Zoology Exam 2
1/146
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Zoology Pennwest Edinboro: Exam 2- Good Luck!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
Phylum Chaetognatha
-arrow worms
-132 spp.
-marine predators 1-12 cm. planktonic
-teeth and 4-14 pairs of curved spines
-tripartite coelom
-simultaneous hermaphodites via spermatophores to partners neck or self fertilization
-eggs planktonic and direct development
Phylum Rotifera
-wheel bearers
-2467 spp.
-mostly freshwater, some marine, and some parasitic
-interstitial and floating spp. some colonial
-ciliated corona and grinding mastax
-1-4 sticky toes
-syncytial epidermis with 900-1000 nuclei
-complete digestive tract and pair of protonephridia
-dioecious but many parthenogenic spp. (95% teste 5% integumentary) amitotic vs mictic eggs
mictic eggs
halpoid. produce M or F
amitctic eggs
diploid. produce F
Phylum Acanthocephala
-1330 spp.
-parasites of vertebrate intestines
-retractible hooked proboscis
-two hydrostatic lemnisci→everts proboscis
-no digestive tract & syncytial integument
-pseudocoloem
-dioecious copulators: acanthor larva shed in feces
Phylum Mesozoa
-mesozoans
-147 spp.
-PARASITES: cephalopod nephridia and various marine inverts
-20-30 outer somatic cells, inner reproductive cells
-no digestive tract
-asexual and sexual reproduction with larval stages
Phylum Entoprocta
-entoprocts/goblet worms
-171 spp.
-stalked sessile animals(solitary or colonial)
-mostly marine→2 freshwater spp.
-mouth and anus of u shaped gut both inside lophophore of ciliated tentacles. pair of protonephridia
-pseudocoloem
-solitary spp.→monoecious colonial spp.→dioecious trochophore larva

Phylum Ectoprocta
-bryozoans/moss animals
-5458 spp.
-stalked or encrusting sessile animals
-mostly marine some freshwater spp.
-almost all colonial, with zooids in secreted zoecia
-lophophore withdraws into zoecium. anus outside of lophophore
-nephridia excretes coelomocytes full of wastes
-mostly monoecious→asexual statoblasts
-fertilization internal or external→many brood in ovicells
-

zooids
lives within a box-shaped compartment
zoecia
house that the animal secretes (calcareous, chitinous, or gelatinous)
Phylum Brachiopoda
-lamp shells
-406 spp.
-solitary marine sessile animals
-much better represented among fossils
-bivalve shell (ventral and dorsal)
-some have fleshy pedicel (anchor)
-two armed lophophore
-3 part enterocoelic coelom
-open circulatory system
-moslty dioecious with external fertilization

Phylum Phoronida
-phoronoids
-19 spp.
-marine worms up to 30 cm
-secreted chitin lines burrow
-lophophore is curved and ridged. anus outside of lophophore
-3 part partitioned true coelom (enterocoely)
-circulatory system largely closed. 2 nephridia
-monoecious or dioecious. some via fragmentation mostly externally fertilized, but some internal via lophophoral spermatophores with brooding on female lophophore
-ciliated hooked actinotroch larva

Phylum Nemertea
-ribbon worms
-1385 spp.
-mostly marine worms
-hydrostatic rhynchocoel houses proboscis→neurotoxins delivered via stylet
-complete digestive system, nerve cords with transverse nerves, closed circulatory system→not heart vessels contract
-several protonephridia
-asexual fragmentation, moistly dioecious external fertilizers, some hermaphrodites

Lineus longissimus
bootlace worm, Northern European coasts, up to 55m in length and up to 10 mm in width

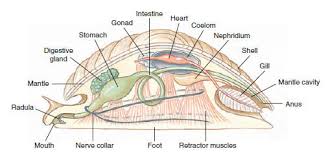
Phylum Mollusca
-87,409 spp.
hypothetical molluscan ancestor:
-hypodermis mantle with mantle cavity housing gills
-hydrostatic foot
-scraping radula
-small true coelom surrounds heart of open circulatory system
-simple nerve cords, few ganglia→circusesophageal
-ciliated trochophore and shelled veliger larvae
Classes Caudofoveata and Solenogastres
-marine elongate worms
-no shell but some fossil spp. had shells
-formerly united in class Aplacophora (no shell)
-scales and calcareous spicules in skin
-most have radula (lost in solenogastres)
-foot is lost in caudofoveates, a vestige in solenogastres
-reduced posterior mantle cavity
-pair of gills in caudofoveates, none in solenogastres
caudofoveates dioecious, solenogastres monoecious
Class Polyplacophora
-chitons
-marine; elongate foot with mantle cavity and gills to either side
-8 piece (rarely 7) shells
-scraping radula
-trochophore metamorphoses into adult

Class Monoplacophora
-monoplacophorans
-marine “living fossils”
-single shell
-broad, hydrostatic foot
-serially repeated gills, gonads, heart Ostia, nephridia, and transverse nerves
-true metamerism or pseudometamerism

Class Gastropoda
-snails, slugs, conchs, whelks, abalones…
->70% of the phylum
-marine freshwater and terrestrial
-single valve shell in most, often coiled
-torsion in larval development
-radula usually present
-gills in some, lungs in others
-monoecious (terrestrial) or dioecious
-copulate or transfer spermatophores
-eggs float, or in masses or capsules
-trochophore & veliger larvae

Class Cephalopoda
-squids, cuttlefishes, octopi, and chambered nautili
-foot→head and tentacles
-shells buoyant in nautili, internal in squids (squidpen) and cuttlefishes (cuttlebone), lost in octopi
-swim by ejecting water from the mantle cavity
-closed circulatory system with 3 hearts
-camera eyes
-radula and keratinized beak
-spermatophores transfer via hectocotyl

Class Bivalva
-freshwater and marine
-2 shells joined at dorsal hinge: adductor muscles close shell
-mostly filter feeders fed by ciliary gill currents via incurrent and excurrent siphons
-no radula
-most move slowly via hydrostatic foot (oysters:sessile) (scallops:swim via adductors)
-trochophore and veliger larva
-parasitic glochidium larva in freshwater mussels

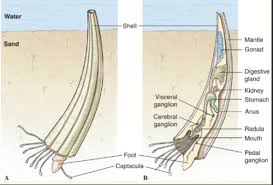
Class Scaphopoda
-Tusk shells
-marine burrowers up to 25cm
-curved tubular shell opens above and below
-mantle cavity’s respiratory current drawn in and out of top hole by cilia and muscular movements
-lower openings captacula (foot and tentacles) for feeding in sediments and respiration
-radula present
Phylum Cycliophora
-first sp. described in 1995 (2 spp.)
-symbionts on lobster oral appendages
-acoelomate
-ring of oral cilia and u shaped digestive tract
-asexual budding
-sexual dioecious larvae
-disperse as lobster molts

Phylum Annelida
-16,349 spp.
-metamerism (repeated segments (metameres))
-septa confine hydrostatic movements (internal partitions between segments)
-circular and longitudinal muscles
-most have setae→used for traction or anchoring
-terminal mouth and anus
-schizocoelous euecoelom (solid mass of mesoderm splits to make coelom)
-closed circulatory system
-dorsal vessel: anterior flow (vein)
-ventral vessel: posterior flow (artery)
-ventral nerve cord, dorsal anterior brain
-trochophore larvae in marine spp.

Annelid Phylogeny
polychaete- many setae; marine
oligiochaete- few setae; freshwater + terrestrial leeches
Class Errantia
-motile polychaetes
-marine crawlers (tubeless)
-fleshy parapodia→legs hydrostatic
-highly developed eyes and statocysts on head
-bundles of setae on parapodia
-saws
-moslty dioecious spawners

Palolo Worm of American Samoa
-Epitoke: seasonal gamete producing segments
-break free of atoke segments for spawning
-only for a few hours a year in the fall after midnight
-eaten raw, fried in oil, baked in bread, or on pizza

Class Sedentaria
-tube dwelling polychaetes, oligiochaetes, and leeches
-marine-tube dwellers; terrestrial and freshwater spp.
-few setae in pairs, or none
-simultaneous hermaphrodites
-clitellum: swollen band involved in reproduction
-mucus for sperm transfer
-chitinous cocoon around eggs
-direct development→leeches and earthworms

Leeches
-mostly freshwater
-flattened with narrow metaverse, generally aseptate and lacking setae
-few anterior septa and setae in one group
-predators or blood sucking parasites
-3 jaws
-2 suckers; posterior and anterior
-salivary anticoagulant
-simultaneous hermaphrodites
-direct development in egg cocoons

Former Phyla relegated to Sedentaria
-Phylum Echiura
-Phylum Pogonophora
-Phylum Sipuncula
P. Echiura
-spoon worms (173 spp.)
-feed using ciliated proboscis
-trochophore larvae (ciliated top)
-males inhabit uterus of female in one sp.

P. Pogonophora
-beard worms (207 spp.)
-absorb nutrients through skin and live off bacteria mutualists

P. Sipuncula
-marine burrowers (205 spp.)
-anterior introvert
-u shaped coiled gut with anus on side
-hydrostatic schizocoelous eucoelom
-ventral nerve cord
-two nephridia
-asexual fission and regeneration
-dioecious with external fertilization (1 sp. monoecious)
-most have trochophore larva (some direct development and some have pelagosphera larva)

Phylum Nematoda
-roundworms
-20,024 spp
-free living marine, freshwater, and terrestrial spp; plant & animal parasites
-collagen in cuticle antagonistic to longitudinal muscles
-pseudocoelom
-complete digestive tract
-eutely -set # of cells when adult
-nerve ring anteriorly and dorsal and ventral nerve cords
-dioecious; male has copulatory spicules to aid in keeping female opening open
-oviparous, direct development (4 molts of the cuticle)

Phylum Nematomorpha
-horsehair worm
-356 spp.
-aquatic adults
-juveniles parasitize hemocoels of arthropods
-insects, spiders, pillbugs, hermit crabs
-some have second invert host
-induce water finding behavior when ready to emerge
-cuticle, pseudocoelom, and longitudinal muscles
-vestigal digestive tract
-absorb nutrients, even as adults
-ventral nerve cord
-no organs for gas exchange, circulation, or excretion
-dioecious
-internal fertilization and oviparity
-nematomorph larva penetrates new host
Phylum Loricifera
-”corselet bearer’
-46 spp.
-marine interstitial animals (<400 μm)
-plated lorica into which the head retracts (corselet)
-scalids: spines on head (setae-like)
-psuedocoelom
-2 protonephridia
-dioecious, internal fertilization
-higgins larva has adhesive toes (some spp. the larva is parthenogenic)

Phylum Kinoryncha
-kinorynchs or mud dragons
-346 spp.
-marine interstitial
-13 zones: retractible proboscis, neck, and 11 body zones with scalds→(like setae)
-anchors and chemo-/mechanoreceptive sense organs
-chitinous cuticle, reduced eucoelom, and longitudinal muscles
-crawl using introvert
-brain and ventral nerve cord
-2 protonephridia
-dioecious
-internal fertilization
-oviparous egg cases
-11 segmented juvenile molts 6 times, adding 2 zonites

Phylum Priapulida
-penis worms
-22 spp.
-marine burrowers
-retractible introvert
-terminal anus
-hollow caudal appendages may be respiratory or chemosensory
-ventral nerve cord
-protonephridia
-dioecious with external fertilization
-larvae have lorical coverings (similar to adult loriciferans)

Phylum Onychophora
-velvet worms
-235 spp.
-terrestrial tropical animals
-metameric and hydrostatic (13-43 pairs of hydrostatic lobopods with chitinous claws)
-antennae with eyes at bases
-slime glands of oral papillae capture prey
-open circulatory system
-coxal glands release urine at base of lobopods
-dioecious with spermatophores deposited on females back→sperm bore through skin
-placentally or aplcentally viviparous or oviparous
-direct development

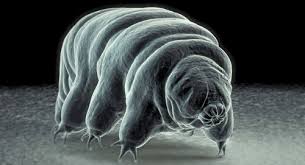
Phylum Tardigrada
-water bears or moss piglets
-1461 spp.
-microscopic animals that live in water film on mosses and lichens
-four pairs of legs
-piercing pair of stylets and sucking pharynx
-ventral nerve cord, dorsal brain (circumesophageal)
-eucoelom and dioecious
-3 excretory malphigian tubules open to gut
-copulate or external fertilization of eggs in shed cuticle of female→some spp. parthenogenic
-directb development
-cryptobiosis: dehydrated state for up to 10 years (tun)
Phylum Arthropoda
-1,177,044 spp.
-tagmata:
head-thorax-abdomen
cephalothorax-abdomen
head-trunk
-cuticle made of chitin which is thinner at joints
-appendage specialization
-almost all dioecious
-copulation or spermatophore transfer in almost all
Arthropod Internal Anatomy
-Dorsal brain, ventral nerve cord with segmented ganglia
-reduced eucoelom
-gills in aquatic spp.
-tracheal system and spiracles in terrestrial spp. or book lungs
-open circulatory system→heart with pairs of ostia
-coxal glands and/or malphigian tubules
-ommatidium make up a compound eye→1 inner cell with 6 outer cells
-84% of animal kingdom
Class Merostomata
-horseshoe crabs (4 marine spp.)
-chelate appendages
-chelicerae
-pedipalps
-4 pairs of legs
-Abdomen: genital opercula and 5 pairs of book gills
-Telson for uprighting
-coxal glands→last pair of legs
-beach spawners with egg capsules

Class Pycnogonida
-sea spiders
-1394 marine spp.
-elongate proboscis, chelicerae, pedipalps, 4 pairs of legs
-exdternal fertilization
-males in some spp. brood on ovigers
-protonymphon larva (3 pairs of appendages)

Class Arachnida
-spiders, scorpions, psuedoscorpions, daddy longlegs,ticks, mites, etc
-95,851 spp.
-chelicerae→fangs in spiders
-pedipalps→spermatophore transfer in males and pincers in scorpions and pseudoscorpions
-4 pairs of legs
-pedicel: cephalothorax/abdomen constriction in spiders→absent in daddy longlegs
-capitulum: projecting head of ticks and mites

Arachnid Silk
-spiders mostly, but also pseudoscorpions and mites & insects & miyriapods
-abdominal glands open via spinnerets
-strong elastic protein
-webs, prey wrapping, draglines, sperm webs, egg cases, and balloons
Subphylum Myriapoda
-tagmata= head + trunk
-loss of compound eye
Class Chilopoda
-centipedes
-3145 spp.
-mandibles & 2 pair maxillae
-venemous maxillipeds with fangs→1st section of trunk
-15-170 pairs of legs (30-340 legs)
-active predators
-spermatophore transfer & some brood
-hatchlings typically have reduced number of legs

Class Diplopoda
-millipedes
-13,179 spp.
-mandibles and 1 pair maxillae
-up to 100 diplosegments have 2 pairs of legs, 2 pairs heart ostia, 2 ventral ganglia, 2 pairs of spiracles (1st segment is not diplosegment)
-herbivores and scavengers
-copulate with gonopods (modified legs) (males in 7th segment) and brood
-hatchlings have 3 pairs of legs

Class Paurapoda
-paurapods (sister to Diplopoda)
-995 spp.
-<1.5 mm
-most have no heart or tracheal system
-scavengers, biramous antennae, mandibles & 1 pair of maxillae
-9-11 pairs of legs on double segments
-spermatophores
-hatchlings have 3 pairs of legs adding legs with each molt

Class Symphyla
-symphylans or garden centipedes (sister to Chilopoda)
-231 spp.
-pigmentless, eyeless, herbivores and detritus feeders
-<8mm
-mandibles and 2 pairs of maxillae
-10-12 pairs of legs on 15-24 segments
-spiracles on head only
-spermatophores, but external fertilization like hotshot crabs & sea spiders
-hatchlings have 6 pairs of legs adding with each molt

Subphylum Crustacea
-biramous 2nd antennae
-2 pairs maxillae
-naupilus larva
-2nd pair of antennae
Class Ostracoda
-ostracods or seed shrimp
-7581 spp.
-bivalve carapace (chitin or CaO4)
-among dominant zooplankton, freshwater and marine and also nocturnal characteristics

Class Branchiura
-fish lice
-32 spp.
-fish ectoparasites
-2nd maxillae modified as suction cups
-4 pairs thoracic appendages

Class Pentastomida
-tongue worms
-6 spp.
-formerly Phylum Pentastomida
-lung parasites of amniote vertebrates
-fish or small mammal intermediate host
-unsegmented

Class Branchiopoda
-fairy, brine, tadpole, clam shrimp; water fleas
-1680 spp.
-legs double as respiratory surfaces
-often have a carapace
-among dominant zooplankton, freshwater and marine
-median eye in water fleas

Class Copepoda
-copepods “oar foot”
-15,068 spp.
-among dominant zooplankton, freshwater and marine
about ½ are ecto- or endoparasites of fish, inverts, or marine animals
-median eye
-tapered abdomen
Class Thecostraca
-barnacles
-472 spp.
-calcareous plates surround sessile adults with bivalve carapaces
-some parasitic
-antennae→cement glands
-6 pairs of biramous cirri with setae
-simultaneous hermaphrodites

Class Malacostraca
-shrimp, crayfish, lobsters, crabs, krill, scuds, pillbug
-43,466 spp.
-marine, freshwater, and terrestrial
-cephalothorax and abdomen
-typically 8 thoracic segments, 6 abdominal segments
-chelae: pincers of crabs, crayfish & lobsters
-crabs: abdomen reduced and folded under

Subphylum Hexapoda
-tagmata= head, thorax, abdomen
-6 legs
-unique tracheal system
Class Entognatha
-entognaths
-10,380 spp.
-coneheads, springtails, and bristletails
-<10mm, most <5mm
-mandibles and 2 pair of maxillae extend from gnathal pouch
-antennae have musculature in every segment
-wingless (not lost, though)
-many are eyeless
Class Insecta
-insects
-983,560 spp.
-mostly terrestrial and aquatic, few marine
-3 pairs ectognathous mouthparts
mandible
maxillae
unpaired labrum
-labium (fused 2nd maxillae)
-antennal musculature only in 2 basal segments
-most have 2 pairs of wings (2nd and 3rd thoracic segment)
-meso and metathoracic
-cuticular outgrowths

Insect Metamorphosis
-direct development in primitive wingless spp.
-winged insects: larvae with instars→divided between 2 successive molts
-hemimetabalous or incomplete metamorphosis→nymph or naiad instars gradually develop wings
-holometabolous or complete metamorphosis→larvae>pupa>adult
Deuterostomia 1 & Bilatera
-complete digestive system
-anus first
-true body cavity→eucoelomate→enterocoely:pocket of gut breaks away→mesoderm
Deuterostome Phylogeny
echiniodermata
hemichordata
chordata
Phylum Echinodermata
-echinoderms
-11,735 spp
-strictly marine
-5 part symmetry as adults (pentaradial symmetry)
-water vascular system of podia (tube feet) along ambulacral grooves
madreporite, ring canal, lateral canals
primitively: passing food to mouth
derived: locomotion
-ossicles (tiny bone)
-pedicellariae: microscopic pinchers (sea star and sea urchins)
-simple nerve ring and poorly developed sense organs
-mostly dioecious, typically with external broadcasting of gametes
-larvae bilateral with tripartite coelom

Class Crinoidea
-sea lillies and feather stars
-sessile with stalk (sea lillies) & holdfast at bottom
or
-sedentary swimmer perched on cirri (feather stars)
-five branching arms with upward facing ambulacral grooves for filter feeding
-U shaped digestive tract
-No spines or pedicellariae

Class Asteroidea
-sea stars and sea daisies
-5 or more arms
-numerous small ossicles and spines
-numerous pedicellariae- lobster claw-like for protection against settling larvae
-mouth ventral, anus dorsal
-paired podia in ambulacral groove→ primarily for locomotion but may also assist in feeding with eversible forward part of stomach
-autotomy and regeneration of arms (replicate into 2 organisms if split in half)
-bipinnaria larva becomes brachiolaria with ciliated arms

Sea Daisies
-3 spp.
-no arms; podia at margin
-2 concentric ring canals in WVS
-originally classified in new class, Concentricycloidea in 1996 but nested phylogenetically with Asteroidea

Class Ophiuroidea
-brittle stars and basket stars
-5 elongate arms with spaces in between at central disk→highly branched in basket stars
-podia used in filter feeding
-locomotion via rapid whip-like arm motions→slower in branched baskets stars
-large articulating ossicles in arms
-5 jaws make star shaped mouth
-10 bursae for gas exchange→around mouth→bursal slits
-asexual fission
-some brittle stars are monoecious

Class Echinoidea
-sea urchins, heart urchins, and sand dollars
-endoskeleton and integrated test
-aristotles lantern in sea urchins and sand dollars
-sand dollars also feed with podia of WVS
-secondary bilateral symmetry in heart urchins and sand dollars
-pedicellariae (sea urchins)
-locomotion:
sea urchins: spines and podia→soft & flexible (spines swivel at base)
heart urchins: spines only
sand dollars: spines only

Class Holothuroidea
-sea cucumbers
-elongate echinoderms that lay on their sides
-very reduced ossicles in leathery skin
-tentacles surrounding the mouth are modified podia of WVS
-locomotion via 3 well-developed rows of tube feet (other 2 are vestigial)
-respiratory trees internally for gas exchange (ass breathers)
-self defense via discharge of toxic cuverian tubules, digestive tract, and/or gonads

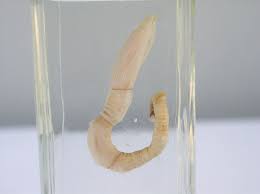
Phylum Hemichordata
-acorn worms
-139 spp.
-marine worms and sessile colonies
-to 2.5m; mostly «1m
-deposit feeders with ciliated proboscis
-in mouth out gill slits
-food ensnared in mucus
-respiration mainly at gill slits
-collar opens to expose mouth
-tripartite coelom
-ventral and dorsal hollow nerve cord
-mostly dioecious
-tarnaria larva also tripartite
Pterobranch Hemichordates
-26 spp.
-colonial (budding)
-only a few mm in length
-proteinaceous tubarium (collagenous tube secreted)
-proboscis→cephalic shield→extension/contraction
-ciliated feeding tentacles
-u shaped digestive tract
-lacks dorsal nerve cord
-dioecious or monoecious

Deuterostomia 2
chordates
Phylum Chordata
-73,976 spp.
-5 Hallmarks
Notochord with myomeres
Dorsal hollow nerve cord
Pharyngeal gill slits
Endostyle
Postanal tail
Subphylum Cephalochordata:Class Cephalochordata
-lancelets amphioxus
-30 marine spp.
-5 hallmarks all readily apparent
-myomeres
-hepatic cecum- unique cellular ingestion/intracellular digestion
-no real brain on dorsal nerve cord
-no heart but ventral aorta pumps blood forward
-dioecious
-external fertilization and larval stage
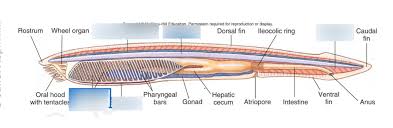
Subphylum Urochordata
-tunicates
-3131 marine spp.
-most sessile filter feeders as adults, after swimming larva→some do not metamorphose and some are not sessile
-cellulose-like tunicin in tunic
-most spp. have 5 chordate hallmarks as larvae, retaining the gill slits, end-style, and a ganglionic vestige of the nerve cord as adults; losing tail and notochord completely

Class Ascidiacea
-ascidians or sea squirts
-2985 spp.
-95% of tunicates
-solitary or colonial
-sessile with rooting stolons
-nonfeeding “tadpole” larva in most
-ciliated pharyngeal basket (buccal and atrial siphon)
-food trapped in mucus enters u shaped digestive tract
-heart reverses flow on a regular cycle
-asexual fission and budding
-moslty simultaneous hermaphrodites with external fertilization

Class Appendicularia
-larvaceans
-68 spp.
-moslty <1cm, transparent
-solitary swimmers
-neotony: retain “tadpole” larval body as adults except tail moves 90% ventrally
-adults show 5 hallmarks
-anus directly to outside
-prey as small as 1µm
-rapid replacement of the tunic can be multiple times a day
-protandrous hermaphrodites (M→F)
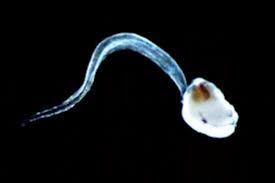
Class Thaliacea
-salps
-78 spp.
-solitary or colonial swimmers
-asexual reproduction via budding in many spp. forming long chains
-larva becomes adult that retains pharynx
-all protogynous, but 3 orders vary in reproductive mode
oviparous with larvae
aplecentally viviparous with direct development
placentally viviparous with asexual proliferation in chains

Subphylum Vertebrata
-vertebrates
-70,815 spp.
-dorsal hollow nerve cord & anterior brain
-notochord→replaced during embryology by bony discs of vertebrae in most
-pharyngeal gill slits→primarily respiration, feeding function in some, lost in terrestrial spp.
-endostyle→thyroid gland
-postanal tail with caudal vertebrae in most taxa→bony vestige in frogs, birds, large old world primates, etc
Class Myxini
-hagfishes/slime eels
-82 spp.
-marine
-no jaws, paired fins, scales, or vertebrae
-predators & scavengers
-”teeth” of keratin on tongue (snail-like radula)
-glands along sides secrete viscous slime
-5-16 pairs of gills
-light detecting eyespots
-ventral heart with atrium and ventricle leading forward to gills
-self knotting behavior
-dioecious with external fertilization

Class Petromyzontida
-lampreys
-47 spp.
-marine, freshwater, and anadromous spp.
-no jaws, paired fins, scales or vertebrae
-jawless parasites of fish or non feeding adults with vestigial digestive tracts (brook lampreys)
-7 pairs of gills
-ventral heart with atrium and ventricle leading forward to gills
-dioecious with external fertilization
-filter feeding ammocoete larva
→chemical larvicides in Great Lakes

Jawed Fishes
-jaws from gills
-bones that support jaws come from the first set & second set of gill supporting cartilage
-5 gills in jawed fishes
Placoid scales
-modified teeth
-found in sharks and cartilaginous fishes

Ganoid scales
-bony fishes

Ctenoid scales
-comb (bluegill, perch)
-teleost fishes
Cycloid scales
-teleost fishes

Heterocercal tail
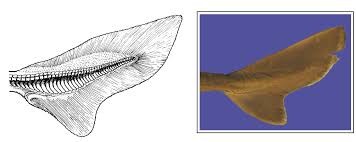
Homocercal tail

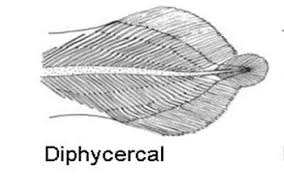
Diphycercal tail
Class Chondrichthyes
-cartilaginous fishes
-1282 spp.
-skeleton of calcified cartilage
-not primitive→derived loss of replacement by bone
-small notochord and calcified cartilaginous vertebrae
-no swim bladder→derived loss
-claspers in males by pelvic fins & cloaca
-oviparous or aplecentally or placentally viviparous
Subclass Elasmobranchii
-sharks, rays, & skates
-937 mostly marine spp.
-some freshwater/estaurine spp.(6 sharks, 1 ray, & 18 skates)
-placoid scales
-multiple gill slits (typically 5 on each side)
-heterocercal tail

Superorder Selachii
-sharks
-537 spp.
-numerous replaceable sharp teeth
-oviparous or aplecentally viviparous

Superorder Batoidea
-skates and rays
-689 spp.
-greatly enlarged pectoral fins
-bottom feeders with ventral mouths & gill slits
-skates
bilobed pelvic fin
tail: no barb, 2 distal fins
small teeth
oviparous with “mermaids purse”
-rays
unloved pelvic fins
tail: venemous barb (stingrays); no fin or single at base
large plate-like teeth
matrotrophic live bearers

Subclass Holocephali
-chimeras/ratfishes/ghost sharks
-56 marine spp.
-no scales
-3 pairs of hard grinding plates on jaws rather than teeth
-single exit from gill chamber
-most have venomous spines in dorsal fins
-diphycercal tail
-oviparous
-eggs laid in “mermaids purse”

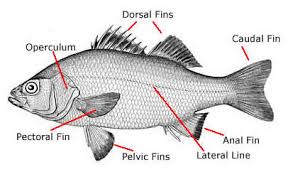
Osteichthyes
-bony fish & tetrapods
-paraphyletic former taxon
-paraphyletic because lobe finned bony fishes are closer relatives of tetrapods than they are of ray-finned fished
-cartilage-replacement bone
-bony operculum over gills (gill plate)
-swim bladder in most→buoyancy
-acts as lung in primitive spp.
Class Actinopterygii
-ray-finned fishes
-32,513 spp.
-bony rays support fins
-most with homocercal tail→basal forms heterocercal or diphycercal
-most with cycloid or ctenoid scales→basal forms ganoid
Subclass Cladistsa
-bichirs and reedfish
-14 freshwater spp.
-7-18 dorsal finlets on branched spine
-diphycercal tail
-ganoid scales
-lungs
