Health Psyc Exam 2 (not complete)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Definition of Coping
thoughts and behaviors used to manage the internal (emotional) & external (materially change/address to move through) demands of stressful situations
Characteristics of Coping
Not a “one time” activity; encompassess a broad range of activities & behaviors; Some more effective than others; Impacted by both the person & their situation
Problem-focused vs Emotion-focused
problem–directly addressing cause of stress through practical solutions & actions; emotion–find other ways to manage your emotions
Definition of Resilience
the process of adapting well in the face of adversity, trauma, or stress
Characteristics of Resilience
Being resilient does not mean you do not experience difficulty, stress, and emotional pain; Not a trait, but a series of thoughts and behaviors that can be learned & adopted (Practice rather than a personality trait)
Optimism to enhance resilience
Significant predictor of physical health; associated with subjective symptom & health scores; More likely to seek out social support
Control to enhance resilience
Having purpose or meaning; Having autonomy & freedom; Being connected
Nursing Home Study
standard of care–nurse taking care of plant + choosing programs for you to attend; enhanced control–choosing programs yourself + taking care of plant yourself; enhanced control group had higher quality of life (more active, happier, healthier, more alert); 30% vs 15% death rate 6 months post-study
Emotion Regulation (Repressive Coping vs Expressive Coping)
repressive–dismissing/ignoring strong emotions; expressive–expressing strong emotions
Psychological Immune System
Strategies for reframing negative events and outcomes that help us feel better about them
Cognitive Reframing
changing your thoughts about a situation to minimize loss (its only one exam i’ll do better next time)
Benefit Finding
the process of deriving positive growth from adversity
Definition of Social Support
information from others that one is loved and cared for, esteemed and valued, and part of a network of communication and mutual obligation.
tangible/instrumental support
Financial support, material goods or services
Informational support
Sharing information or giving advice
emotional support
involves affection, love, trust, and caring; empathetic listening or physical touch
Perceived vs. Received Support
Do not always perceive what other person does as support; Perceived support more consistently associated with positive health & well-being; Two people have the same amount of meals cooked for them, but only one reports feeling supported while other doesn’t
Matching Hypothesis
social support is most effective when there is a match between what is needed & what is available from one’s social network; ex complaining about money and someone offers you money → if really desperate, that would help, but if not, then it could feel bad
Loneliness and health
very common among gen z & millennials; adults under 50 more likely than older adults to feel lonely; ages 18-29, those not living with a partner, didn’t go to college → highest loneliness
What is a meta-analysis?
analysis strategy that combines data from multiple studies; 1. Select criteria for meta-analysis; 2. Search literature to find studies that fit criteria; 3. Summarize data to estimate overall effect
Social relationships and mortality meta-analysis (Holt-Lunstad et al., 2015)
Social relationships were stronger predictors of mortality than other factors (smoking, alcohol, physical activity, weight, air pollution, flu vaccine)
Gurung definition of Culture
A dynamic, yet stable, set of goals, beliefs and attitudes shared by a group of people
Marks definition of Culture
A system of meaning and symbols. This system shapes every area of life, defines a world view that gives meaning to personal and collective experience, and frames the way people locate themselves within the world, perceive the world, and believe in it; beliefs are at the core of what we mean when we talk about culture
Four considerations for culture
- Culture can include but is not the same as ethnic/racial identity 2. A person can belong to multiple cultures, which can influence them at different moments (Cultural beliefs/values can contradict, Every cultural group has variation within them) 3. Culture is less obvious when its ours (False consensus effect
Cultural influences on health (5)
Definitions of wellness & wellbeing (western medicine says absence of disease) 2. Ideas about the origins and causes of illness (Lia lee’s soul being frightened by her sister slamming the door) 3. Priorities for treatment (keep you alive as long as possible vs don’t prolong life in misery) 4. Beliefs in the interaction between biopsychosocial factors in treatment (Geriatric doctors (old people doctors) may focus more on psychological + social factors for them to see how their quality of life is) 5. Interaction with health care systems + providers (canadians norm to not hesitate going to doctor cuz universal healthcare; america we delay to avoid paying)
Medical anthropology definition
The study of how people in the different cultures and social groups explain the causes of illness and health, the type of treatments they believe in, and to whom they turn when they become ill
Cross-cultural meanings of health
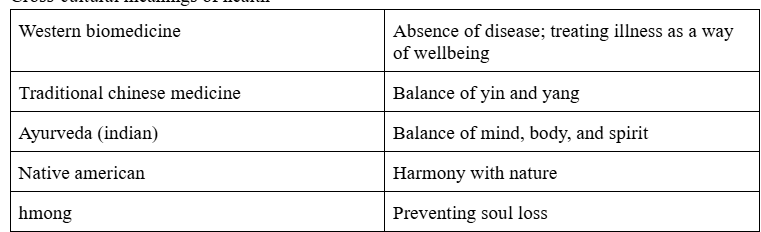
Culture of western biomedicine
objective scientific fact; focus on the body as sole source of health; hierarchical division of labor; cure + longevity prioritized over relief; positivism (observation + experimentation); underestimates role of values and beliefs
Disease vs. Illness (Kleinman, 1976)
disease–malfunctioning of biological + psycho-physiological processes; illness–experiences of disvalued changes in states of being + social function; physicians treat disease not illness
Illness Representations (Leventhal, 1984)
Patients create their own models or representations of their illness to navigate the experience of illness
Identity: name/label; connection to illness with a name “cancer survivor”
Time-line: acute, chronic, cyclical
Consequences: major/minor → do these symptoms impact my ability to live my life?
Cause: hereditary, internal, external, religion
Controllability: can it be treated/cured
Cultural competence Definition
The ability to work effectively with individuals from different cultural and ethnic backgrounds, or in settings where several cultures coexist
Kleinman’s Model for Increasing Cultural Sensitivity
What do you think has caused your problem?
Why do you think it started when it did?
What do you think your sickness does to you?
How severe is your sickness? Short or long course?
What kind of treatment do you think you should receive?
What are the most important results you hope to receive from this treatment?
What are the chief problems your sickness has caused for you?
What do you fear most about your sickness?
Cultural competence issues
not a “skill” that can be learned, cultural factors not always central nor static, individual might not conform to cultural stereotypes
Dimension of Religion (4)
Public participation, Religious Affiliation, Private Religious Practices, Religious Coping
Prevalence of Religious Beliefs in U.S.
Most U.S. adults believe in God or a universal spirit, the existence of a human soul, and that there is something spiritual beyond the natural world; decline in people affiliating with Christianity → more people unaffiliated
Impact of Religion on Health and Illness
creates system of meaning, increases community and social support, shapes behavior; spirituality associated with greater life satisfaction, personal happiness, fewer negative consequences of traumatic life events; attending services once a week → fewer illnesses; religious surgery patients → fewer complications; religion as coping with illness recover quicker
Religious services study
relative risk of mortality over a time period compared to their attendance at services; referent group–never attended services; The more people attended weekly services, they had lower relative risk of mortality – ALTHOUGH they are choosing to do it meaning they enjoy it already
Direct effect religion has on physiological reactivity
promoting positive emotions
Indirect effect religion has through coping
shaping processes of emotion regulation, providing social support + feelings of belonging
Indirect effect religion has through health practices and behavior
promoting health behavior; ex–religions prohibit consumption of alcohol
Hope and Health Study (Krause et al., 2015)
sample of U.S. residents who attend Christian church 3x a year, self-report emotions (spiritual support + gratitude to God) → both associated with more hope → hope related to better self-rated health
Sense of coherence
global orientation that includes a pervasive, enduring feeling of confidence; way of thinking about challenges to help us make sense psychologically; comprehensibility (is life structured/predictable), manageability (do i have resources to meet demands), meaningfulness (are challenges worth it?) → spirituality can enhance this by giving easy answers to hard questions
Negative Religious Coping
cancer study showed it causes more depression, pain, low energy; seeing health problems as punishment, questioning faith, wondering about abandonment (why would God forsake me with this challenge?)