IR class flashcards
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Marxist ideology in IR
examine how international organizations such as the World Bank, IMF, and WTO have helped to construct the global capitalist system through their programs, policies, and loans.
-analyze IR by class
-IOs promote the interests of capital through their work, creating a global market by advocating for free trade, opening states to foreign direct investment, and allowing the unimpeded movement of capital across borders.
Constructivismo ideology
- It questions how and why international organizations function the way they do and not in another way;
-It does not consider international organizations to be spheres in which states act passively (states build international organizations, and international organizations build and, in some ways, constrain states
- It observes how international organizations create, establish, and disseminate new norms and standards of conduct.
-think of the cycle (actors shape global norms/standards, and global norms help shape actors’ decisions)
Liberalismo ideology
IOs continue working for the common good.
• IOs cannot force states to agree and have no coercive power, but they can foster cooperation or establish moral norms and principles of international law.
-importance of multilateralism
what are examples of international campaign led by civil society?
-Arab Spring
-Me2 Movement
-Syrian civil society
La Escuela Inglesa (and its authors)
Authors: Hadley Bull, Adam Watson
Main Idea: despite global anarchy, states form an "international society" with shared norms, rules (like diplomacy, law, war), and institutions, bridging realism and liberalism
-examines the expansion of international society from European states to the rest of the globe.
-studies the transformation of a society formed in Europe and dominated by Europeans into the current global international society of almost two hundred states, the vast majority of which are not European.
Main institutions/beliefs of contemporary internacional society (SI)
Los principios de soberanía y no intervención.
• Las instituciones de la diplomacia.
• El equilibrio de poder.
• Derecho Internacional.
-importance of sovereignty and diplomacy
Bull’s def of SI
States w/ shared common interests/values establish rules and institutions to work together and guide their relations.
-importance of norms and shared interests
what are the 3 reasons SI is based in (in La Escuela Ingles)
Reason of the state
Reason of the system
Reason of civilization
-interprets contemporary international society as the product of a European core
Reason of the state
-Began w/ Peace of Westphalia in 1648
- The sovereign state is the principal unit of the international system.
- The state is the institution responsible for the security of the population, a task on which the legitimacy of its monopoly of force is based.
Reason of the system
-The system must be composed of sovereign nation-states that only recognize other sovereigns as legitimate (violent) actors
Reason of civilization
- The “standard of civilization” is the logic that constructed the discourses of conquest/colonialism on a civilizing and humanitarian basis, and which formulated as its objective the creation of “humanity” and “civilization” in other societies considered inferior to European/Western society.
- The standard of civilization drove, justified, and legitimized European expansion throughout history and reached its historical climax in the 19th century
Historical Conformation of SI:
imperalism and colonization
Following WW1, Nation-states were rapidly becoming the hegemonic political structure of the international order and needed to consolidate their legitimacy. The League of Nations allows for the continuation of colonial relations through mandates
Decolonization through Resolution 1514 (1960): “Declaration on the Granting of Independence to Colonial Countries and Peoples
Critiques of La Escuela Inglesa
-For Bull and Watson, international society originated in Europe. For them, international society is a European cultural artifact.
Postcolonialists argue: La Escuela Inglesa generates a narrative where international agency and norms are seen as products of this European/Western core, rather than of the interaction and struggle (under unequal conditions) among diverse actors, particularly non-Western societies—both state and non-state actors—and other civilizations
How does Foucalt define power?
“A network of social relations and discourses that operate subtly and complexly to regulate and control the behavior of individuals and social groups.”
It is not inherently negative, but it can be used coercively to impose worldviews by those with more power.
What can we take from Foucalt’s panopticon?
-power is productive and everywhere
-themes of biopolitics and constant surveillance
-freedom resides in an individual’s ability to rob power of the monopoly it has on controlling you
what are the 3 theoretical positions of globalization?
hyper-globalizadores,
escépticos
transformacionalistas
Position of hyper-globalizadores
Globalization is entirely new and is primarily an economic phenomenon, but also a social one, driven by capitalism and tech
The power of states has been severely eroded
Position of escépticos
"globalization" processes are better explained by other concepts
2 main critiques: 1. The limits of capital mobility; 2. The continued importance of the state.
position of transformacionalistas
most states have transformed themselves by adopting a more neoliberal stance compatible with the globalization of the world economy
Structure: a power configuration arising from the relationships between actors
-international structure is defined as the result of the interaction of three interdependent forces: material resources, institutions, and ideas.
def of war
Political activity that involves violence
-violence carried out in the name of a political unit is not war unless it is directed against another political unit
what was Clausewitz’s philosophy of war
War is an "act of force to compel our enemy to comply with our will" and is “the continuation of politics by other means."
difference between old and new wars
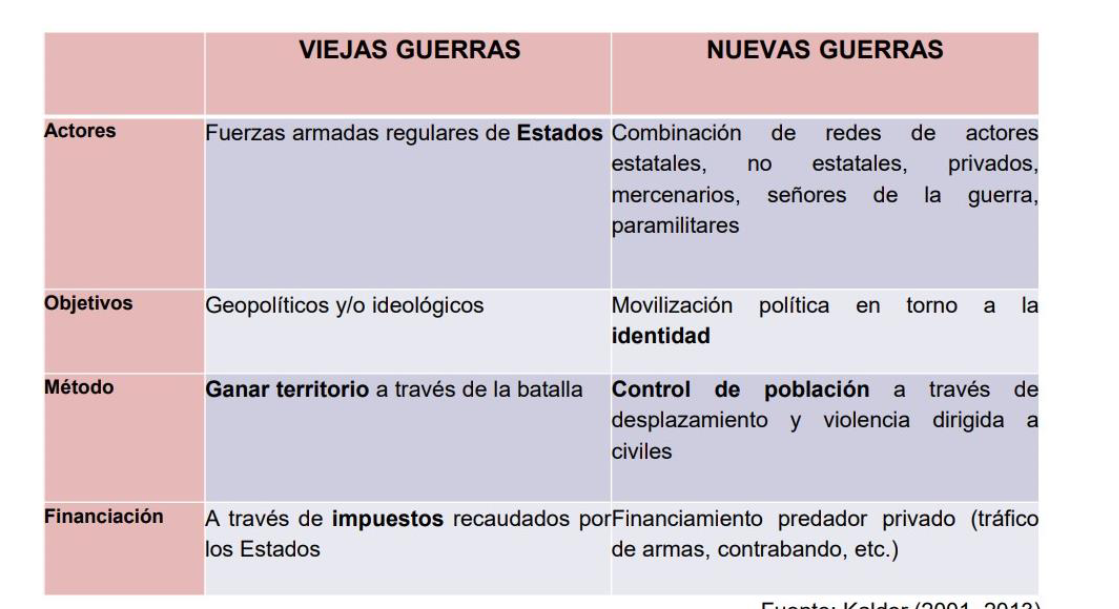
t/f intrastate war is the most common form of war
true
changes in warfare
Changes in Warfare
• In conventional warfare, the objective is the capture of territory by military means.
• In guerrilla warfare, territory is captured through political control of the population and battles are avoided as much as possible.
• The new warfare also tends to avoid battle and control territory through political control of the population and borrows counterinsurgency techniques of destabilization designed to sow fear and hatred.
What is the Copenhagen School of Thought/ Theory of Securitization
-involves invoking an exceptional existential threat to "us" (the audience).
-demanding and justifying extreme and exceptional measures, but also promising to use all necessary means to eliminate the threat.
4. Securitization also implies a sense of urgency
-Audience is a key actor: based on the audience's perception of the threat, revealing how security is a subjective process dependent on identity.
What is the Paris School of Thought
Security occurs once a problem is bureaucratized: procedures are implemented and established as the norm,
• Security becomes “real” not during an emergency, but when it becomes an item on the agenda and is tangible
The expansionist thought about security post Cold War
The end of the Cold War has changed both the security agenda and its actors.
-security is more multidimensional then ever before and includes climate change, WPS, health, etc
-Idea of human security
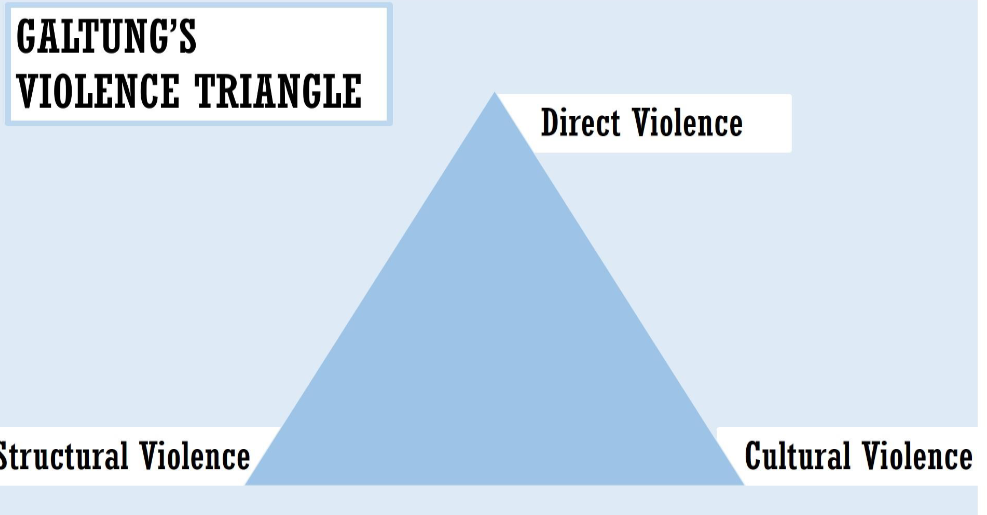
What was Galtung’s violence triangle and theories of peace?
Negative peace (absence of direct violence) and positive peace (overcoming structural and cultural violence).
Johan Galtung argued that true peace requires the absence not only of overt violence, but also of structural violence
According to Patricia Simón, what is the role of the media in international politics?
-A way to disseminate information worldwide
-to promote and support democracy
-to spread the truth that allows international systems to hold countries accountable
-To reveal accurate information that allows people to form their own opinions about political events
What is Resolution UNGA 1514
"Declaration on the Granting of Independence to Colonial Countries and Peoples," in 1960
-necessity of ending colonialism in all its forms, affirming the right to self-determination for all peoples, and demanding the transfer of power to dependent territories without conditions or reservations.
Can the theoretical framework of the English School be applied to Res UNGA 1514?
-reflects the idea of the importance of institutions, norms, and a unified society to guarantee peace.
-But, at the same time, the reconfiguration was determined by Western countries, which, prior to this, had used the international system to assert their hegemony and maintain the subjugation of African, Asian, and other countries.
What can we say about the standard of civilization in relation to Resolution 1514
- evolution in thinking about the purpose and responsibilities of states to themselves and other states. It also reveals a shift in thinking about human rights and the application and distribution of those rights.
-affirms the legitimacy of states but also solidifies the importance of a social society with shared ideas and rights.
How do countries of the Global South challenge eurocentric stereotypes?
forming alliances/ diplomatic agreements with countries like Russia and China.
They focus on internal development.
What are the dynamics of “new wars” in Syria?
The war in Syria involved numerous state and non-state actors who collaborated with and opposed the Assad regime. Various rebel groups and non-state actors fought in the civil war against the regime, while actors such as Russia provided financial support to the government and Turkey supported rebel groups like Hayat Tahrir al-Sham.
Furthermore, the regime employed disproportionate levels of violence against the civilian population, including the bombing of Homs, the unjust detention of journalists, activists, and others, and other violent acts not typical of conventional warfare.
What are “old war” dynamics in Syria?
The objectives and methods of old wars were present
1. Rebel forces sought geopolitical power and control of Syria. This could be considered old wars because rebel groups sought to overthrow and replace the Syrian government, essentially seeking political control over the country.
2. One way to consolidate geopolitical power was through the conquest of certain territories in Syria. During the overthrow of Assad in late 2024, they resorted to an old war tactic by taking territories like Aleppo.