INTRODUCTION TO INTERPRETING LABORATORY DATA
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Sensitivity – the ability of the test to identify positive results in patients who have the disease (true positive rate)
rule out condition
Specificity – the ability of the test to identify negative results in people without the disease (true negative rate)
rule in condition
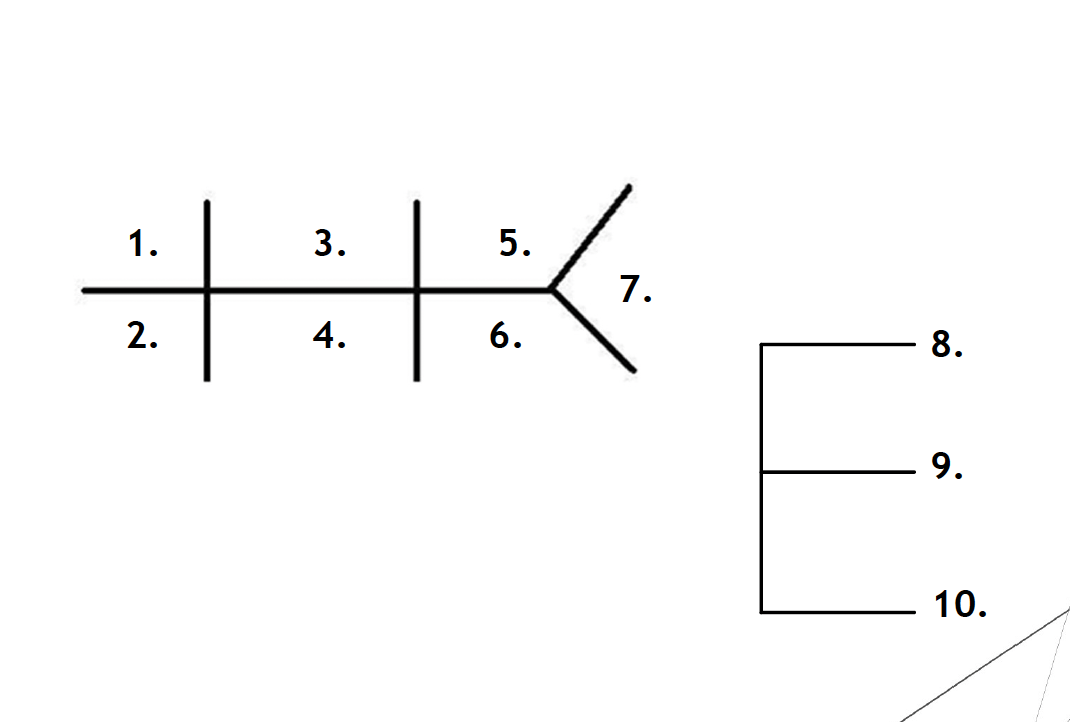
List the chem 10 name
Na
K
CL
CO2
BUN
SCr
Glu
Ca
Mg
PO4
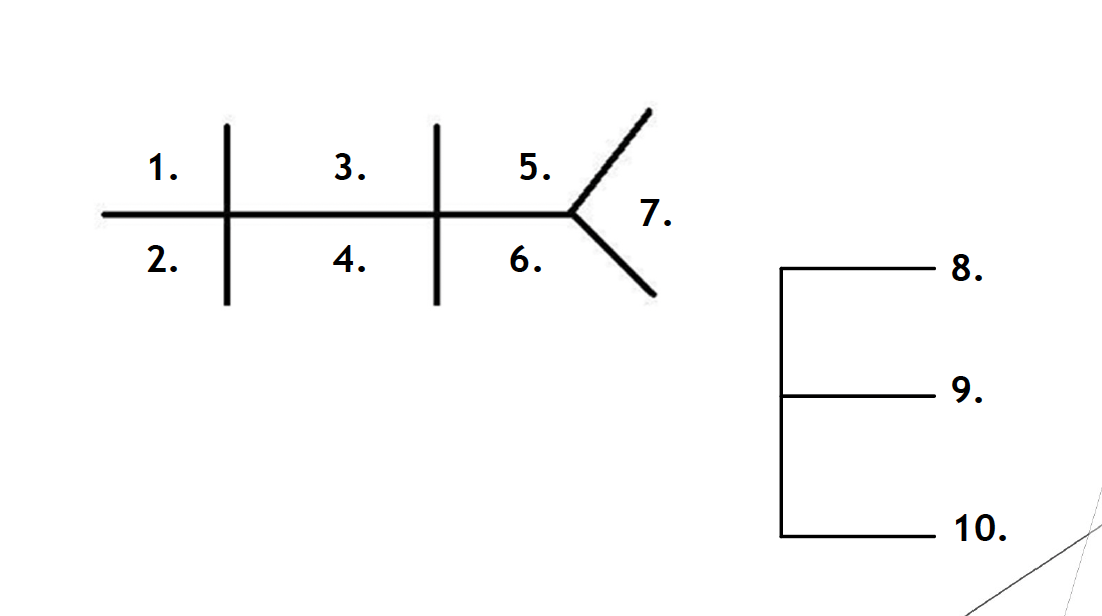
List the chem 10 values
136-145 mEq/L
3.5-5 mEq/L
96-106 mEq/L
24-30 mEq/L
8-20 mg/dL
0.7-1.5 mg/dL
70-110 mg/dL
8.5-10.8 mg/dL
1.5-2.2 mEq/L
2.6-4.5 mg/dL
what molecules are found in intracellular fluid (ICF)
PO4, K
the plasma and the interstitial fluid makes up the
extracellular fluid (ECF)
what is found in interstitial fluid
Na, Cl, CO2
what is found in plasma (intervascular fluid)
Na, Cl, CO2
range of Sodium Na+
Primary extracellular cation
Regulates serum osmolality
Maintains electric potential for neuromuscular function
Excreted primarily by the kidneys
136-145 mEq/L
Hypernatremia
Water loss greater than sodium loss
Causes: profuse sweating and diarrhea
Signs/Symptoms: thirstWater loss without sodium loss
-Causes: fever, burns, diabetes insipidus
-Signs/Symptoms: thirst, confusion, weaknessIncrease in total body sodium - increase ECF
-Causes: Cushing's, hypertonic saline
-Signs/Symptoms: thirst, confusion, weakness, increased urine sodium
>145 mEq/L
Hyponatremia
Solutes shift water from ICF to ECF
Cause: hyperglycemia
Signs/Symptoms: thirst, dry mucus membranes, diminished urine output
Extracellular volume depletion
Causes: hemorrhage, diarrhea, vomiting, kidney damage, burns
Signs/Symptoms: confusion, seizures, dehydration
Accumulation of water is greater than sodium dilution
Causes: heart failure, cirrhosis
Signs/Symptoms: confusion, seizures, edema
<136 mEq/L
range of Potassium K+
Primary intracellular cation
Regulates muscle and nerve excitability
Maintains acid/base balance
Regulated by insulin, glucose, aldosterone, acid/base
balance, renal function, GI and skin losses
3.5-5.0 mEq/L
Hyperkalemia
Can start to see symptoms at 5.5 mEq/L
Causes: renal disease, diabetes, Addison’s disease,
medications
Signs/Symptoms: diarrhea, muscle weakness,
**arrhythmia/EKG changes
>5.0 mEq/L
Hypokalemia
Causes: vomiting, GI losses, Cushing’s disease,
medications
Signs/Symptoms: constipation, muscle weakness, confusion, EKG changes
<3.5 mEq/L
range of Chloride Cl-
Primary extracellular anion
Maintains resting membrane potential
Maintains acid/base balance
Regulated by the kidneys
Increased Cl-:
Metabolic or respiratory ____
Decreased Cl-:
Metabolic or respiratory ____
96-106 mEq/L, acidosis, alkalosis
range of Carbon Dioxide
24-30 mEq/L
CO2
Integral component of carbonic acid/bicarbonate buffer system (acid bae balance)
Acts as an acid
Excreted by the lungs
Increased CO2:
Causes: metabolic alkalosis (increased HCO3-), respiratory acidosis, hypernatremia
Decreased CO2:
Causes: metabolic acidosis (↓ HCO3-), respiratory alkalosis, hyponatremia, GI loss, nasogastric suction, vomiting
24-30 mEq/L
Blood Urea Nitrogen
BUN: Concentration of urea nitrogen in the serum and end product of protein metabolism
Produced in the liver, filtered by the kidneys
Increased BUN:
Acute/chronic renal failure
Dehydration
GI bleeds
High protein diet
Decreased BUN:
Liver disease
8-20 mg/dL
Serum Creatinine (SCr) range
The product of muscle breakdown
Filtered and secreted but not reabsorbed
Limitation of SCr as a predictor of kidney function:
Age
Increased SCr:
Medications
Renal disease
Decreased SCr:
Low muscle mass
0.7-1.5 mg/dL
Glucose range
Energy source for cellular function
Obtained from carbohydrates
Stored in the liver and skeletal muscle as glycogen, stored in adipose tissues as fats and triglycerides
Regulated by glucagon, insulin, cortisol, epinephrine, and other hormones
70-110 mg/dL
Hyperglycemia
Causes: food, diabetes, post-MI, infection, medications
Signs/Symptoms: polyphagia, polyuria, polydipsia
>126 mg/dL
think “___!” for signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia
poly
Hypoglycemia
Causes: exercise, poisoning
Signs/Symptoms: palpitations, weakness, sweating, irritability, headache
<70 mg/dL
Calcium Ca2+ range
Most abundant mineral in the body, found primarily in the bones
50% of calcium is protein bound
Low albumin → correct calcium level
Role - muscle contraction, blood coagulation, nerve impulse, bone and tooth metabolism
Regulated by vitamin D, serum phosphate, parathyroid hormone, and calcitonin
8.5-10.8 mg/dL
Hypercalcemia
Causes: bone neoplasms, ATN, antacids, chronic diuretics
Signs/Symptoms: muscle weakness, anorexia, GI disturbances, EKG
>10.8 mg/dL
Hypocalcemia
Causes: hypoparathyroid, Vitamin D deficiency, alcoholism, drugs
Signs/Symptoms: numbness or tingling of the fingertips and around the mouth, fatigue, tetany, coma
<8.5 mg/dL
Magnesium Mg2+
Second most abundant intracellular cation
50% in bone, remainder is exchanged between intracellular and extracellular space
Maintains neuromuscular and enzymatic functions
Co-factor for the movement of Na+, K+, and Ca2+ in and out of cells
Excreted by the kidneys
1.5-2.2 mEq/L
Hypermagnesemia
Causes: renal failure, hyperparathyroid, lithium, magnesium antacids
Signs/Symptoms: muscle weakness, n/v, confusion, respiratory depression, arrhythmia
>2.7 mEq/L
Hypomagnesemia
Causes: diarrhea, thyroid, diuretics, alcohol, hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia
Signs/Symptoms: muscle tremors, ocular nystagmus, altered mental status, arrhythmia, seizures
< 1.5 mEq/L
decrease in Mg also leads to decrease in
K+ and Phosphorous
Phosphorus range PO43-
Primary intracellular anion
Found in bone
Role – energy metabolism, bone integrity, release of oxygen from hemoglobin
Regulated by equilibrium of calcium
2.6-4.5 mg/dL
Hyperphosphatemia
Causes: renal failure, bone disease, medications
Signs/Symptoms: calcium deposits in soft tissue, bone pain
>4.5 mg/dL
Hypophosphatemia
Causes: acute ETOH intoxication, malabsorption, starvation, aluminum antacids, steroids, diuretics, anticonvulsants, DKA
Signs/Symptoms: muscle weakness, bone pain, rhabdomyolysis (muscle tissue breakdown leads to release of harmful substances), seizures, coma
<2.6 mg/dL
HPI: Jeff is a 50 y/o male with a PMH significant for BPH, DM,
HTN, and hyperlipidemia who presents to the PCP office
complaining of dizziness, fatigue, headache, muscle spasm,
and tingling around the mouth.
TINGLING AROUND MOUTH* usually indicates ___ to be abnormal
calcium