Lecture 6: Countercurrent Multiplier System
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Increase H2O reabsorption Results
urine is hyperosmotic, concentrated
Decrease H2O reabsorption results
urine is hypo-osmotic, dilute
Max [urine] Osmolarity #
1400 mOsmol/L
Plasma Osmolarity #
300 mOsmol/L
Min amount of urine excreted per day #
0.5L/day
If we were stranded on an island (dehydrated), why would we still excrete this minimum amount of urine?
Your body still works to flush certain minerals out of the body
Where does urine concentration take place?
tubules & collecting duct
Why does urine concentration occur?
Medullary interstitial fluid is very hyperosmotic
How is there hyperosmolarity?
1. Countercurrent anatomy at Juxtamedullary Loop of Henle
2. Reabsorption of NaCl in ascending limb
3. Impermeability of water in ascending limb
4. Urea entrapment in medulla
5. Vasa recta loops minimize changes
Vasa recta
hairpin loops
changed with the tubule
helps to maintain hyperosomolatiy of medullary IF
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Reabsorbs most water and solutes at the same rate: filtrate is non-cellular (no protein)
same as plasma - 300 mOsmol/L
Osmolarity of filtrate entering descend limb is...
tubular fluid entering descending limb 300 Osmol/L
Ascending Limb
1. NaCl reabsorption into medullary interstitial fluid
- thick limb: active mediated transport
- thin limb: simple diffusion
summary - treat as active
2. Impermeable to water.
- water does not follow sodium
- Becomes hyperosmotic
Descending limb
1. no NaCl reabsorption
2. Highly permeable to water.
- diffusion of water into medullary
How do we maintain hyperosmolarity in the renal medulla?
Diffusion of urea from the collecting duct
Countercurrent mechanism
Horizontally: isosmotic
Vertically: multiplier
at lowest: 1400 mOsmol in medullary
What is most important in the whole system?
1. Active NaCl transport
2. Urea entrapment. (solute)
- some urea follows flow of water
- increase osmolarity
Why is the tubular fluid entering the DCT hypoosmotic?
because of the active pumping occurring in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle.
Entering the distal convoluted tubule...
- TF is hypo osmotic
- additional reabsorption of water and solutes
- reabsorption of water due to ADH
Entering the collecting duct...
- TF is hypo osmotic
- dependent on aquaporins and ADH
- Inc. ADH, urine is hyperosmotic
ADH role in water absorption
ADH induces expression of water transport proteins in the late distal tubule and collecting duct to increase water reabsorption.
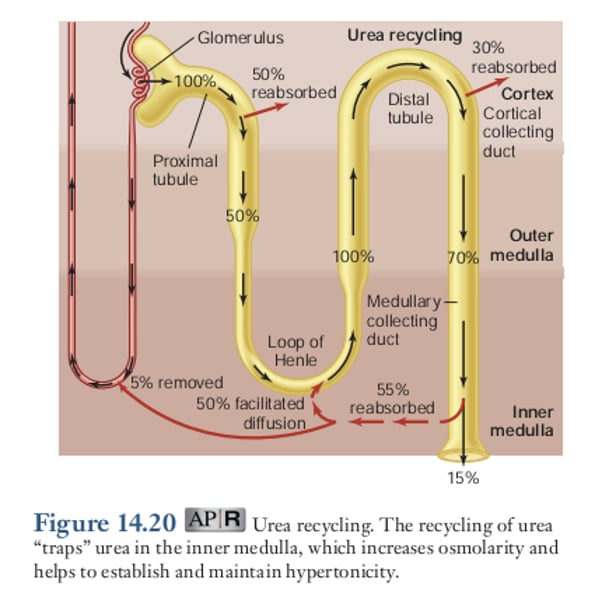
Urea Recycling