Molecular orbitals
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
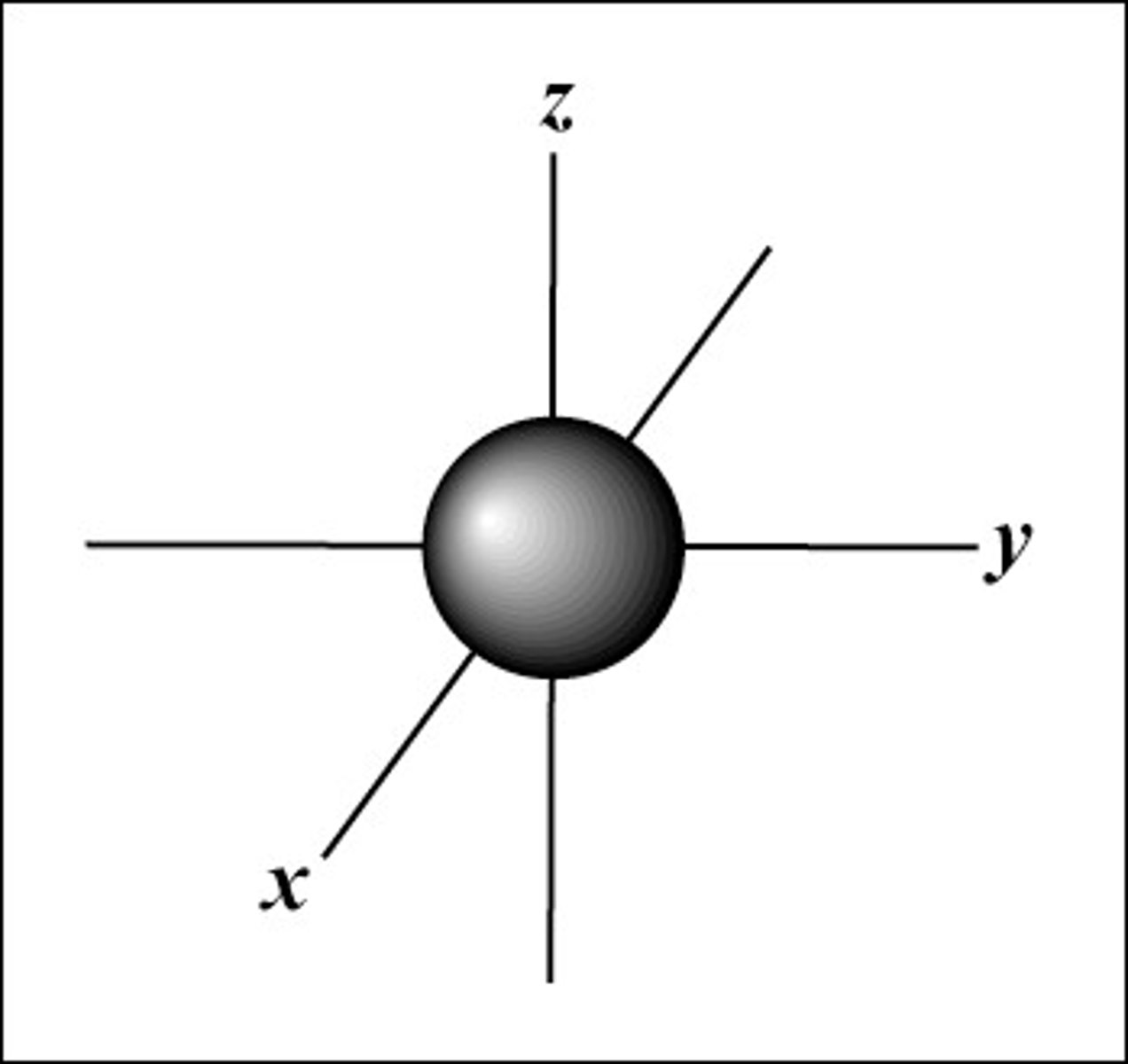
s orbital
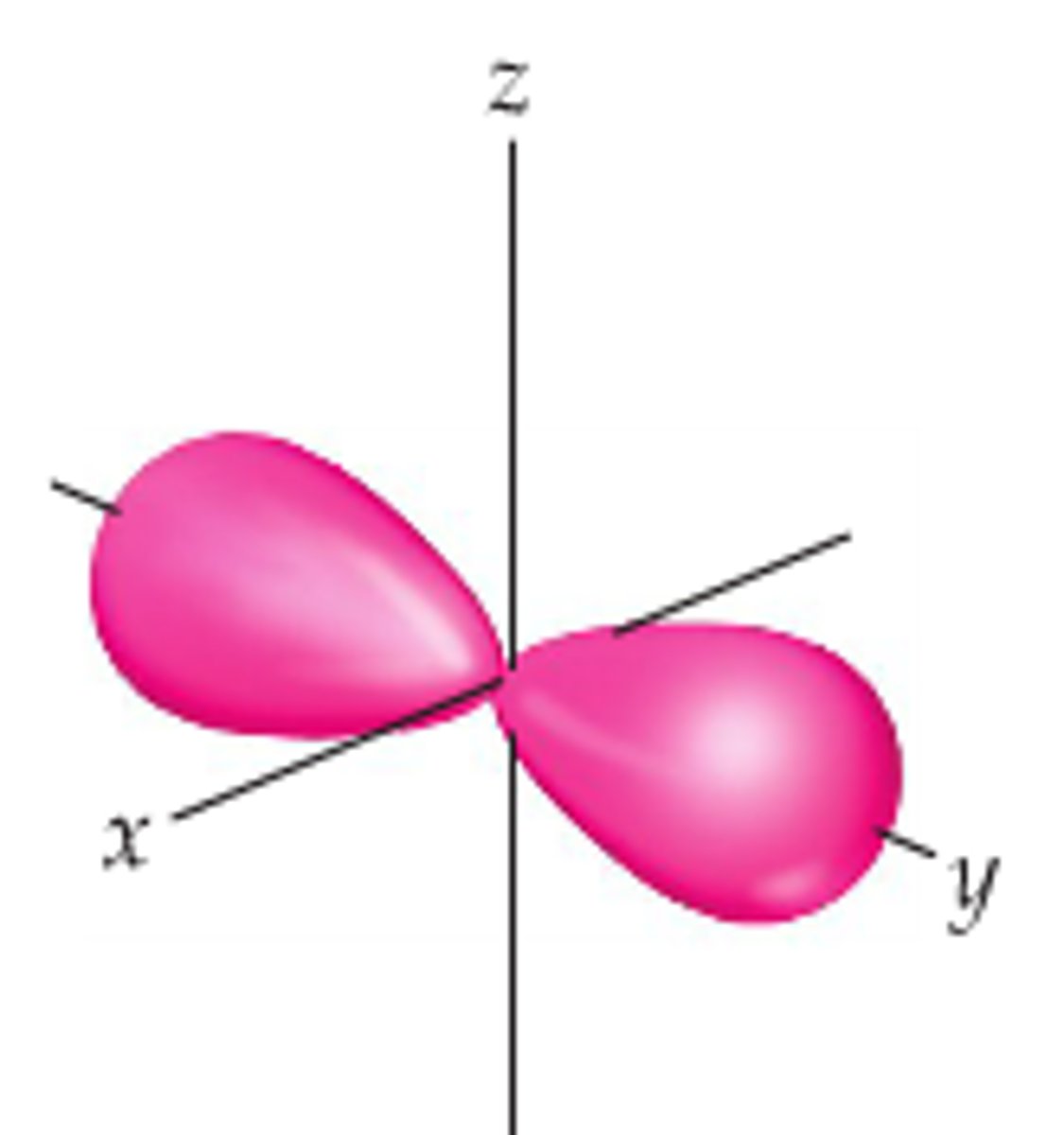
Py orbital
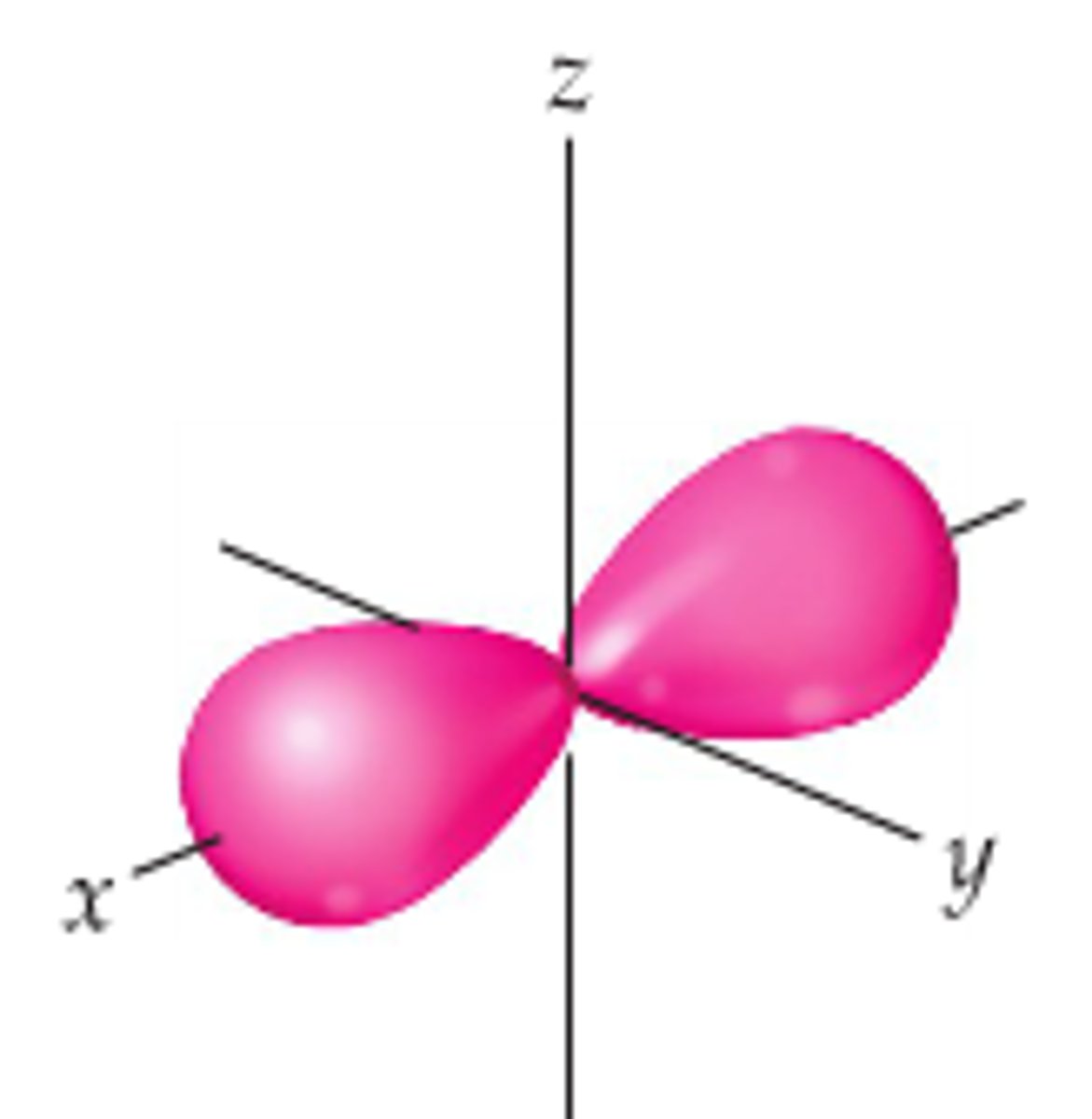
Px orbital
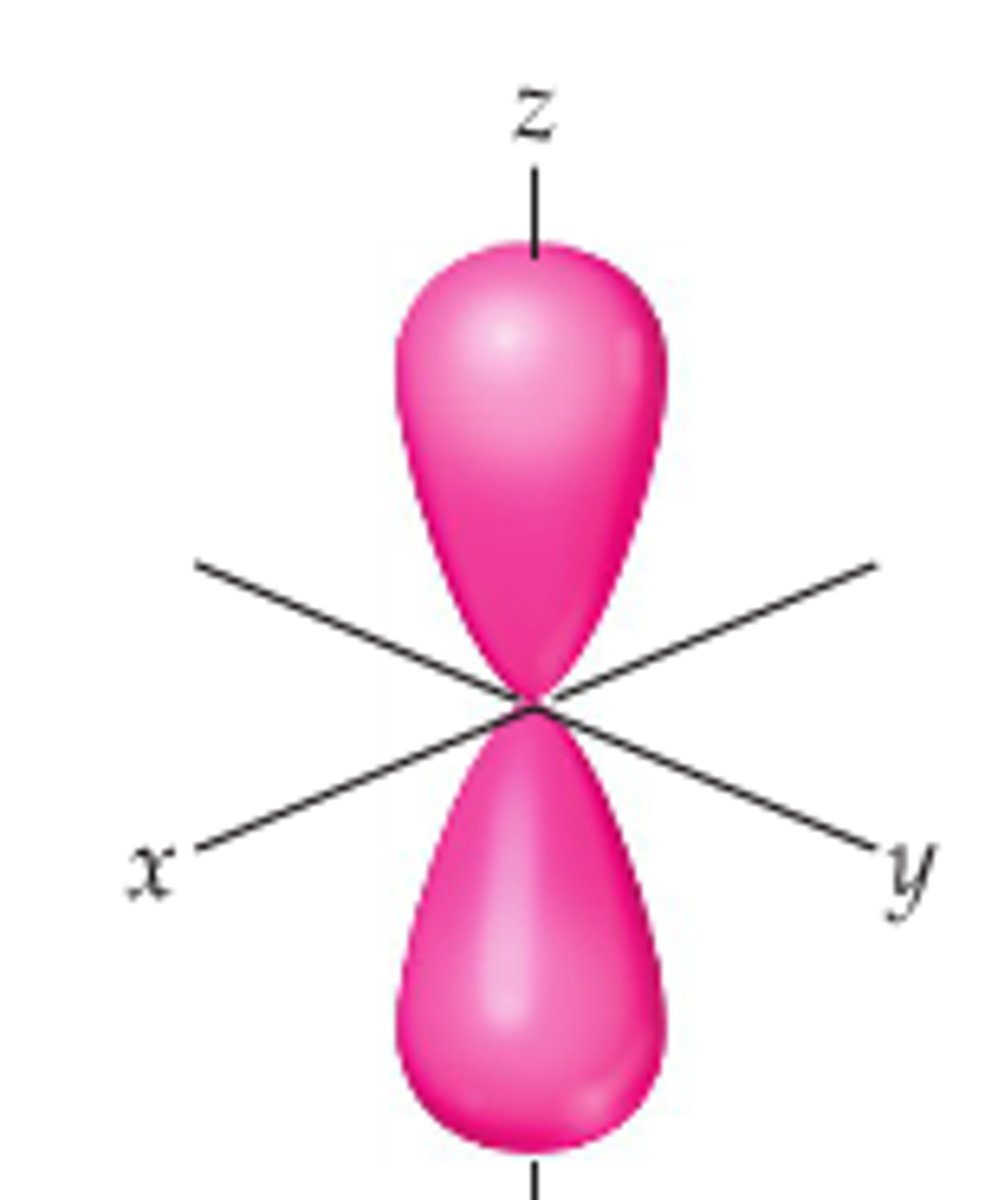
Pz orbital
sigma s orbital
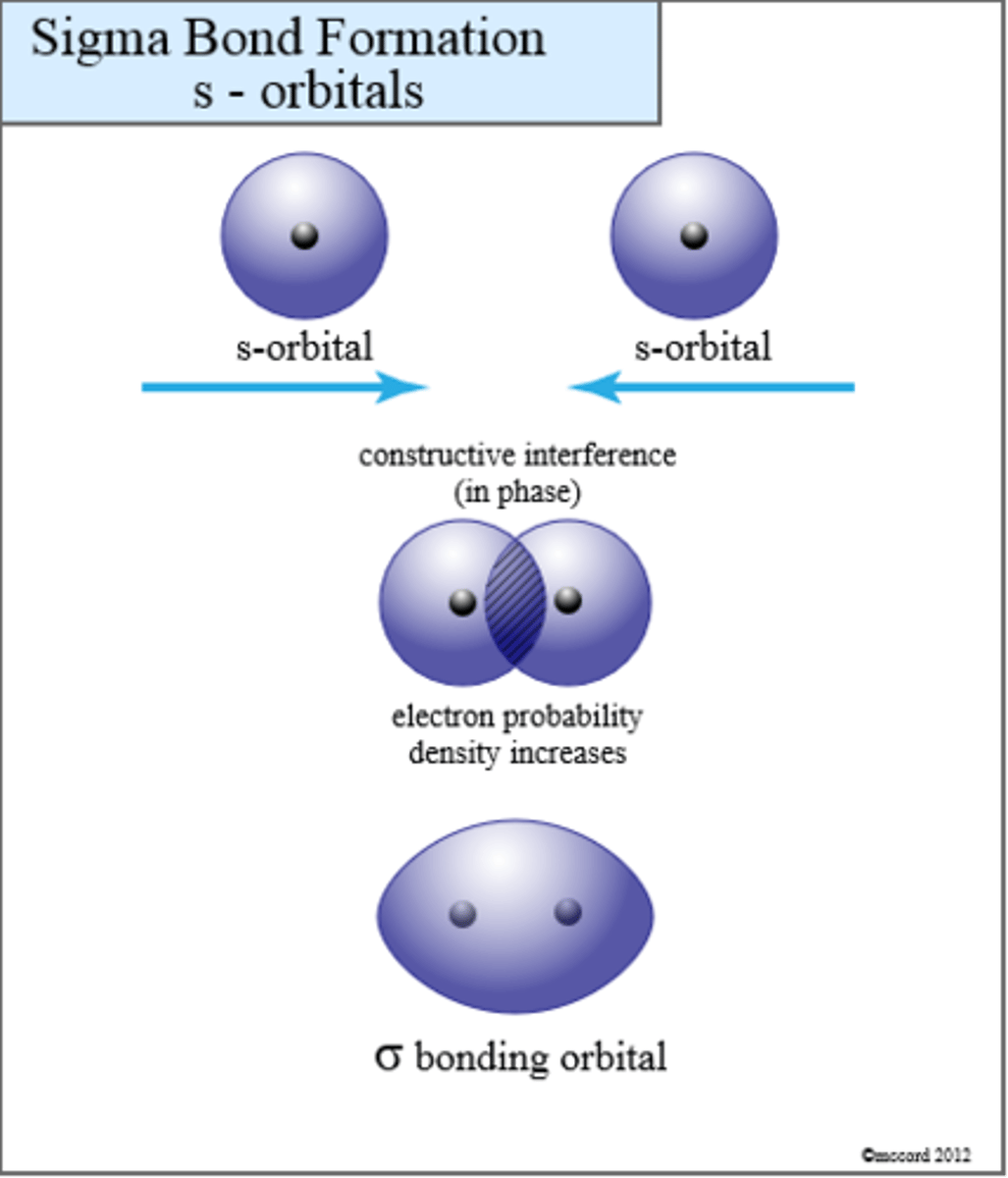
Bonding orbitals: energy
Bonding
- lower in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they were formed
-due to increase in shielding by nucleus
Antibonding orbitals: energy
Antibonding
-higher in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they were formed
-due to decrease in nuclear shielding
Adding electrons to bonding orbitals and stability
Makes the system of atoms more stable because the electrons are moving from the higher energy atomic orbitals to the lower energy molecular orbitals.
-So binding atoms into molecules (which is done by sharing electrons) would destabilize
Adding electrons to antibonding orbitals and stability
Makes the system of atoms less stable because the electrons are moving from the lower energy atomic orbitals to the higher energy molecular orbitals
-so binding atoms into molecules increases the energy of the system which destabilizes the system
In-phase vs out-of-phase and electron density characteristics for bonding and antibonding
-bonding: In-phase (orientation of AO's favorable) combination of AO's; bonding atoms into molecules increases the density of electrons between the atoms: (o) + (o) yields ( o )
-antibonding: out-of-phase (orientation of AO'S not favorable); bonding atoms makes electron scared of being between atoms bc they are repulsed: (o) + (o) yields ( o)l(o ) where they have different signs
Constructive and destructive interference in bonding and antibonding
-Bonding: constructive interference of AO'S so they come together.
-antibonding: destructive interference of AO'S so they repulse each other
A 1s orbital will form the lowest energy bond if bonded with _
Another 1s orbital. Just an example. Molecular orbitals are best formed from AO'S of like energies, eg 2s and 2s. This applies to bonding and antibonding
MO's that are symmetrical about the axis of the bond
Sigma bonds
MO diagram for H2 atom
AO 1H. . .MO.H2 . . AO 2H
. . . . . . ____sig* . . . . .
1s__l__ . . . . __l__1s
. . . . . . .__ll__sig . . . . . . .
Bonding and antibonding p atomic orbitals
http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/@api/deki/files/10231/sigma_bond.jpg?revision=1
How many molecular orbitals to put
How ever many atomic orbitals were used to make them
In-phase P atomic orbitals form__ MO's while out-of-phase p AO's form__MO's
-bonding
-antibonding
Pi bonding compared to Sigma
-side to side overlap so there is no electron density along the axis; only above and below it
Pi bonding MO
( )
o----o
( )
Pi antibonding MO
http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/@api/deki/files/10228/Pi_Antibonding_Dcylinder.jpg?size=bestfit&width=534&height=133&revision=2
What does a p AO look like?
O
.
O
where the period is the nucleus and O's are orbitals. Can also be horizontal.
-Sigma bonds can contain what two types of AO's?
-Pi bonds can contain what two types of AO's?
- s, pz (dbl check)
-px, py
Px and Py orbitals in pi MO are
Degenerate (have exact same energy)
Steps in drawing an MO diagram
1. Determine number of valence electrons on each atom
2. Place atomic orbitals according to energy in left and right columns. S gets one line and P gets 3. Draw orbitals under each line
3. Write LCAO equations and place MO's. Also label them. Draw lines connecting each MO to its primary AO
4. Fill electrons in for each AO
5. Determine total # of valence and fill in middle column
__ electrons are only important ones in MO theory
Valence because they form the bonds and are the only ones you will distribute along the MO's
Bond order
.5(# electrons in bonding - # electrons in antibonding)
Bond order of:
-zero
-one half
-one
-two
-three
-no bond and molecule not stable (eg He2)
-partial bond, eg H2+
-one covalent bond
-double bond
-triple bond
Born-Oppenheimer Approximation
--The motion of the nuclei and the electrons can be separated and the electronic and nuclear problems can be solved with independent wavefunctions.
-Since the nucleus is way heavier in mass compared to the electron, its motion can be ignored while solving the electronic Schrödinger equation; that is, the nucleus is assumed to be stationary while electrons move around it.
-Allows us to do everything else in this section
gerade
-German for even, these configurations are symmetrical relative to inversion.
Psi(x,y,z)= Psi(-x,-y,-z)
ungerade
-German for uneven, these configurations are asymmetric relative to inversion.
Psi(x,y,z)= -Psi(-x,-y,-z)
When to write g for gerade on MO's on energy diagram
for sigma MOs, if it's bonding, write a g. If antibonding, write a u.
for pi MOs, write a g if anti bonding and a u of bonding.
LCAO theory
-linear combination of atomic orbitals
- Gives you the wave functions for MO's
-gives a qualitative picture of the MOs in a molecule and provides a good way of predicting bonds; each AO contributes a certain amount to the shape and energy of the overall MO.
Homonuclear MO Diagram for O2 and F2 will look like (Naive MO)
_ 3 sigma u
_ _ 1 pi g
_ _ 1 pi u
_ 3 sigma g
_ 2 sigma u
_ 2 sigma g
Homonuclear MO Diagram for B2, C2, and N2
_ 3 sigma u
_ _ 1 pi g
_ 3 sigma g
_ _ 1 pi u
_ 2 sigma u
_ 2 sigma g
Coulomb integral
α
resonance integral
β
overlap integral
S