Lecture 28: More Complications and Non-Mendelian Inheritance
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
11/5/2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What is the difference between identical (monozygotic) and non-identical (fraternal, dizygotic) twins?
Identical twins come from a single fertilized egg that splits, having nearly the same genotype. Non-identical twins come from two separate fertilized eggs and have different genotypes
What does “concordance” mean in the context of twin studies?
Concordance refers to the occurrence of a trait in both twins
What does GWAS stand for?
Genome Wide Association Studies
What is GWAS’s primary function?
To correlate nucleotide differences in DNA with the occurrence or strength of a trait
What is the key limitation of GWAS?
GWAS can show correlation but does not prove causation
What are some potential problems with GWAS?
Can lead to incorrect correlations and may be affected by linked gene problems
What type of data is needed for GWAS?
GWAS needs DNA and trait data from many individuals
What is the significance of recombination in the context of GWAS?
Infrequent recombination between nearby genes can make it difficult to determine which nearby mutation is important
What is epistasis?
Epistasis is when genes interact to produce complex traits
What is non-disjunction?
The failure of chromosomes to separate properly during cell division
What are new mutations?
New mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can lead to altered traits
What are expanding mutations?
Expanding mutations are mutations where the number of repeats of a DNA sequence increases, leading to genetic disorders
What is organelle DNA?
Organelle DNA refers to the DNA found in organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts
What is horizontal gene transfer?
Horizontal gene transfer is the movement of genetic material between organisms that are not parent and offspring
What is epigenetic inheritance
Epigenetic inheritance involves changes in gene expression that are not due to changes in the DNA sequence itself
What is the significance of “Sonic Hedgehog” in the context of the material?
Sonic hedgehog is a gene that, when dysregulated, can contribute to cancerous growths
How many chromosomes do humans have?
Humans have 8 of every chromosome
What is the difference between germline and somatic mutations?
Germline mutations occur in cells that make gametes and can be passed on to offspring, while somatic mutations occur in non-germline cells and are not passed on
Where do germ cells (PGCs) and somatic cells separate in the embryo?
In many species, the “primary” germ cell (PGC) line and somatic cells separate in the very early embryo
What is the process that germ cells undergo to become gametes?
Germ cells (PGCs) undergo mitosis, then meiosis to make gametes
What is the fate of somatic mutations?
Somatic mutations may affect the adult but will not be passed to offspring
What is the main characteristic of expanding mutations?
Expanding mutations are not faithfully replicated and can worsen in successive generations
What type of mutations are discussed in the material?
Trinucleotide repeat mutations
Give an example of a trinucleotide repeat mutation
CAGCAGCAG
What can happen to the replication of the repeat?
Replication of the repeat is prone to “slippage” between template and replicating strands
Which strand binds to 5’-CAG-3’?
3’-GTC-5’
What can expanding mutations lead to?
Extra replication and extra repeats (expansion) in the new strand
What is the mode of inheritance for Huntington’s disease?
Autosomal dominant
What type of repeat is associated with Fragile-X syndrome?
CGG repeats
What is the main presentation of Myotonic dystrophy?
Intellectual disability or psychiatric symptoms can occur but main presentation is usually with muscle weakness, etc
What is the relationship between the number of CAG repeats and the onset of Huntington’s disease?
The number of CAG repeats in the coding region of the Huntington protein correlates with the severity and age of onset
What does CAG create in protein?
CAG creates poly-glutamine (poly-Q) tract in protein
What two organelles are mentioned as containing DNA?
Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
Describe the shape of the DNA found in mitochondria and chloroplasts
Small and circular
How do mitochondria and chloroplast organelles reproduce?
By fission, similar to bacteria
What are some characteristics that make mitochondrial and chloroplast organelles similar to bacteria?
They have ribosomes and other molecules that resemble bacteria
What is the primary mode of inheritance for mitochondrial DNA?
Maternal inheritance
Why is mitochondrial DNA inherited maternally?
Because sperm do not donate organelles during fertilization in most species, so organelle genes are inherited only from the egg
Can a single egg have organelles with different mutations?
Yes
What does mtDNA stand for?
Mitochondrial DNA
What problems can mitochondrial mutations cause?
Mitochondrial mutations can lead to problems with cellular respiration
Is it possible to fix mitochondrial mutations?
Yes, it is possible to fix mitochondrial mutations
What are some ethical issues related to human genetic engineering?
The material mentions ethical issues for all types of human genetic engineering
What is eugenics?
The “improvement” of humans through selective reproduction
What is the approximate age of “Mitochondrial Eve”?
Approximately 200,000 years ago
What does “MRCA” stand for?
Most Recent Common Ancestor
What types of DNA can be used to trace paternal ancestry?
Y chromosome
What is horizontal gene transfer (HGT)?
Non-sexual transfer of DNA fragments and genes between cells
Where is HGT common?
In prokaryotes
What are the 3 mechanisms of HGT in prokaryotes?
Transformation
Conjugation
Viral Transfer (Transduction)
Where is HGT infrequent?
HGT is infrequent in eukaryotes
Give an example of HGT in eukaryotes
Transfer of bacterial genes into eukaryotic chromosomes
What is the easiest way to detect HGT?
The best-match similarity approach
What is the best-match similarity approach?
A method that identifies a gene in one organism that has a high-similarity match to a gene in a distantly related species
What is epigenetic inheritance?
Reversible change in gene expression passed on to offspring
What are some factors involved in epigenetic inheritance?
Transcription factors
Histone modification
DNA methylation
What is the effect of adding methyl groups to nucleotides?
It silences transcription
How is the local state of DNA methylation maintained during mitosis?
The old methylated strand acts as a signal to methylate the newly synthesized strand
What are some examples of organisms where epigenetic inheritance has been observed?
Plants
Some invertebrate animals
What is a challenge in studying epigenetic inheritance in mammals?
Distinguishing epigenetic effects from the effects of the womb environment on the offspring’s health
What happens to most DNA methylation after fertilization?
Most DNA methylation is lost after fertilization
Explain how new mutations or expanding (trinucleotide repeat) mutations arising in germ-line cells would disrupt typical Mendelian analyses of crosses and pedigrees
Some genes have repeated sequences (like CAGCAGCAG)
These repeats can expand when passed to offspring, causing disorders that worsen over generations (e.g. Huntington’s disease)
New mutations in germ-line cells may not follow expected Mendelian rations because they appear spontaneously
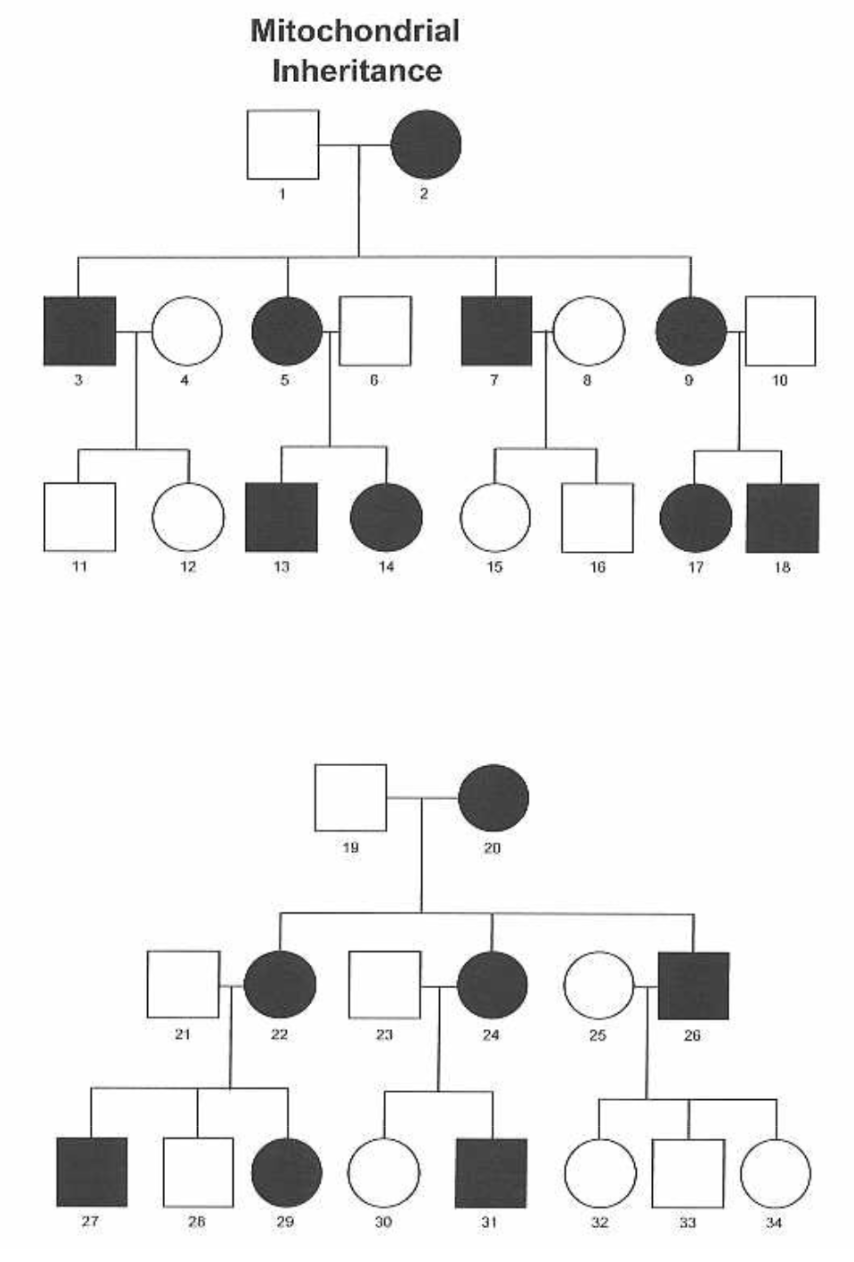
Diagram how maternal inheritance of mitochondrial mutations would look in a pedigree
Mitochondria have their own DNA, inherited only from the mother
In a pedigree, ALL children of an affected mother inherit the mutation, but an affected father passes none to his children
Explain how horizontal gene transfer differs from gene inheritance from parental cells
Vertical inheritance: Genes passed from parent to offspring
Horizontal gene transfer: movement of genetic material between unrelated organisms (common in bacteria, e.g. antibiotic resistance transfer)
Define genome-wide association studies (GWAS)
studies linking genetic variants across the genome to specific traits or diseases
Define epistasis
interaction where one gene masks or modifies another’s effect
Define germ-line mutations
occur in egg/sperm → heritable
Define somatic mutations
occur in body cells → not inherited
Define trinucleotide repeat mutation
repeated three-base sequence that can expand and cause genetic disorders
Define non-nuclear DNA
DNA found outside the nucleus (e.g. mitochondrial DNA)
Define mitochondrial genome
Small circular DNA in mitochondria, maternally inherited
Define horizontal gene transfer
gene transfer between unrelated organisms, not through reproduction