AS 2
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
what is abstraction
removing irrelevant data to provide a solution
what’s an example of when abstraction is used
maps - it only shows what’s required, like roads
what are the benefits of abstraction
program development time is reduced as the model is simplified, meaning it can be delivered to the client quicker, client satisfaction as they don’t have irrelevant features, and the program is smaller so it takes less memory space and has quicker download time
what are the steps to creating a model
identify the purpose, find sources of info needed, and use this information to decide which details are needed
what is decomposition
breaking a problem into smaller and simpler parts so it’s easier to examine and develop a solution
what are the benefits of decomposition
tasks are easier to understand/ solve, programming or maintaining smaller problems are simpler, and sub-problems can be given to different teams
what’s pattern recognition
it identifies which parts of a program are similar and could use the same solution, leading to reusable code, i.e. subroutines, but each final part is written and tested with a separate procedure or function
in a flowchart, what represents the input or output
a parallelogram
in a flowchart what represents an IF or CASE statement
a diamond
in a flowchart how is FOR, REPEAT, and WHILE presented
an arrow
how is something assigned in a flowchart
a rectangle
what is a record
when several data types can be used under the same identifier
what is an array
a data structure containing several elements of the same data type
what is step-wise refinement
it’s the process of splitting problems into sub-tasks into smaller sub-tasks until its just one statement from which the task can be programmed
what’s the point of an array
multiple data types under the same identifier can be stored in a neat and accessible way. And each item can be accessed separately using an index
what’s the benefit of an array
it simplifies algorithms, and it has fast random access, where an item can be found using its index, whereas you must traverse through a linked list
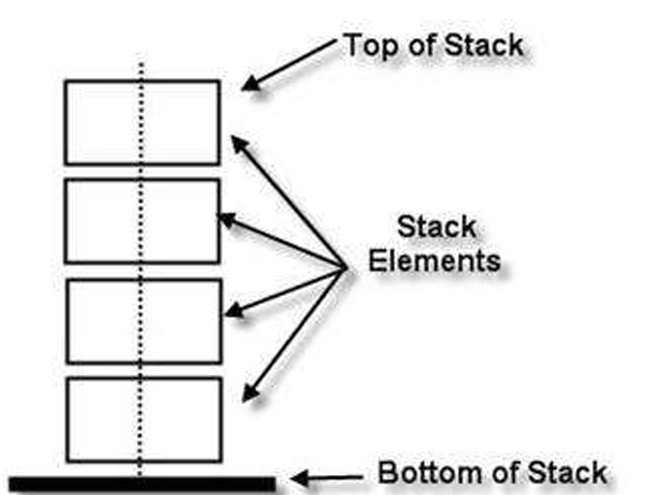
how does a stack operate
the last data in is the first out
how does a queue work
the first data in is the first out
how does a linked list work
each item points to the next item on the list
how do pointers work in a stack
There’s a base pointer at the first slot, and a top pointer at the last item. When there’s only one item in the stack, the pointers both point to it.
how do pointers work in a queue
it uses two pointers, a front pointer (the lower bound) at the first pointer, and a rear pointer (the upper bound) at the last. When they are equal, there’s only one item in the queue
how do pointers in linked list work
it uses a smart pointer that points to the first item in the linked list, every items is stored with a pointer to the next item, called a node, and the last item has a null pointer
what is a pointer in a linked list
a variable that stores the address of the node it points to
what are some features of a queue
it has a limited size so can become full, the position of the queue doesn’t change and so should be managed as a circular queue and the front/rear pointers are updated everytime the queue is
what are some features of a linked list
it uses two 1D arrays, one for the linked list and one for the pointers, linked lists can become full, and items can be removed from any position in list, the empty position must be managed as an empty linked list
how does a stack move its items
items can be added (push) or removed (pop)
how are items managed in a queue
items can be added (enqueue) and removed (dequeue)
how are items managed in a linked list
a new items will always be added to the start of the list
what are stacks used for
memory management, expression evaluation and recursion in backtracking
what are queues used for
to manage the files sent to a printer, buffers used with keyboards and scheduling
what are the advantages of a linked list
Due to its dynamic size, data is easier to add/delete, and it’s better for memory as it only uses what it needs, whereas array sizes are fixed, so empty spaces just waste storage
what’s the disadvantage of a linked list
more storage space is needed for the pointer fields , and its more complex to set up
how is a new node added in a linked list
check for an empty node, assign data to first empty node in free list (A), set A’s pointer to node after insertion (B), pointer previously pointing to B is now at A, and update the free list pointer to the next empty node
how is a linked list implemented
Two 1D arrays are declared, one for data and one for pointers, and elements from the same index is represented as 1 node, the variables for the start pointer and next free node pointer is declared, and an appropriate value is defined for the null pointer
how do you insert or add a new value in a queue
check the queue isn’t full, increment the end pointer, increment the variable storing the no. items in the queue, and store the data in the location pointed to by the end pointer
in a queue, how is a value removed
a check is made to ensure the queue isn’t empty, then the value at the queue pointer is removed & the pointer is incremented
how is a stack implemented
declare a 1D array (type string), the number of elements show how big the stack needs to be and assign the stack pointer/ size of stack/ max value of pointer variables.
use the stack pointer as index to array, initialise pointers and variables to indicate empty stack, store each item on stack as one array element, and push or pop routines used to operate it
what’s a linked list’s purpose
to use an array to implement a stack, queue or binary tree
what’s the purpose of a program development lifecycle
to develop a successful program or suite of programs that is going to be used by others to perform a specific task
what are the stages of a program development lifecycle
analysis, design, coding, testing and maintenance
what is the analysis stage
where the problem is identified, investigated, and alt solutions are proposed
what is the design stage
using the program specification to show how the program should be developed
what is the coding stage
writing the program or suite of programs
what is the testing stage
testing the program to make sure it works under all conditions
what is the maintenance stage
the process of making sure the program continues to work during use
what is the waterfall model
a linear program cycle, where each stage is completed before the next is begun
How does the waterfall method work
it’s linear, well documented - as documents are completed at every stage, and it has low customer involvement, only at the start and end of the process
what are the benefits of the waterfall model
it’s easy to manage, understand and use. The stages don’t overlap and it works well for smaller programs, when the requirements are known and understood.
what are the downsides of the waterfall model
it’s difficult to change the requirements at a later stage, not suitable for programs where the requirements could change, or longer / more complex projects, and the working program is produced late in the cycle
what is the iterative model
a program development cycle where a subset of requirements are found and expanded, after each iteration, repeating until the whole system is finished.
what is the iterative model’s principle
it uses iterative development, parts of the system are produced after every iteration. It has high customer involvement as it can be presented after every iteration
what are the benefits of the iterative model
working programs are developed early on in the lifecycle, it’s easier to test and debug smaller programs, it’s more flexible - easier to alter requirements, and customers are involved at every iteration, no surprises
what are the drawbacks of the iterative model
The whole system needs to be defined at the start so it can be broken down, it needs good planning overall and for each stage, and it’s not suitable for short/ simple projects
what is rapid application development
when different parts of the requirement are developed in parallel, using prototyping to provide early user involvement in testing
what are the principles of rapid application development
it reuses previously written code / use automated code generation where possible, requires minimal planning, and it has high customer involvement as they can use prototypes during development
what are the pros of rapid application development
it has reduced development time, quick and frequent customer feedback, it’s flexible as requirements can be changed, and due to parts being developed side by side, modification is easier as each part must work independently
what are the downside of rapid application development
the system must be able to split into modules, it needs a strong team of skilled developers and it’s not suitable for short/ simple projects
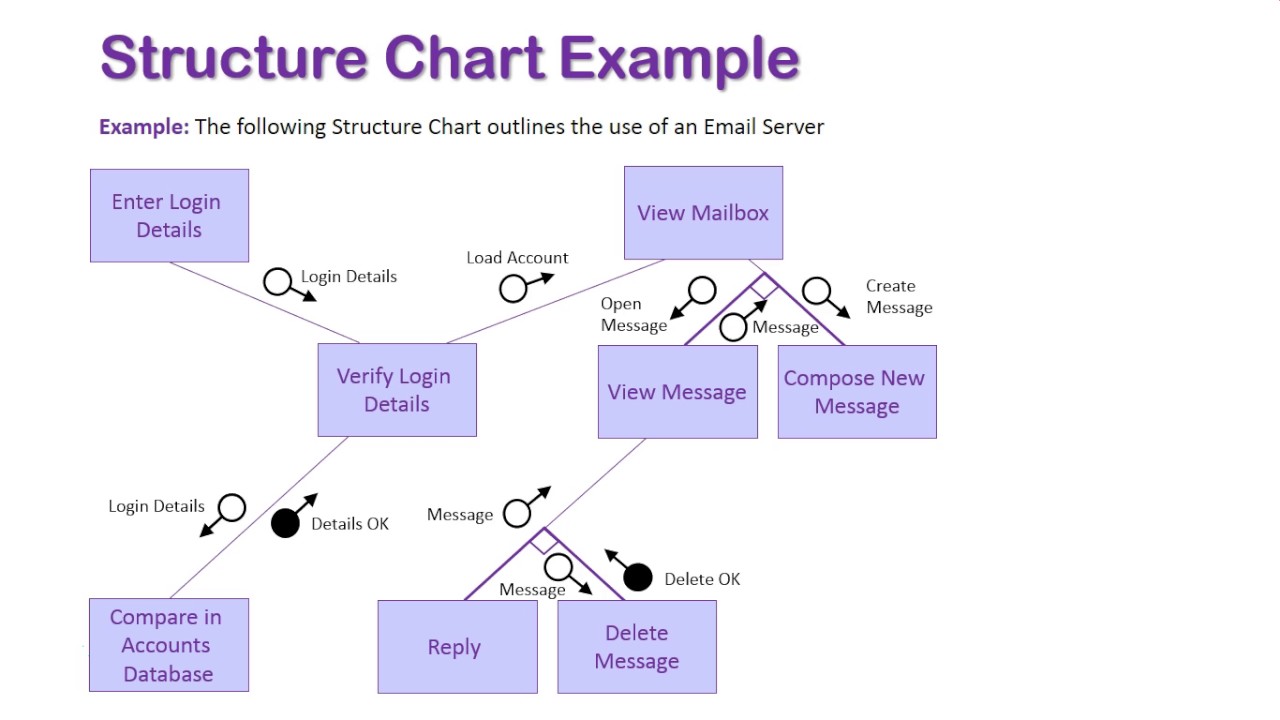
what’s a structure chart
a modelling tool used to break down a problem into a set of subtasks; it shows the structure of different modules and how they connect/interact with each other. It shows selection and or repetition
what are the arrows in a structure chart
parameters
what is a state transition diagram
it’s a diagram showing the behaviour of a finite state machine
how does a state transition diagram look
states are nodes (circles), transitions are interconnecting arrows, events are labels on the arrow, a condition is specified in square brackets after the event label, an initial state is shown via an arrow with a black dot, and a stopped state is shown by a double circle
fault in executable code means an error in what, and how do we avoid this
a fault in the program design, to avoid this create a detailed specification at the end of the analysis stage and use structured methods, i.e. structure charts
how are errors avoided in the coding stage
by keeping details private, and bundling data to avoid interference
where may faults or bugs show up and how do we fix this
bugs will be exposed in the testing stage, and are corrected during the maintenance stage
what are the three types of error
syntax, logical and run-time errors
what is a syntax error
an error in the grammar of code, these need to be fixed before the program is executed, and many IDEs offer how to fix them
what is a logic error
a problem with the logic of a program, resulting in the program not knowing what to do, these are found when the program is tested and most IDEs let you single step through the program to find these errors, a trace table is used to manually check
what’s a run-time error
an error found when a program is executed, it may stop unexpectedly or go into an infinite loop
what is a test strategy
A general overview of the testing principles needed to meet the requirements of a program. It shows how and when the program should be tested
what is a test plan
a detailed list showing all the stages of testing and every test that will be performed for a particular program
what is a walkthrough
a formalized version a dry run, it uses predefined test cases, where someone takes the team through the dry run process
what testing may occur during the design stage
during the design stage, pseudocode may be written and tested using a dry run, which works through a program or module manually
what are the types of data
normal, abnormal, extreme and boundary
what is normal data
(i.e. if given range 10<= x<=30
data accepted by a program and used to show the program is working as expected (i.e. 10-30)
what is abnormal data
(i.e. if given range 10<x<30)
data rejected by a program as it is unsuitable or could cause problems
(i.e. 78)
what is extreme data
(i.e. given range 10<= x <= 30)
data on the limit of what is accepted by the program
(i.e. 10 would be the lower limit and 30 would be the upper limit)
what is boundary data
(i.e. 10<= x <= 30)
data on limit of what is accepted or data just outside the limit of thar rejected
(i.e. accept 10 and 9 as the lower limit and accept 30 and 31 as the upper limit, or 9 and 31 should be rejected)
while a program is being developed, what kind of testing are used
white box, black box, integration, and stub testing
what is a white box
where every aspect of a procedure is tested in detail, involving the structure and logic of every path in a module
what is a black box
it tests a module’s input and output
what is integration
where separately written modules are tested to make sure they work together, done during the testing phase
what are the types of testing used when a program is completed
alpha, beta and acceptance testing
what’s the order of testing a program when it’s completed
alpha testing is first, then beta, then acceptance
what is alpha testing
the completed or nearly finished program is tested by the development team
what is beta testing
when a small group of users test the completed program before it’s released
what is acceptance testing
testing of a completed program to show the customer it works as required
what are the types of program maintenance
corrective, perfective and adaptive maintenance
why is program maintenance needed
to fix programs that don’t work in unforeseen circumstances
what is corrective maintenance
the correction of any errors that appear during use, changes are made to correct bugs
what is perfective maintenance
used to improve performance of a program during use
what is adaptive maintenance
altering a program to perform new tasks due to a change in the specification/ requirement
how is a set of data stored into a file
a set of data is collapsed into a single line, separated by a special character
what are the advantages of storing data in a file
data is saved after the computer is switched off (stored permanently) and data doesn’t need to be re-entered when a program is re-run
what are some features that make code easier to understand
indentation, white space, comments, capitalised words etc.
why is ‘good practise’ important
it makes code easier to understand. describes the purpose of code/ identifies and makes code easier to debug and maintain
what are constants and why are they useful
used for fixed values, helps avoid changing values accidentally, and it makes a program easier to maintain / understand
what’s the benefit of using a program library/library routines during development
its already been tried and tested free of errors, it performs a function a user may not be able to program themself, and it speeds up development time
what is the use of a program library/ library routine
it can be used where code is repeated many time within the code, it reduces the complexity of a program and it makes testing / debugging easier
when are while/ repeat loops used
when the number of iterations (repetition) is not known