skin
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
skin
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
1
New cards
Epidermis
outermost, thin cellular membrane
2
New cards
Dermis
middle layer, dense fibrous, connective tissue
3
New cards
Subcutaneous tissue
thick, fat-containing tissue
4
New cards
Hair
cells filled with the hard protein
(keratin)
(keratin)
5
New cards
Hair follicles
shafts that hold the hair
6
New cards
Nails
hard keratin plates covering the toes and fingers
7
New cards
Glands
sebaceous and sweat
8
New cards
Sebaceous glands
secrete oily sebum into the hair follicle to lubricate, subject to bacterial growth
9
New cards
Sweat glands
secrete into pores to moisten and cool, subject to bacterial growth
10
New cards
basal layer
Deepest region of the epidermis, gives rise to all the epidermal cells
11
New cards
collagen
Structural protein found in the skin and connective tissue
12
New cards
cuticle
Band of epidermis at the base and sides of the nail plate
13
New cards
eccrine sweat gland
Most numerous sweat-producing exocrine gland in skin
14
New cards
epithelium
Layer of skin cells forming the outer and inner surfaces of the body
15
New cards
hair follicle
sac where hair grows
16
New cards
integumentary system
The skin and its accessory structures such as hair and nails
17
New cards
lunula
Half-moon-shaped, whitish area at the base of a nail
18
New cards
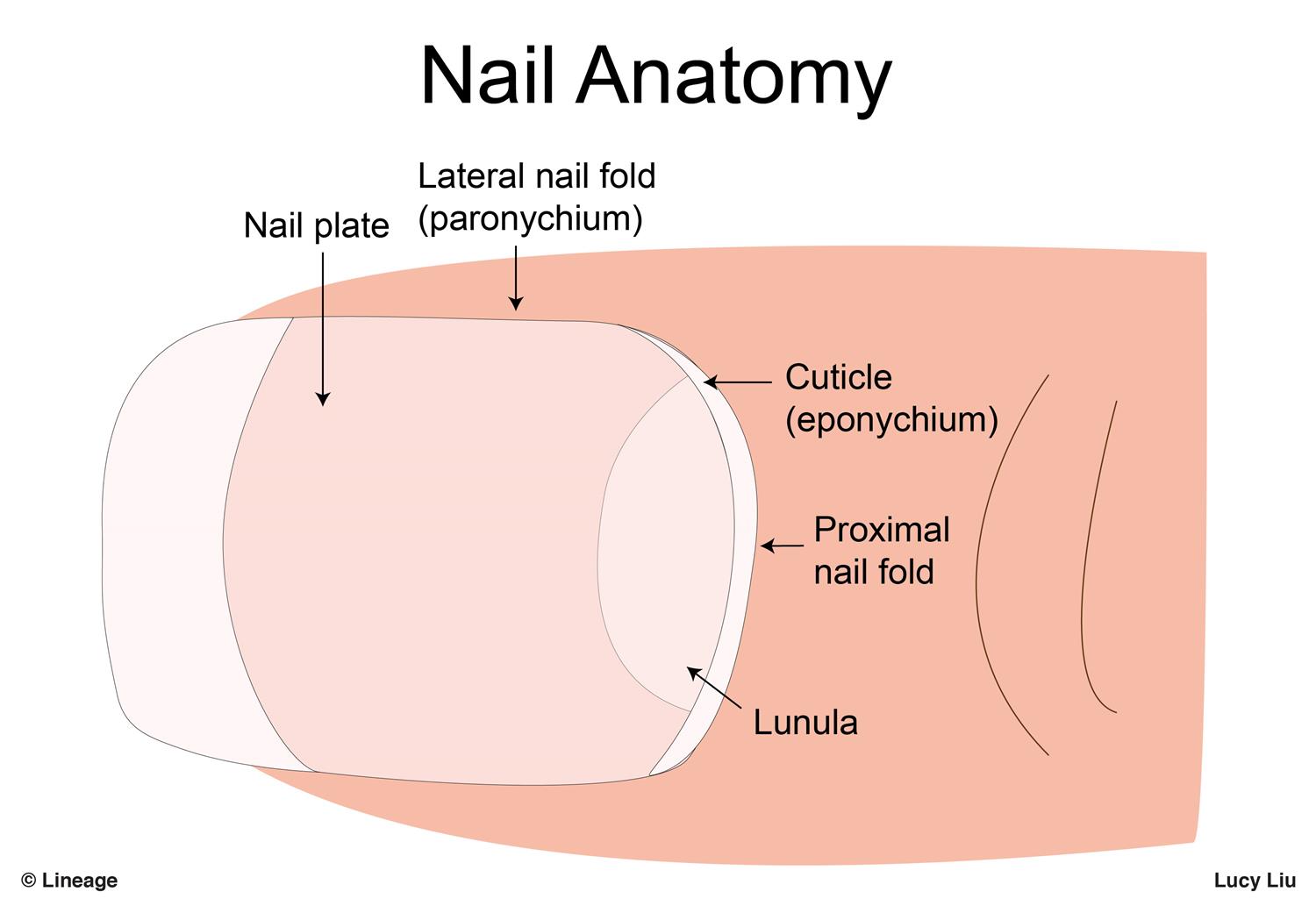
paronychium
Soft tissue surrounding the nail border
19
New cards
squamous epithelium
Flat, scale-like cells composing the epidermis
20
New cards
stratified
arranged in layers
21
New cards
stratum (plural - strata)
A layer (of cells)
22
New cards
stratum corneum
Outermost layer of the epidermis consists of flattened, keratinized cells
23
New cards
adip/o
fat
24
New cards
albin/o
white
25
New cards
caus/o
burn, burning
26
New cards
cauter/o
heat, burn
27
New cards
cutane/o
skin
28
New cards
derm/o
skin
29
New cards
dermat/o
skin
30
New cards
diaphor/o
profuse sweating
31
New cards
erythem/o
redness
32
New cards
erythemat/o
redness
33
New cards
hidr/o
sweat
34
New cards

ichthy/o
scaly, dry
35
New cards
kerat/o
hard, horny tissue
36
New cards
leuk/o
white
37
New cards
lip/o
fat
38
New cards
melan/o
black
39
New cards

myc/o
fungus
40
New cards

onych/o
nail
41
New cards
phyt/o
plant
42
New cards
pil/o
hair, hair follicle
43
New cards
py/o
pus
44
New cards
rhythid/o
wrinkle
45
New cards
seb/o
sebum
46
New cards
squam/o
scale-like
47
New cards
steat/o
fat
48
New cards

trich/o
hair
49
New cards
ungu/o
nail
50
New cards
xanth/o
yellow
51
New cards

xer/o
dry
52
New cards
anthrac/o
black
53
New cards
chlor/o
green
54
New cards
cirrh/o
tawny yellow
55
New cards
cyan/o
blue
56
New cards

eosin/o
rosy
57
New cards
jaund/o
yellow
58
New cards
lute/o
yellow
59
New cards
melan/o
black
60
New cards

poli/o
gray
61
New cards
pustul
pus-filled
62
New cards
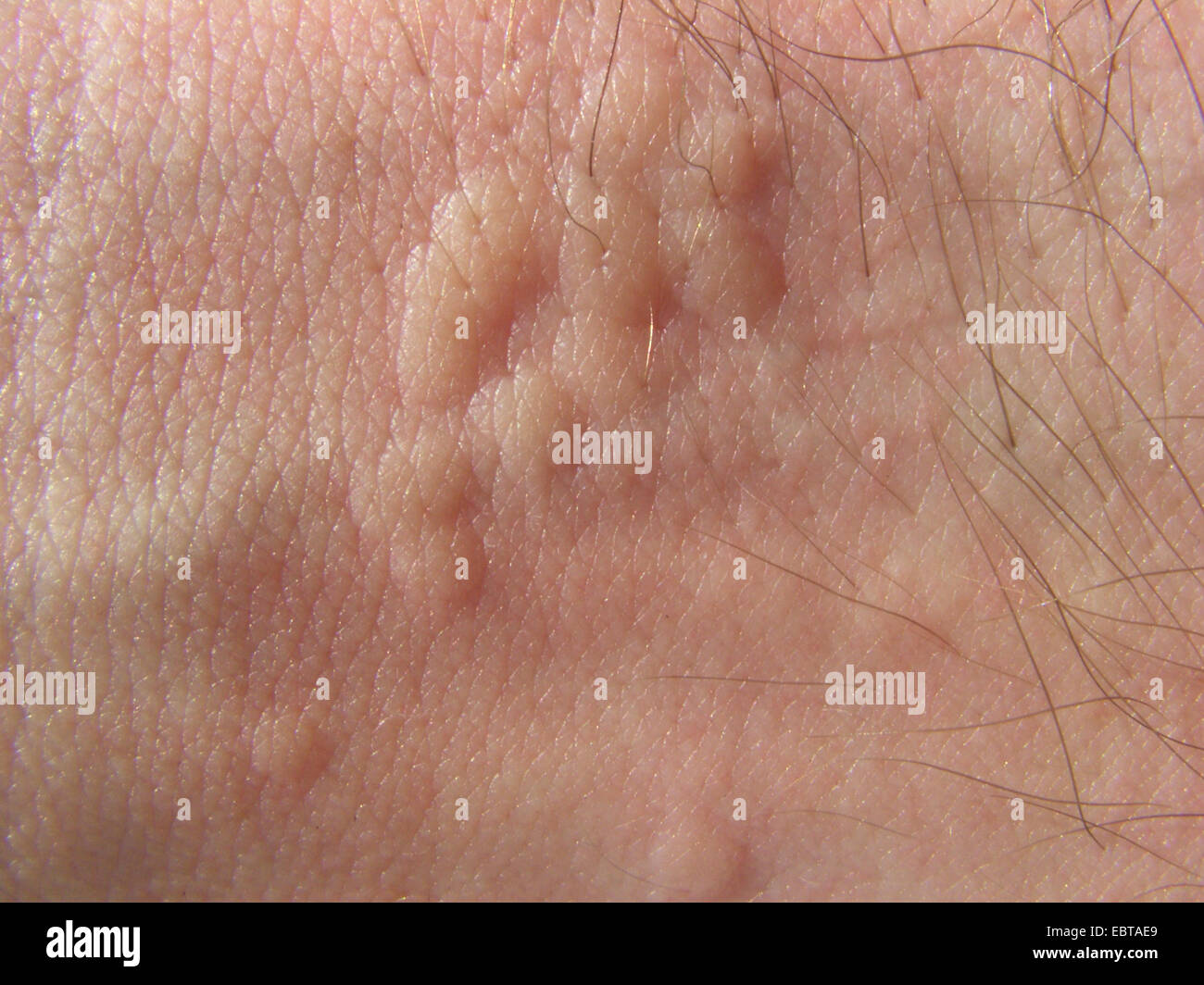
whea
clear fluid, blister
63
New cards
cys
fluid or semisolid thick-walled filled sac
64
New cards
vesicl
clear fluid, blister
65
New cards
crust (scab)
dried serum and cellular debris
66
New cards
poly
benign growth extending from mucous membrane surface
67
New cards
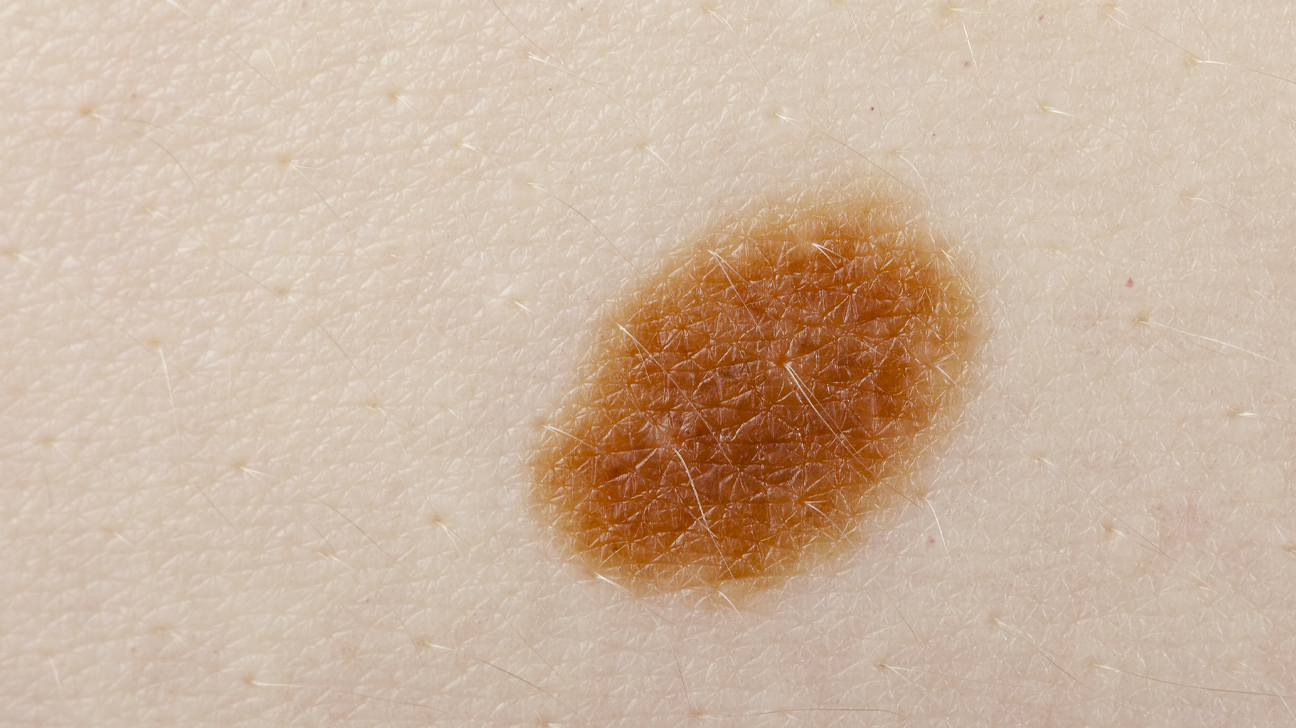
macul
discolored, flat
68
New cards
erosio
wearing away, loss of epidermis
69
New cards
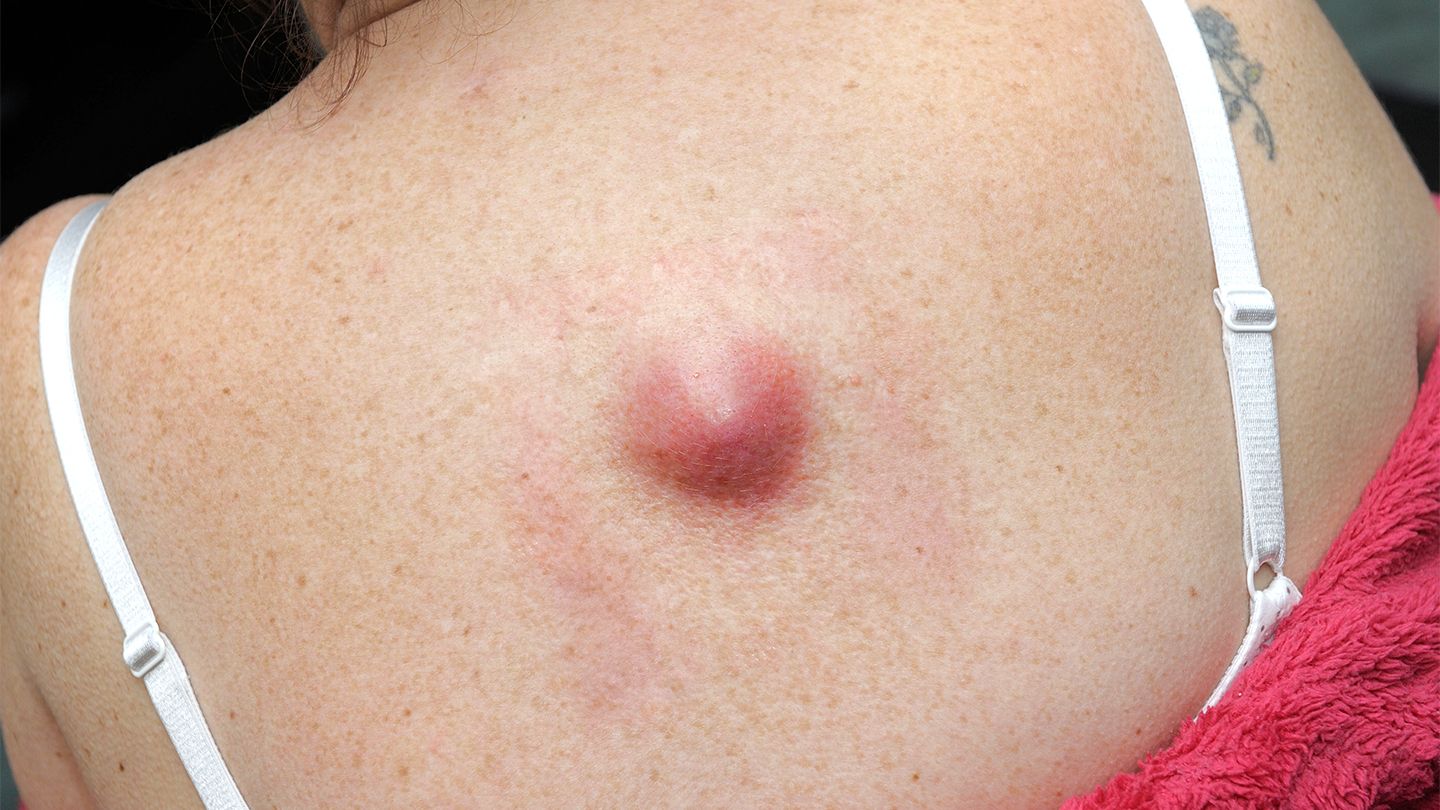
nodul
solid, elevated mass, more than 1 cm
70
New cards
fissur
slit, groove
71
New cards
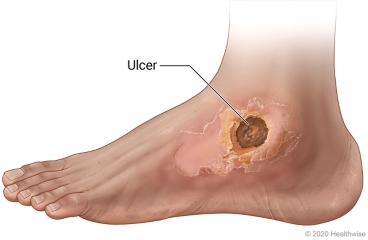
ulce
open sore on skin or mucous membrane
72
New cards
papul
small, solid elevation, pimple or plaque
73
New cards
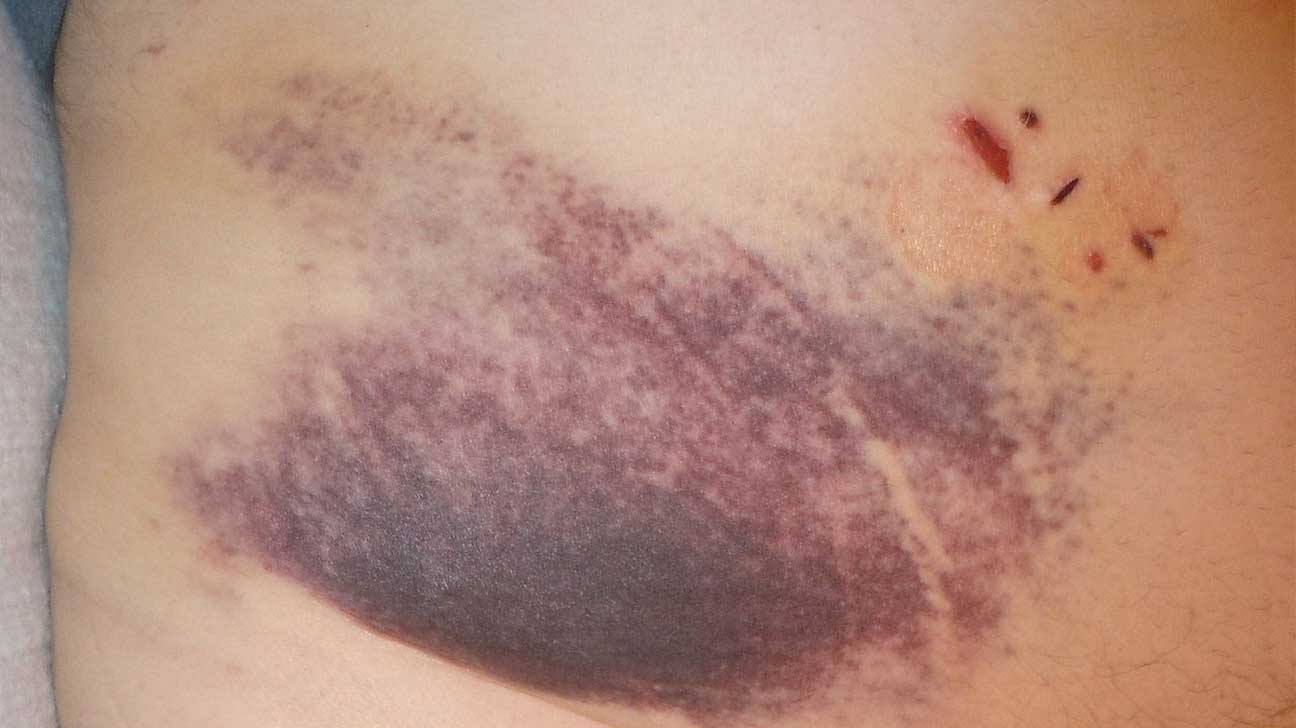
Ecchymosis
blue-black marks on the skin, bruise
74
New cards
Petechia
small pinpoint hemorrhage
75
New cards
Urticaria
an acute allergic reaction with red, round wheals on the skin (hives)
76
New cards
Acne
papular and pustular eruption of skin with increased production of sebum
77
New cards
Cellulitis
a diffuse acute infection of the skin
78
New cards
Eczema (atopic dermatitis)
inflammation of the skin with erythematous and papulovesicular lesions caused by allergy
79
New cards
Exanthematous viral diseases
a rash due to virus (for example, rubella)
80
New cards
Gangrene
the death of tissue with loss of blood supply
81
New cards
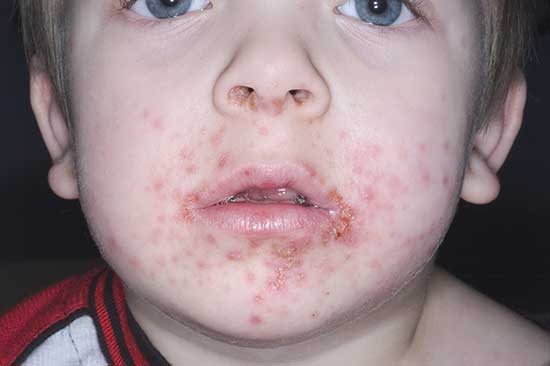
Impetigo
contagious pyoderma caused by staph or strep
82
New cards
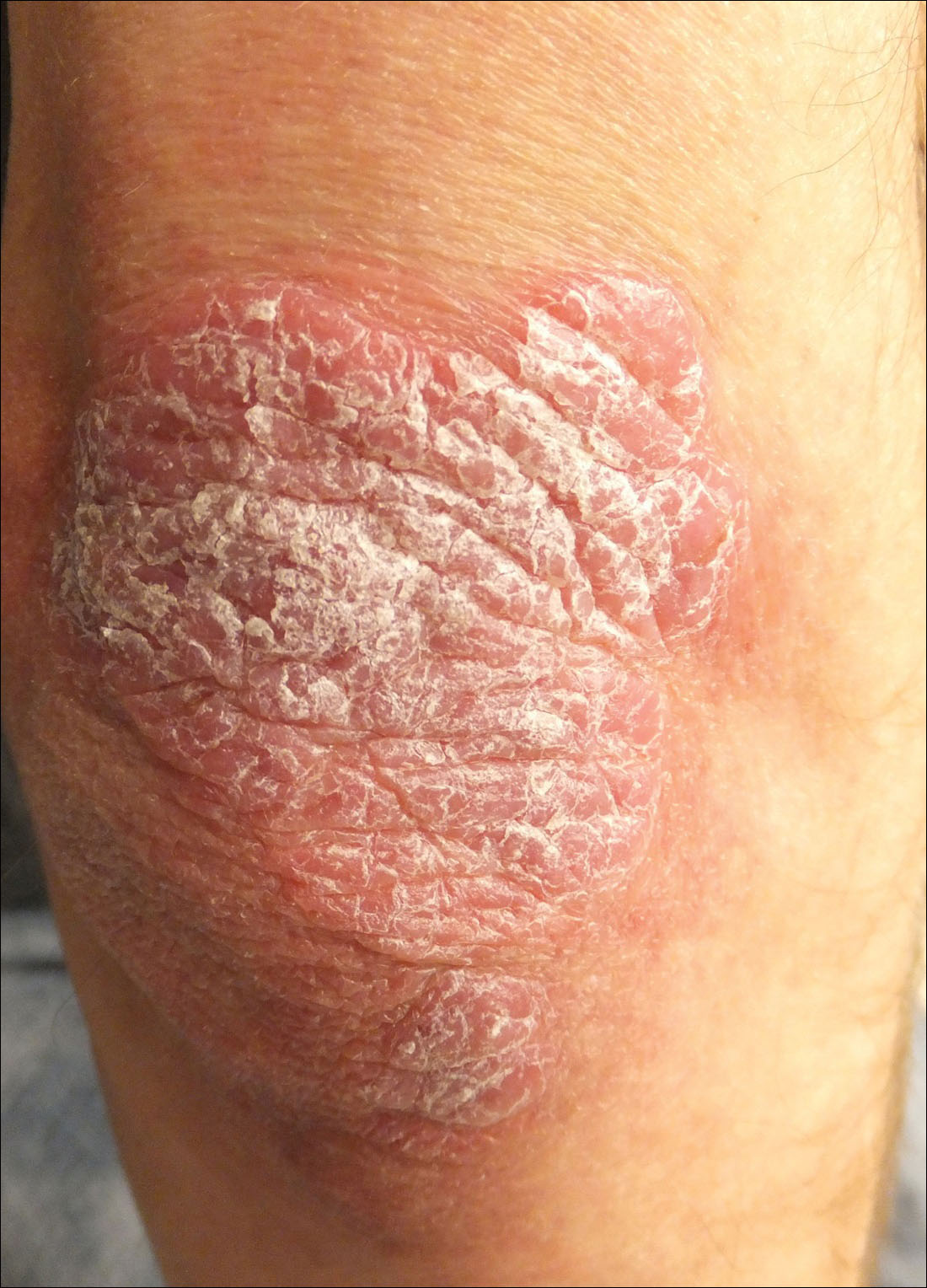
Psoriasis
chronic recurrent dermatosis with silver gray scales that itch
83
New cards
Scabies
parasitic (tiny mites) and infectious pruritus
84
New cards
Scleroderma
chronic and progressive disease of the skin with hardening of connective tissue
85
New cards
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
an inflammatory disease of collagen in the skin, joints, and internal organs
86
New cards
Urticaria (hives)
an acute allergic reaction in which red, round wheals develop on the skin
87
New cards
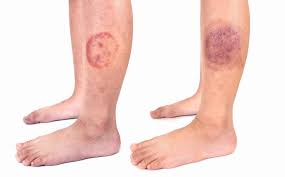
Tinea
infection of the skin caused by a fungus
88
New cards
Keratosis
thickened area of epidermis
89
New cards
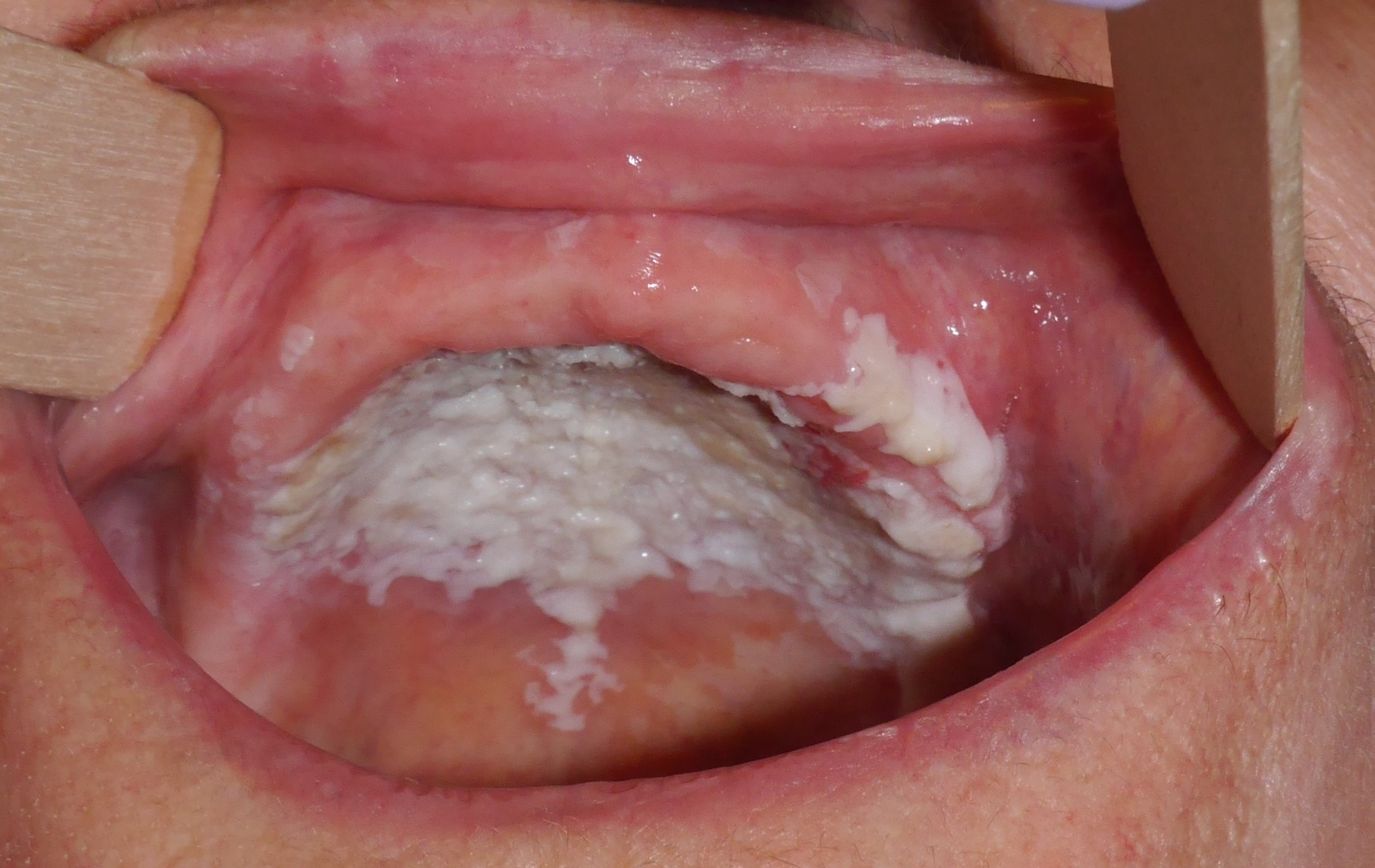
Leukoplakia
white, thickened patches on tongue or cheek
90
New cards
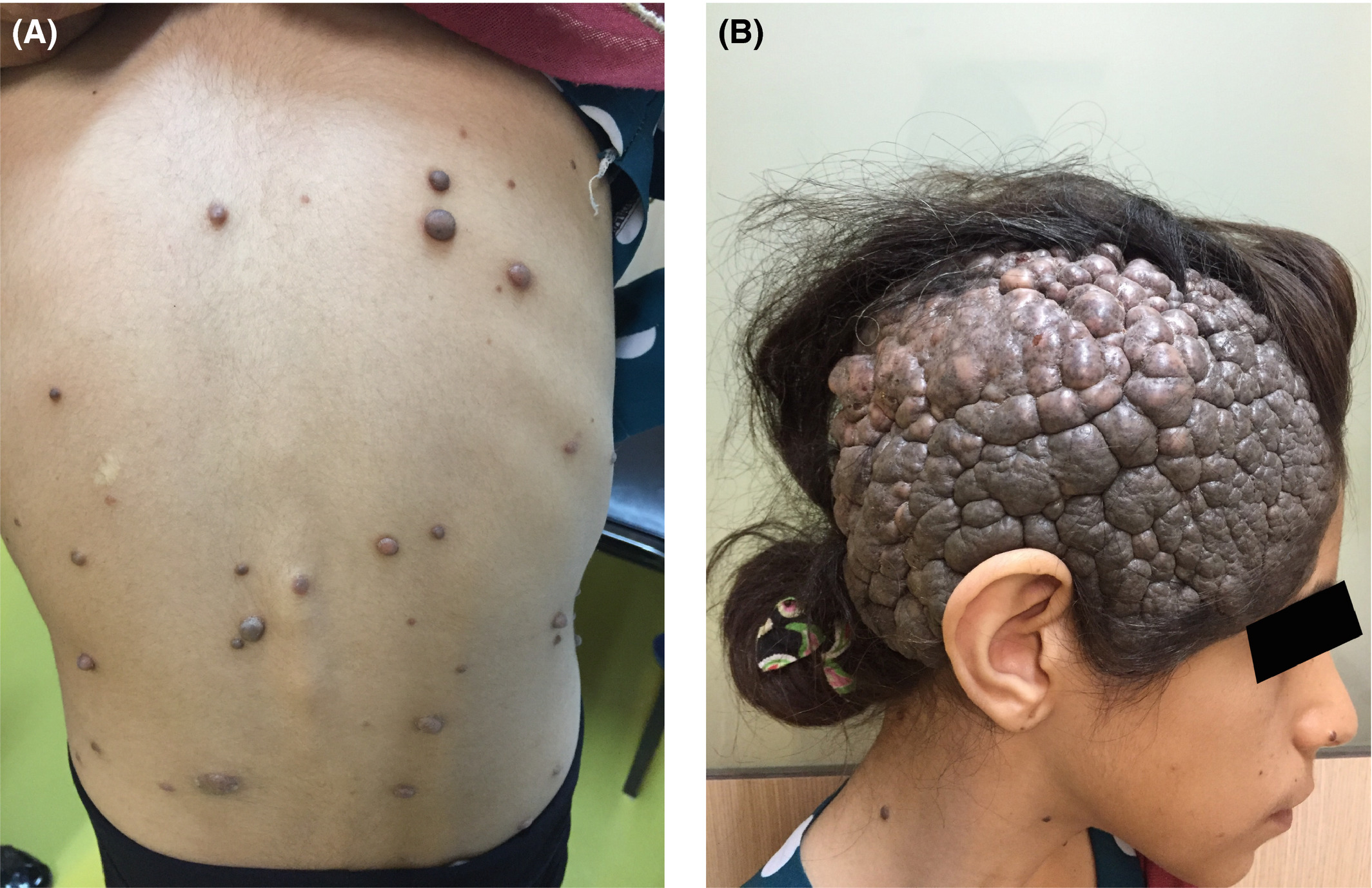
Nevus (pl. nevi)
pigmented lesion
91
New cards
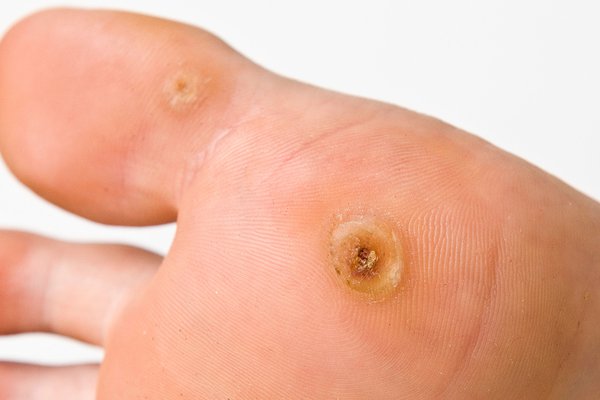
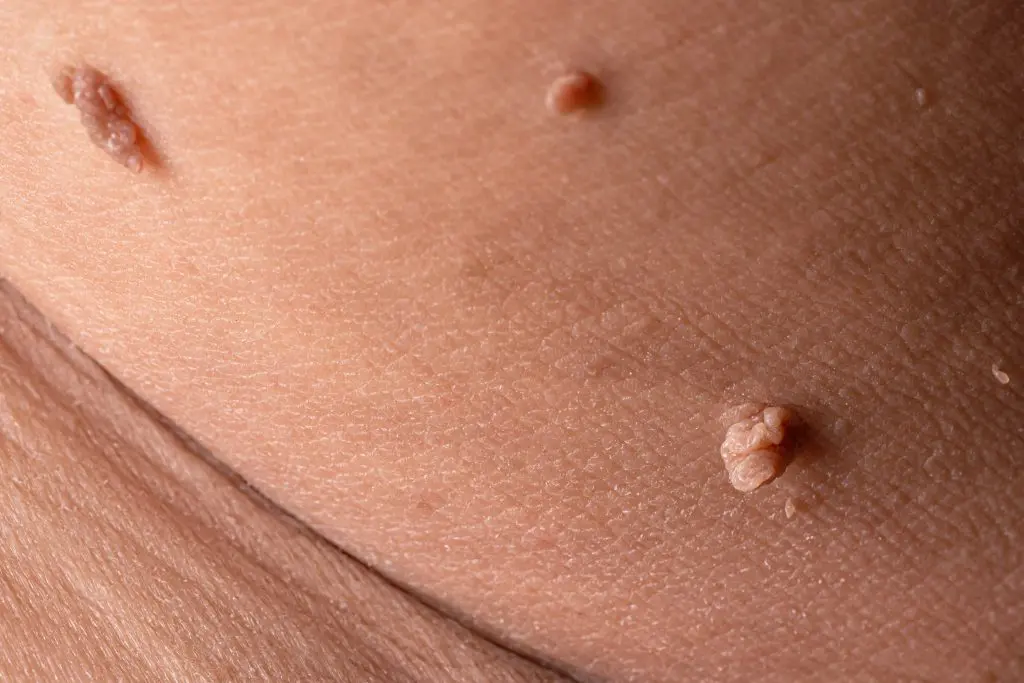
Verruca
warts caused by virus
92
New cards
\-plakia
plaque