Kinematic terms
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Displacement (s)
Vector quantity: Final position-initial position so change in position
Distance
Scalar quantity, measures amount travelled
Speed
Scalar quantity, change in distance over change in time v=d/Δt
Velocity
Vector quantity, change in displacement over change in time v=Δs/Δt or 2πr/T or wr
Acceleration (a)
Vector quantity, change in velocity over time. Δv/Δt. Centripetal acceleration = v2/r
Initial Velocity (u)
Velocity at the start
Final velocity (v)
Velocity at the end
Time (t)
Scalar quantity In seconds
Linear momentum (p)
Vector quantity in kilograms in meters per second. Found with p=mv. To find with tow objects use
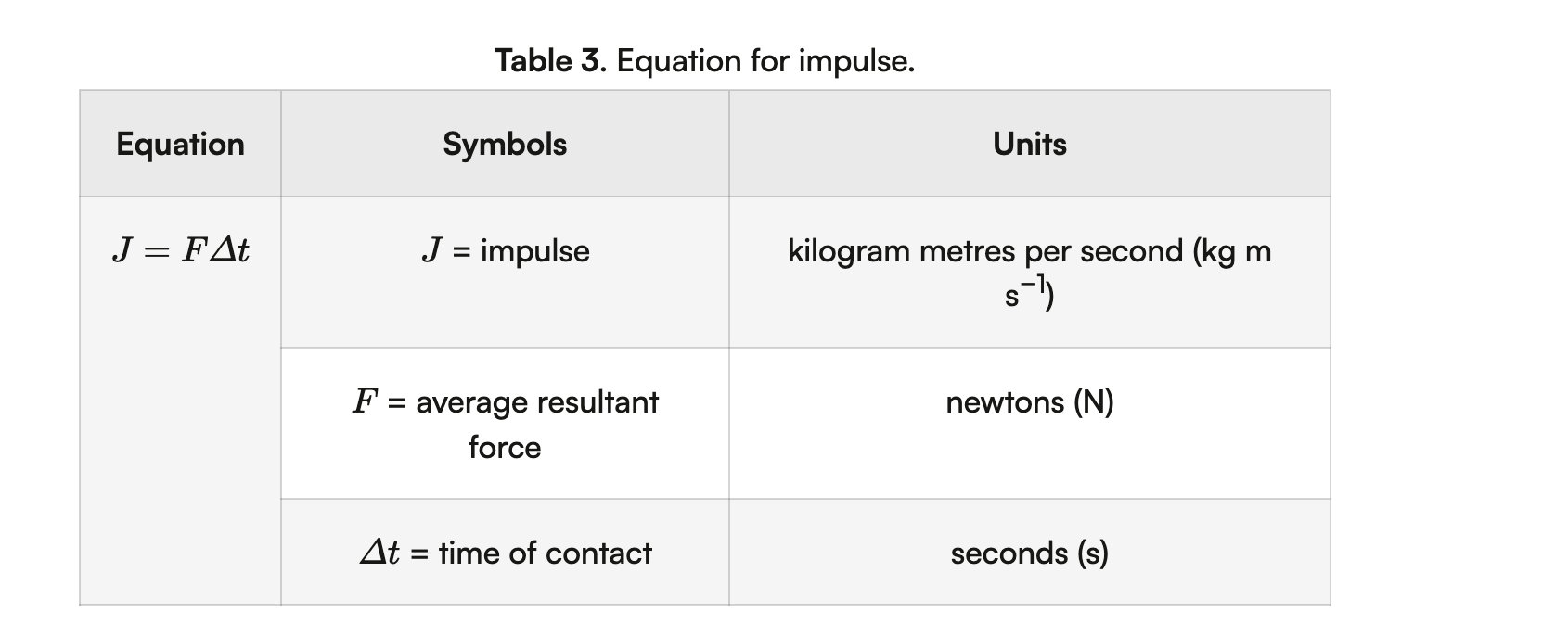
Impulse (J)
Vector quantity, Change in momentum found with J=F⋅Δt
Angular Velocity (w)
Rate of change of the angle covered by the body measured in rad/s.
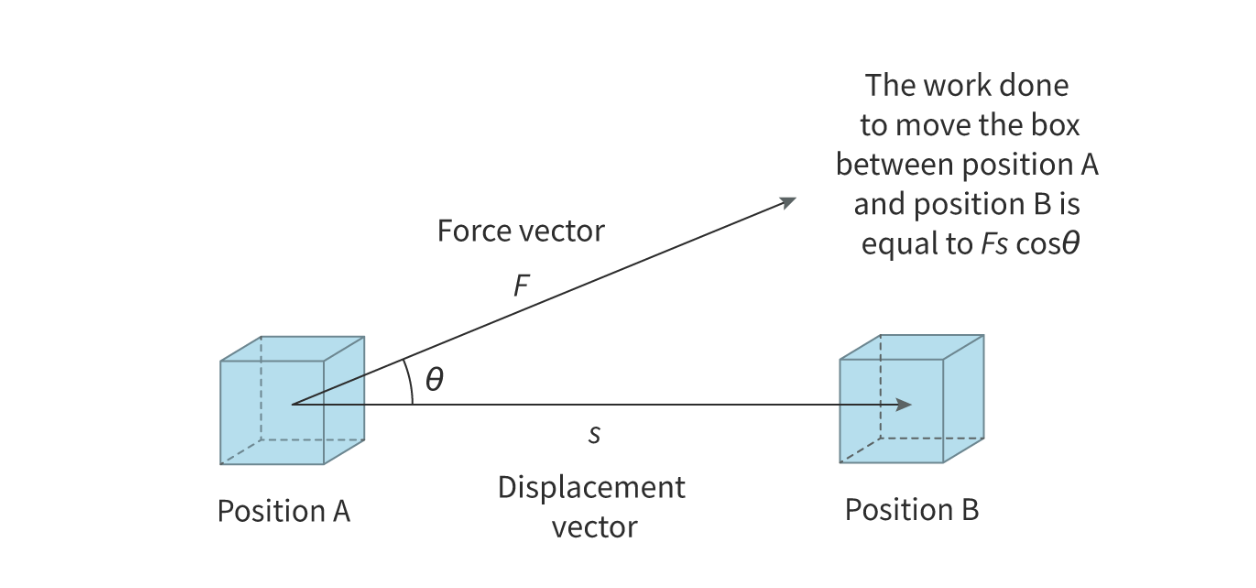
Work (W)
Scalar quantitymeasured in joules. W=Fscos(Θ). (Force x displacement x cos (angle between force and displacement).
Kinetic Energy (Ek)
Is Scalar and measured in joules. Energy object posess due to motion. Ek=1/2mv2 (mass x velocity)
Gravitation potential energy (Eg)
Scalar quantity measured in joules. ΔEg=mgΔh (mass x gravitational field strength x height
Elastic potential Energy (Eh)
Scalar quantity measured in joules ΔEh=1/2kΔx2. (spring constant x change in length)
Power (P)
Scalar quantity measured in watts P=W/t (Work over time)
Energy density (u)
Scalar quantity e/v