or two) letter code(s) used for elements, often as an abbreviation of their name.
Atomic Numbers
Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The atomic number determines which element an atom is.
Relative Atomic Mass
A number that compares the mass of atoms to an agreed mass; such as 112 of the mass of a carbon-12 isotope.
Mass Number
Number or protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
Alkali Metals
Very reactive metals in group 1 of the periodic table.
Alkaline Earth Metals
Reactive metals in group 2 of the periodic table.
Halogens
Non-metal elements in group 17 of the periodic table.
Noble Gases
Elements in the last column of the periodic table. They are extremely inert.
Transition Metal Block
Block of metallic elements in the middle of the periodic table. (Staircase)
Metals
Elements that conduct heat and electricity; shiny solids which can be made into thin wires and sheets that bend easily. Mercury is the only liquid metal. (Left hand side). Metals lose electrons.
Non-Metals
Elements that do not conduct electricity or heat; they melt and turn into gases easily, and are brittle and often coloured. (upper right hand side). Non-metals gain or share electrons.
Metalloids
Elements that have the appearance of metals but not all the other properties of metals.
Molecules
Particles with two or more atoms joined (bonded) together.
Bohr Diagram
Diagram showing electrons in their shells around the nucleus of an atom.
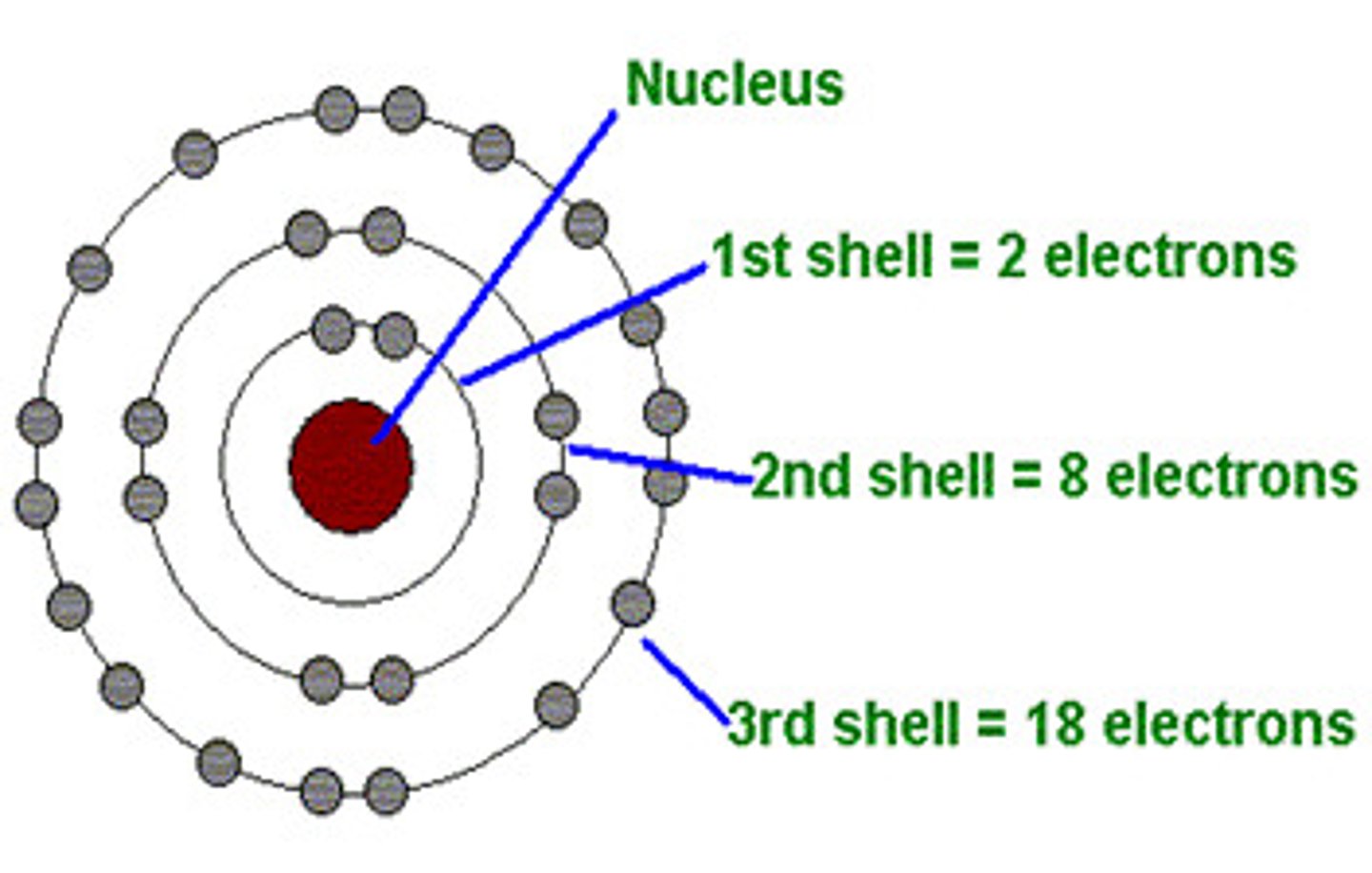
Shells
Energy levels surrounding the nucleus of an atom into which electrons are arranged.
Electron Configuration
An ordered list of the number of electrons in each electron shell, from inner (low energy) to outer (high energy) shells.
Neutral
Having equal amounts of negative and positive electric charge and, therefore, no overall electric charge. Atoms are neutral whereas ions have either a positive or negative electric charge.
Ions
Atoms or groups of atoms that have lost or gained electrons.
Cations
Atoms or groups of atoms that have lost electrons and are positively charged.
Anions
Atoms or groups of atoms that have gained electrons and are negatively charged.
Ionic Compounds
Compounds containing positive and negative ions held together by the electrostatic force.
Ionic Bond
Attractive force between ions with opposite electrical charge.
Aqueous Solutions
Solutions of ionic compounds in which water is the solvent.
Covalent Compounds (Also Known As Molecular Compounds)
Compounds in which the atoms are held together by covalent bonds.
Lewis Dot Structures
Diagrams using dots to represent the electrons in the outer shell of atoms and to show the bonds between atoms in molecules.
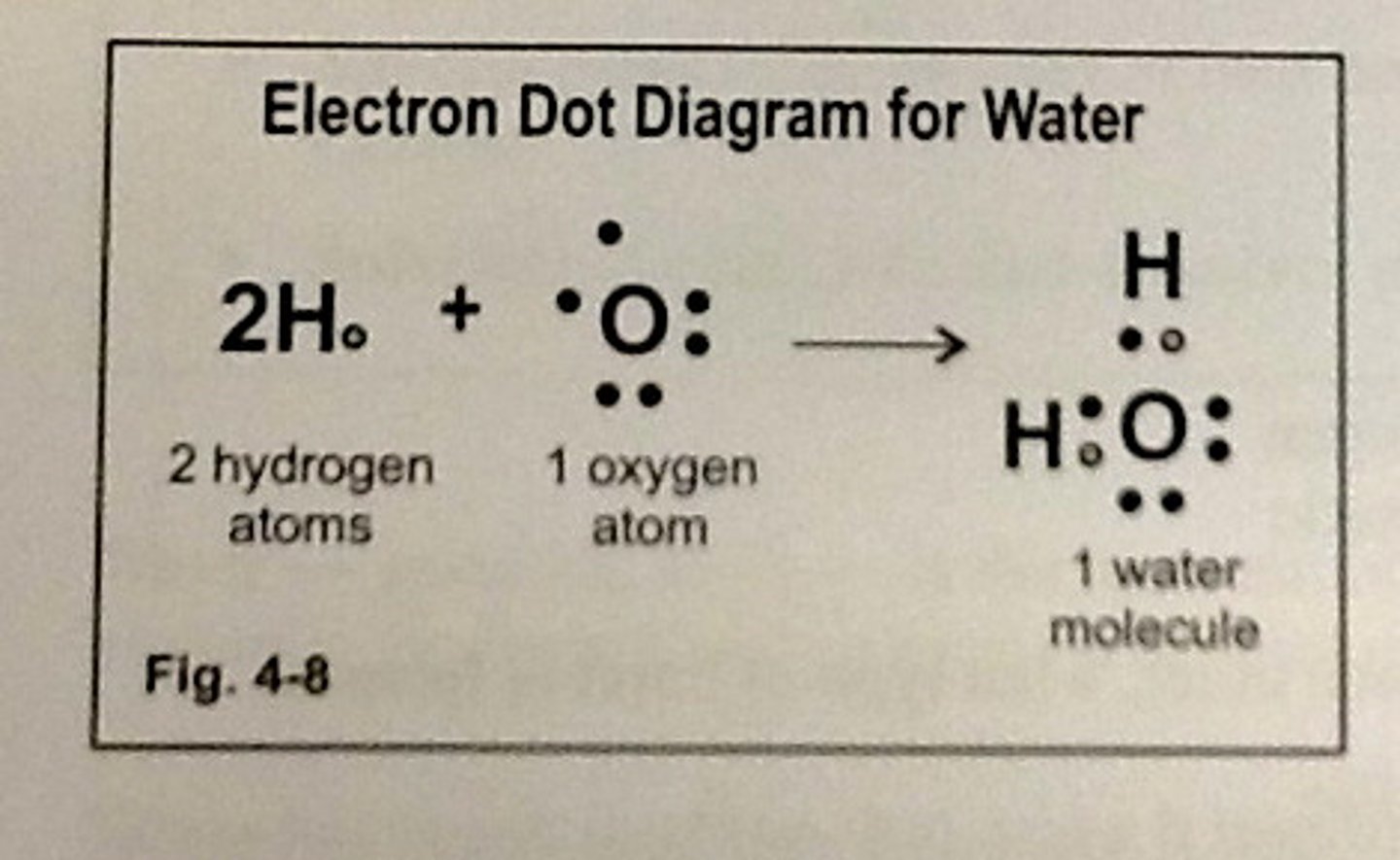
Bonding Electrons
Shared electrons holding two atoms together.
Structural Formula
Diagram showing the arrangement of atoms in a substance with covalent bonds drawn as dashes.
Chemical Formula
Shorthand statement of the elements in a substance showing the relative number of atoms of each kind of element.
Molecular Formula
Shorthand statment of the elements in a molecule showing the relative number of atoms of each kind of element.
Valency
Equal to the number of electrons that each atom needs to gain, lose or share to fill its outer shell.
Electronegativity (not in Sci 10)
a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons.
Matter
The substance of substances of which any physical object consists or is composed.
Element
A substance of atoms which all have the same number of protons. (Same atomic number)
Compound
A substance formed when two or more chemical elements are chemically bonded together.
Chemical Change
Occurs when a substance combines with another to form a new substance.
Physical Change
Change that does not involve changing the substance's chemical identity. e.g. changing between solid, liquid and gas
Atom
The smallest particle of a chemical element that can exist.
Molecule
A group of atoms bonded together, representing the smallest fundamental unit of a chemical compound.
Proton
A stable subatomic particle occurring in all atomic nuclei, with a positive electric charge equal in magnitude to that of an electron.
Neutron
Subatomic particle of about the same mass as a proton but without an electric charge, present in all atomic nuclei except those of ordinary hydrogen.
Electron
A stable sub-atomic particle with a charge of negative electricity, found in all atoms and acting as the primary carrier of electricity in solids.
Nucleus
The positively charged central core of an atom, consisting of protons and neutrons and containing nearly all of its mass.
Isotope
each of two or more form of the same element that contain equal numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
Reactant
A substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction.
Product
The compound(s) that are formed when a reaction is completed.
Hydrogen Bond
is an attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative atom, often oxygen or nitrogen
intermolecular forces
forces of attraction between molecules
intramolecular forces
bonding forces that hold the atoms of a molecule together
adhesive forces
intermolecular forces that bind a substance to a surface
cohesive forces
intermolecular forces that bind similar molecules to one another
Covalent bonds
Bonds created by sharing electrons with other atoms.
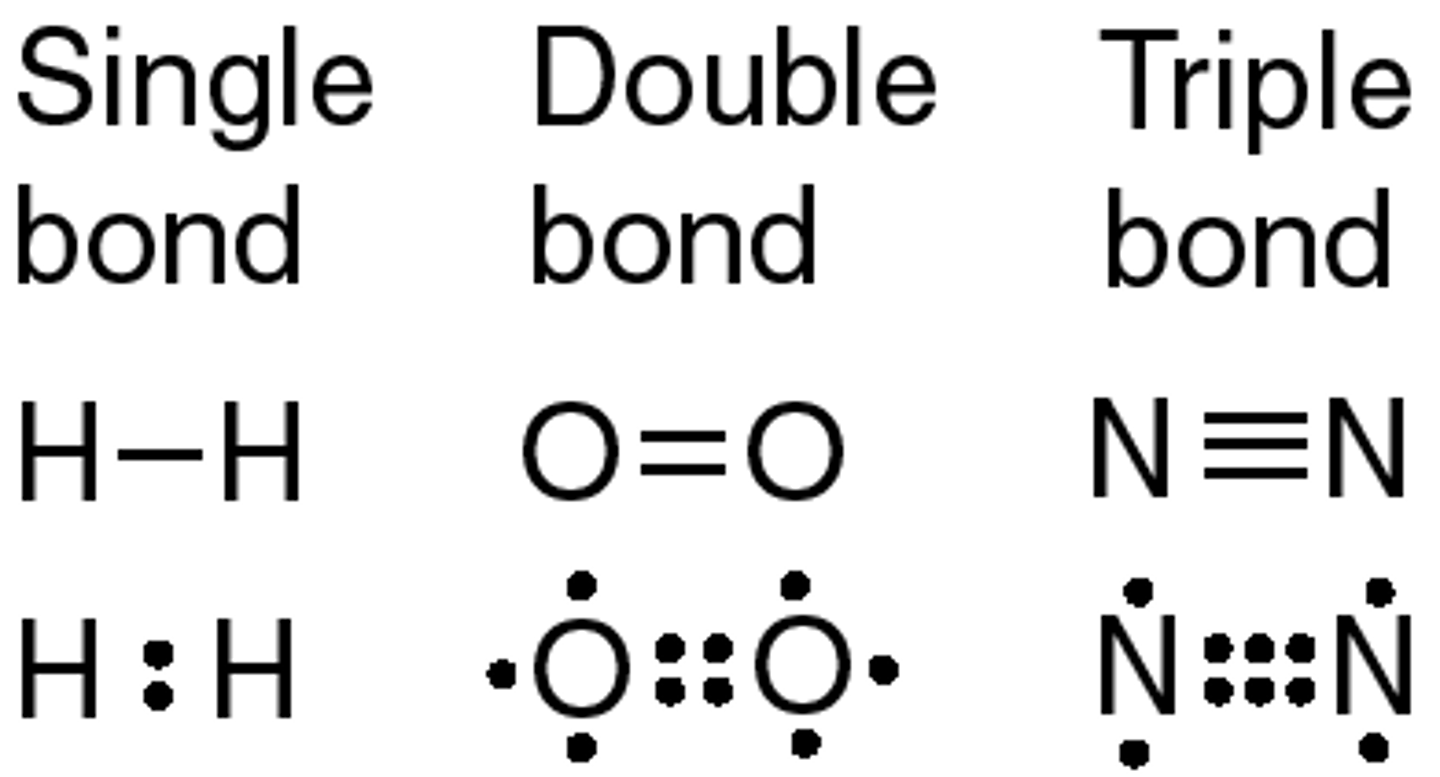
Niels Bohr
1913- discovered that electrons move around the nucleus in orbits called electron shells.
Ernest Rutherford
1909-solar system model of the atom, gold foil experiment- fired negative ions at thin sheet of gold foil, discovered the atomic nucleus and proposed a nuclear model of the atom .
J. J. Thomson
Discovered electrons and suggested Plum pudding model showing atoms composed of electrons
John Dalton
English chemist and physicist who formulated atomic theory that atoms are indivisible and distinct for each element.
Schrodinger (not in Sci 10)
studied energy of electrons and helped develop electron cloud model (orbitals)