Endosymbiotic Theory
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What does “endo-” mean?
inside
What does “symbiotic” mean?
living together
Symbiosis involves ____ __________ ______ living together
2 separate species
What came first? Prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes
Mitochondria and chloroplast lived as…
free living bacteria
How did membrane bound organelles come to be?
In some large prokaryotes, the cell membrane folded inward to make “pockets” inside the cell.
What happened to the cells that didn’t fold inward?
Remained prokaryotes
How was the nucleus formed?
Infolded cell membrane surrounded the cell’s DNA
When was the start of infolding of cell membrane to make the nucleus (estimate)?
About 2.5 billion years ago
How were mitochondria created?
Some primitive eukaryotes engulfed a small energy producing prokaryote
After mitochondria were created, _______ _____ were created
animal cells
How were chloroplast created?
Some ancient animal cells engulfed a small photosynthetic prokaryote
After chloroplast were created, ________ _____ were created
plant cells
What is the evidence of endosymbiotic theory?
Both the mitochondria and chloroplast are roughly the same size as prokaryotic cells
Have double membranes
Have their own DNA and ribosomes
Are autonomous
Why is it significant that both mitochondria and chloroplast have double membranes?
Because their own original membranes consist of molecules that are more “prokaryotic” in structure
The newer membrane is gained from being engulfed, wish consists of molecules that are more “eukaryotic” in structure
Why is it significant that both mitochondria and chloroplast have their own DNA and ribosomes?
Their DNA are more circular, similar to prokaryotic cells’ DNA
Their ribosomes have the same size and structure as prokaryotic ribosomes
What does it mean for the mitochondria and chloroplast to be autonomous?
They grow and divide on their own—separate from the rest of the cell, similar to bacteria
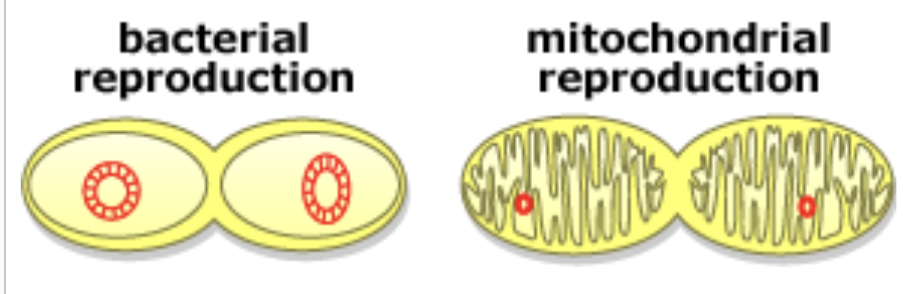
Why is endosymbiotic theory in this specific order? (bacteria cell + mitochondria = animal cell + chloroplast = plant cell)
Animals only have one mitochondria, whereas plant cells have mitochondria and chloroplast; Cells are more likely to gain 1 organelle then another than to gain 2 then lose 1
What is The Endosymbiotic Theory order?
Bacteria cell + mitochondria → animal cell; animal cell + chloroplast → plant cell
Cells are more likely to _____ ___ organelle then another than to _______ ____ then _____ ____
gain 1; gain 2; lose 1
Mitochondria multiply by _______ in _____
pinching; half
What reproduction process is similar to mitochondria’s?
bacteria
Every new mitochondrion must be produced from a _______ mitochondrion
parent
If a cell’s mitochondria are removed, can it build new ones from scratch?
No