Biology Systems and Processes: Photosynthesis, Respiration, Homeostasis
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is the primary function of chloroplasts in plant cells?
Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using light energy.
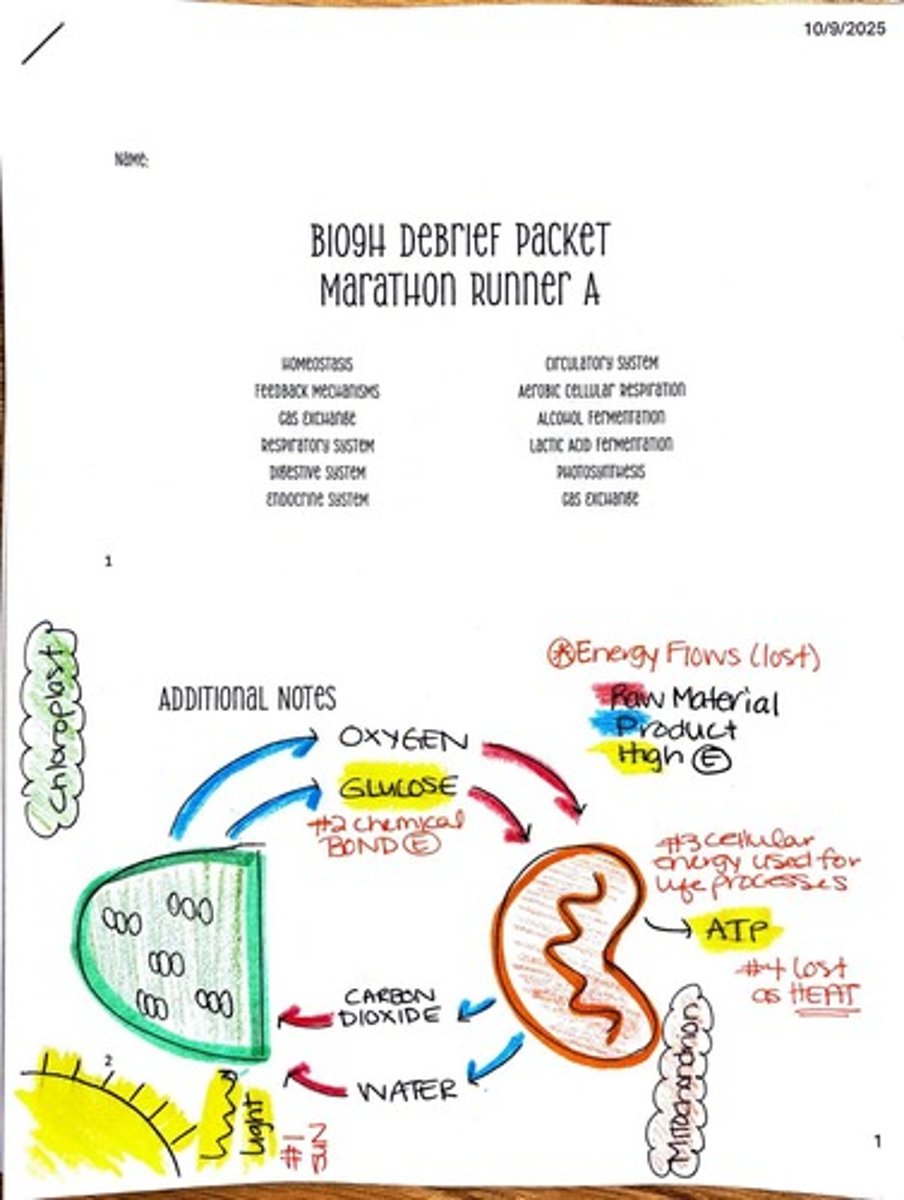
What is homeostasis?
Homeostasis is the process by which biological systems maintain stability while adjusting to changing external conditions.
What is the role of the respiratory system?
The respiratory system facilitates gas exchange, allowing oxygen to enter the bloodstream and carbon dioxide to be expelled.
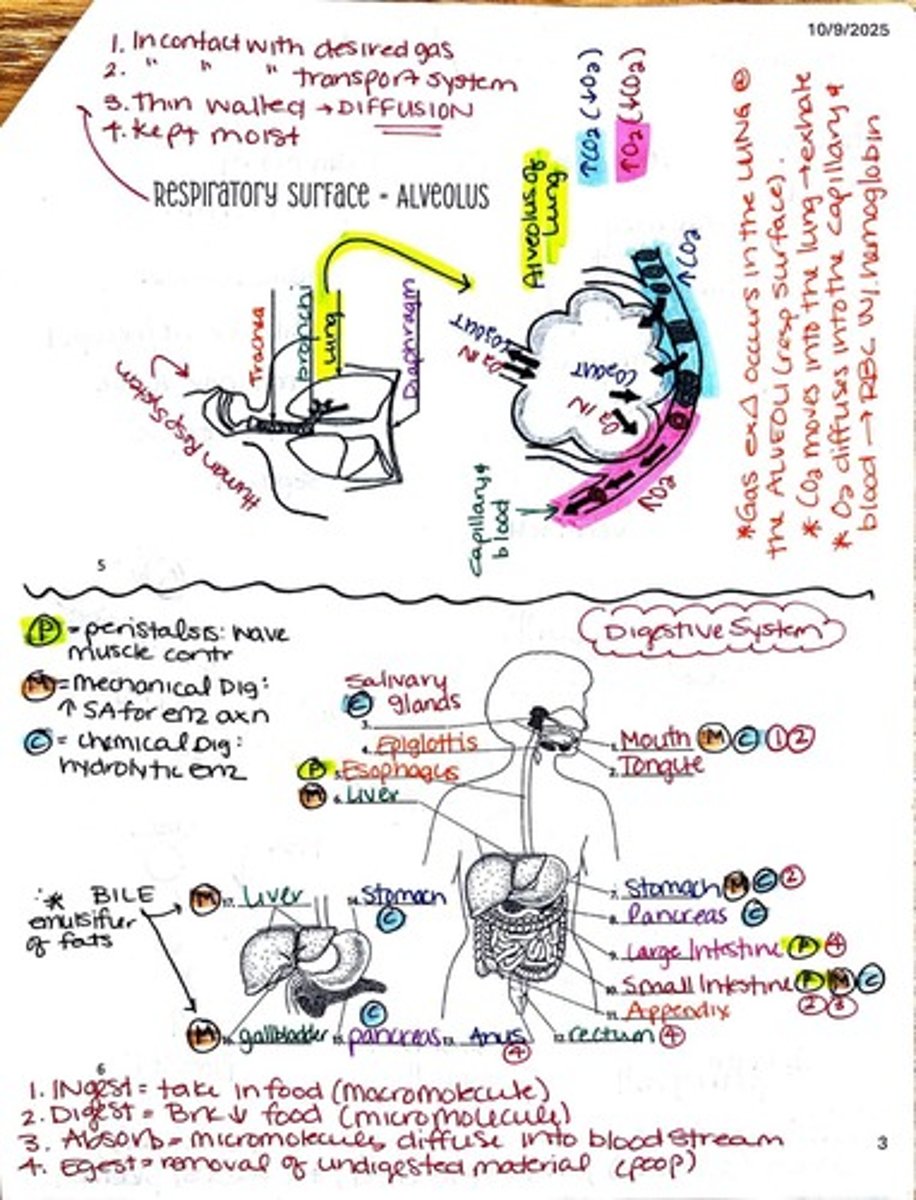
What is the function of the digestive system?
The digestive system breaks down food into macromolecules, absorbs nutrients into the bloodstream, and eliminates waste.
What is aerobic cellular respiration?
Aerobic cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into ATP, carbon dioxide, and water.
What is fermentation?
Fermentation is an anaerobic process that converts glucose into energy, producing byproducts like lactic acid or alcohol.
What is the significance of the alveoli in the respiratory system?
Alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs, allowing oxygen to diffuse into the blood and carbon dioxide to diffuse out.
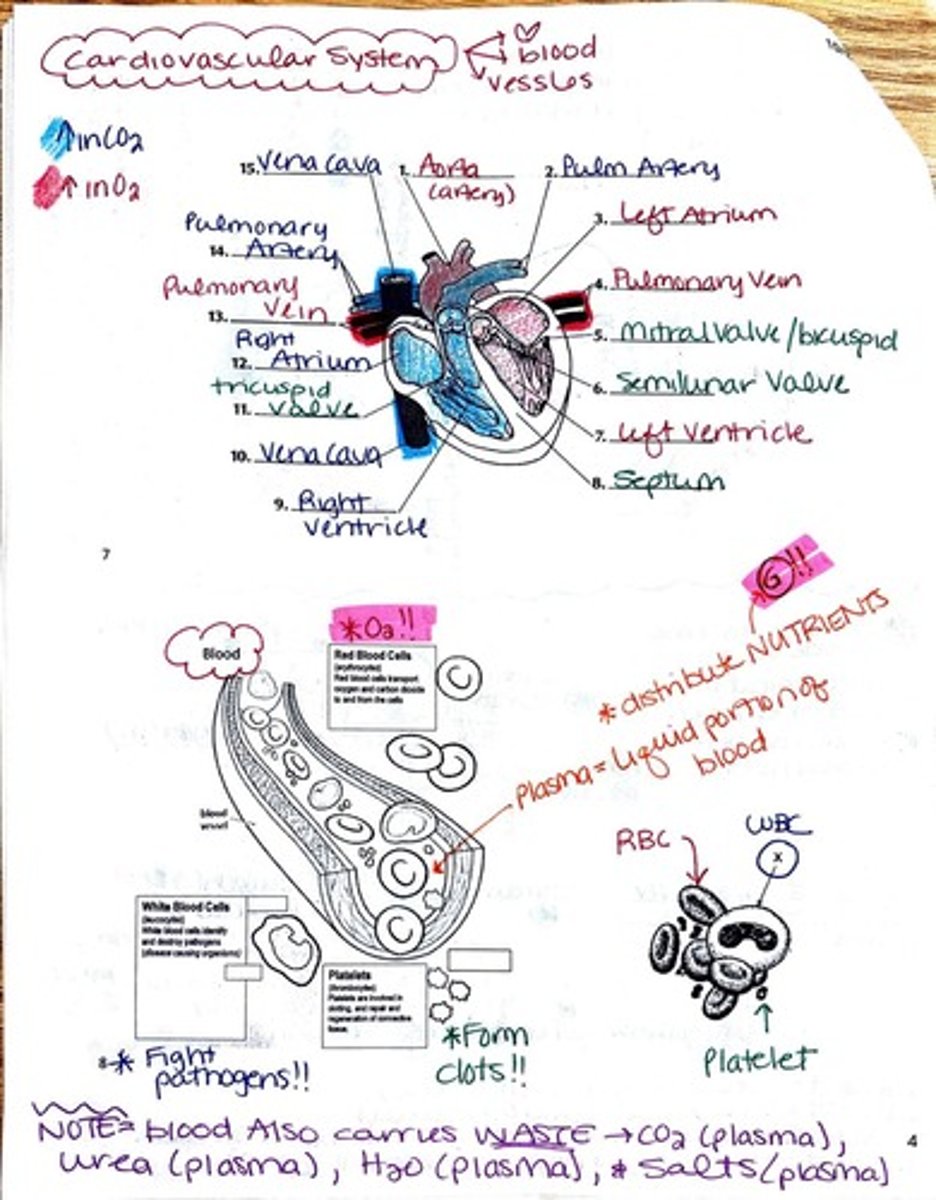
What are the main components of the circulatory system?
The circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, which transport nutrients, gases, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
What is the function of insulin in blood sugar regulation?
Insulin is a hormone that lowers blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells.
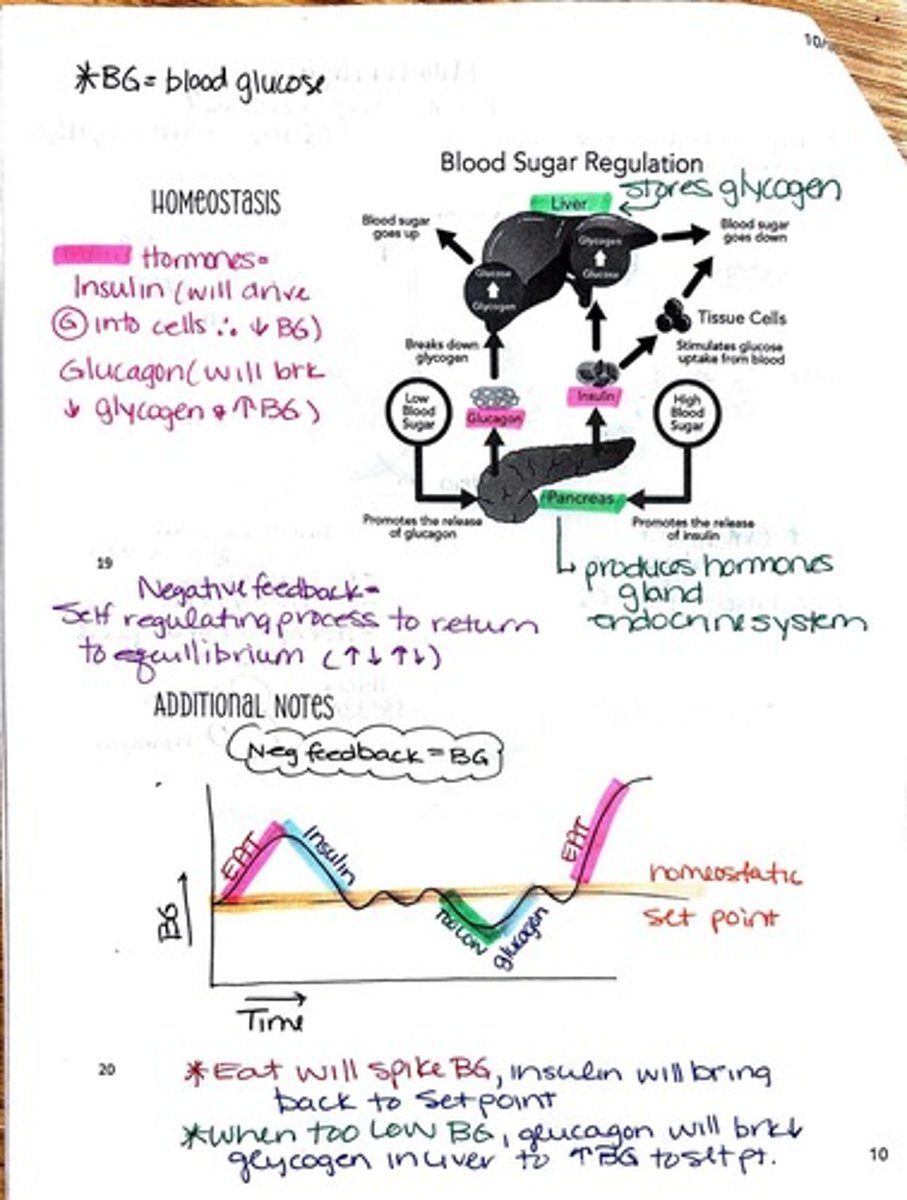
What is the role of glucagon in blood sugar regulation?
Glucagon is a hormone that raises blood sugar levels by promoting the breakdown of glycogen into glucose in the liver.
What is the function of ribosomes in cells?
Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis, where amino acids are assembled into proteins based on genetic instructions.
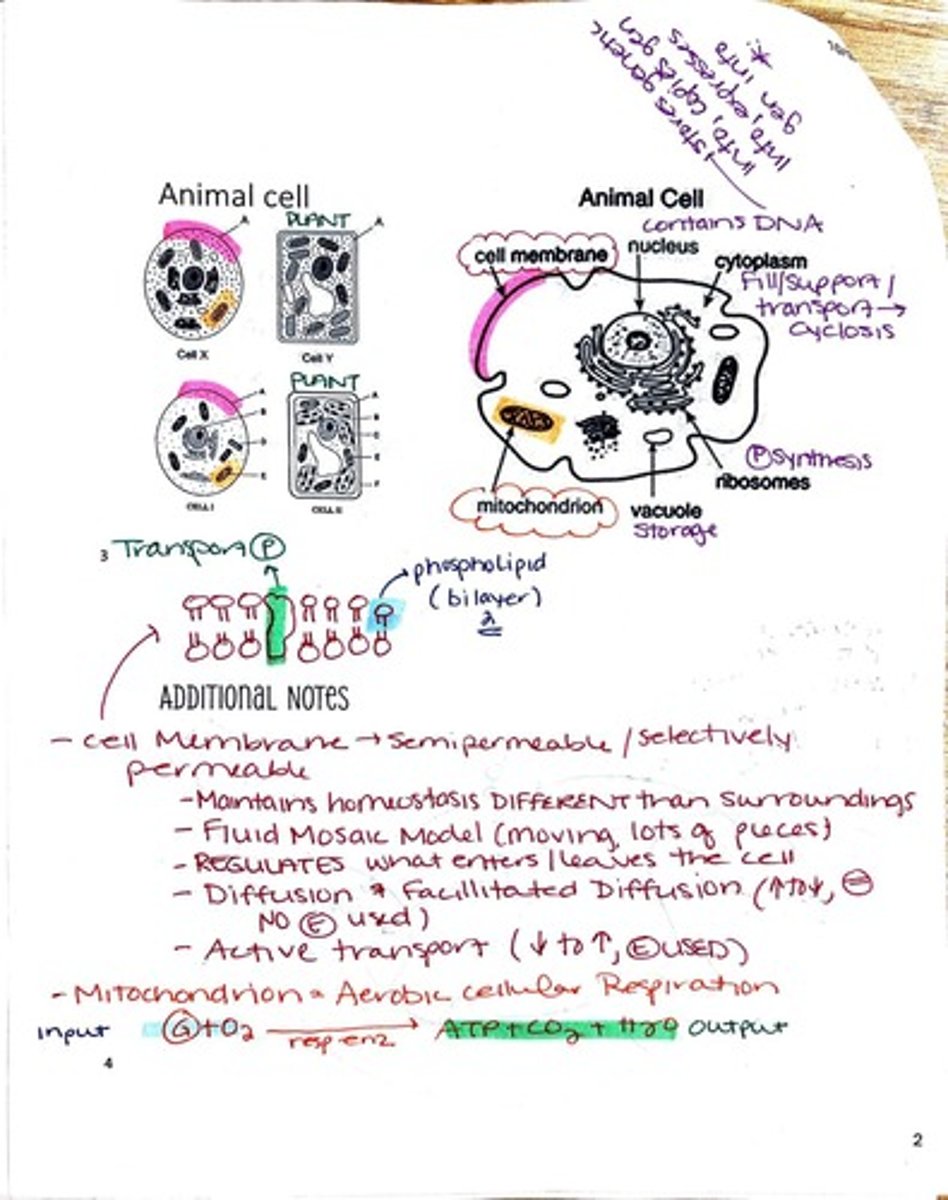
What is the fluid mosaic model?
The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of cell membranes as a flexible layer of phospholipids with embedded proteins that move laterally.
What is the role of guard cells in plants?
Guard cells regulate the opening and closing of stomata to control gas exchange and water loss in plants.
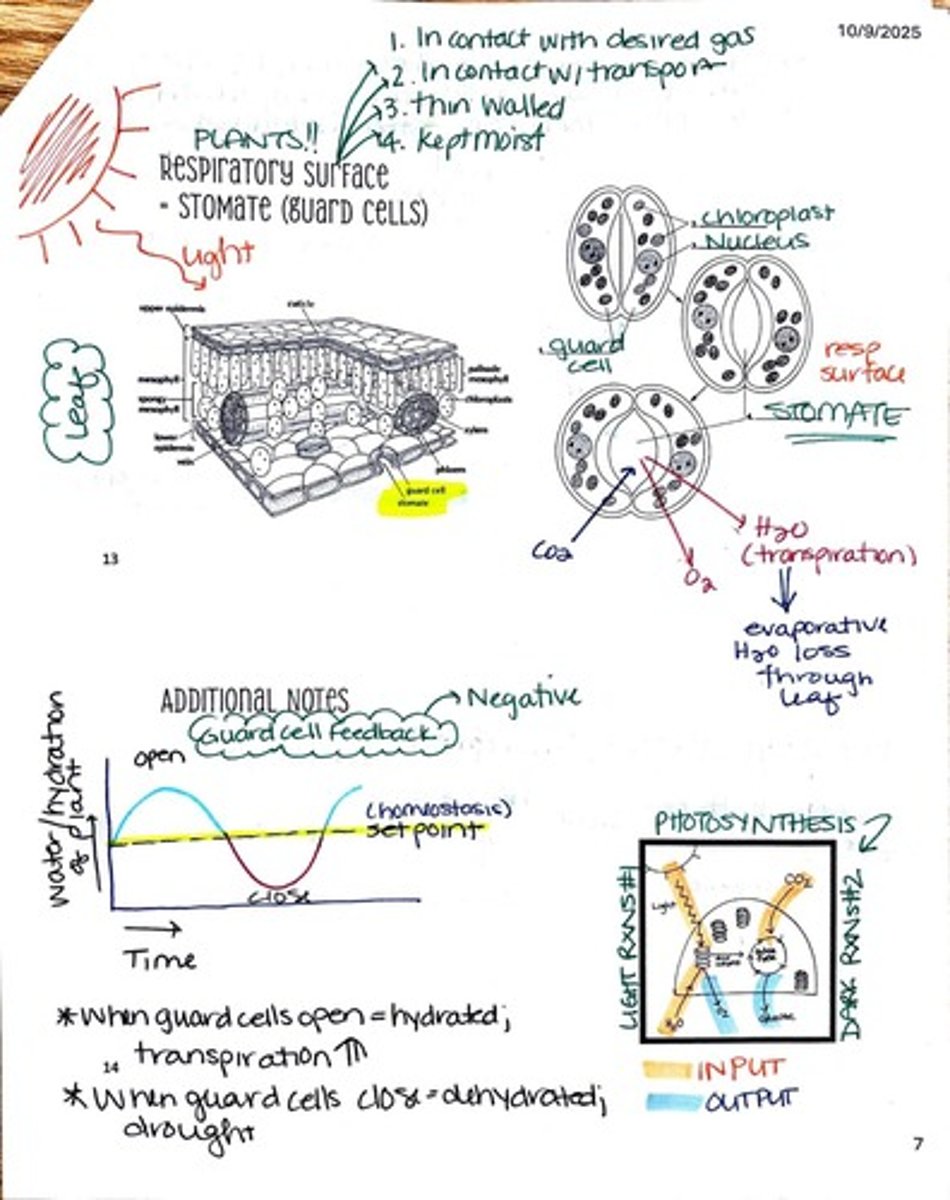
What is the process of diffusion?
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
What is the primary purpose of the endocrine system?
The endocrine system regulates bodily functions through the release of hormones into the bloodstream, affecting target cells.
What is the role of mitochondria in cells?
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, generating ATP through aerobic respiration.
What is the significance of the small intestine in digestion?
The small intestine is the primary site for nutrient absorption, where digested macromolecules enter the bloodstream.
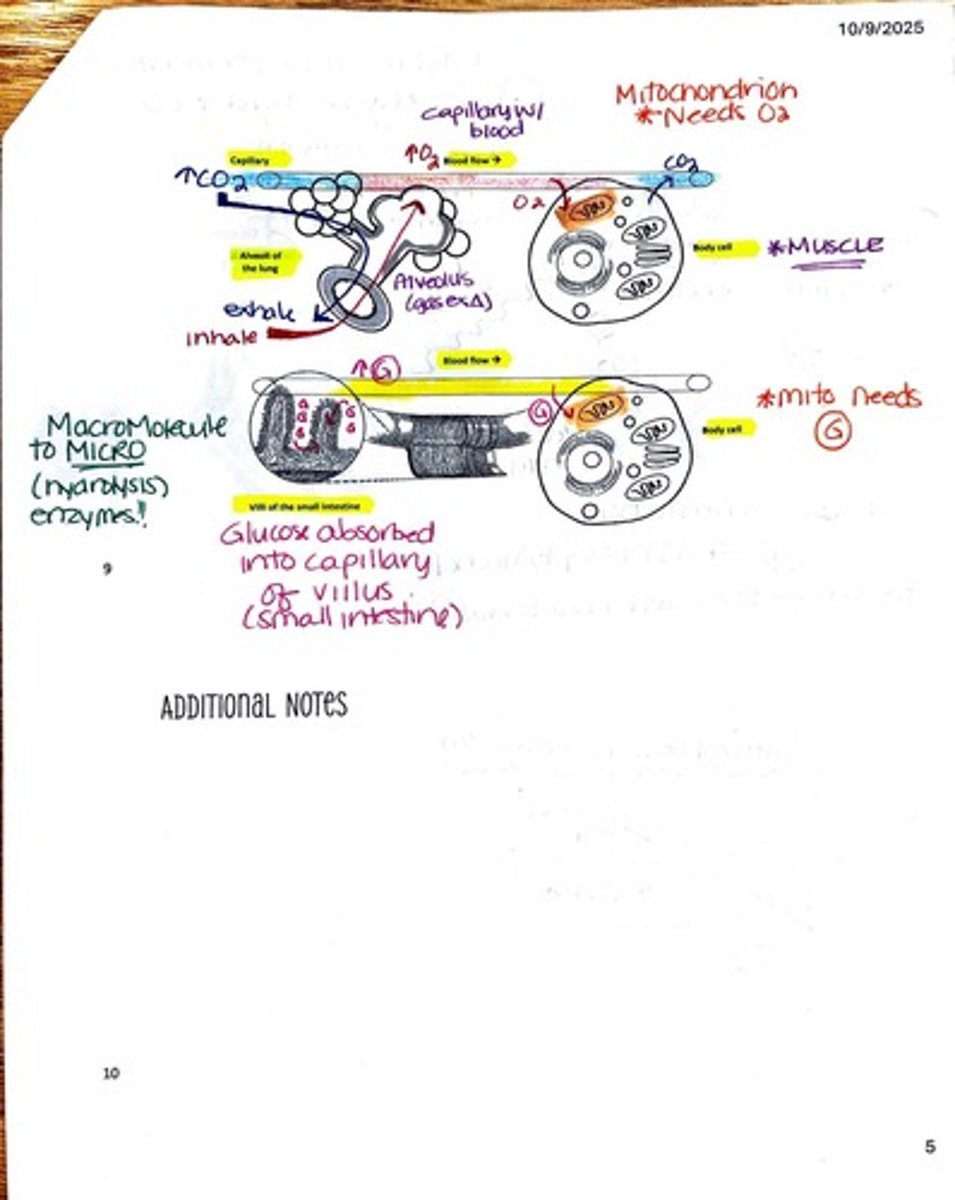
What is the function of platelets in the blood?
Platelets are involved in blood clotting and the repair of damaged blood vessels.
What is the role of the liver in glucose metabolism?
The liver stores glycogen and regulates blood sugar levels by converting glycogen back into glucose when needed.
What is the function of the diaphragm in respiration?
The diaphragm is a muscle that contracts and relaxes to facilitate breathing by changing the volume of the thoracic cavity.
What is the process of peristalsis?
Peristalsis is the wave-like muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract.
What is the primary role of red blood cells?
Red blood cells transport oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and carry carbon dioxide back to the lungs.
What is the role of the xylem in plants?
Xylem transports water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves.
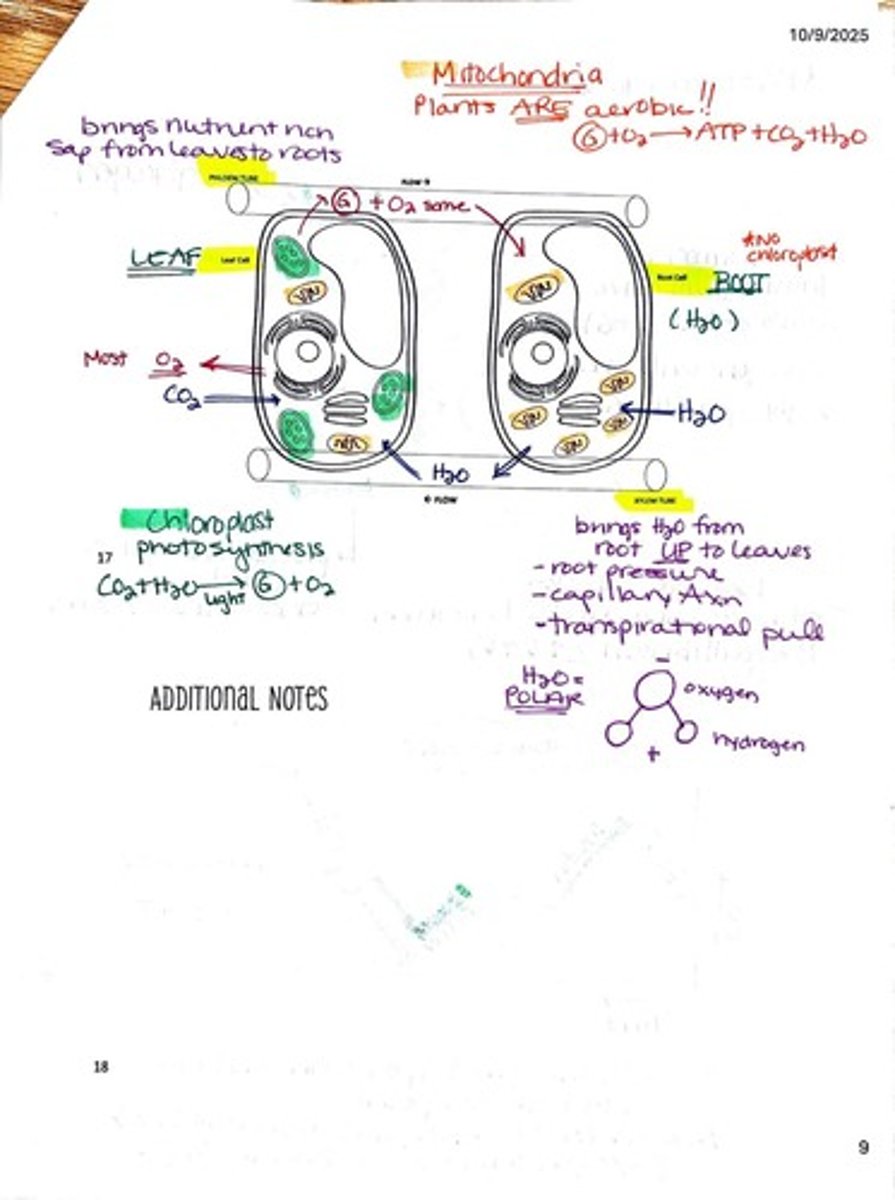
What is the role of phloem in plants?
Phloem transports sugars and nutrients produced during photosynthesis from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
What is the significance of the Calvin Cycle in photosynthesis?
The Calvin Cycle is the set of chemical reactions that occur in the chloroplasts, converting carbon dioxide into glucose using ATP and NADPH.