Neuro205 Exam 1 Study Guide 5
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Define synapse and what happens at a synapse
a junction between neurons where impulses pass by neurotransmitter diffusion
Define the structure of an electrical synapse, how electrical synapses work, and where they are typically found in humans
an electrical synapse is a connexon that is made up of 6 connexins
They allow for the passive diffusion of ions and small molecules
Common in early development
Found in glial cells, inhibitory neurons, and some excitatory neurons
Describe the structure of a typical chemical synapse (include presynaptic terminal, synaptic vesicles, NT, active zone, postsynaptic membrane, NT receptors, extracellular matrix in the synaptic cleft)
Presynaptic terminal: sends signal
Synaptic vesicles: release neurotransmitters
NT: what pre synaptic cell sens to post synaptic cell
Active zone: the area where vesicles bind to the membrane
Post synaptic membrane: receives signal
NT receptors: NTs bind to them and they’re on the postsynaptic membrane
Extracellular matrix in synaptic cleft: in between the pre and post synaptic membranes
Explain the difference between axodendritic, dendrodendritic, axosomatic, and axoaxonic synapses
Axodendritic: axon→dendrite
Dendrodendritic: dendrite→dendrite
Axosomatic: axon→soma
Axoaxonic: axon→axon
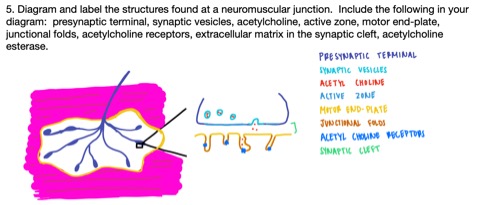
Diagram and label the structures found at a neuromuscular junction (include presynaptic terminal, synaptic vesicles, acetylcholine, active zone, motor end-plate, junctional folds, acetylcholine receptors, extracellular matrix in the synaptic cleft, acetylcholine esterase)
Describe where these types of neurotransmitters are created and stored (amine/amino acid NT, and peptide NT)
Amine/amino acid NT are synthesized in the synaptic terminal and stored in synaptic vesicles
Peptide NT are synthesized in the rough ER (and modified in the Golgi) and stored in the secretory granules (carried down the microtubules)
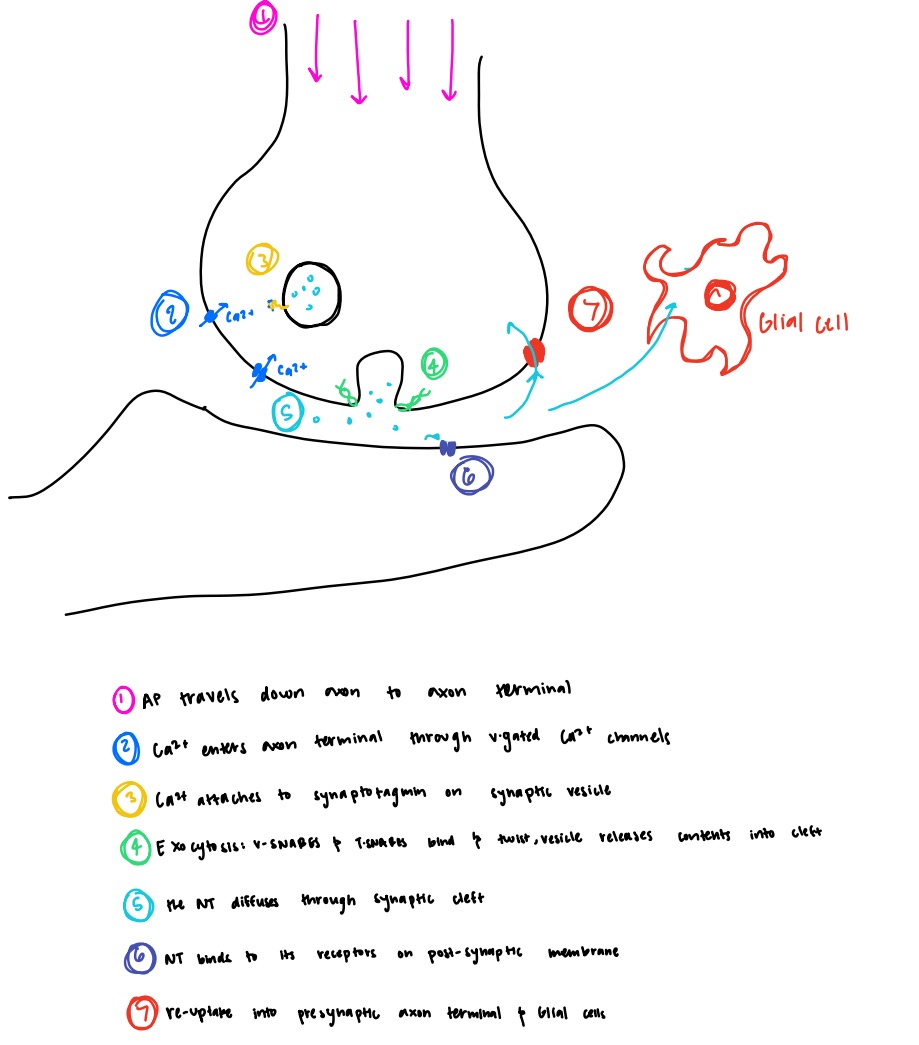
Explain the trigger and basic mechanisms of neurotransmitter release
Describe the basic structure and action of transmitter-gated ion channels (These are neurotransmitter IONOTROPIC receptors)
neurotransmitter binds to the receptor
Channel opens
Ions flow across membrane
Explain the difference between excitatory and inhibitory synapses
excitatory:
Tend to be on or around dendrites
Really powerful ones on the soma
EPSP: membrane depolarized; glutamate; influx of cations (excitatory postsynaptic potential - if enough add up it becomes an action potential in that neuron)
Inhibitory:
Tend to be in the soma and axon hillock
They “shut down” the dendrite or cell
IPSP: membrane hyperpolarized; GABA; influx of anions/efflux of cations (Inhibitory postsynaptic potential)
Explain the functions of metabotropic receptors (G-protein-coupled receptors)
Not as direct as an ionotropic receptor (the ion neurotransmitter gated channels)- the neurotransmitter binds and then that activates the G protein, which can do one of 2 things
The shortcut approach (this is fast, and direct, but perhaps doesn’t have as widespread of reach) - the G protein directly goes and opens or closes an ion channel (exciting the neuron or inhibiting it)
Or the second messenger approach where the G protein activates enzymes which produce second messengers that amplify the signal and leads to longer lasting effects
Describe the function and location of autoreceptors
Location: presynaptic neuron
Function: modifies release of neurotransmitters based on how much there is in the cleft- sort of regulation