Diagnostic Imaging of the Urinary System
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
How large should the kidneys of dogs and cats be on radiograph?
Dogs 2.5-3.5 x size of L2
Cats neutered 1.9-2.6/entire 2.1-3.2 x L2
What are radiographic contrast studies useful for assessing?
Intrapelvic structures (urethra)
Bladder rupture
With an intravenous urography can see kidneys and ureters
What are the possible contrast medias?
Negative: air, CO2
Positive: iodine based
What should you do before a contrast study?
Take plain images
Enema (easier to see when colon is empty)
What is negative contrast cystogram (pneumocystogram) best for assessing?
Bladder position and wall thickness
What is a positive contrast cystogram best for assessing?
Bladder position, bladder rupture, etc
What is a double contrast cystogram?
Combination of 1-5mL of contrast and then air
What is a double contrast cystogram best for assessing?
Position, luminal content, wall thickness
Which type of bladder contrast study is most useful?
Double contrast cystogram
How is contrast for urethra assessment administered for males?
Retrograde urethrogram: catheter in distal urethra
Demonstrates urethra and possibly prostate
How is contrast for urethra assessment administered for females?
Retrograde vaginourethrogram: catheter through vulva
Demonstrates vestibule, vagina, urethra
Could also inject the contrast into the vestibule rather than using a catheter
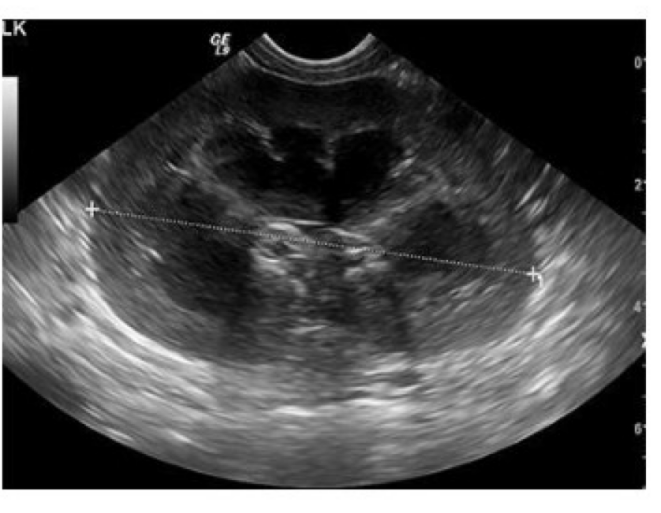
Is this short axis or long axis view of the kidney?
Long axis
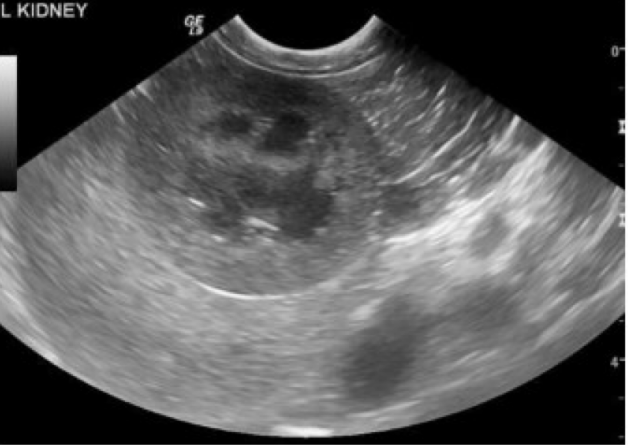
Short or long axis?
Short
Which kidney is more difficult to image on ultrasound? Why?
Right because it can be quite cranial and dorsal and is often within the ribcage
In which species is the kidney more mobile and rounded (cat or dog)?
Cat
Are ureters usually visible on ultrasound?
Not unless they are distended but can see the proximal aspect at the renal pelvis
What characteristics should you assess about the kidneys during ultrasound?
Location
Size
Shape
Margins
Component (cortex, medulla, corticomedullary junction, pelvis, ureter)
Echogenicity
Echotexture
If you see diffuse parenchymal changes what would be on your differential list?
Acute renal disease/failure
Chronic renal disease
Renal dysplasia
Chronic endstage kidney
Neoplasia (eg lymphoma esp if it is affecting both kidneys)
If you see pelvic dilation/hydronephrosis what would be on your differential list?
Obstruction
Pyelonephritis
Neoplasia
If you see focal changes what would be on your differential list?
Neoplasia
Calculi
Cysts
Abscesses
What does acute renal disease look like on ultrasound?
Rounded, hazy kidney
Reduced corticomedullary definition
Nephritis
Tubular necrosis
Acute renal failure
Appearance could be normal in acute disease
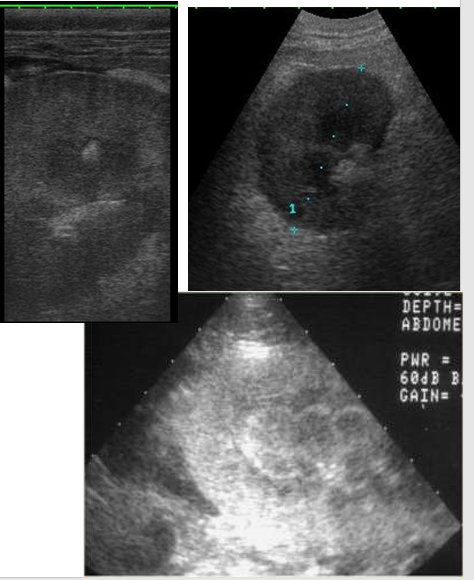
What does chronic renal disease look like on ultrasound?
Changes are non-specific and often bilateral
Heterogenous corticies
Reduced cortico-medullary definition
Indentations suggest old infarcts
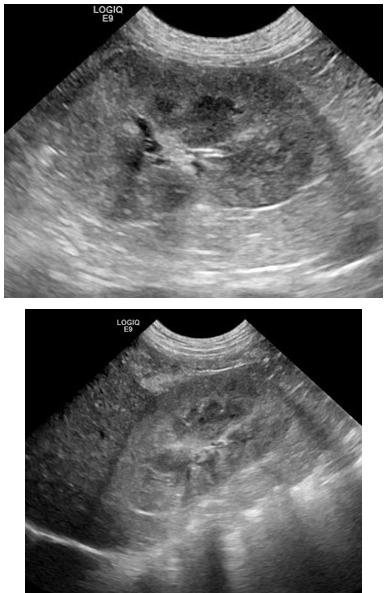
What does renal dysplasia look like on ultrasound?
Changes can range from mild to severe
Loss of corticomedullary definition
Distorted outline/abnormal shape
Small/difficult to recognize
Usually seen in young animals
What does chronic endstage kidney disease look like on ultrasound?
Loss of normal architecture
Small/difficult to identify kidney
Often in older animals
Which view is best for viewing pelvic dilation/hydronephrosis?
Short axis view
What does a ureteral obstruction look like on ultrasound?
Normal pelvis shape
Ureter visible to point of obstruction
Check bladder neck and other kidney!
What does neoplasia look like on ultrasound?
Irregular/abnormal shape to pelvis
Disrupted architecture
What do renal masses look like on ultrasound?
Disruption of normal renal architecture
Distortion of outline/abnormal shape
May be difficult to identify kidney if it has been fully infiltrated by the lesion
How are renal masses diagnosed?
Seen on ultrasound, FNA/biopsy for diagnosis
What do calculi look like on ultrasound?
Hyperechoic with shadowing
Located in calyces/pelvis
What do cysts look like on ultrasound?
Anechoic/cloudy
Located anywhere
Can be single or multiple
Usually well defined
What causes renal cysts?
Can be congenital
Associated with chronic inflammation
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD)
What do abscesses look like on ultrasound?
Anechoic/cloudy
Irregular margins
Surrounding reaction
Located anywhere
Different to differentiate from cyst
How thick should the urinary bladder wall be on ultrasound?
1-2mm thick
Is it better if bladder is full or empty when assessing with ultrasound?
Full
More difficult to locate if empty
Must be distended to assess wall thickness
If wall changes are seen on ultrasound of the bladder what should be on your differentials list?
Cystitis
Mass (neoplasia or inflammatory polyps)
Rupture
If contents are seen on ultrasound of the bladder what should be on your differentials list?
Calculi
Blood clots
Cell debris
Emphysematous cystitis
How thick will the bladder walls appear with cystitis?
>0.2cm
What are the differentials for bladder masses? How would you distinguish them?
Neoplasia or inflammatory polyps
Neoplasia can look irregular and can be extensive
If you see layers in the mass it is likely a polyp
What should you check for when ultrasounding bladder masses?
Check for ureteral obstruction or hydronephrosis
What does bladder rupture look like on radiograph?
Free fluid → loss of serosal detail
Defect not visible
Extravasation of contrast
Which types of calculi can you see on radiographs and which can you not?
Can see Struvite and Oxalate (they are radio-opaque)
Cannot see Cysteine or Urate (lucent)
What does gas in the bladder seen on radiograph indicate?
Could be either iatrogenic or emphysematous cystitis
What could suspended content in the bladder seen on a radiograph be?
Concentrated urine
Cell debris
Hemorrhage
Mucus
How can you tell if gas in the bladder is iatrogenic or emphysematous cystitis?
If it is little bubbles that adhere to walls it is emphysematous cystitis
What landmark can you use when finding the prostate on ultrasound?
The proximal urethra - follow the urethra to find it
What does the prostate look like on ultrasound?
Bilobed
Echogenicity similar to spleen
Capsule
How common is benign prostatic hyperplasia and what types of dogs are most susceptable?
VERY common
Entire male dogs
What does benign prostatic hyperplasia look like on ultrasound?
Hyperechoic
Heterogenous
Radiating pattern
Often associated with cysts but not always
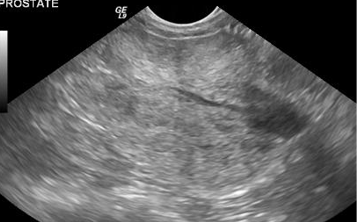
What does prostatitis look like on ultrasound?
Acute inflammation: hypoechoic
Chronic inflammation: hyperechoic and mottled
What does prostatic neoplasia look like on ultrasound?
Mottled
Mineralization
Locally invasive
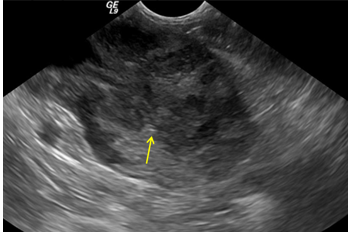
Which dogs are prone to prostatic neoplasia?
Castrated
Where are you likely to see metastasis from prostatic neoplasia?
Pelvis and lumbar vertebrae
Lungs
Differentiate prostatic cysts vs abcesses
Cysts: within prostate, variable size, well defined
Abscess: indistinct margins, cloudy contents, surrounding reaction
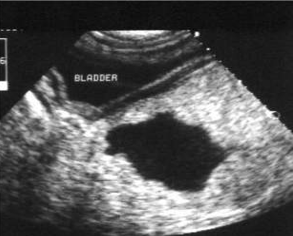
Is this a cyst or abscess?
Cyst
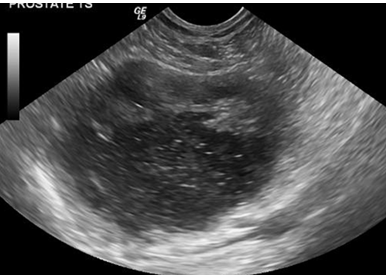
Cyst or abscess?
Abscess
Where are para-prostatic cysts located?
Outside the prostate/adjacent to it
What does a para-prostatic cyst look like on imaging
Mineralized rim on radiograph (not all of them)
Looks like multiple bladders on ultrasound
Could be displacing the bladder
Is an ectopic ureter visible on ultrasound?
Only if distended
If insertion is beyond pelvic inlet it is not visible
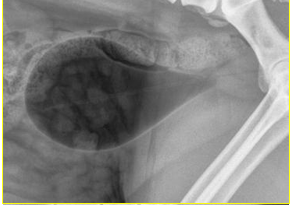
What type of contrast study?
Negative contrast cystogram (pneumocystogram)
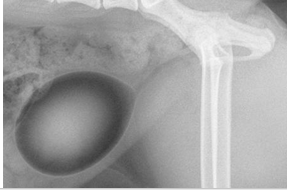
What type of contrast study?
Double contrast cystogram
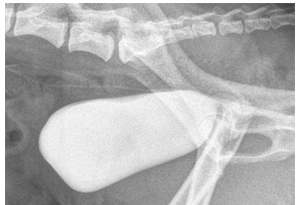
What type of contrast study?
Positive contrast cystogram