Weeks 1-2 Jeopardy & Sample Images
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
"ABCS"
_______ is the GOLD standard (structured approach) when it comes to reading plain film radiographs
More clinical info and context passed along to a radiologist
Q: benefits of PT-ordered imaging studies vs. a physician intermediary
Radio-opaque (ex: heavy metal, bone)
Q: this image shows up white on plain film due to high density
1987
Q: in this year Direct Access Language was adopted for the state of Wisconsin
Radiology Technician Practice Act
Q: from 2013-2017, this healthcare provider's practice act prompted a stop to PT's ordering plain films in WI
We had proof that we were ALREADY doing it!!
Bonus question: why did amending the Radiology Technician Practice Act work?
Full-body CT scan (necessary in major, multi-trauma incidents, but worrisome when a series is performed in a short period of time)
Q: this imaging modality can expose a person to some of the highest radiation doses
Polarized atoms
Q: the moving of direction from this type of matter, magnetized, is what makes up the physics for MRI
Deep intra-articular ligaments (ex: ACL or PCL)
NOTE: you CANNOT see these w/ ultrasound (however, when it comes to the MCL and LCL, ultrasounds are AMAZING)
Q: MRI is the BEST tool to visual these types of ligaments
TRUE!! (however, when it comes to the MCL or LCL, ultrasounds are AMAZING because you can perform dynamic tests)
True or false: you cannot see deep intra-articular ligaments with ultrasound
PT-ordered imaging will not get reimbursed by insurance
What is an unfounded concern by PT's that is NOT consistent with evidence when it comes to ordering imaging?
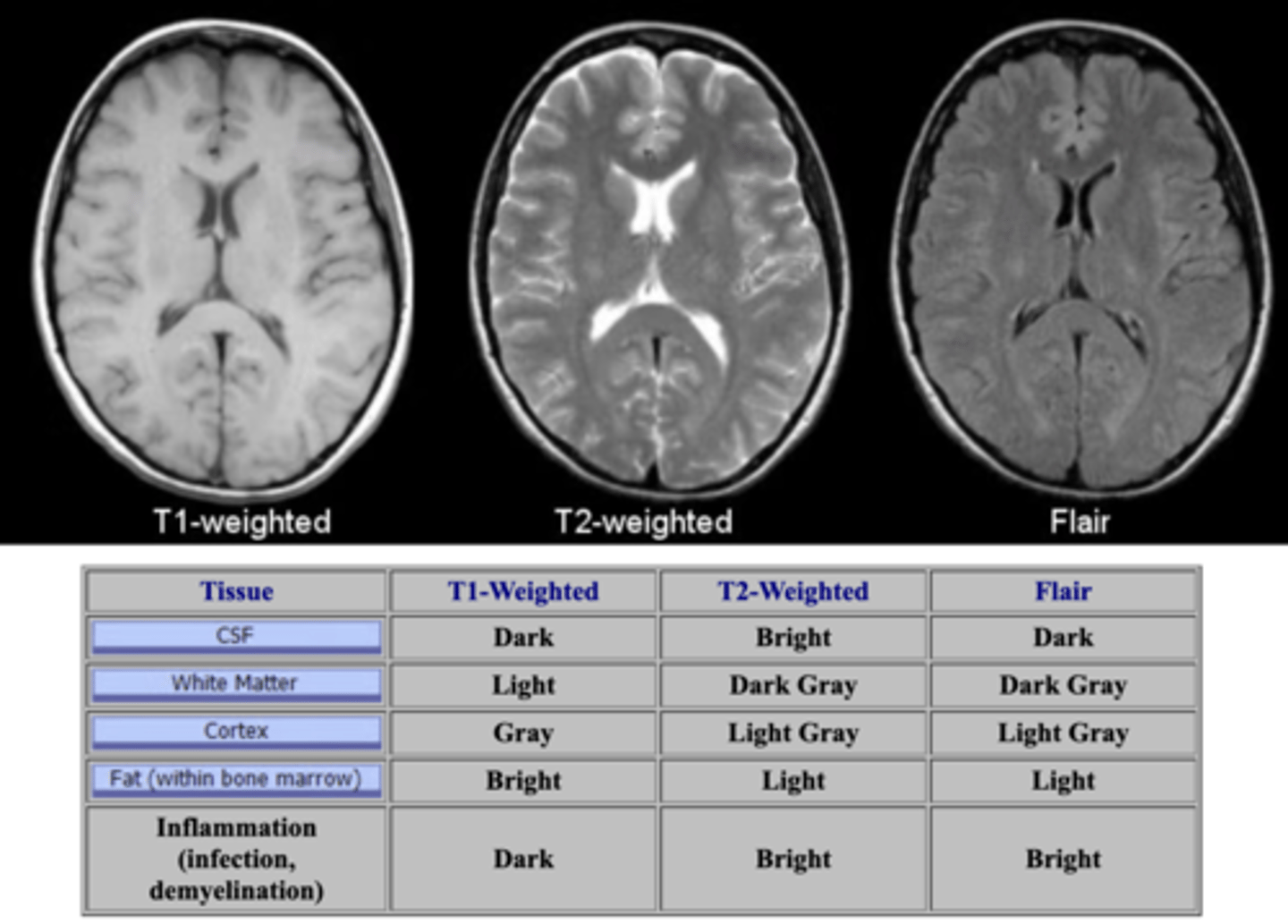
T2 MRI
Q: fluid is BRIGHT on this MRI sequence
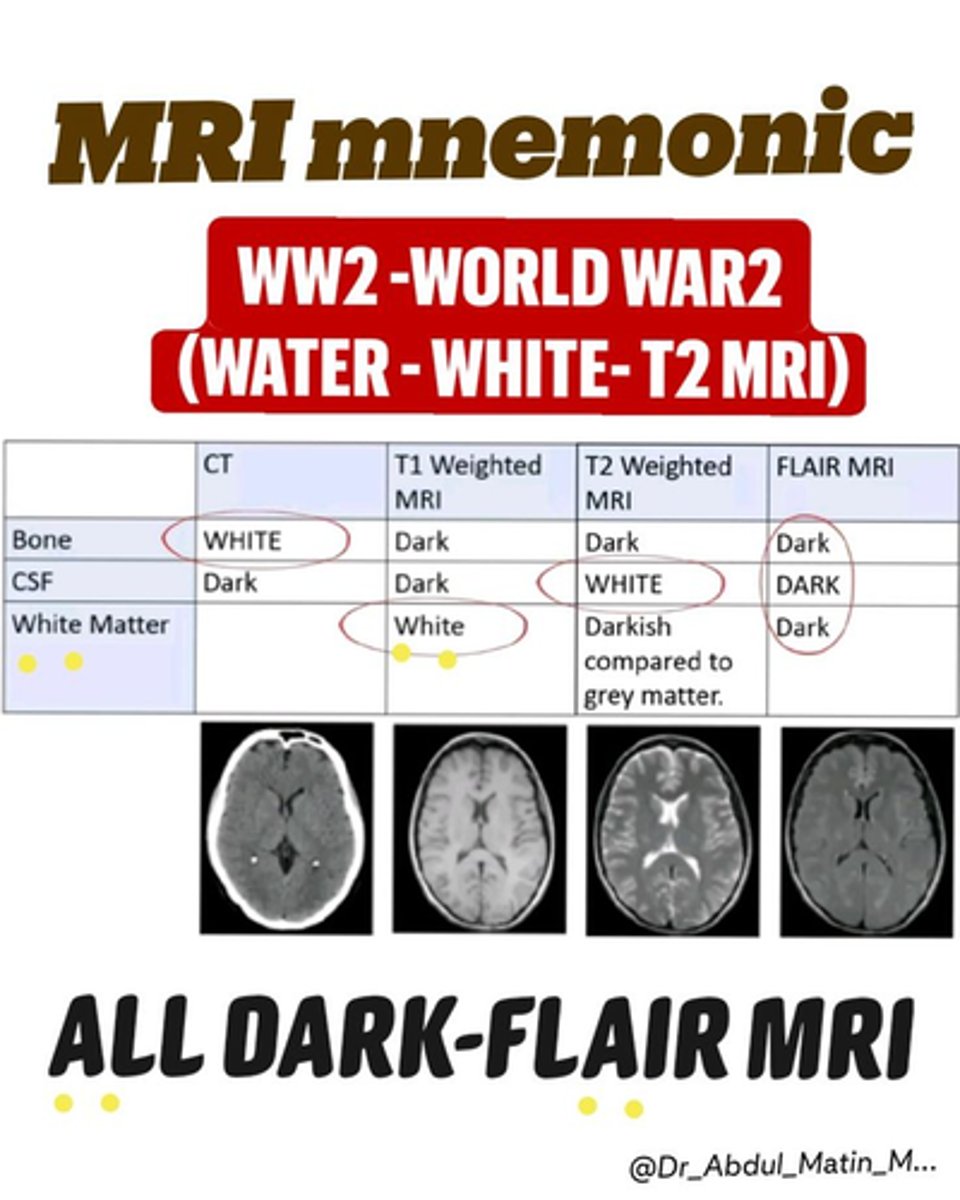
T1 MRI
Q: fat is bright under this MRI
Radiolucent (ex: air)
Q: these tissues show up dark on plain film due to low density
1. DPT degree
2. Board certification specialization (OCS)
3. Fellowship/residency
Q: to order a plain film study in the state of WI, a PT must hold the following...
Radiation
Q: MRI is very safe in that is does not emit __________
Fluoroscopy
Q: these video x-rays are commonly used in the operating room
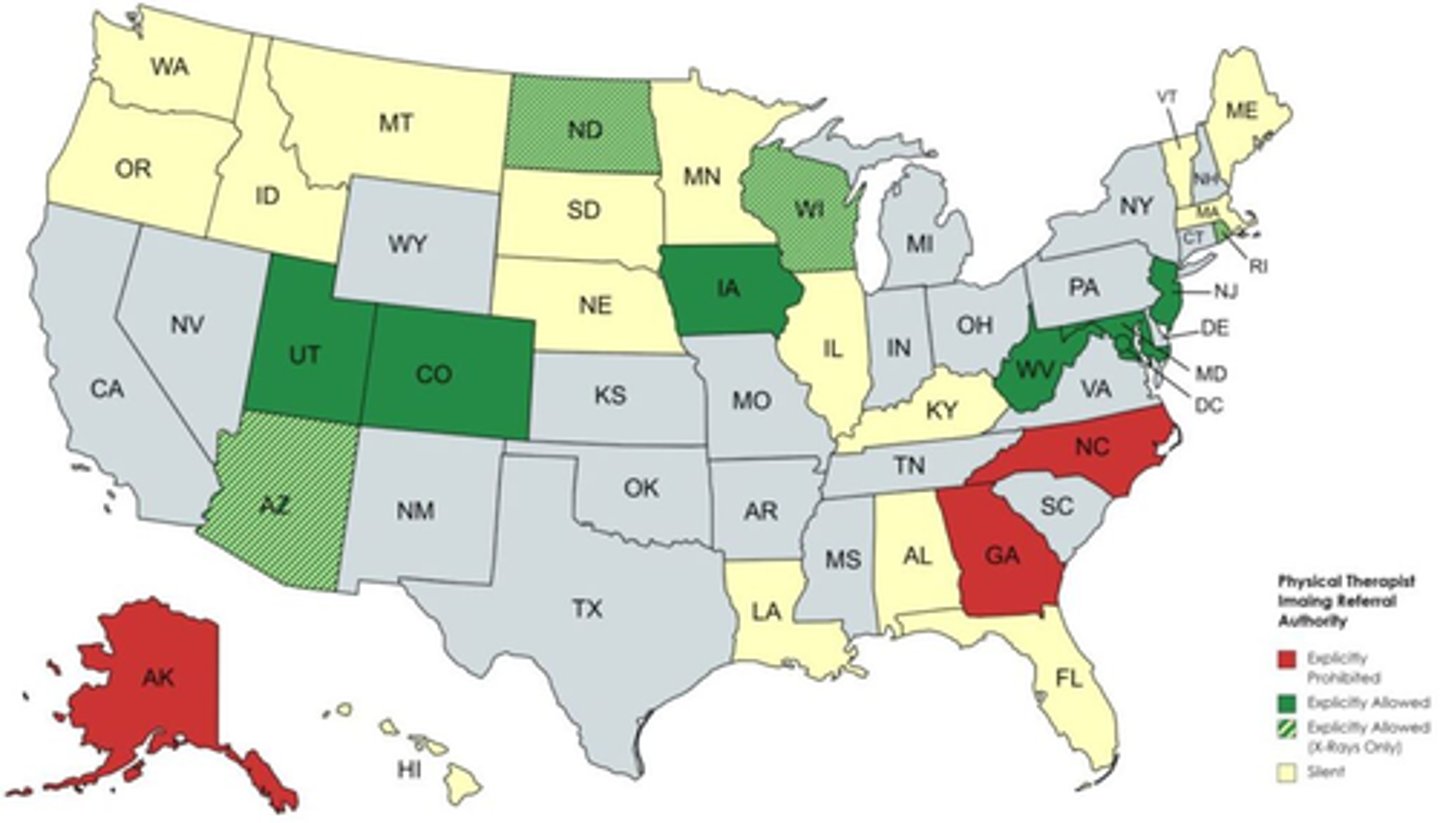
Colorado, DC, Maryland, Utah, NJ, WV, Iowa (2023)
Q: these states permit a PT from not only ordering plain films but also MRI
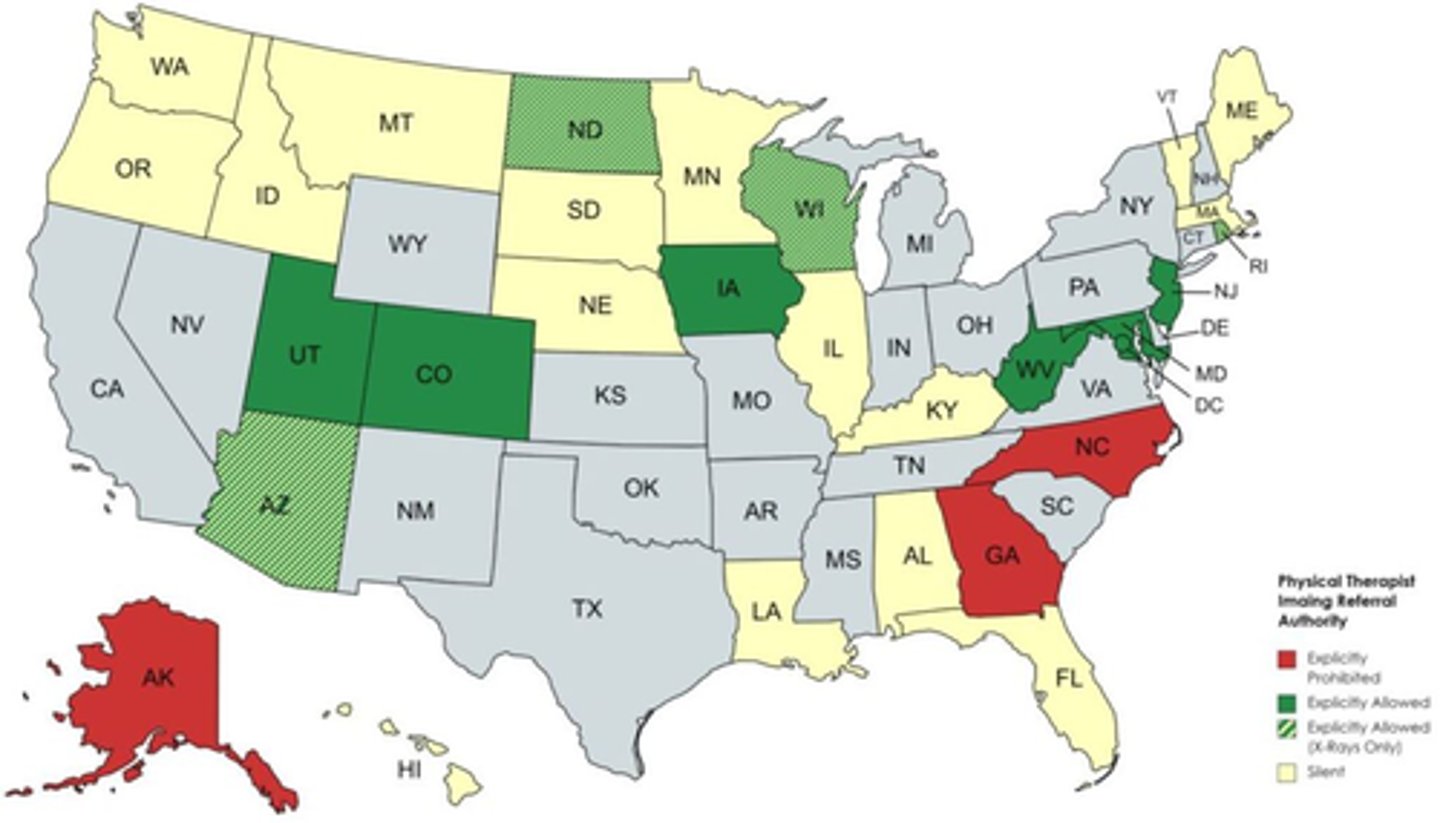
Iowa
Bonus: which state most recently granted PT's the right to order plain films AND MRI?
American College of Radiology (ACR) Appropriateness Criteria
Q: gold standard in decision making for ordering imaging studies
VOMIT and BARF
Which acronyms describe the over-utilization and inappropriate use/interpretation of imaging?
Brainless Application of Radiological Findings
What does 'BARF' stand for?
Victim of Medical Imaging Technology (note: the image is slightly off what we learned in class)
What does 'VOMIT' stand for?

Board Certified Specialists
Q: Mabry et al, 2022 publication identified this group as having the strongest imaging skill performance across the PT profession
Diagnostic ultrasound
Q: this imaging modality has the lowest student competency rate for faculty evaluation
Chest x-ray
Q: a coast to coast flight is similar in radiation exposure dose to which imaging modality
Air + bone = radiolucency
Bone + bone or bone + organs = radio-opaque
In terms of superimposition, air upon bone creates more ________ while bone on bone or organs on bone creates more ________
View: AP
Structure: left shoulder
State the type of view and structure being depicted.

View: right lateral
Structure: right knee
State the type of view and structure being depicted.
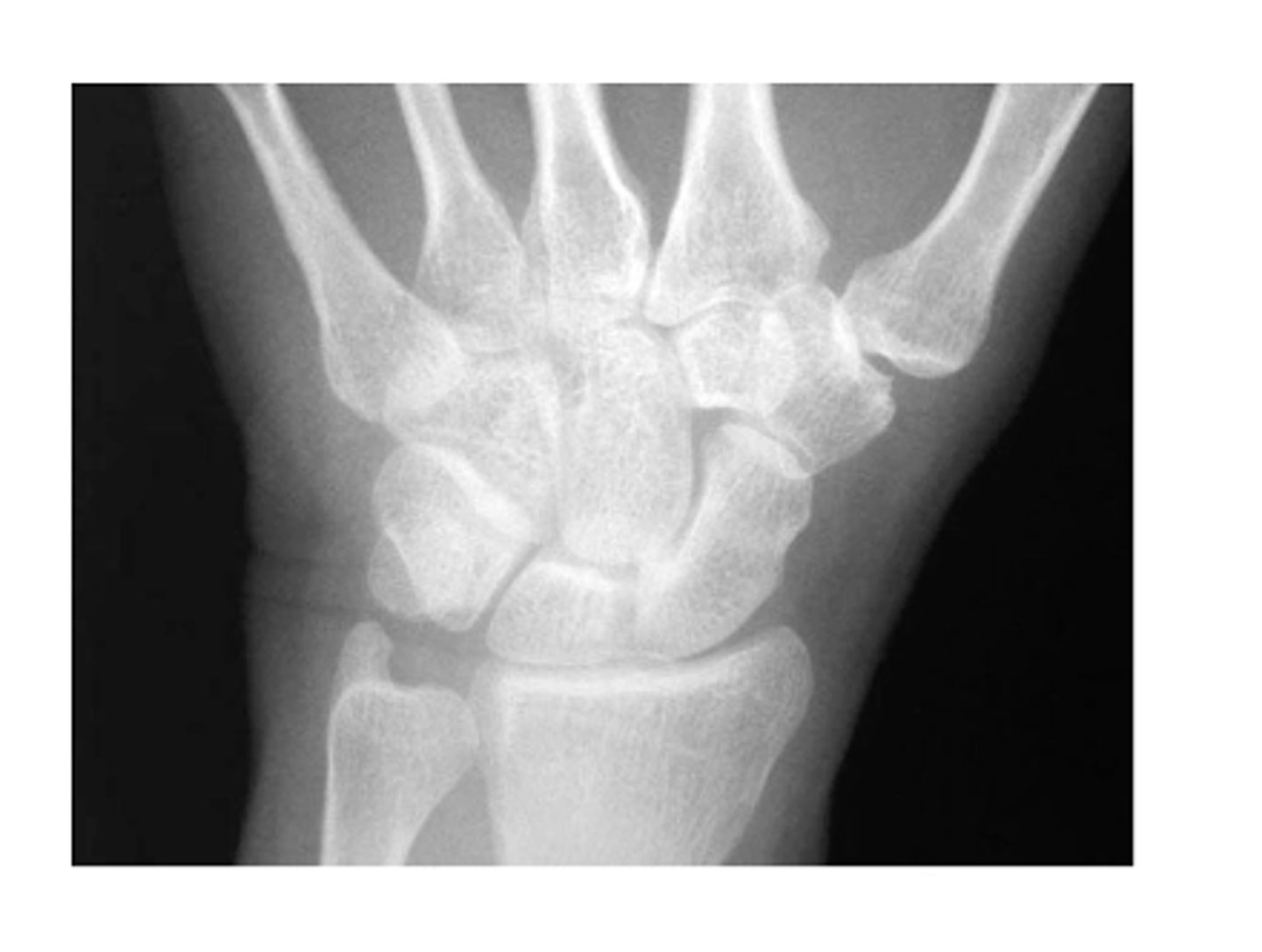
View: PA
Structure: left wrist
State the type of view and structure being depicted.
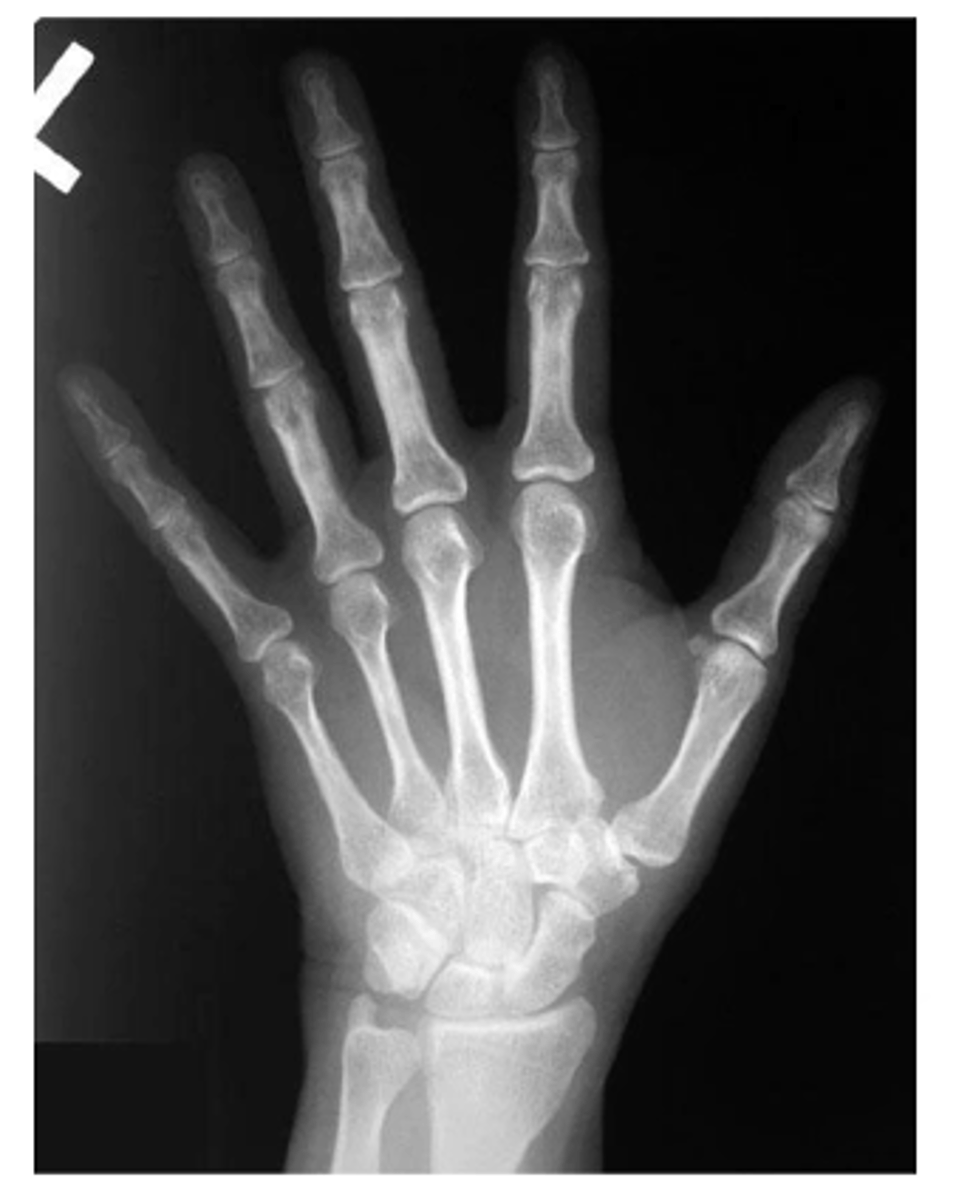
View: PA
Structure: left hand
State the type of view and structure being depicted.
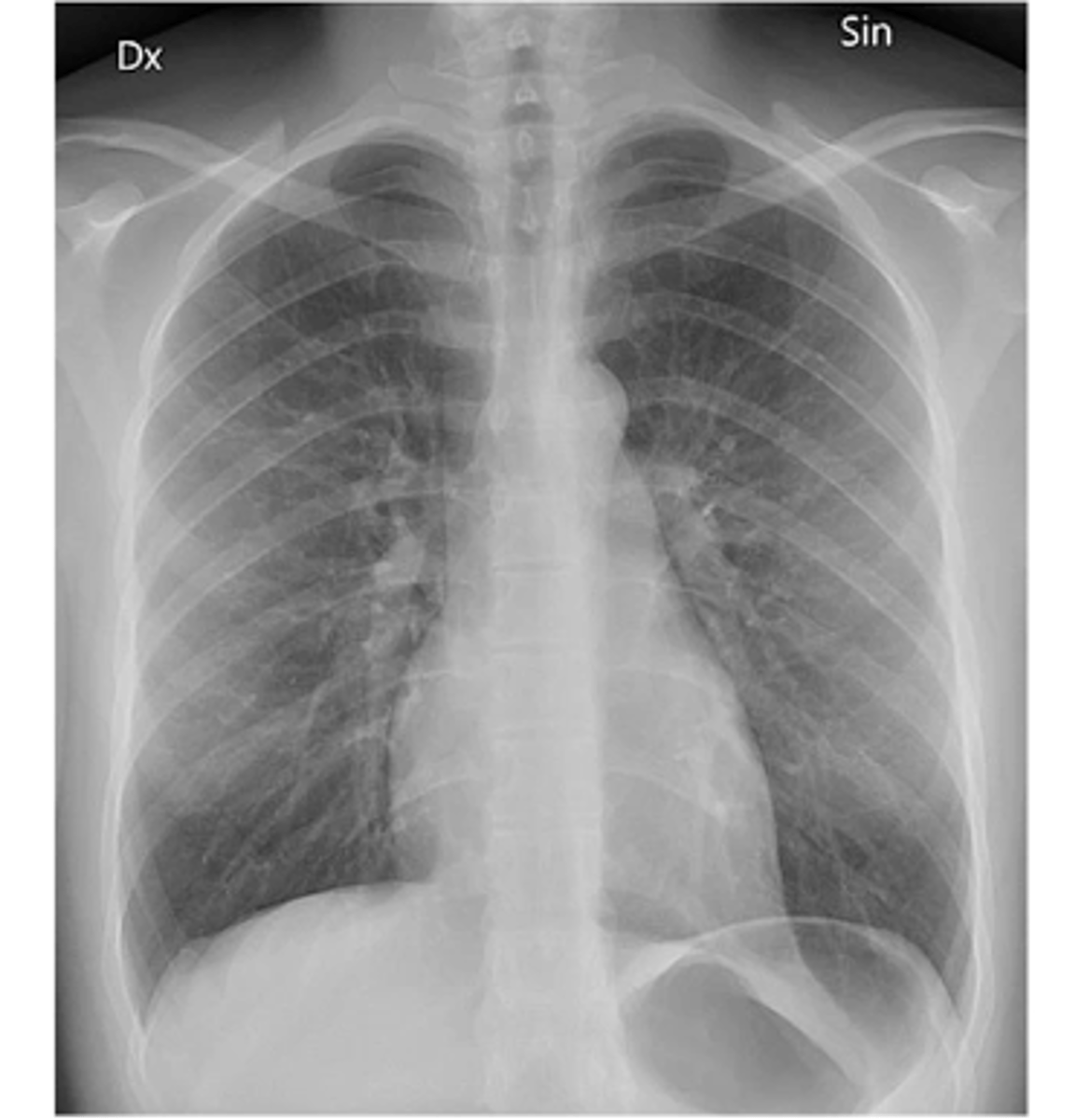
View: PA
Structure: chest
State the type of view and structure being depicted.
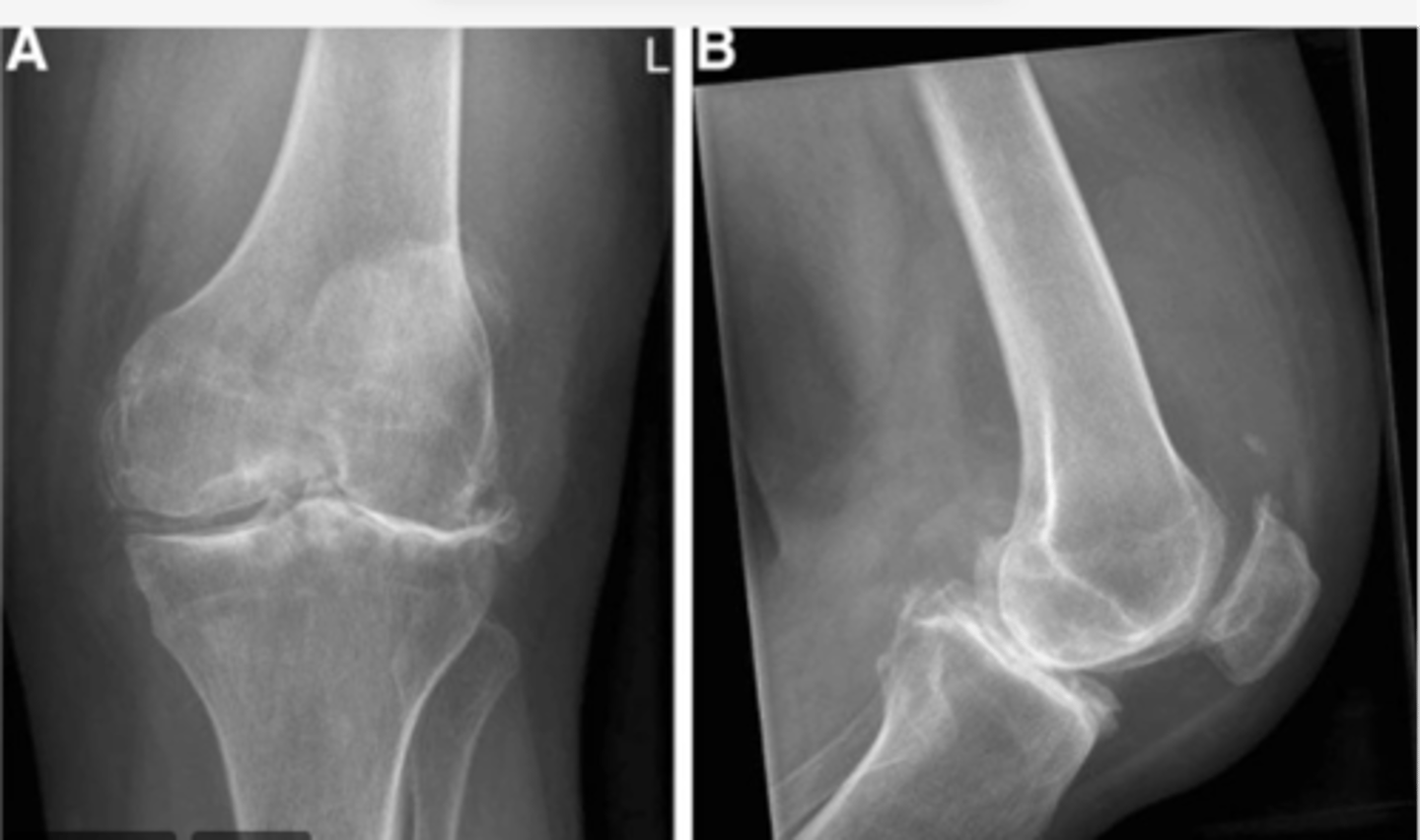
Femur shifted MEDIALLY over tibia; patella shifted SUPRALATERALLY; bone spur on the lateral tibial plateau
Work through your "ABCS". Start with A: alignment.
- General architecture (aberrant size, supernumerary, congenital abnormalities, absence, developmental deformities)
- General contour (irregularities, cortical outline, spurs and osteophytes, fracture)
- Alignment related to adjacent bones
In general, what encompasses "A: alignment"? (hint: 3x)
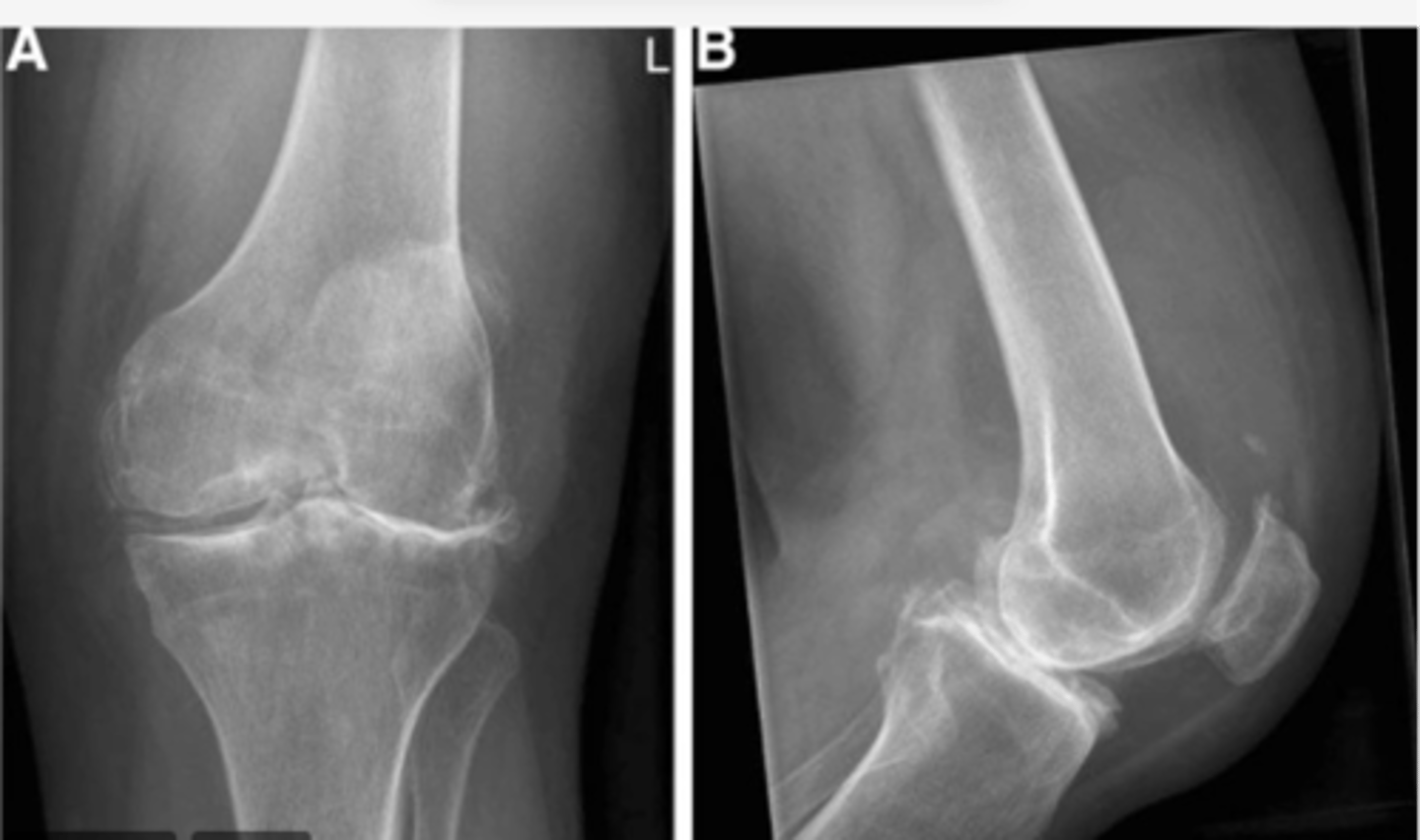
Sclerosis along bilateral tibial plateaus -- more pronounced laterally (hallmark of OA, along with the bone spur noted in "A: alignment")
Work through your "ABCS". Start with B: bone density.
- General (contrast b/w bone and adj. soft tissue, bone vs. bone)
- Textual abnormalities - trabeculae
- Local density changes - sclerosis
In general, what encompasses "B: bone density"? (hint: 3x)
Loss of joint space along the lateral tibiofemoral component. Diminished joint space along the medial side.
Work through your "ABCS". Start with C: cartilage space.
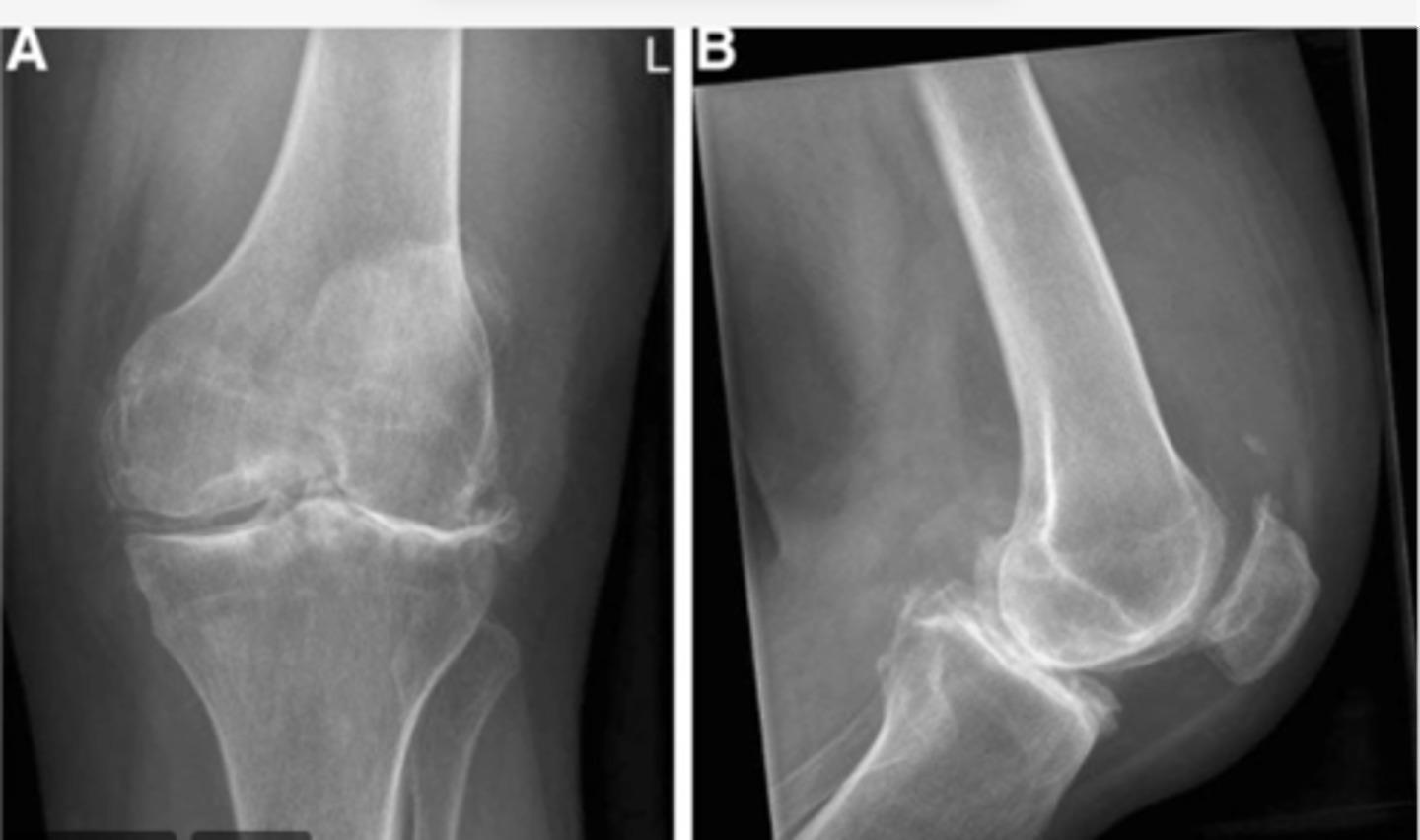
- "Space" can be an indirect assessment of radiolucent cartilage
- Subchondral bone: sclerosis vs. erosions
- Epiphyseal plates
In general, what encompasses "C: cartilage space"? (hint: 3x)
Calcification superior to the patella, Baker's cyst on the posterior side, LOTS OF SWELLING
Work through your "ABCS". Start with S: soft tissue.
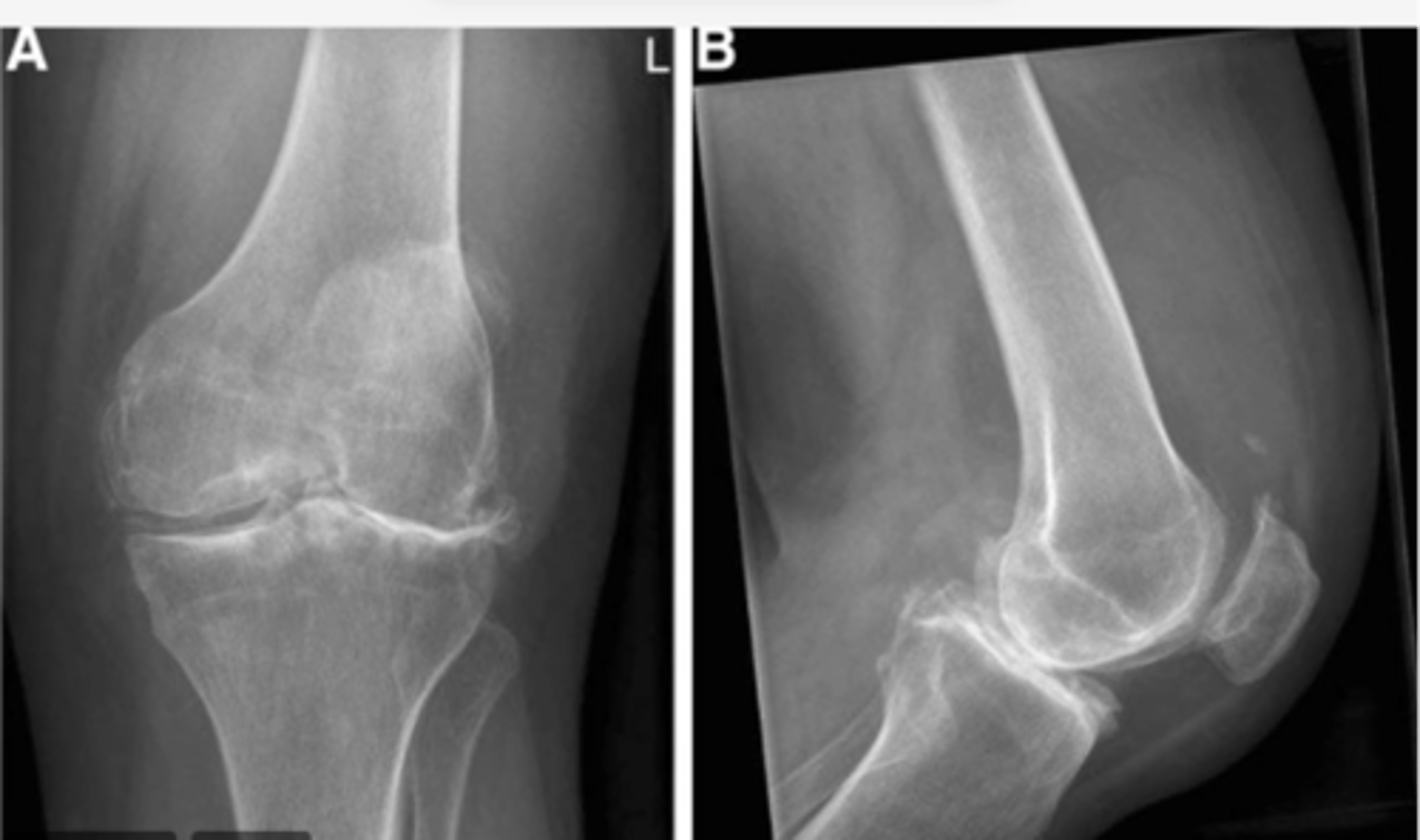
- Muscles, atrophy, swelling
- Fat pads and fat lines
- Joint capsules (effusion)
- Periosteum (solid, laminated, sunburst, Codman's triangle)
- Misc. (foreign bodies, calcifications)
In general, what encompasses "S: soft tissue"? (hint: 5x)
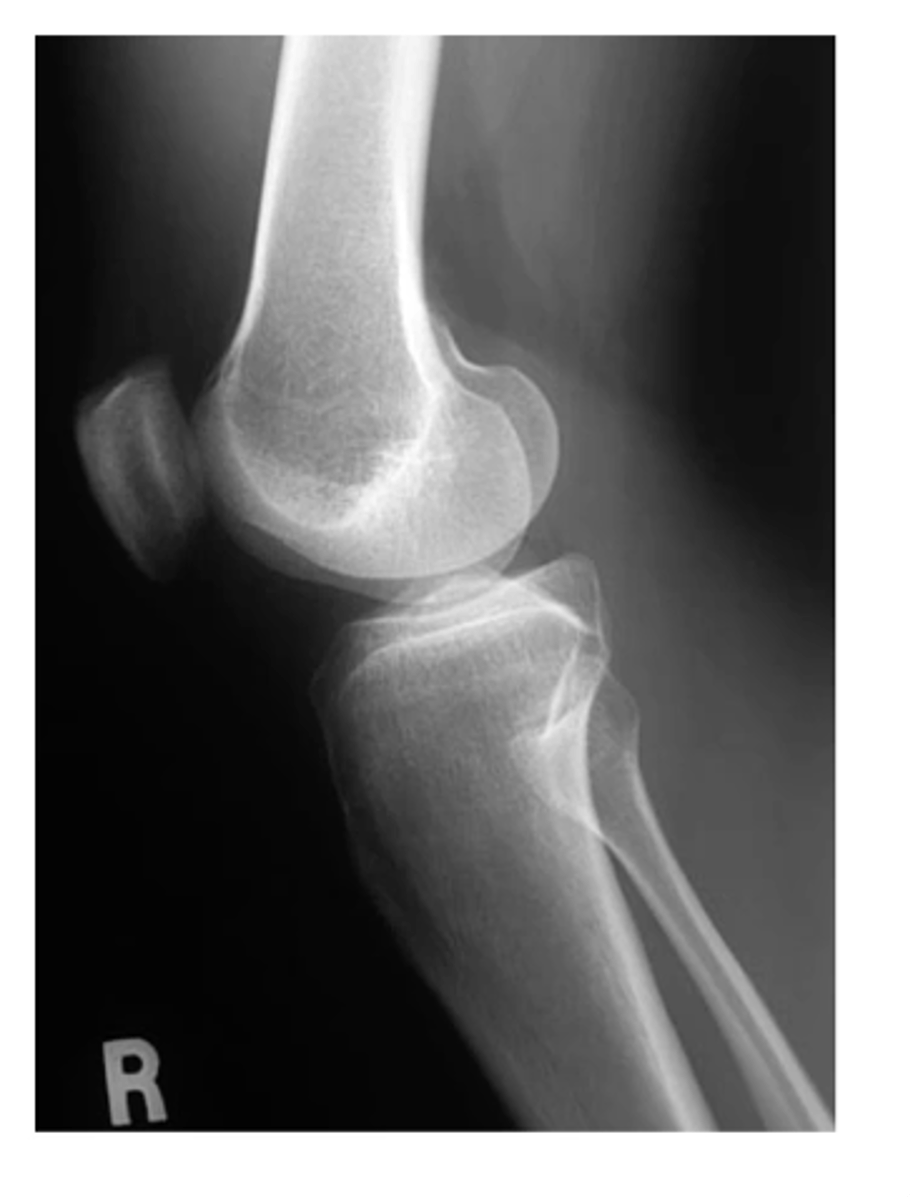
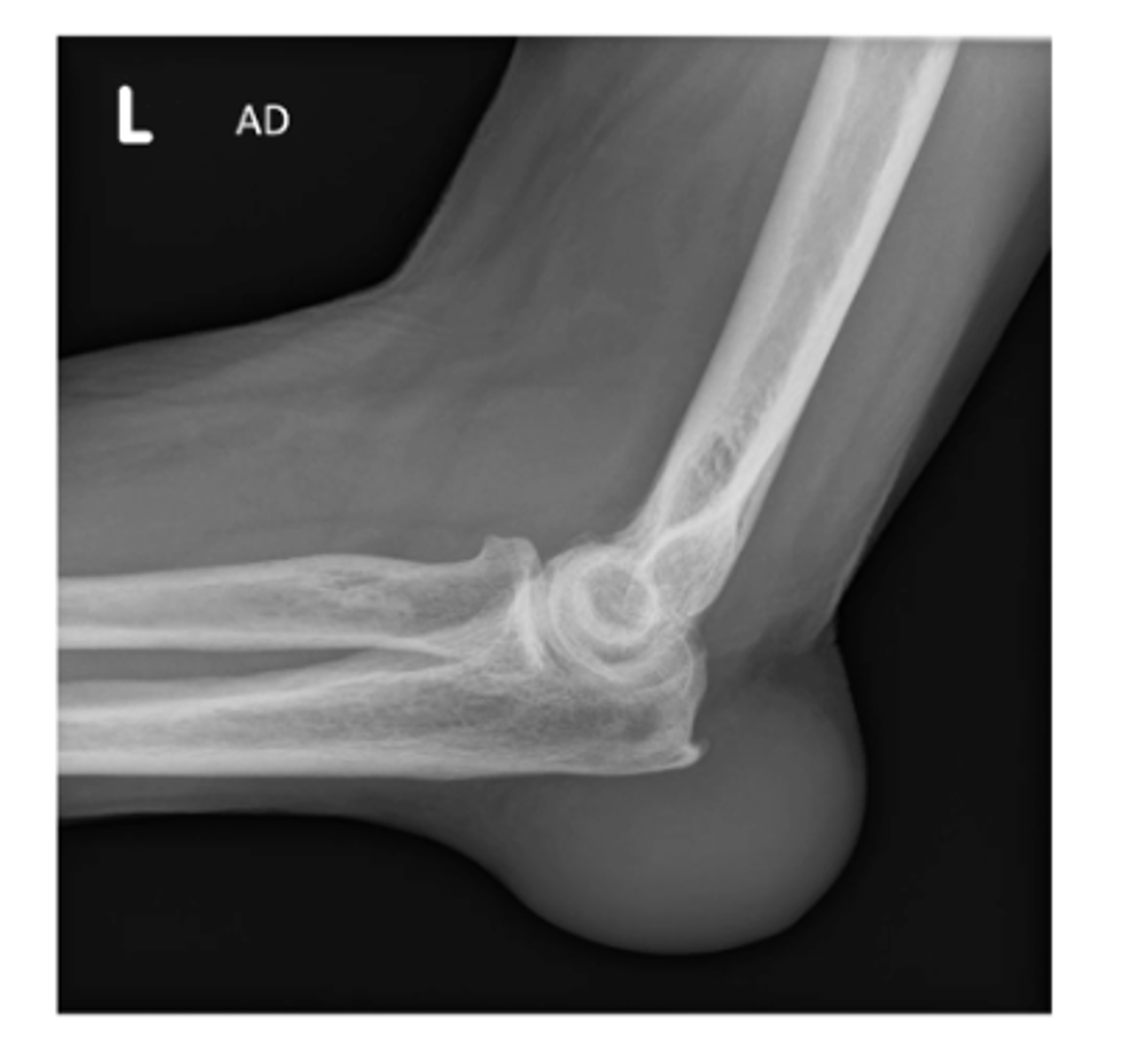
S: soft tissue...olecranon bursitis (typically caused by trauma or patients wearing slings due to the rubbing/friction)
Describe the MOST obvious "ABCS" component.
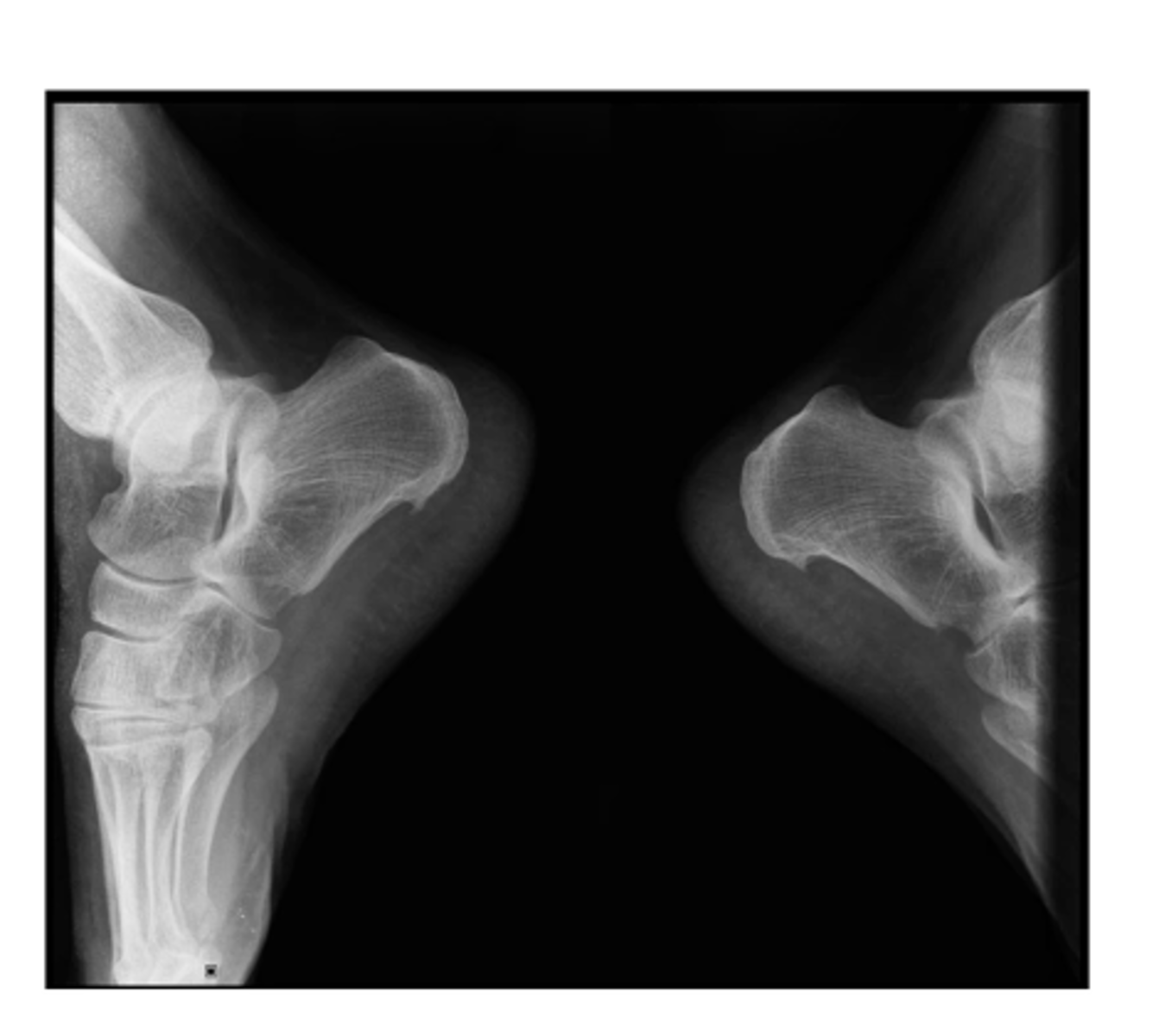
A: alignment...bilateral plantar heel spurs (associated w/ plantar fasciitis)
Describe the MOST obvious "ABCS" component.
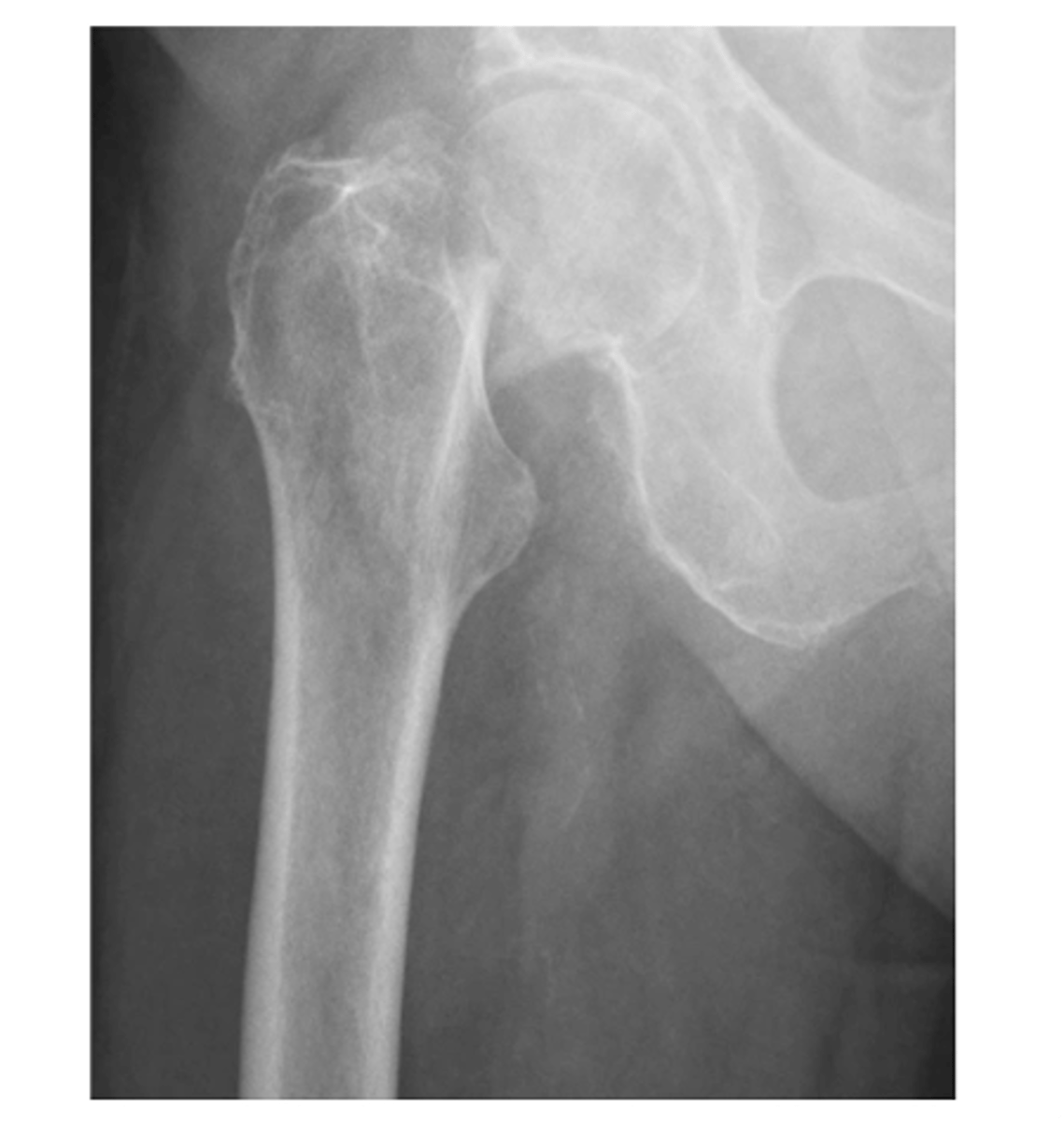
A: alignment...femoral neck fracture (the greater trochanter is superimposing on the head)
Describe the MOST obvious "ABCS" component.