Pharm Exam 3 Diabetes
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Which clients are at risk for developing metabolic syndrome? SELECT ALL THAT APPLY
35 year old male with triglycerides of 140
48 year old female with fasting blood glucose of 105
55 year old female with waist size of 40 inches
28 year old male with blood pressure of 135/85
42 year old female with high density lipoprotein (HDL) level of 55
48 year old female with fasting blood glucose of 105
55 year old female with waist size of 40 inches
28 year old male with blood pressure of 135/85
What are the ranges for fasting blood glucose, non-fasting blood glucose, and HgBA1C in normal clients without DM?
Fasting- Under 100 mg/dL
Non-fasting- 70-115 mg/dL
HgBA1C- Under 6.5
What is the main purpose of the Hgb A1C?
To check for compliance of care plan
Type 1 DM- Insulin compliance
Type 2 DM- Diet & Exercise
What are the three main S/S of hyperglycemia (Over 115 blood glucose or 6.5 Hgb A1C) ? (3 P’s)
Polyuria- Increased urine
- Polydypsia- Increased drinking and thirst
Polyphagia- Excessive Eating
What are some acute causes of hyperglycemia? (4 S’s)
Sepsis (Infection is #1 Cause)
Stress (surgeries or hospital stays)
Skip Insulin
Steroids (prednisone)
What are some S/S of hypoglycemia?
H- Headache
I- Irritable
W- Weakness
A- Anxious and Trembling
S- Sweaty “Diaphoresis”
H- Hunger
Hypoglycemia is…
Most deadly, can lead to brain death
How do we treat hypoglycemia?
A-Awake
A- Ask them to eat: Juice, Crackers, Soda, Low fat milk
NOT FOODS OR DRINKS HIGH IN FAT, SLOWS DOWN SUGAR ABSORPTION
S-Sleep
S- Stab them with IV D50 (Dextrose IV)
Reassess sugar every 15 minutes
What are the main causes of hypoglycemia?
Exercise, Alcohol, and Insulin peak time
A client with type 1 diabetes is only responsive to painful stimuli with a blood sugar of 42, what is the FIRST action taken by the nurse?
Repeat the blood sugar assessment
Give dextrose IV push
Call the HCP (doctor)
Give them foods high in sugar
Give dextrose IV push
Which medication could cause hyperglycemia?
Labetalol
Albuterol
Spironolactone
Prednisone
Prednisone (Steroid)
What are some complications of diabetes?
Renal Failure (Creatinine over 1.3)
Retinopathy (blindness)
Neuropathy
HTN
Atherosclerosis
CVA “strokes”
The non diabetic client is admitted for a kidney infection that has now turned septic. The blood sugars have increased from 150 to 225, what is the best answer to give a family member who is asking why insulin is being used?
The client now has type 2 diabetes because of the infection
Insulin is given to control the hypoglycemia
High sugar is common during infection and stress to the body, the insulin will help lower the sugar until the infection resolves
You can ask the HCP (doctor)
High sugar is common during infection and stress to the body, the insulin will help lower the sugar until the infection resolves
What is the main difference between type 1 and type 2 DM?
Type 1 has NO INSULIN production, is genetic and leaves you dependent on insulin for life.
Type 2 is caused by habits you have, such as diet and exercise. Few insulin receptors are working
What are the 7 rules of insulin? (PART 1)
Peaks+Plates= Give pts food during insulin peak times. Highest chance of hypoglycemia during this time
Deadly Hypoglycemia (70 or less). Main S/S are shakey, pale, cool, sweaty and clammy
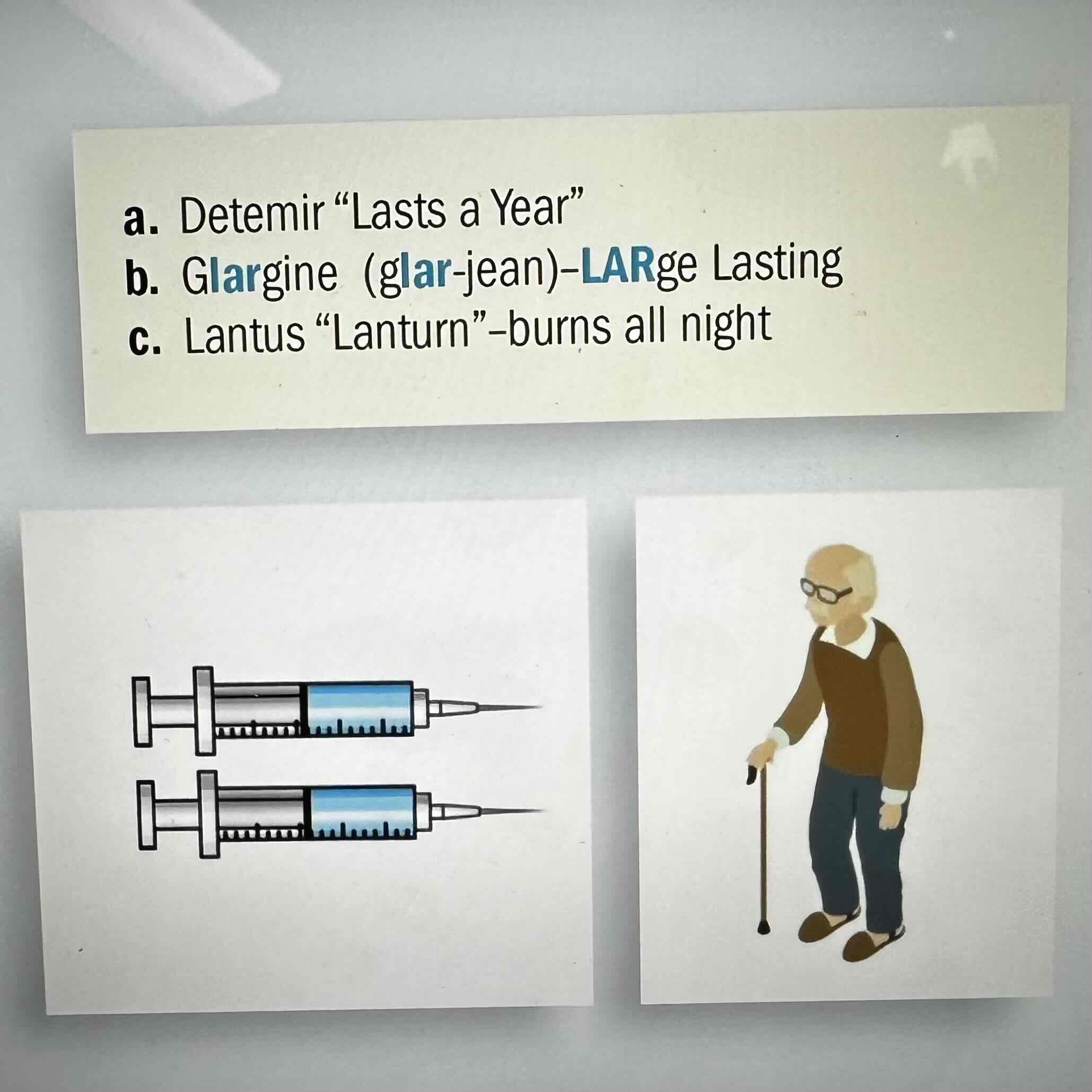
NO Peak NO mix = Long acting insulins should never be mixed and be pulled in separate syringes (Detemir, Glargine, Lantus)
What are the 7 rules of insulin? (PART 2)
IV ONLY INSULIN= Regular Insulin (R-Regular insulin, R-Right into the vein)
Draw up clear insulin before cloudy (Regular before NPH, RN)
Rotate locations every 2-3 weeks, abdomen is best site
DKA- Type 1- “sick days” (give insulin on days pts are sick and not eating, just MONITOR carefully)

Long Acting Insulin
No peak, No Mix
Detemir, Glargine
Duration is 24 Hours+
NPH Insulin (Insulin Isophane Suspension)
“Cloudy” insulin
Given 2x a day
Duration is 14+ hours
Peak is from 4-12 hours
When mixing regular and NPH, always draw out Regular first (R→N)
Regular Insulin (Humulin R)
Only IV insulin (push or bag)
Duration is 5-8 hours
Peak is 2-4 hour
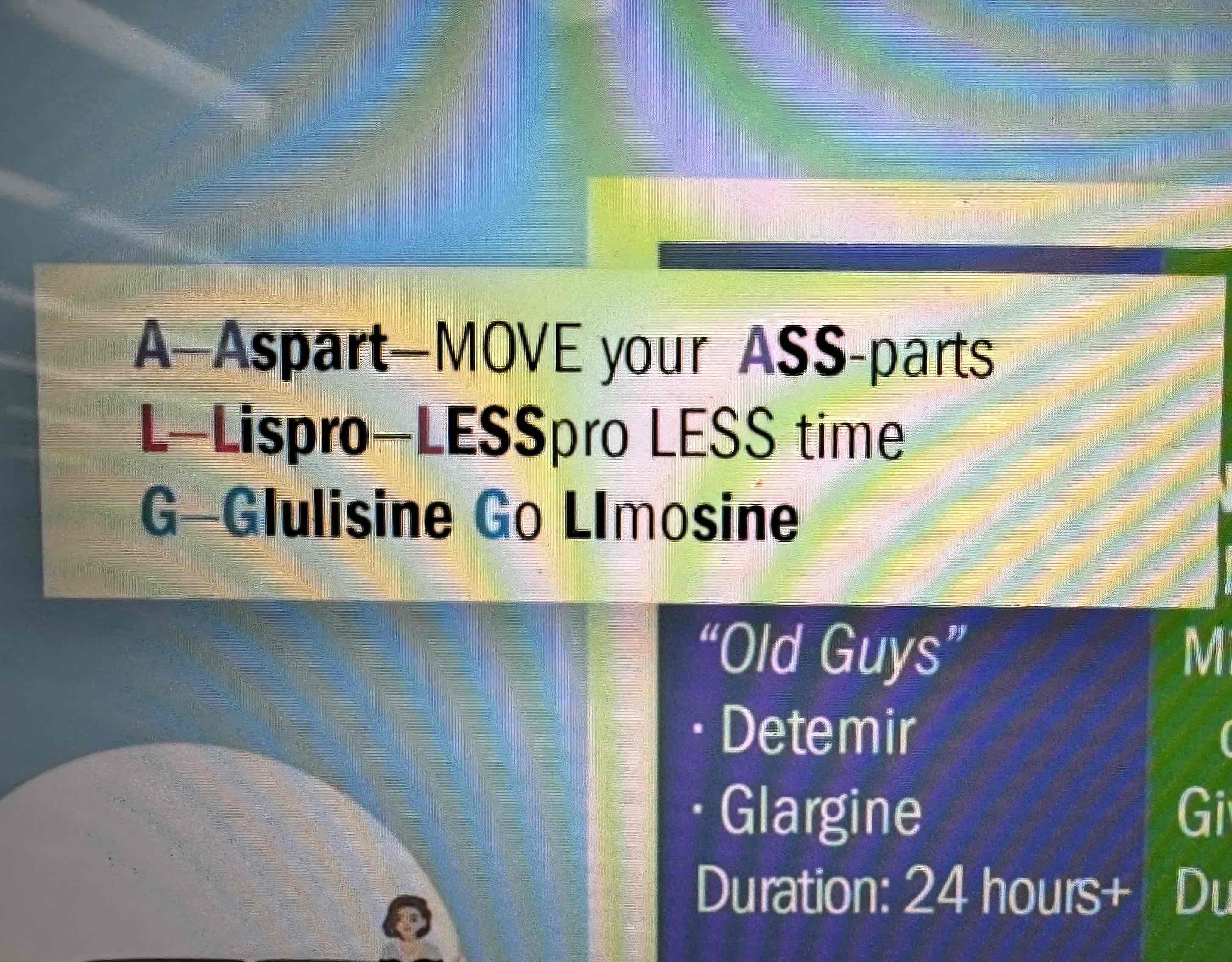
Rapid Insulin
Aspart, Lispro, Glulisine
Duration 3-5 hours
MOST DEADLY- 15 minute onset
Peak 30-90 minute
Pt must have food available to begin eating after administration
The nurse gives regular insulin at 12 pm for lunch, but the pt doesn’t finish their food. When is the greatest risk for hypoglycemia?
Greatest risk is between 2-4pm (Peak time is 2-4 hours)
A client is on aspart insulin. When should the nurse advise them to eat?
As soon as possible, between 10-15 minutes. (15 minute onset, peak time 30-90 minutes)
The client on glargine is asking the nurse when the best time to eat is during this insulin. What should the nurse respond?
Glargine is long acting with no peaks, so there is no specific time the client has to eat
The client is taking NPH insulin with dinner at 7 pm. What time is the client most at risk for hypoglycemia?
Peak is 5.5 to 6 hours after taking it, so the time they will be at greatest risk for hypoglycemia is midnight or shortly after
Oral medication for type 2 diabetes include…
Metformin (Biguanide)
Glipizide, Glimepiride, & Glyburide (Sulfonylureas)
Not for alcohol or liver failure patients
Metformin
Decreases glucose output from the liver and increases insulin sensitivity. Should not be used with liver and renal disease
Sulfonylureas
Glipizide, Glimepiride, & Glyburide
Oldest group on antidiabetic drugs, increases insulin release and decreases secretion of glucagon. Should NOT be used with insulin, are contraindicated in pts with heart problems (Hx of MI and HF)