Lecture 19: Domestication
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is domestication?
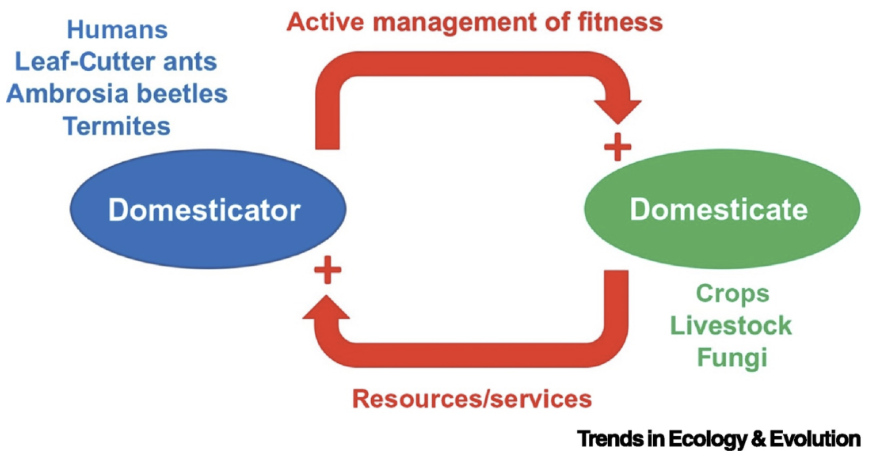
“a broad biological definition of domestication is that it is a coevolutionary process that arises from a mutualism, in which one species (the domesticator) constructs an environment where it actively manages both the survival and reproduction of another species (the domesticate) in order to provide the former with resources and/or services” -Purugganan 2022 TREE
Purpose of giving us food (plants, meat, milk, etc)
Gives other services (pets to kill mice, hunting partners, etc)
Doesn’t have to be done by humans
What is the differencing between taming and domestication?
Taming refers to development process where a species is acclimated to living with humans and is comfortable with their presence
Domestication is an evolutionary process that involves selection for a whole lineage to have traits that make them more appropriate at human livestock or pets
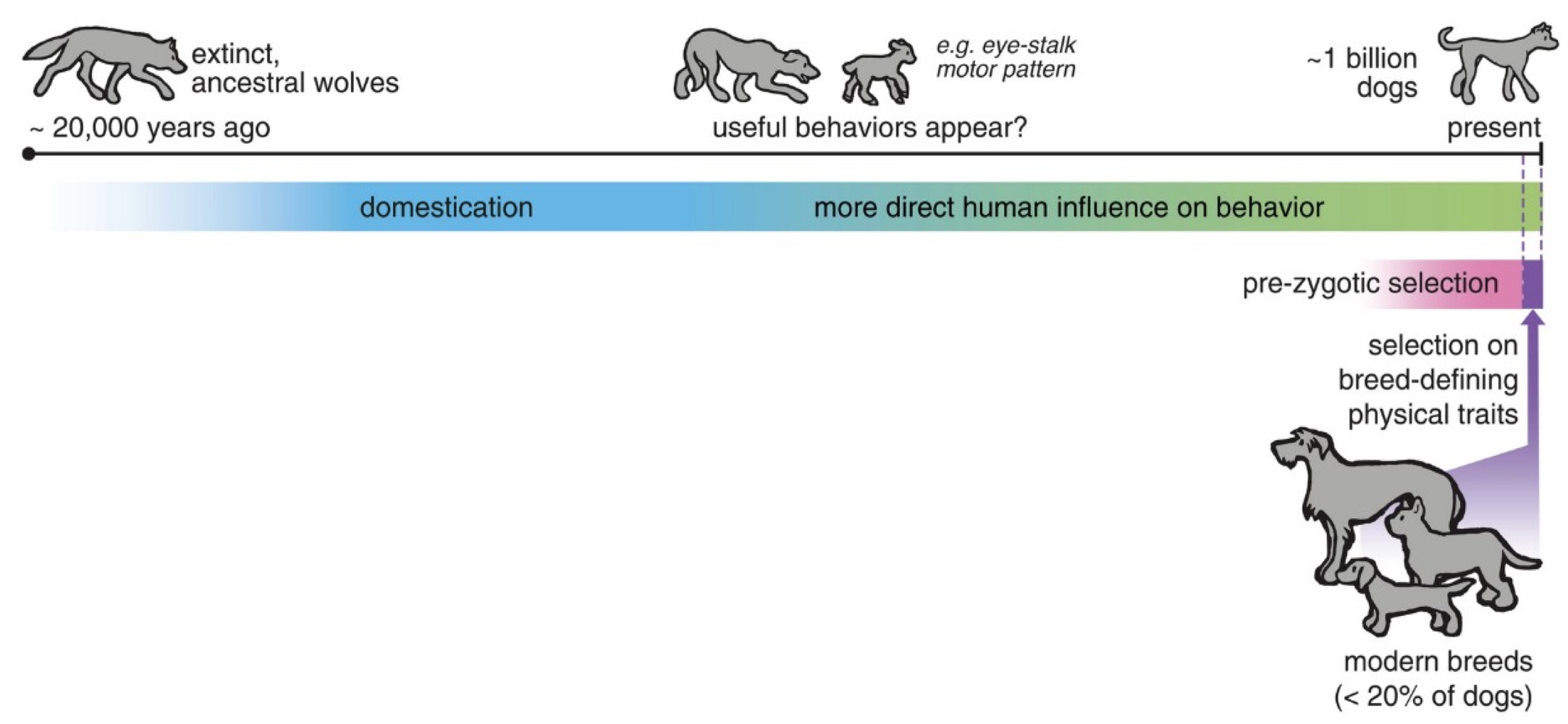
Is domestication a process?
Yes, the evolutionary process of domestication can have many phases with different levels of selection on traits over time
Example: modern dog breeds as we know them have only appeared in the last few hundred years. Even among the total global dog populations, a small percentage of dogs are part of purebred breeds
Other species that are domesticated vary in the extent to which they have been modified from their wild ancestors
What is fertilization?
A return to wild living
Change selective pressure → reverse domestication
Animals that escape from humans or otherwise are rewilded can be under selection for traits that are not seen in domesticated species
What does a feral animal mean?
Feral: The wild descendants of formerly domesticated animals
Example: Feral hogs in the southern US are a major ecological concern
What is an example of domestication done by a non-human species?
Leaf cutting ants farm fungi
This is mutualism
The fungus life cycle is completely controlled by the ants. This is an example of domestication in a non-human species
These fungi live only with ants
What do Leaf cutting ants do to aphids?
The ants are farming the aphids. They tend them and guard them
Since leaf cutting ants farm the aphids, are the aphids considered domesticated?
The aphids are not domesticated. The ants do not control their whole life cycle. They farm and tend the aphid ‘flocks’ that they happen to find of plants. They do not rear them from year- to-year
Only tend during spring/summer
What is the hypothesis for dog domestication?
Current hypothesis is that some wolves may have initiated a ‘self domestication’ process by tolerating humans and being less afraid of approaching their groups and camps
Friendly wolves were tolerated by humans and eventually provided benefits with hunting. At some point they began living with humans and gave up a free-living life as wolves
Thousands of years later we have modern dogs
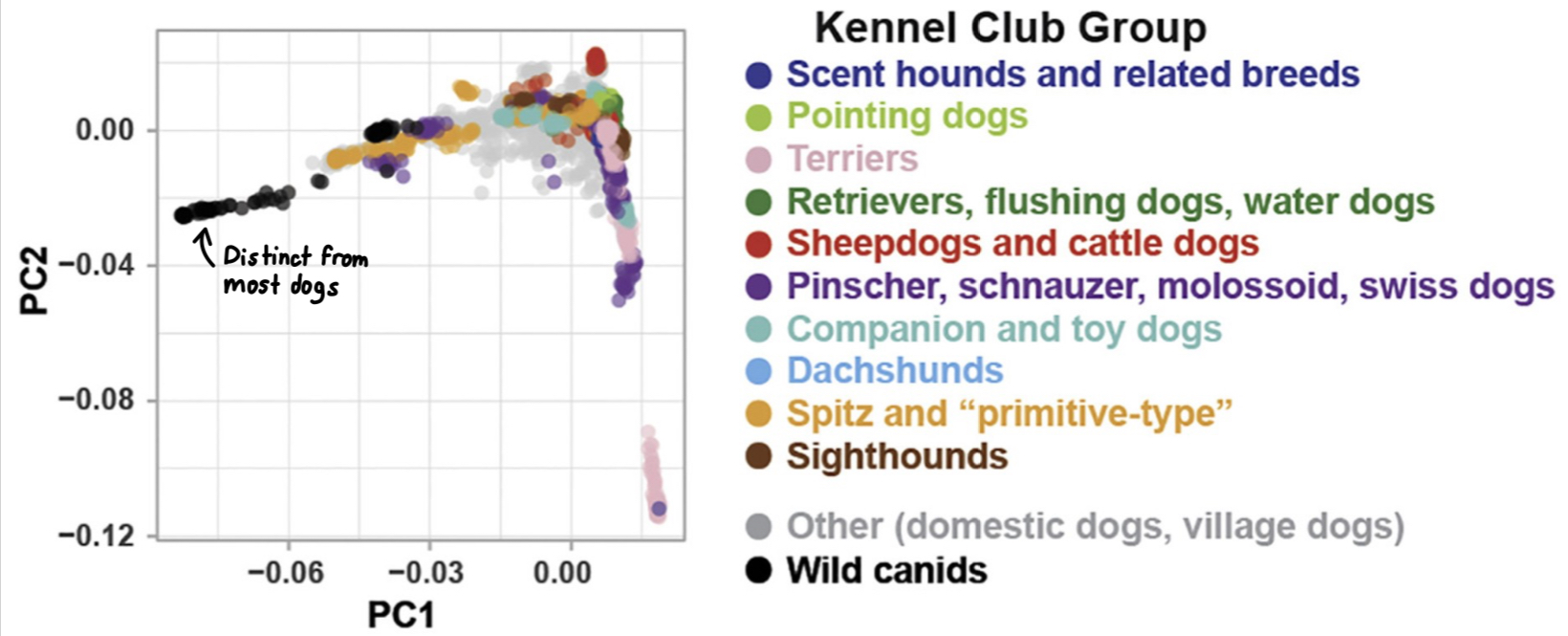
Do dog breeds vary in their genetic similarity to wild wolves?
Yes. On the graph, the closer they are → the closer they are related
This graph provides a clear visual of how domestication has led to genetic diversity among dog breeds, with some retaining more ancestral traits than others
If we wanted to measure whether there are genetic differences between groups, what must we think about?
How variation in behavior arises
What may cause individuals to differ in behavior?
Their genetics or their environment or most likely a combination of both
What is heritability?
Heritability is the proportion of phenotypic variation that is explained by genetic variation
What makes up phenotypic variation?
Genetic Variation and Environmental Variation
(Phenvar = Genovar + Envirovar)
What is the formula for heritability?
H2 = VG/VP
(Heritability = genetic variation divided by phenotypic variation)
What is the range for heritability?
0 to 1
How do we measure heritability?
To estimate heritability, we need to compare some physical, physiological, or behavioral trait among individuals and relate that to differences in their genetics
What are the 2 approaches to measure heritability?
Compare traits between family members across lots of families
Use genetic data to related genotypic similarity to phenotypic similarity
Interpret the following graph regarding how parent-offspring regression is used to estimate heritability:
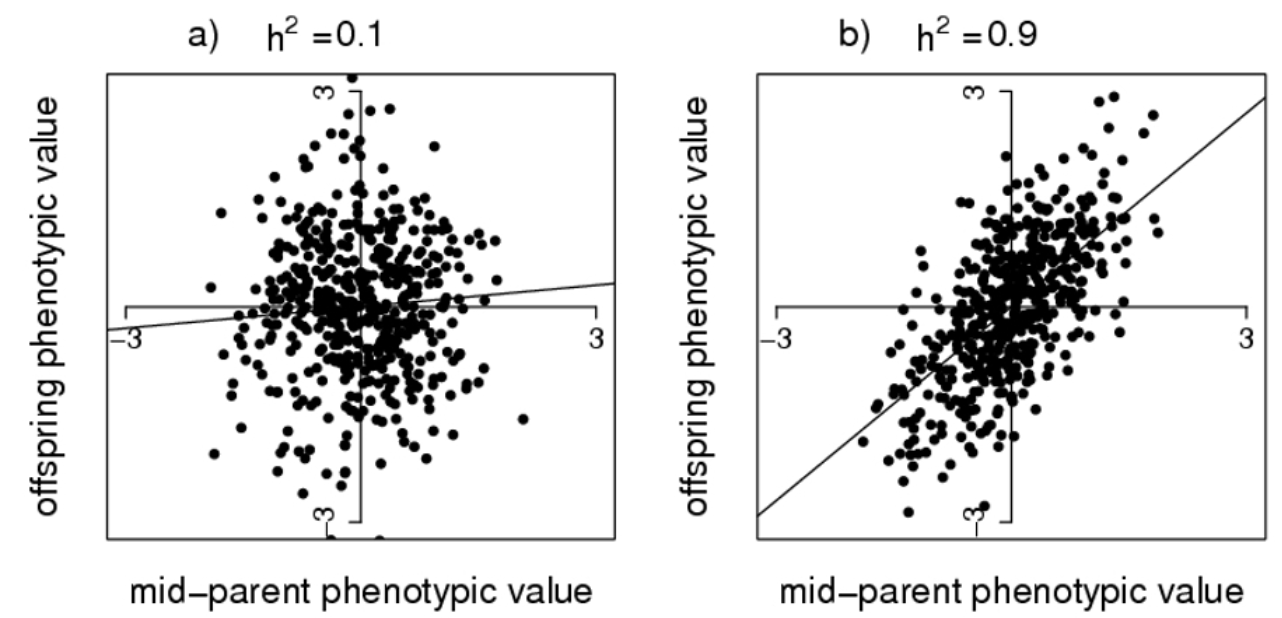
X-axis: Mid-parent phenotypic value (average of parents' trait values)
Y-axis: Offspring phenotypic value
Slope of the regression line = Heritability (h2)
Comparing Panels:
(a) h2=0.1 → Weak relationship between parent and offspring traits (scattered points, shallow slope). This suggests the trait is mostly influenced by environment rather than genetics
(b) h2=0.9 → Strong relationship (points tightly clustered along the line, steep slope). This means the trait is mostly determined by genetics
Interpretation: If a trait has high heritability, offspring will resemble their parents closely. If low heritability, environmental factors play a bigger role in shaping the trait

What can we use genetic sequence to measure?
Genetic variation among individuals and relate that to traits
Example: in dogs, many behaviors show only modest heritability. Breed is not a great predictor of many behaviors
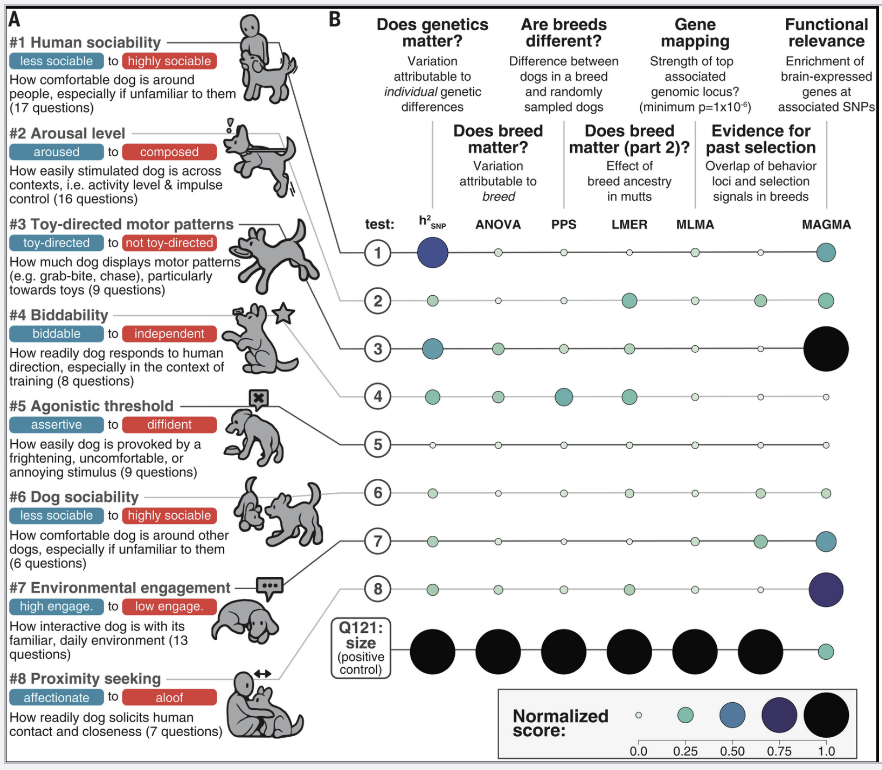
What are the caveats in heritability?
Heritability is a measure of how much variation in is trait is related to variation in genetics. It does not tell us whether a trait’s development involves genes
ALL trait development involves genes --- that is how cells function and organisms grow
Traits can have zero heritability because there is either little/no variation in the trait, or the variation is not related to genetics
Heritability is a measure of a specific population of individuals in a specific context
Heritability estimates will differ between populations if they have different levels of phenotypic or genetic variation (or both)
Environment also matters
Heritability is sensitive to environmental variation and the environment a population experiences
Heritability is NOT a fixed number. It can change over time as populations and environments change
Heritability is NOT fate. It is a description of the portioning of variance
What is the best estimate for the heritability of leg number in humans?
Close to 0