BLoOdD
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
what type of tissue is blood?
connective tissue, only liquid tissue in the body
What are the four elements of blood?
erythocytes, leukocytes, thrombocytes and plasma
What are the main functions of blood?
Transport substances and gas exchange
erythrocytes, leukocytes, thrombocytes meaning?
red, white, platelets
what is the average blood volume in a human body?
w 4-5 m 5-6
what is a hematocrit?
the amout of red blood cells, 45%
what are erythrocyte’s main functions?
carry oxygen via hemoglobin
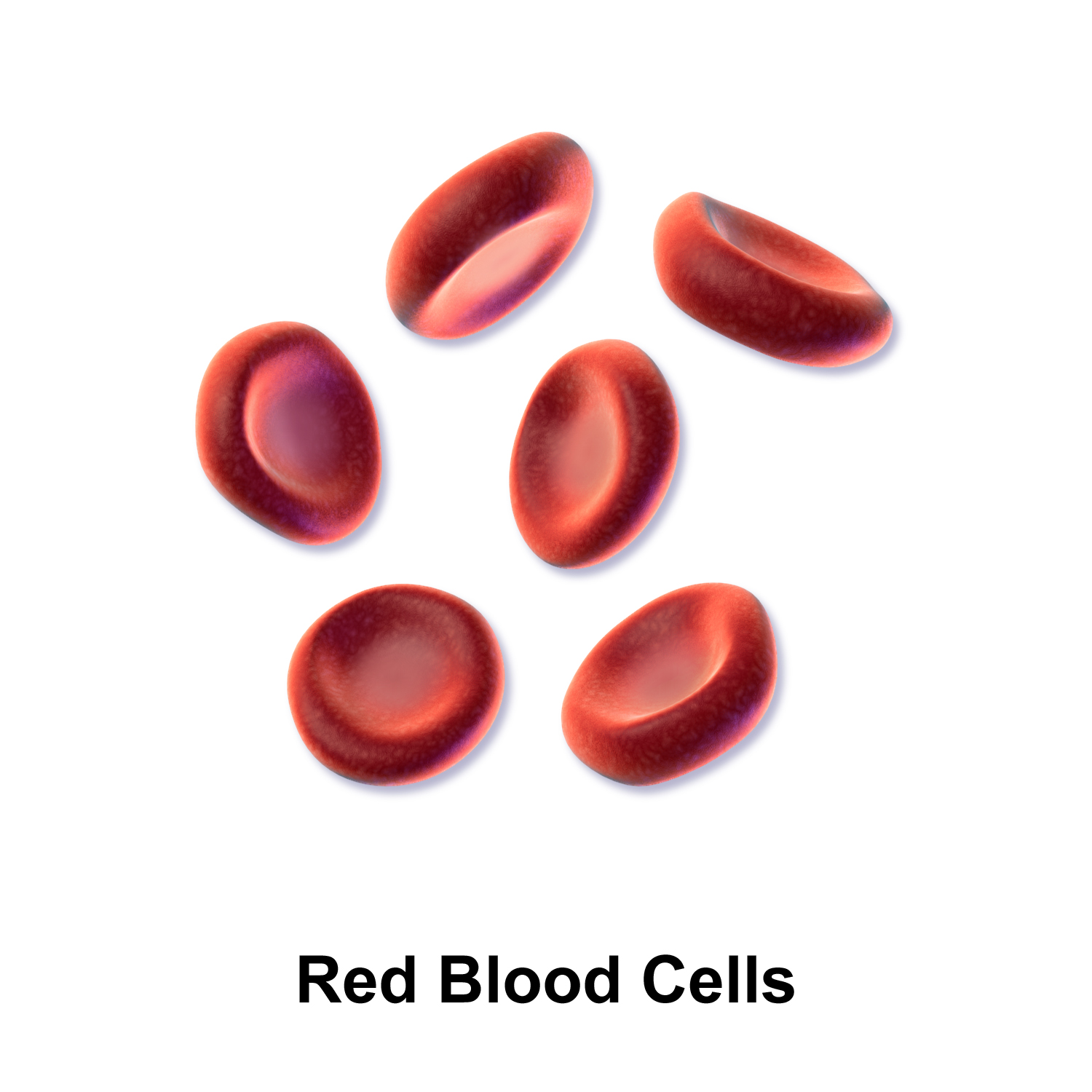
what do erythocytes look like?
biconcave disk
why do erythocytes not have nucleus?
to have more room for hemoglobin
what is hemoglobin made of? what does it carry? what is it most part of?
Is made out of 4 proteins, carries oxygen, is most part of erythocytes
what gives blood its color?
hemoglobin
what is anemia and how is it different to polycythemia?
anemia is low ability to carry oxygen which causes fatigue, and headaches, polycythemia is the opposite too much red blood cells from the red bone marrow
what is polycythemia?
is when there is too much red blood cells, causeing the blood to be too thick, making clots, strokes and high blood preassure
what is leukocytosis?
over 10k white blood cells, which are too many, meaning there is an infection, also little red blood cells
what is leukopenia
less than 5k white blood cells, this becasue many iseases like aids or chicken pox, also can cause tumors
what is granulocytes?
white blood cell with granules, they control immune system
what does neutrophil kill? what is its main characteristic? what does it look like?
is a granulocytes, actively kill bacteria, quicket cell in infections, has 3 lobes
what does eosinophil kill? what is its main characteristic? what does it look like?
kill parasyte, controls inflamation, bilobed nucleus
what does basophil realeses? what does it look like?
uses heparine to start clotting, uses histamine to increase blood flow, has s shaped lobes
what does heparine do?
produces clotting
what does histamine do?
increases blood flow
what does monocyte kill? what is there special ability?
they kill bacteria, and they can go out of the bloodstream
where are lymphocytes made? for the first type what does it produce and what does it attack?
made in red bone marrow, b lymphocytes, produce antibodies that attack foreing molecules
what is the second type of lymphocyte attached to? where is it produced?
T lymphocytes are produced in the red bone marrow, and are attached to microorganism and transplanted cells
what are thrombocytes?
platelets, they are the ones who do the clotting
What is hemostasis?
Is the process to stop bleeding
first step of hemostasis?
vascular span - the blood vessels tightens so the blood preassure slows down
second step of hemostasis?
platelet plug- plalets stick to the brocken vessel
third step of hemostasis?
coagolation- a fibrin net forms aorund the plug, creating a seal
What is the matrix of the blood?
plasma
what is plasma made of? what is its purpose?
is made of water and a bunch of other things, its porpuse is to maintain pH
What determines the type of blood of a person?
the antigens in the surface of their arythocytes
people with blood A type what antigens do they produce and what antibodice do they produce?
they produce A antigens and B antibodies
people with blood O type what antigens do they produce and what antibodice do they produce?
they produce NO antigens and A and B antibodies
What is the importance of RH group?
Becasue of the second pregnancy, if the baby is + and the mother is - the baby will die
What is cardiovascular made of?
heart and blood vessels
What is the cardiovascular system’s main function?
transport nutrients and gas exchange
what are the 2 circuits involved in the cardiovascular system?
Pulmonary and vascular system
What is the pericardium?
the outer layer of the heart that reduces the friction
what is important about the pericadium cavity?
it has liquid that reduces friction
first layer of the heart?
epicardium, reduces friction
second layer of the heart?
myocardium, thick cardiac muscle that is use for beating
third layer of the heart?
endocardium, soft layer inside the heart
What is the importance of coronary arteries?
the coronary arteries carry the heart its own blood supply
What is myocardial infarction?
lack of blood flow in the heart, heart attack
why are valves important in the heart?
they prevent back flow of blood, and are controled by chordae tendinae
What is a leaky valve called?
valver regurgitation, make the heart murmur
what is systole?
contraction of the chamber
what is diastole?
relaxation of the chamber
What is an electrodiagram?
medical test that records electrical activity of the heart
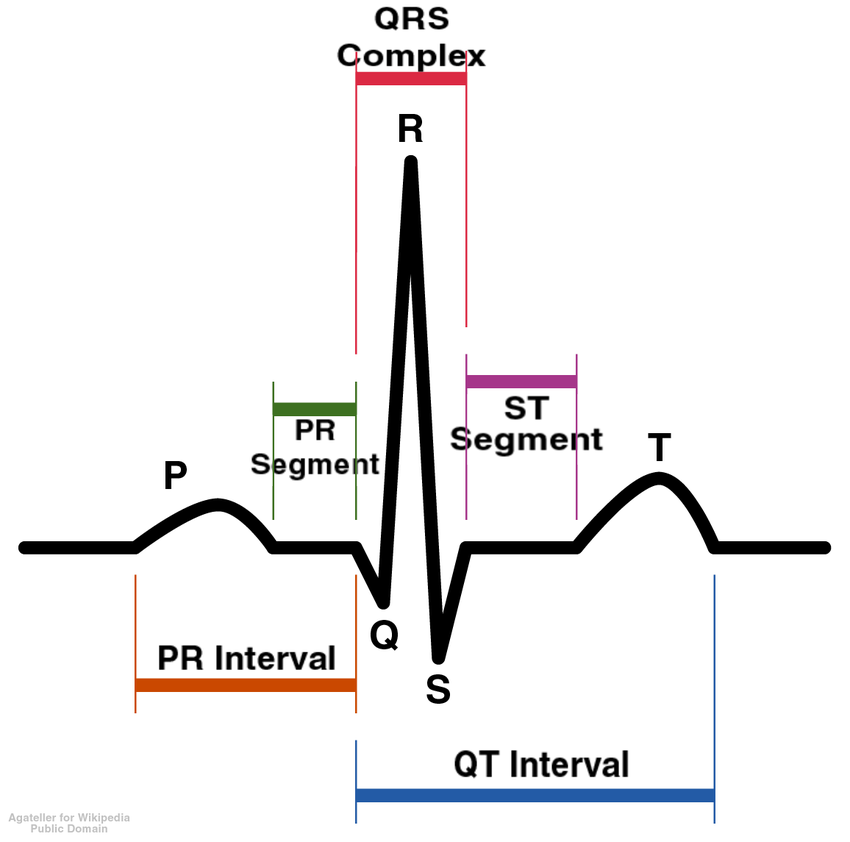
What is happening at R?
The atria is relaxing so blood will go to the ventricle
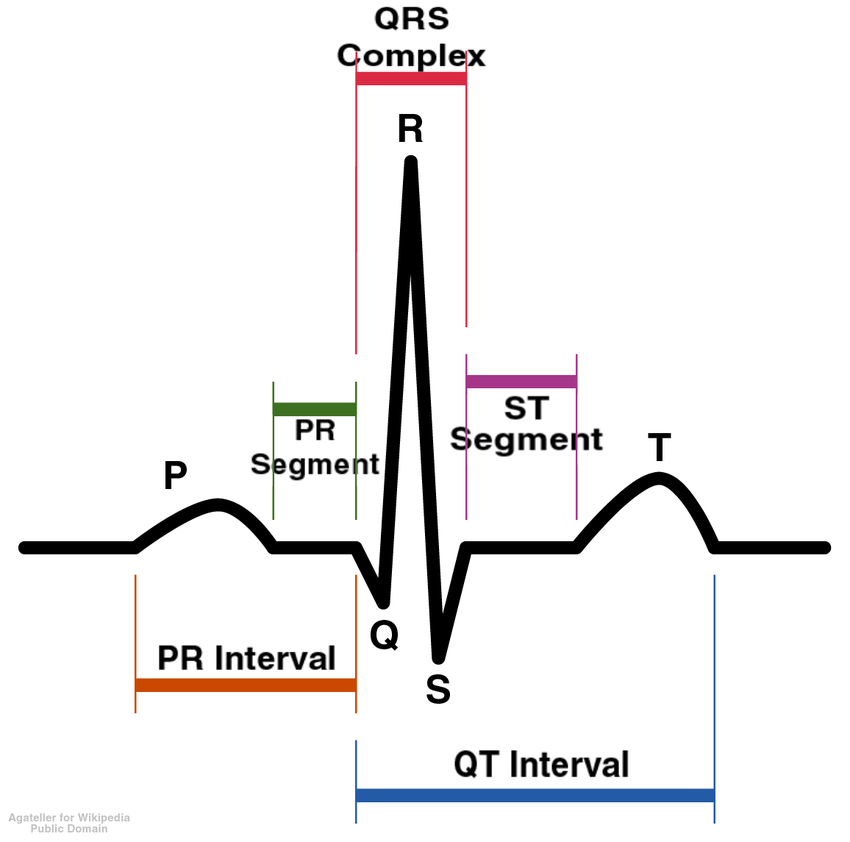
Q
small deflection before R
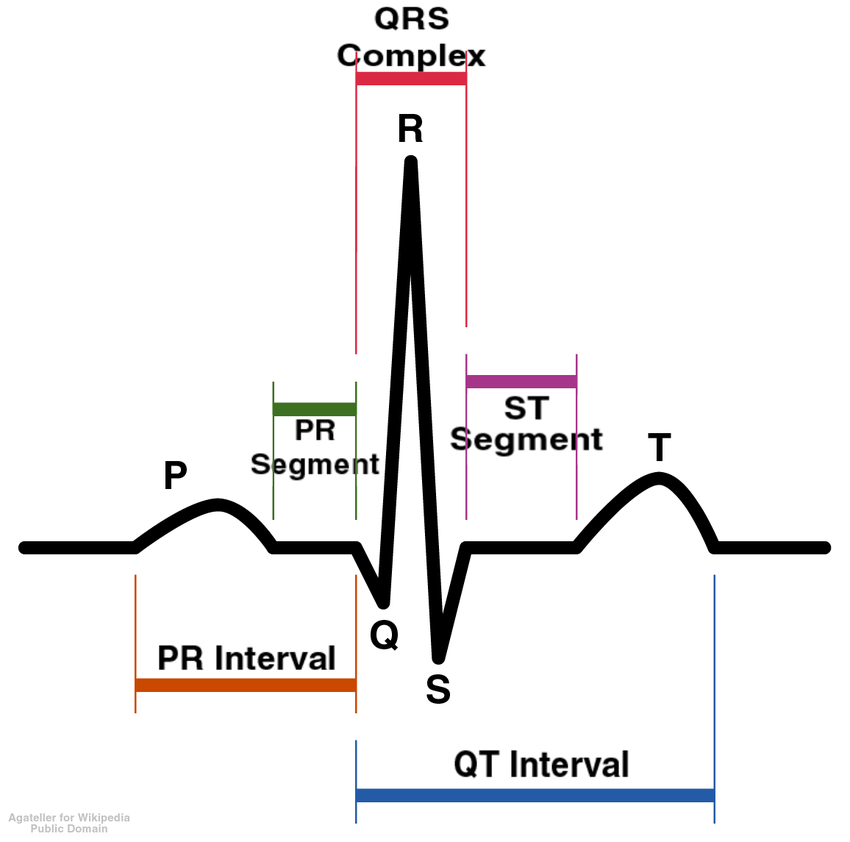
R
Strong ventricle contraction
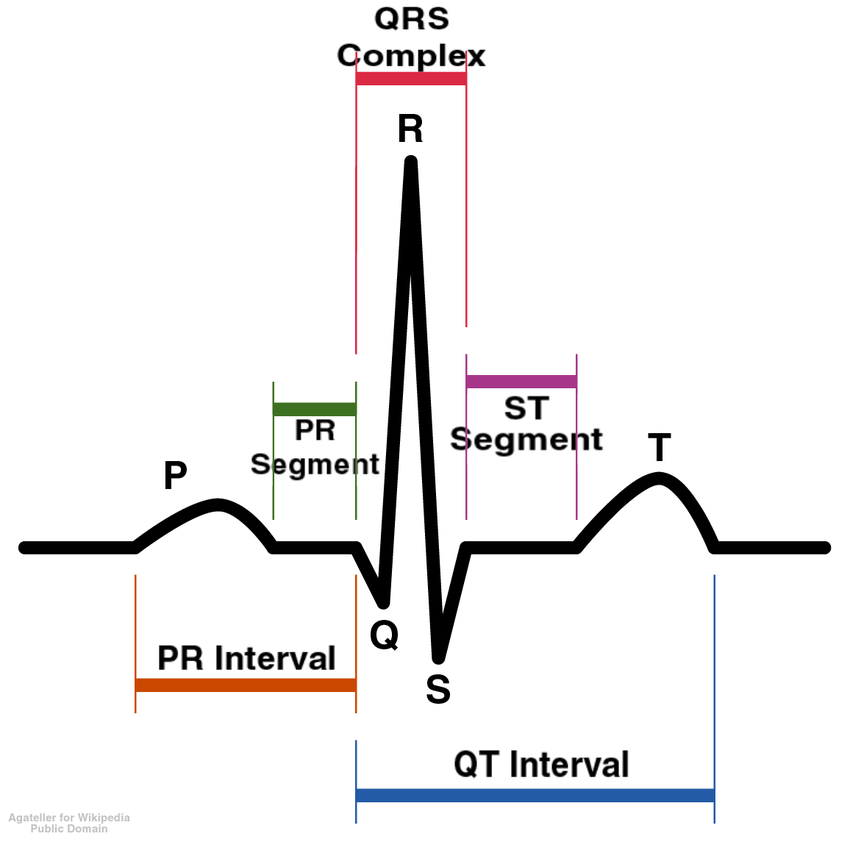
S
small deflection after R
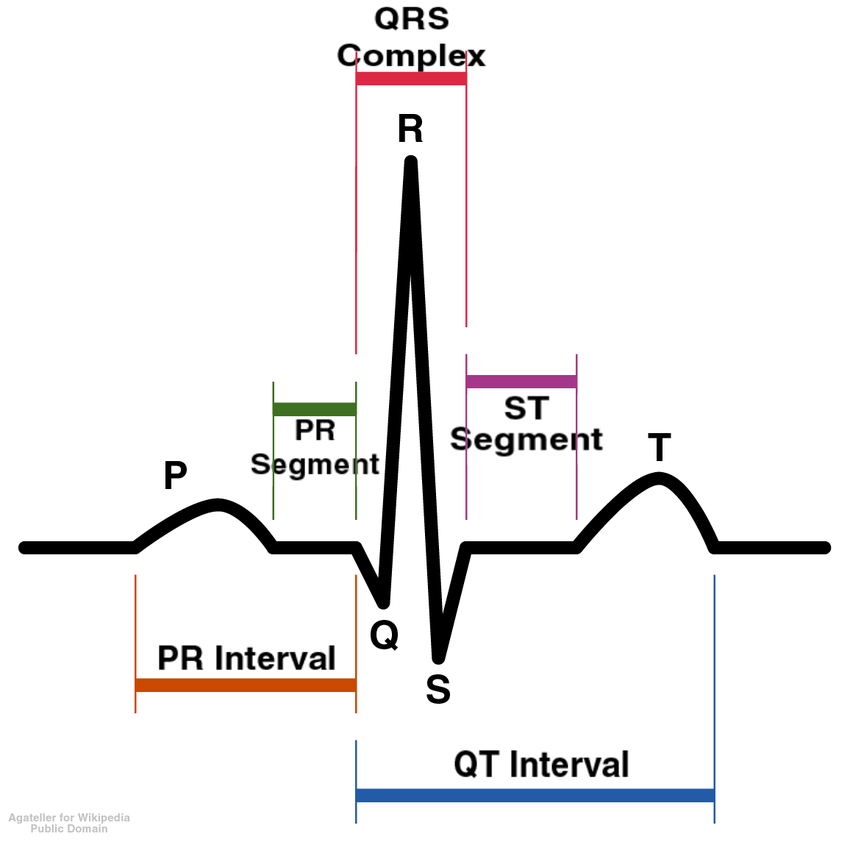
T
ventriculas repolarization
what is the first structure of the heart?
sinoatrial, is the peace maker of the heart, located at the right atrium near the vena superior vena
what is the second structure of the heart?
antrioverticular node, located on the superior
what is the third heart structure?
bundle of his, fibers that run thorought the septum
what is the fourth structure of the heart?
purkije fibers
what is the foramen ovale?
the hole that connects the right atrium with the left atrium
What part of the brain controls the heart rate?
medulla oblaganda, acetylcholine and norepinephrine
what are capilarries and what are they responsable of?
They are reponsable for the exchange between blood and other liquid tissues, also they connect arteries with veins
What is hypertension?
High blood preassure