L5 physics and gravity
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
speed
rate at which object moves, distance/time in m/s
velocity
speed AND direction e.g. 10 m/s due east
Galileo showed that g is
same for all falling objects regardless of mass
momentum changed by
a net force, usually meaning an acceleration
angular momentum
rotational momentum of a spinning or orbiting object
what is needed to change an object’s angular momentum
a torque
mass
a measure of amount of matter in an object
weight
the force that a scale exerts upon an object
why are astronauts weightless in space
there is gravity and in a continued state of free fall
what did newton do
extrapolated physical laws of Earth to heavens, laws of motion and gravity, experiments with light, invention of calculus
newton’s first law of motion
an object moves at constant velocity unless a net force acts to change its speed or direction
newton’s second law of motion
force = mass x acceleration = rate of change in momentum
newton’s third law of motion
for every force there is always an equal and opposite reaction force
conservation of momentum
objects continue at constant velocity, total momentum of interacting objects cannot change unless an external force is acting on them + they exchange momentum through equal and opposite forces
conservation of angular momentum
figure skater bringing arms in makes them go faster
types of energy
kinetic = motion, radiative = light, potential = stored
conservation of energy
energy can transfer between objects or change forms, but cannot be created or destroyed
thermal energy
the collective KE of many particles, depending on both temperature and density
temperature
measure of the average KE of many particles in a substance
on Earth, gravitational potential energy depends on
object’s mass, strength of gravity, and height above the ground
object/gas cloud and gravitational potential energy
has more when it is spread out than when it contracts, which converts it to thermal energy
mass energy relationship
E = mc² - small mass, big energy
concentrated energy can spontaneously
turn into particles
universal law of gravitation
every mass attracts every other mass with Fg = Gm1m2/d²
G is gravitational constant, d is distance between them
types of orbital paths
bound (ellipses) and unbound (parabola, hyperbola) e..g extra-solarsystem comet that just leaves
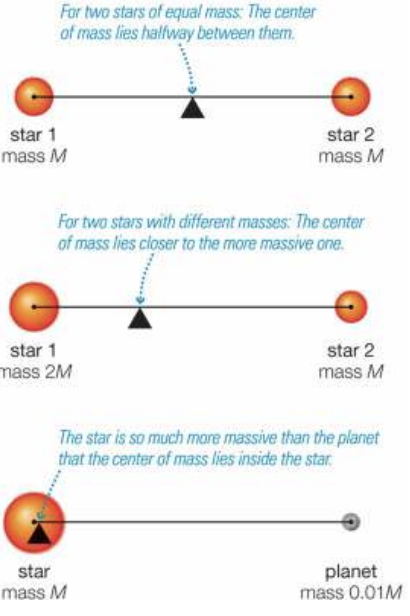
center of mass and orbits
because of angular momentum conservation, orbiting objects orbit around their combined center of mass
gain or loss of orbital energy from
gravitational encounter, friction or atmospheric drag
escape velocity
if an object gains enough orbital energy, it may escape (change from bound to unbound orbit
angular momentum equation
mass x velocity x radius
total mass of a system from orbits/ newton and kepler’s third law
M1 + M2 = 4π²a³/Gp² (p = orbital period, a = avg orbital distance between centers)
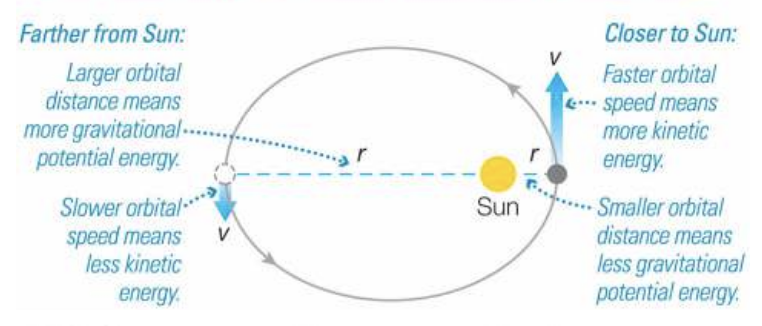
total orbital energy is
constant ; gravitational potential + kinetic energies
causation of tides
Moon’s gravity pulls harder on near side of Earth than on far side
tidal friction
gradually slows Earth’s rotation and makes Moon get farther, caused Moon’s tidal locking - removal of energy from the system
spring tide
new moon and full moon, tidal forces of Sun and Moon work together to create lowest lows and highest highs
neap tide
first and third quarters, Sun and Moon work against each other, highest lows and lowest highs
relationship between gravitational acceleration and mass
DOES NOT EXIST