lecture 3 plant anatomy
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
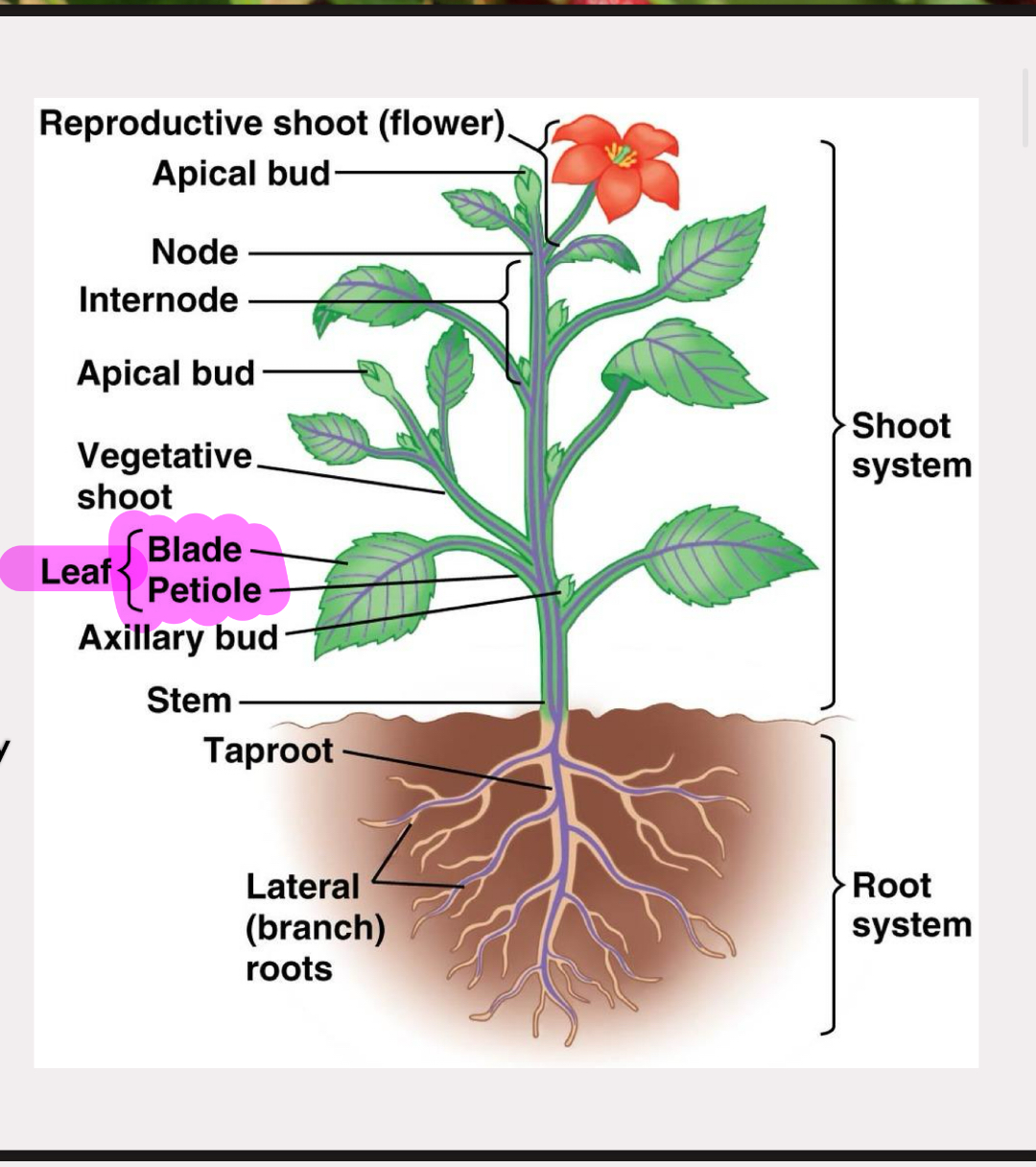
shoot system
leaves for photosynthesis
stem supports plant and transports water and minerals by vascular system
nodes and internodes
terminal/apical bud and lateral/axillary buds for growth
flowers for reproduction
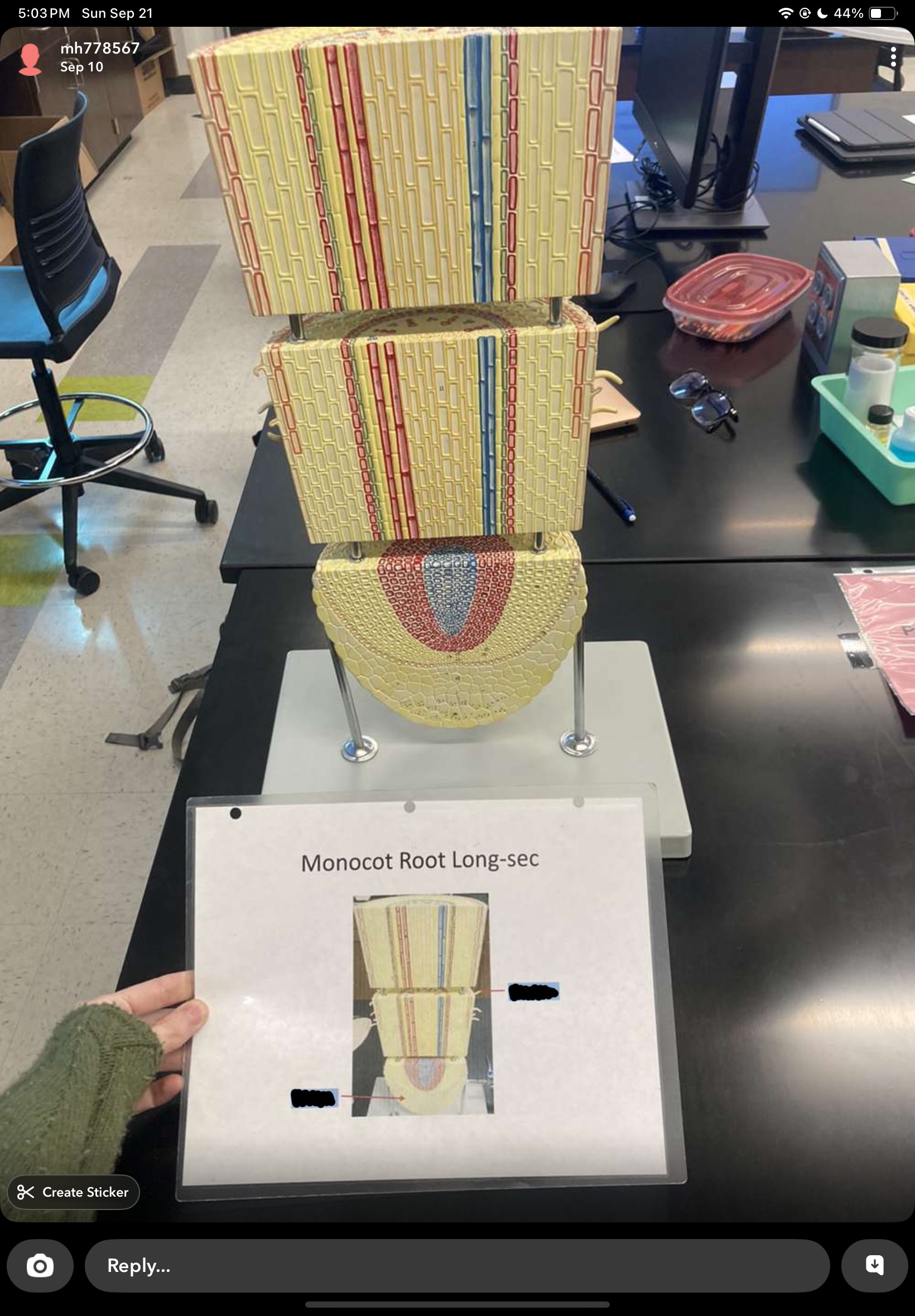
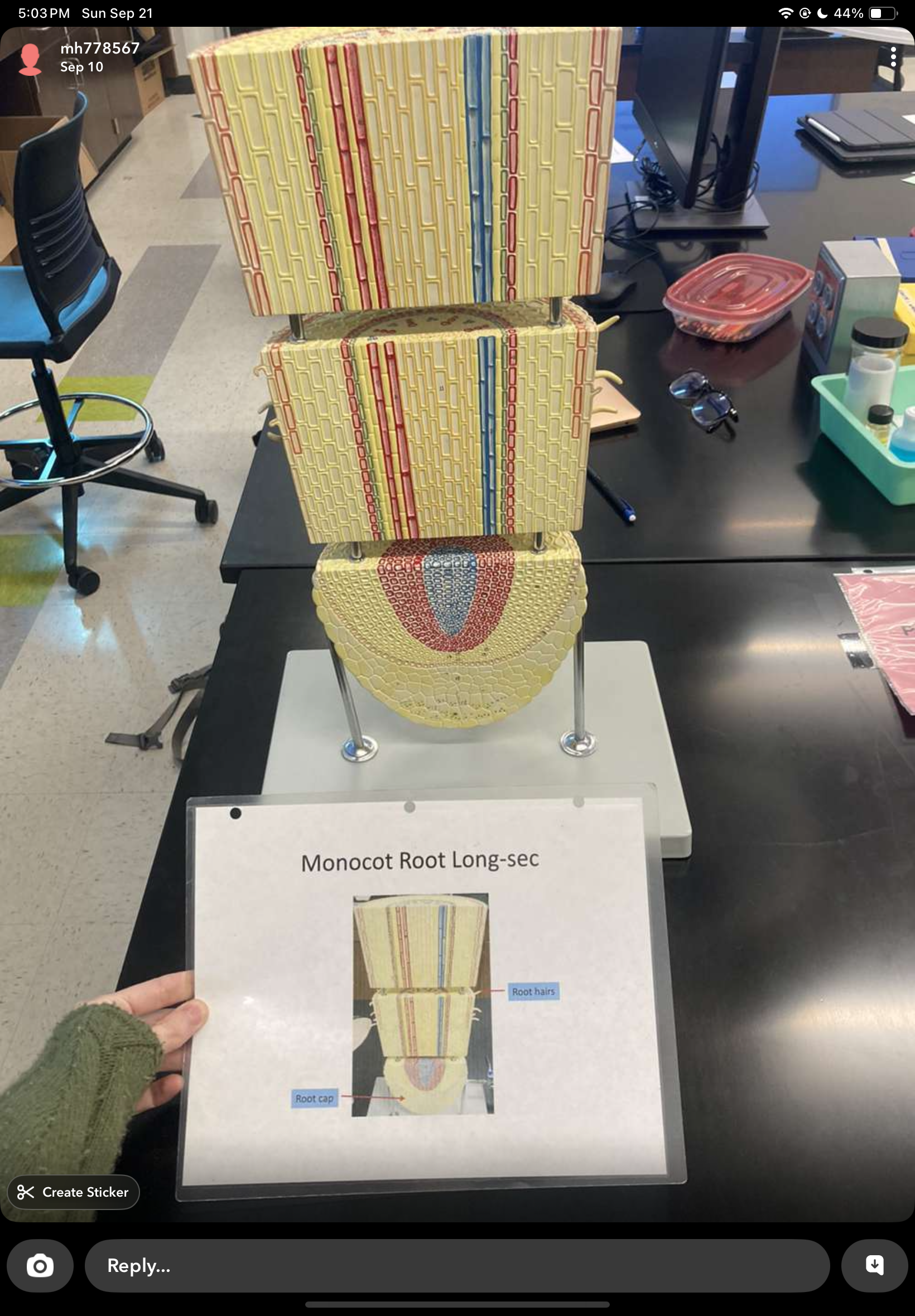
root system
anchors plant and stores nutrients
brings in water and minerals
root hairs increase surface area
3 types:
adventitious - from stems (strawberries)
taproot - tapering root (shrubs, carrot)
fibrous - thin, spread out roots (grasses)
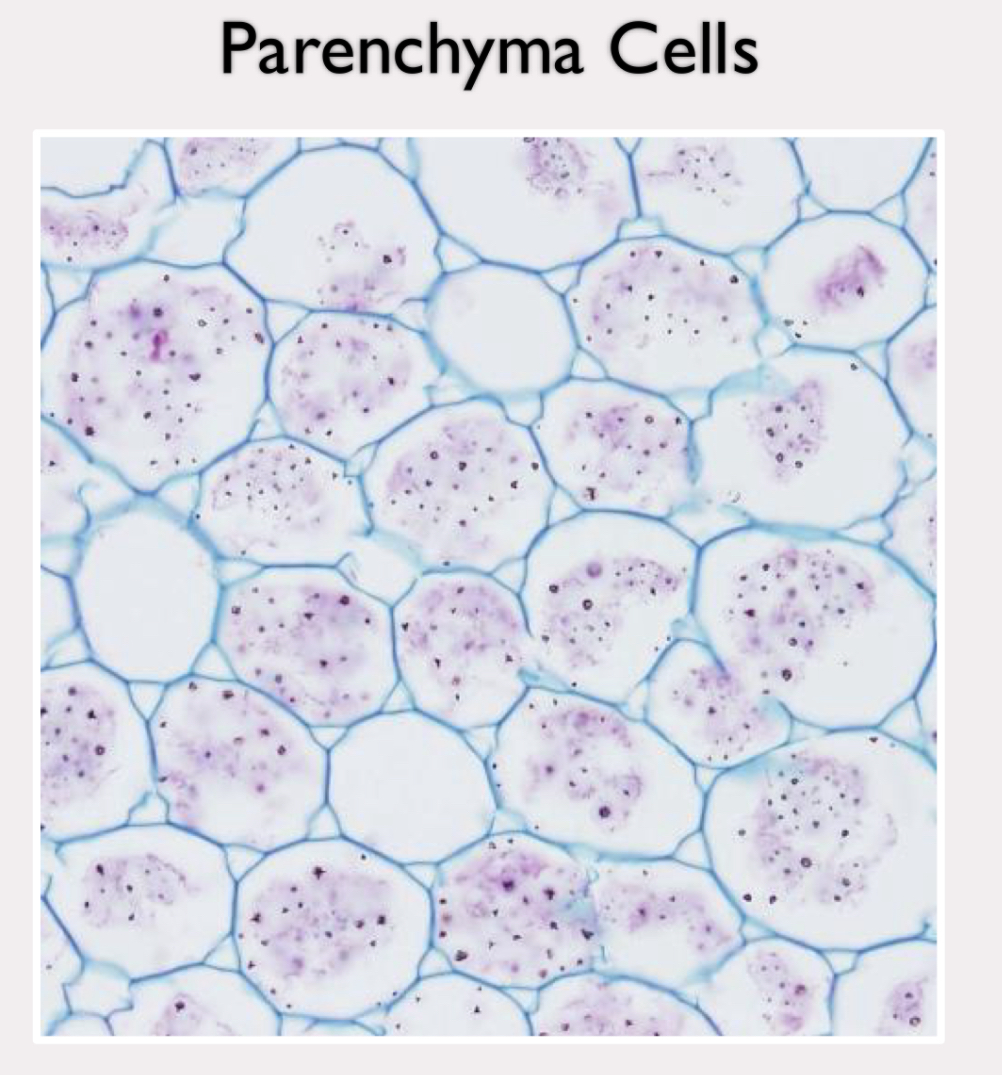
Parenchyma cell
least specialized
no secondary cell wall
thin primary cell wall
holds water and stores nutrients in large central vacuole
location of most metabolism to support plant
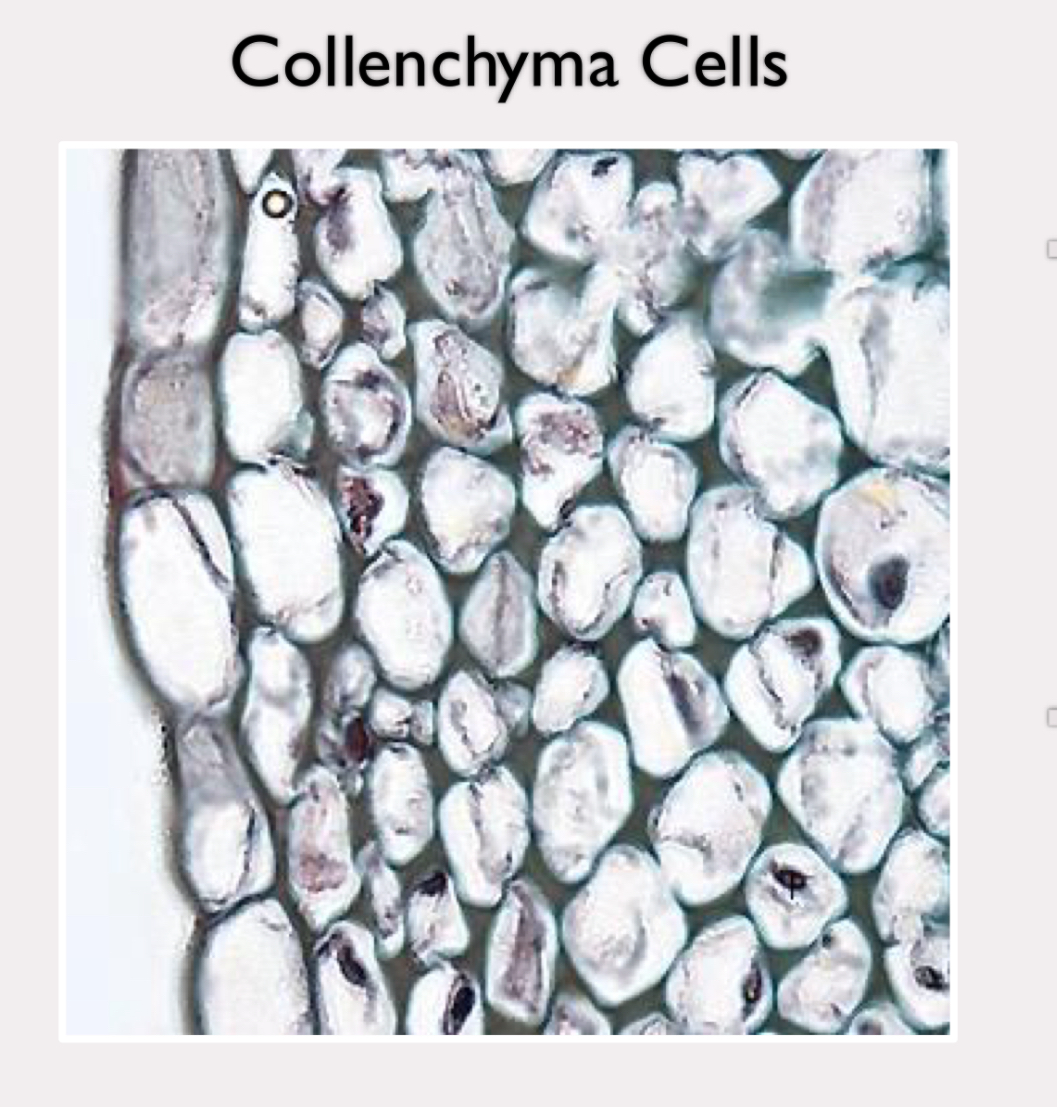
Collenchyma cells
no secondary cell wall
more rigid primary cell wall
important in support of young plants and stems of nonwoody plants
capable of elongation
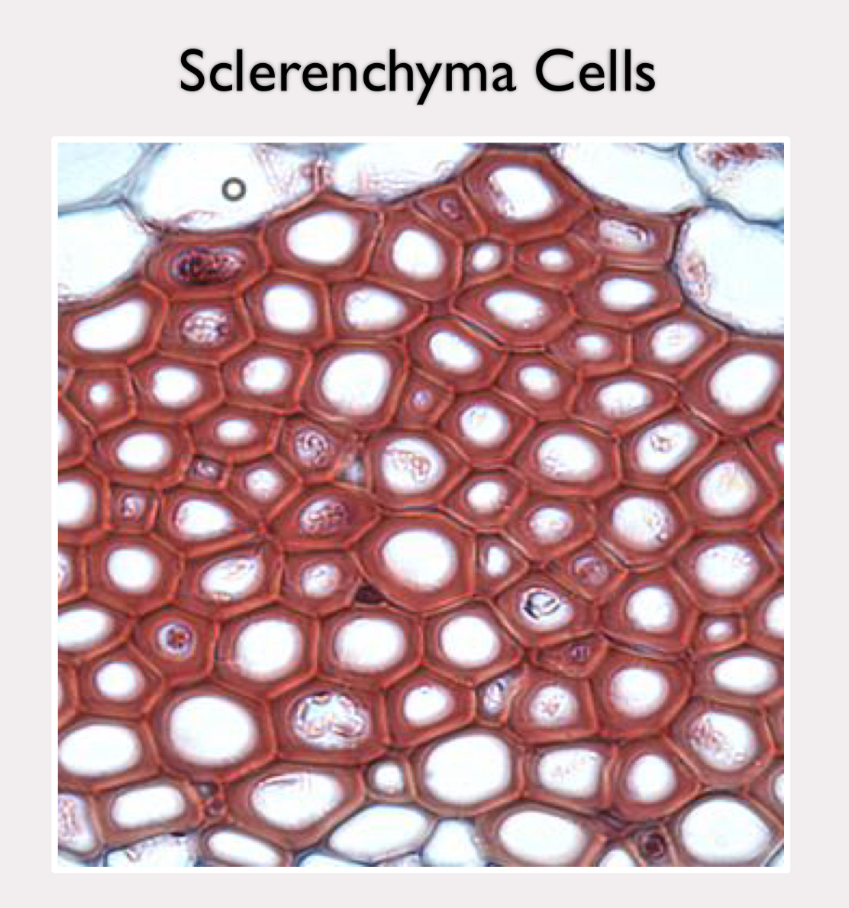
Sclerenchyma cells
secondary cell wall containing lignin
dead tissue, but important in support
found in areas that have stopped growing
fossil fuels
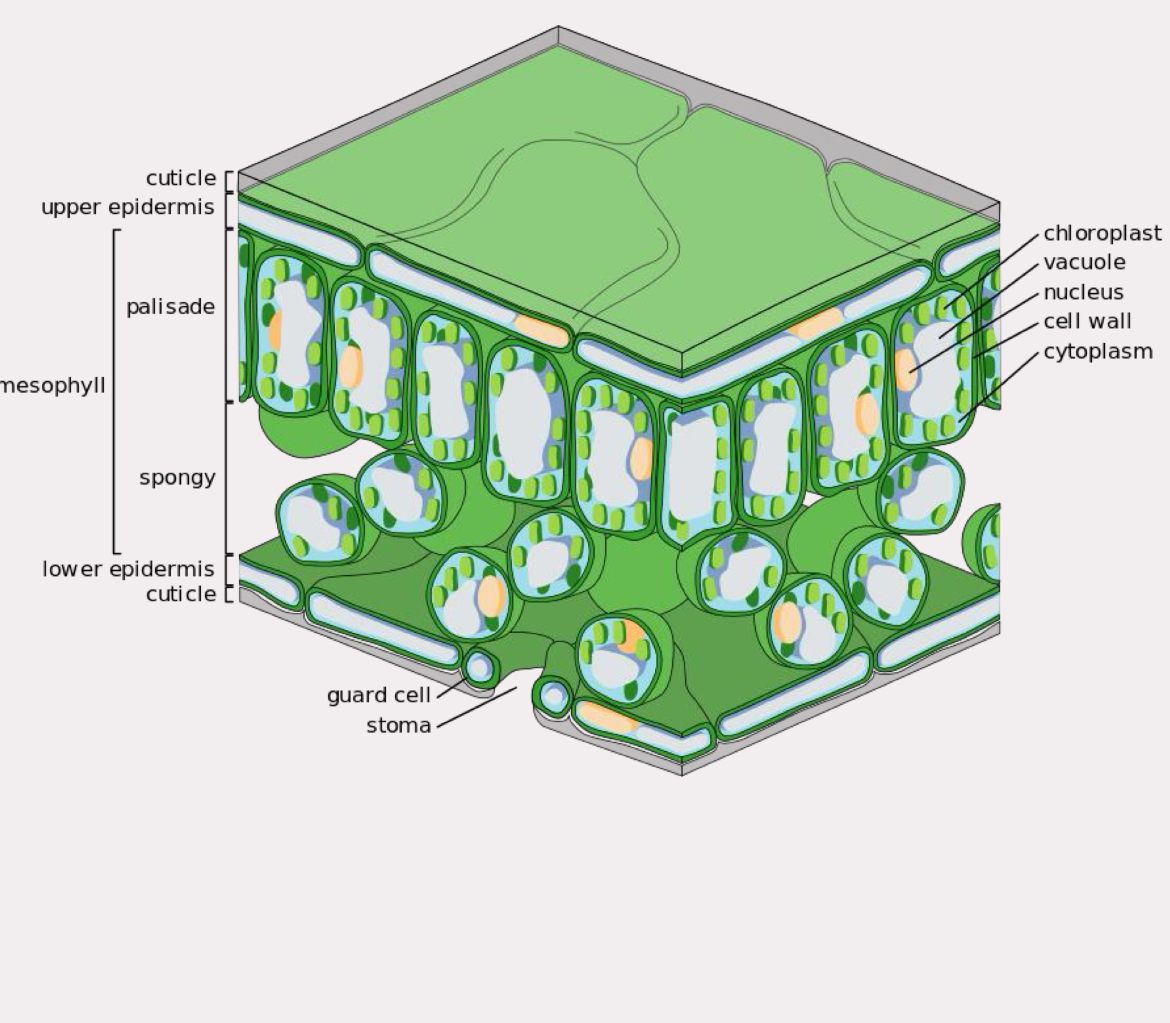
epidermis
protection, but can be more specific
single layer of tightly packed cells, effectively skin
leaves and sometimes stems have cuticle
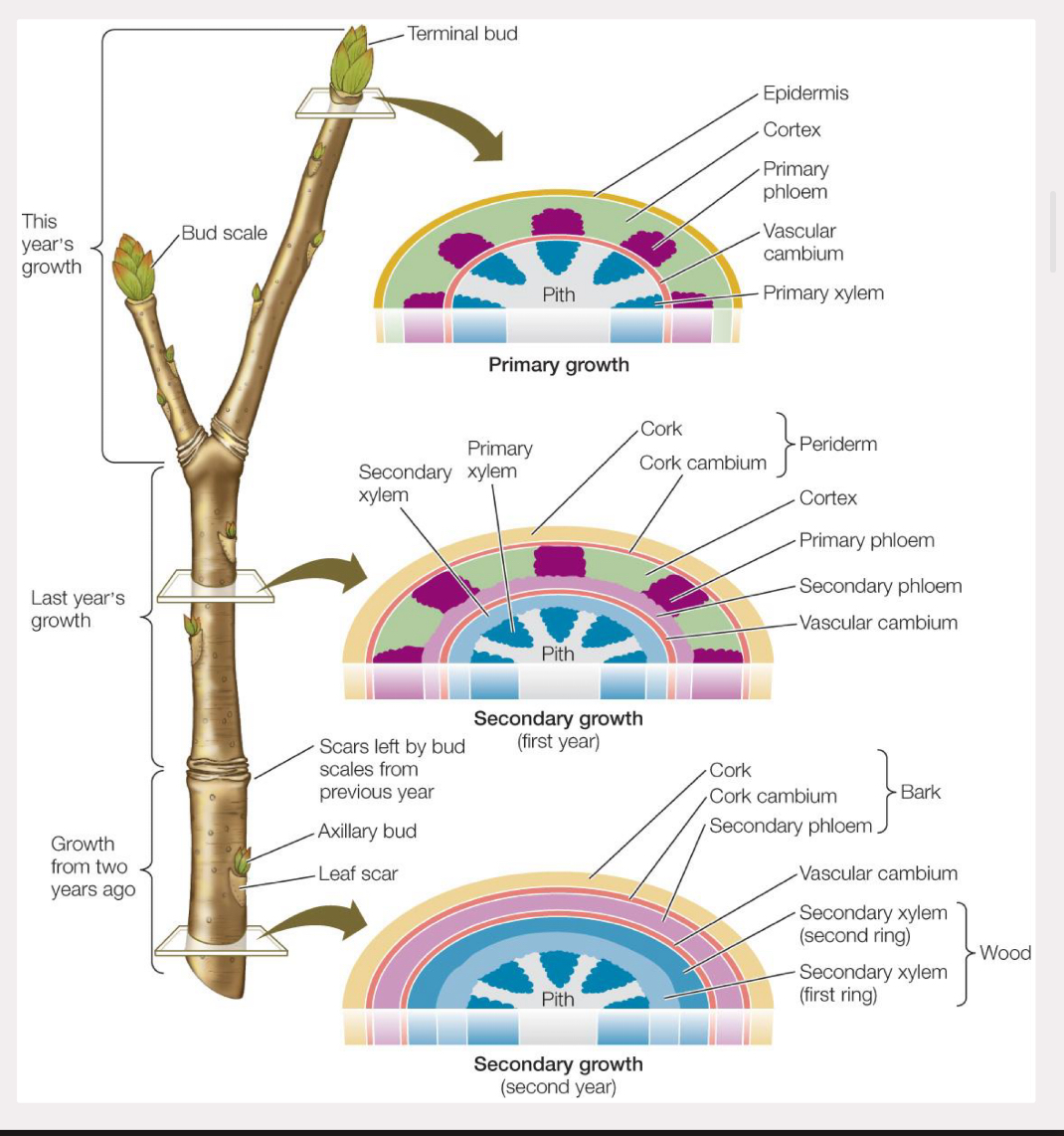
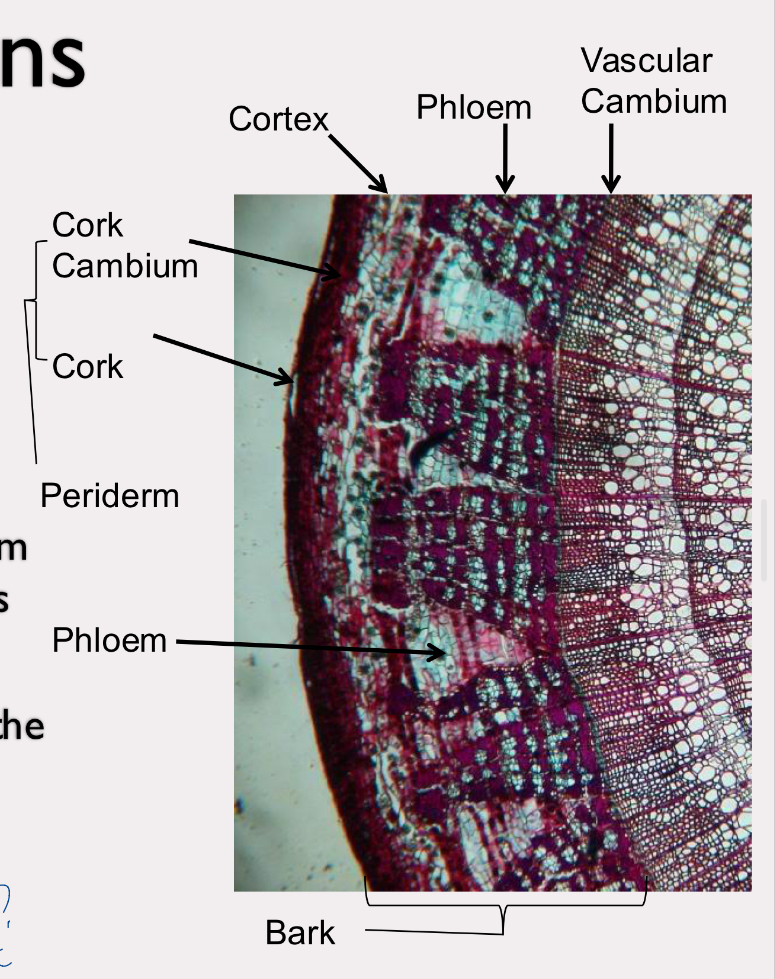
periderm
replaces epidermis during secondary growth
the cork and cork cambium
dead tissue
arises from ground meristem
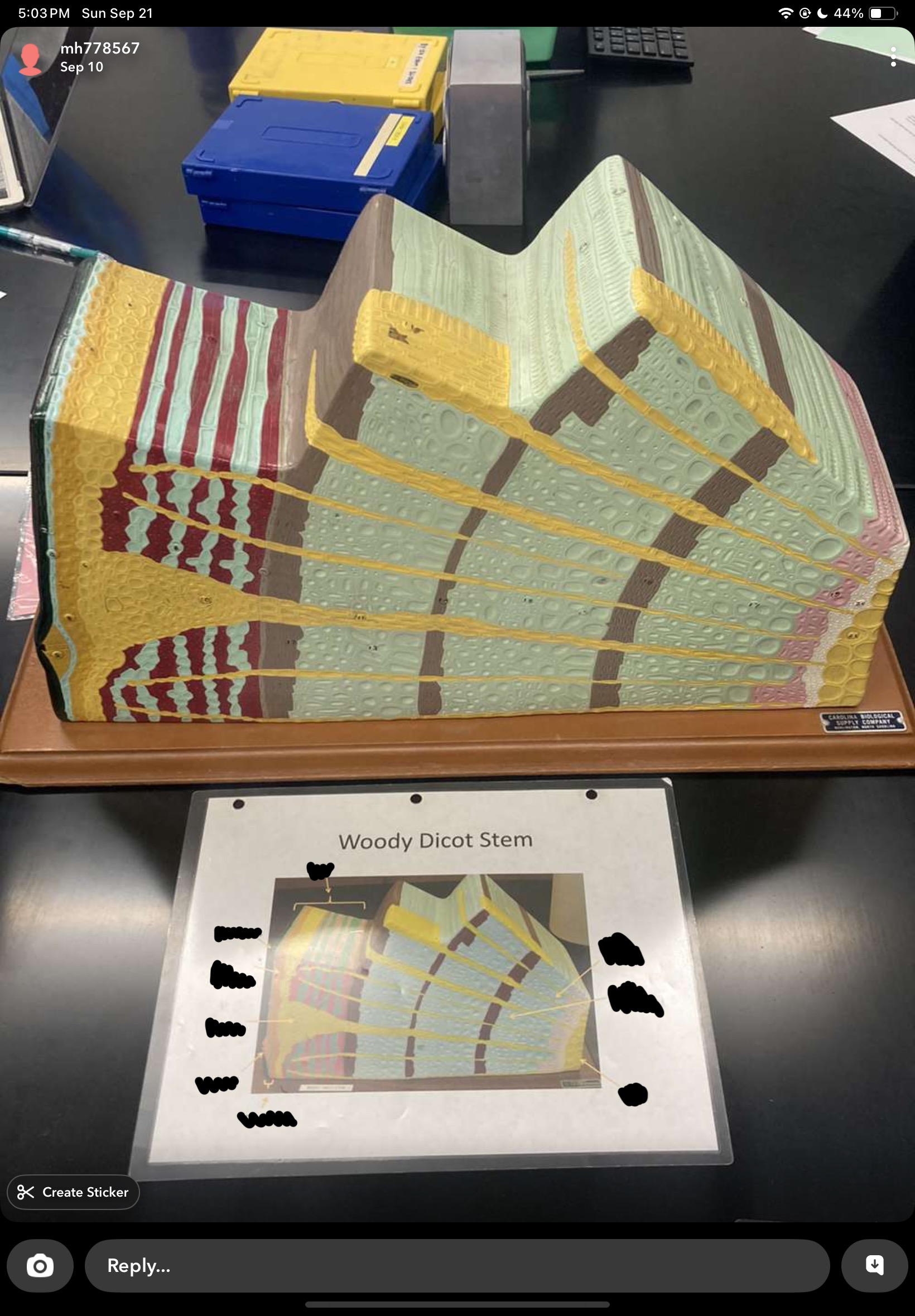
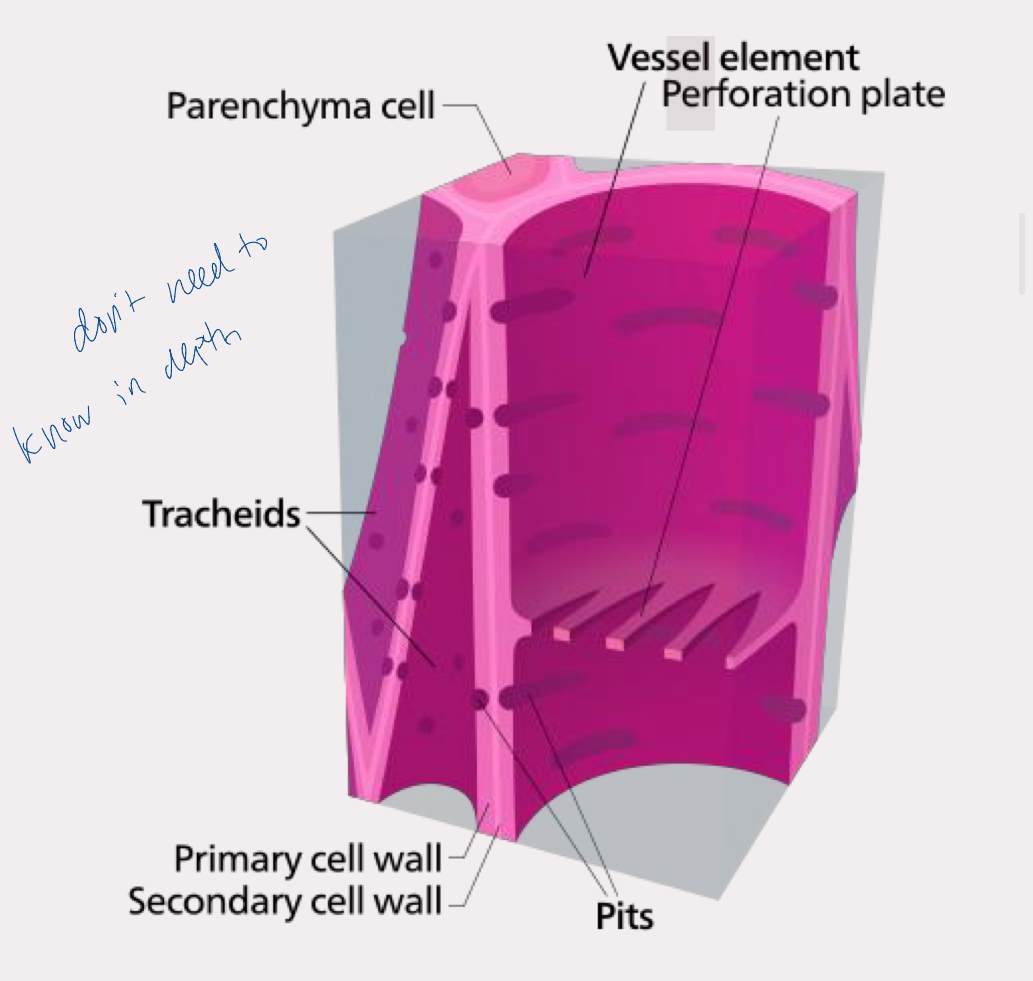
xylem
dead at maturity
transports water up from the roots
contains tracheids and vessel elements in angiosperm
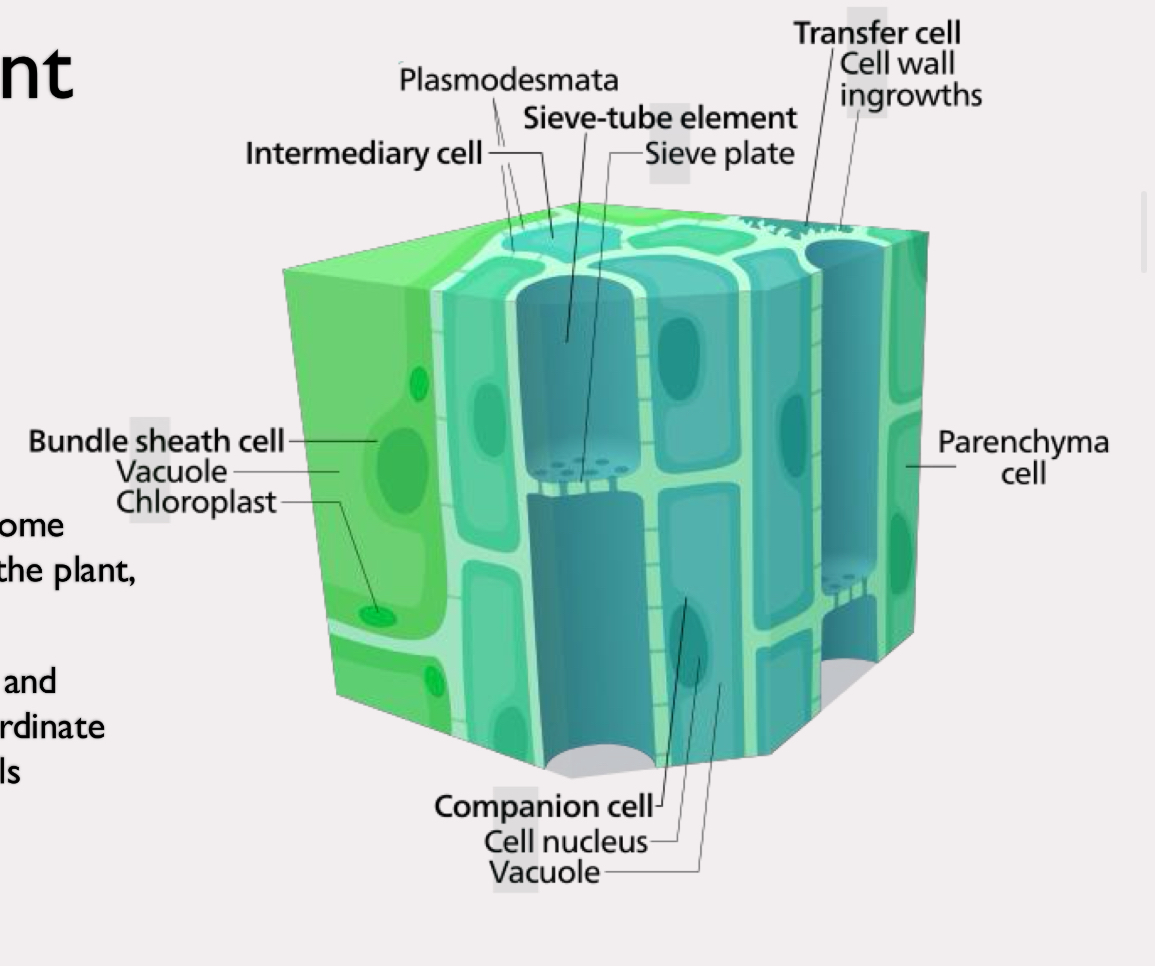
phloem
transports sucrose and some mineral ions throughout the plant, both up and down
contains sieve tube cells and companion cells that coordinate function of sieve tube cells
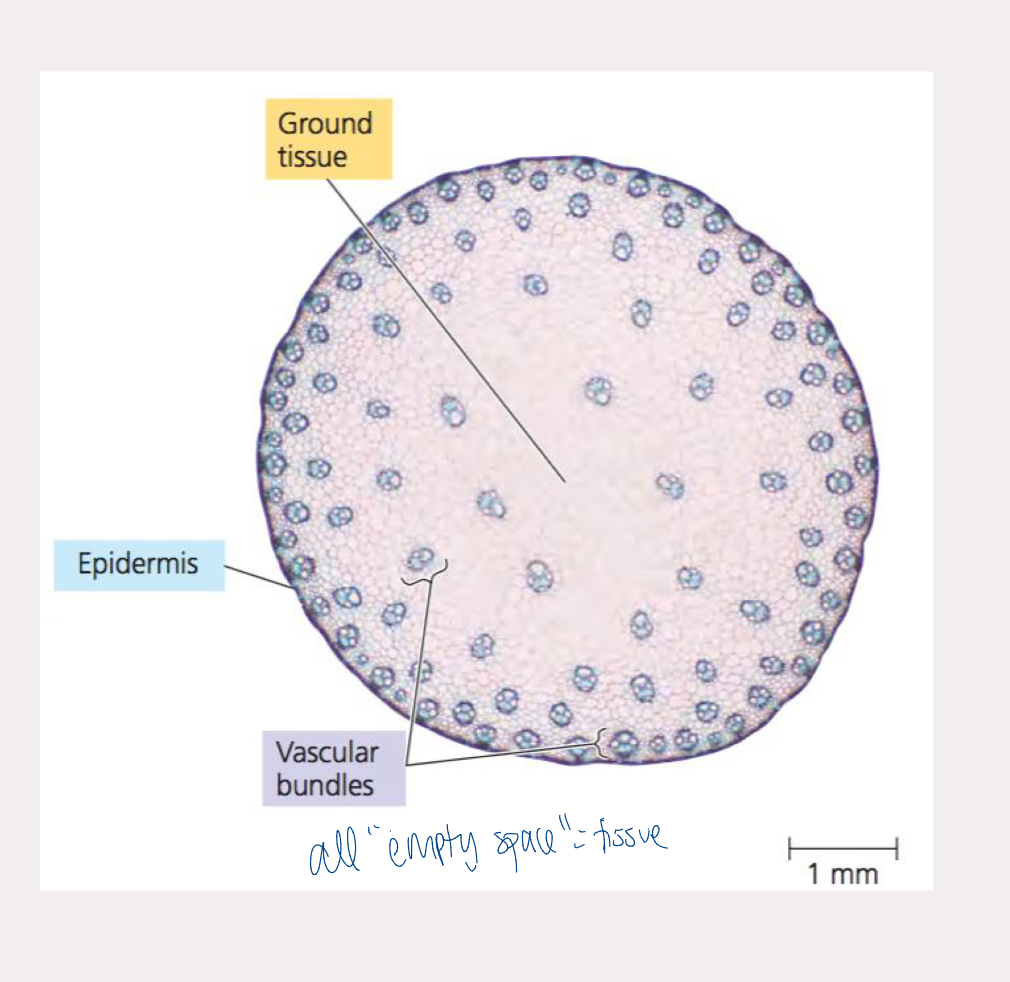
ground tissue
aka pith or cortex depending on location
usually made up of parenchyma cells
located between dermal and vascular tissues
acts in photosynthesis, storage, and support
indeterminate growth
continues throughout entire life of organism
in plants, occurs at meristems via mitosis and cell elongation
determinate growth
occurs until organism reaches a certain size
in humans, occurs in hte long bones until maturity is reached during mid to late teens up to early 20s
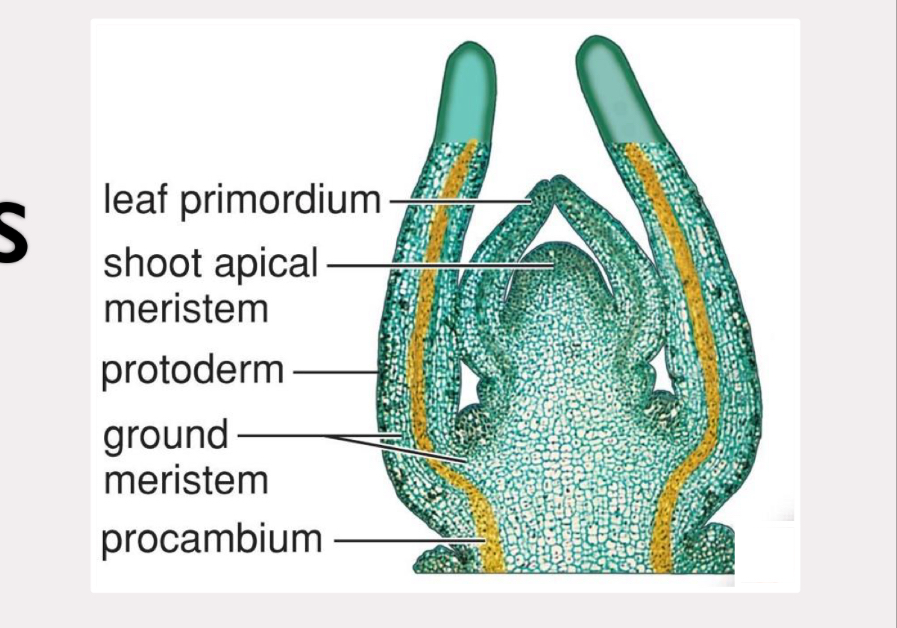
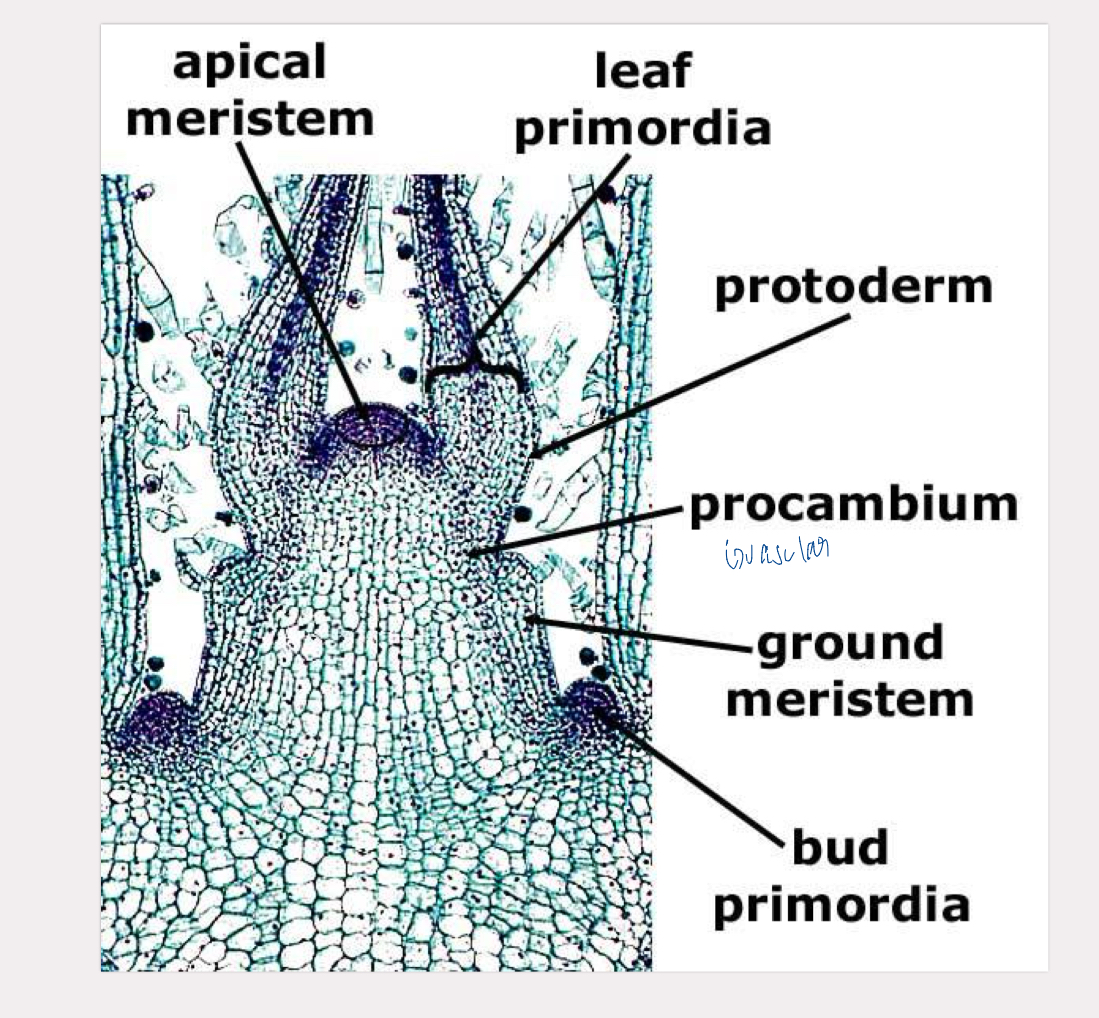
protoderm
turns into epidermal tissue
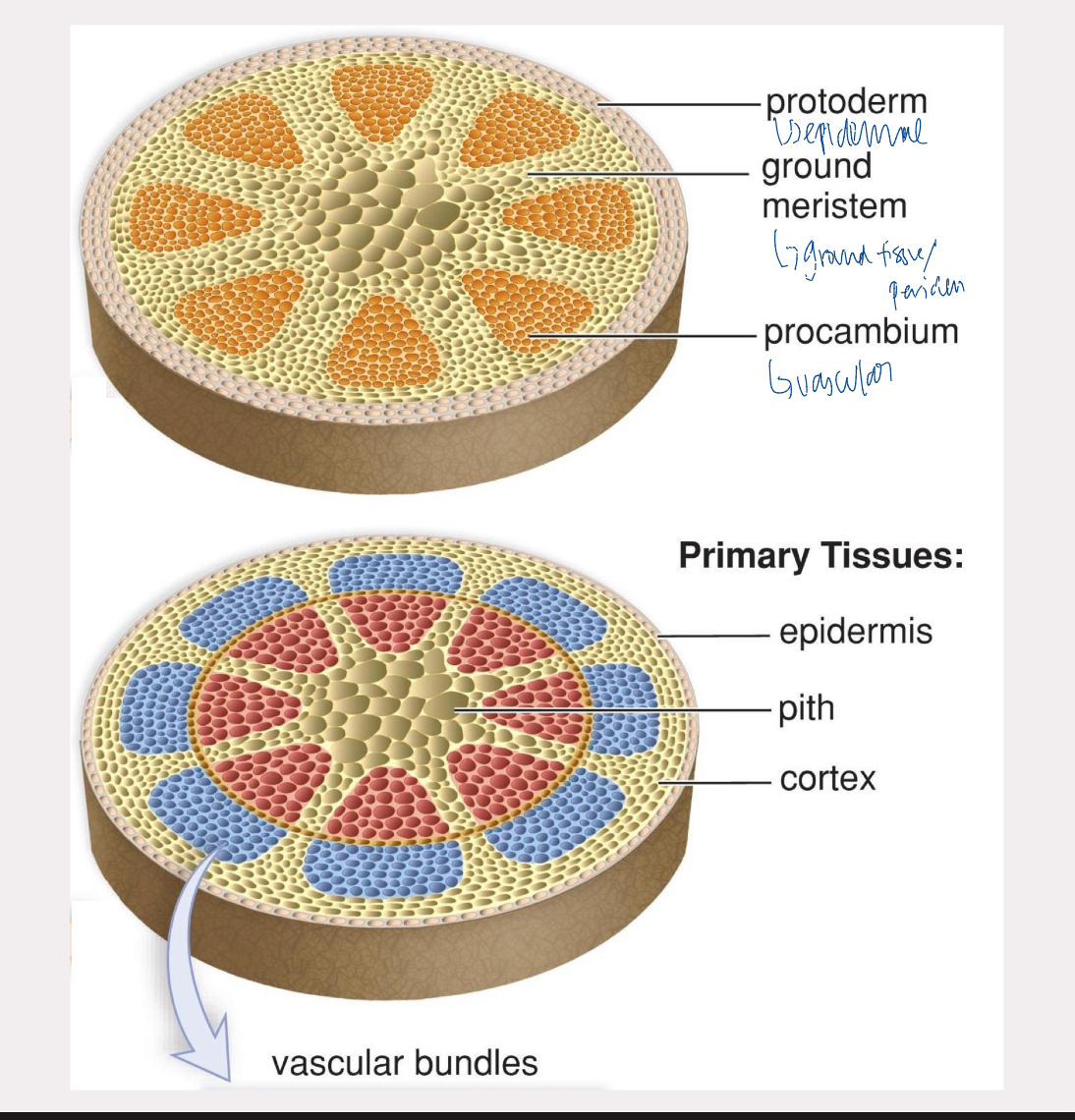
procambium
turns into vascular tissue
ground meristem
turns into ground tissue and periderm
apical meristem
located at root and shoot tips
responsible for primary growth
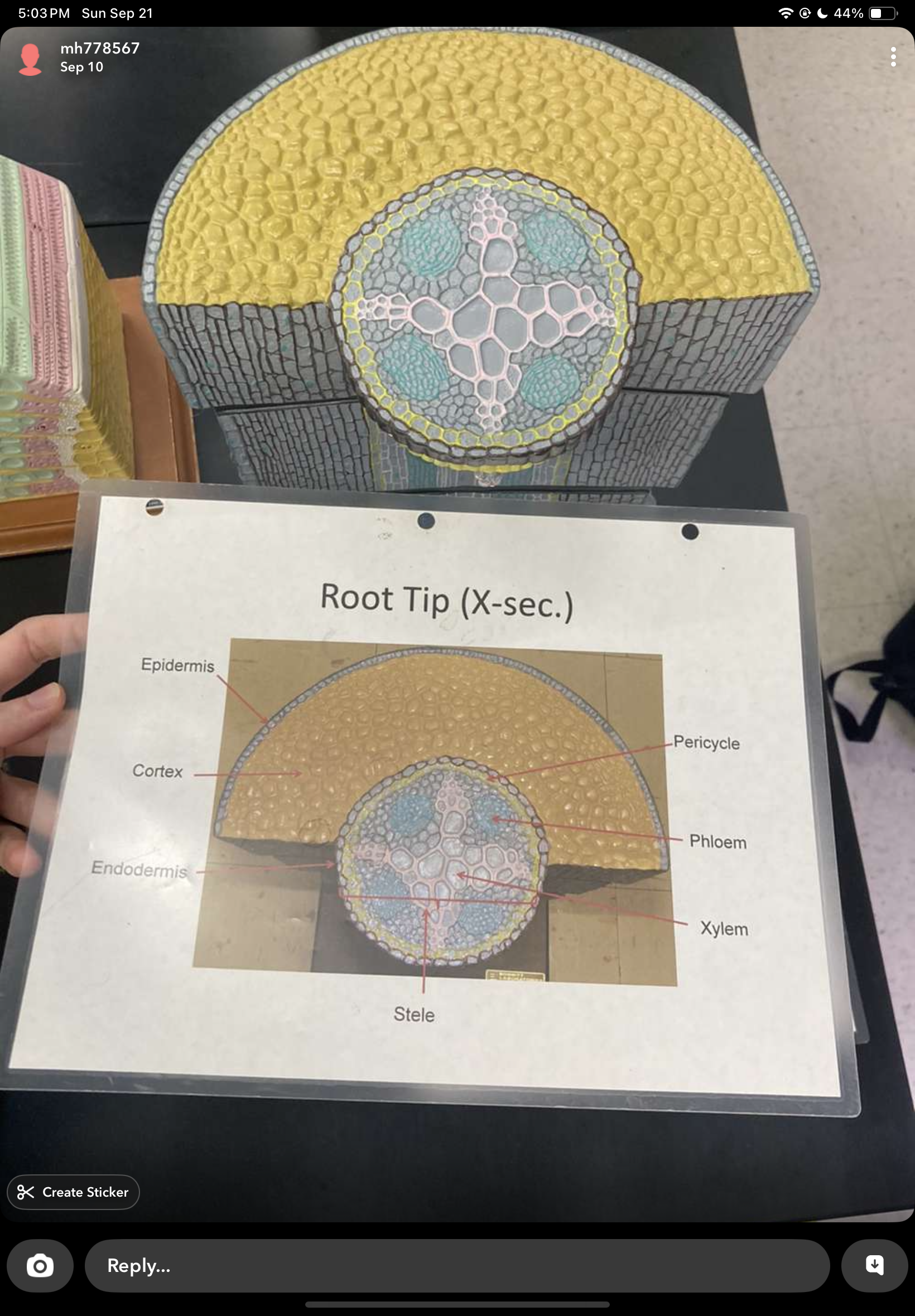
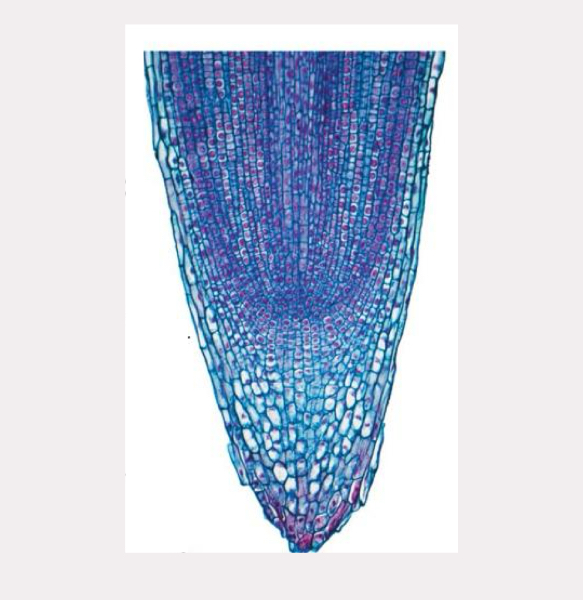
root cap
protects apical meristem of the root
secretes slimy substance to help lubricate root as it moves

lateral meristem
seocondary growth from cork cambium in woody perennial dicots
epiderms is replaced by periderm
cork cambium produces phelloderm and cork, and waxy substance suberin thats added to cork
cork cambium, phelloderm, and cork are periderm
bark is periderm and phloem
coleus stem tip
pyrus root tip
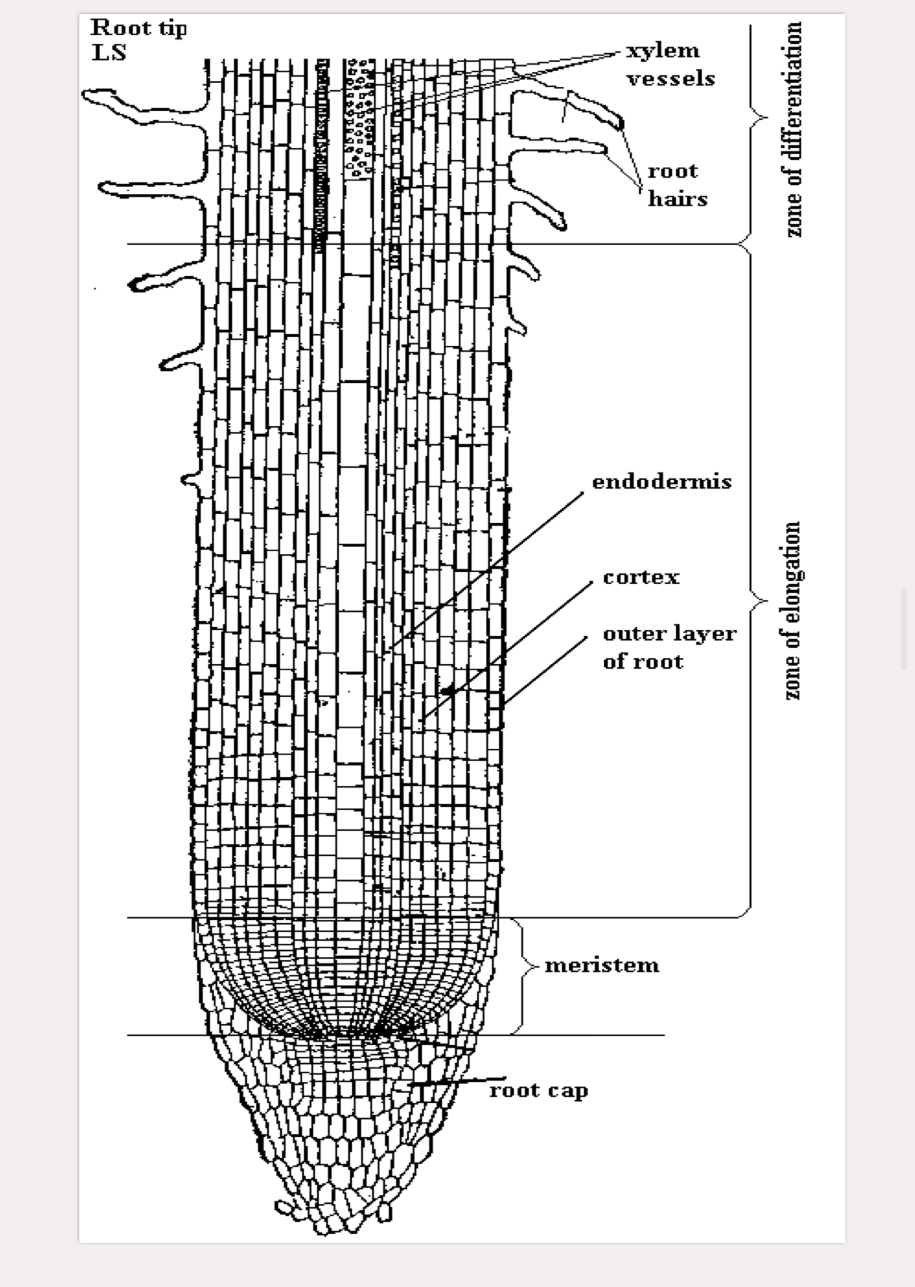
zone of cell differentiation/maturation
major tissue types present, contains root hairs and lateral rotos
zone of elongation
cells take in water and elongate
zone of cell divsion
growth via mitosis
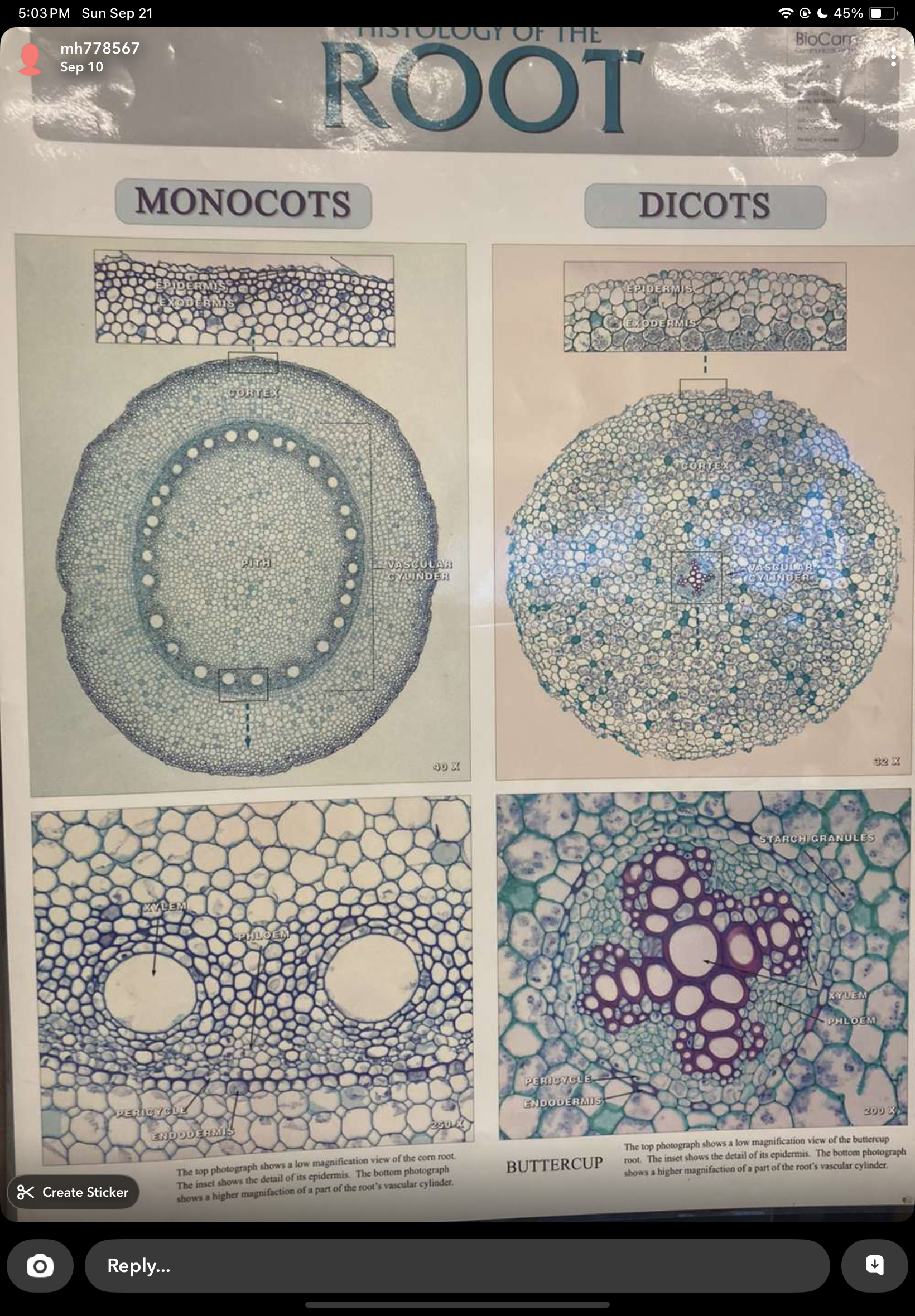
ranunculus root
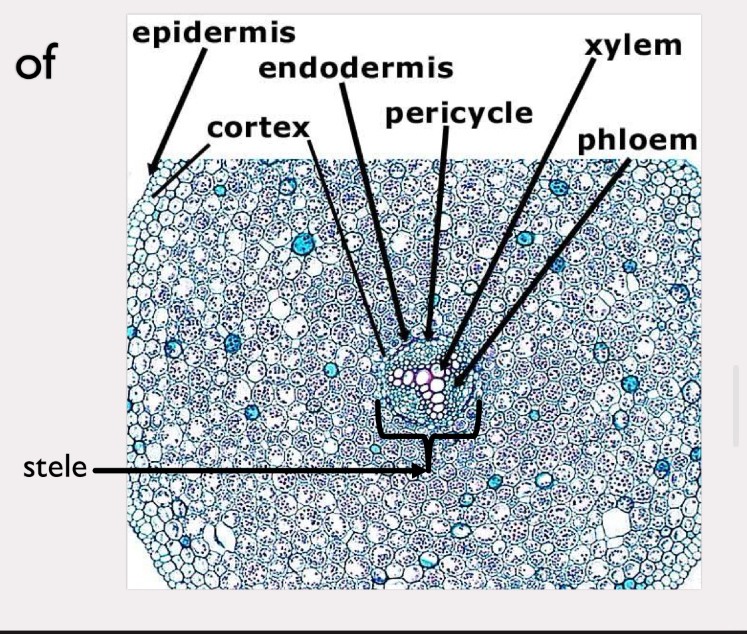
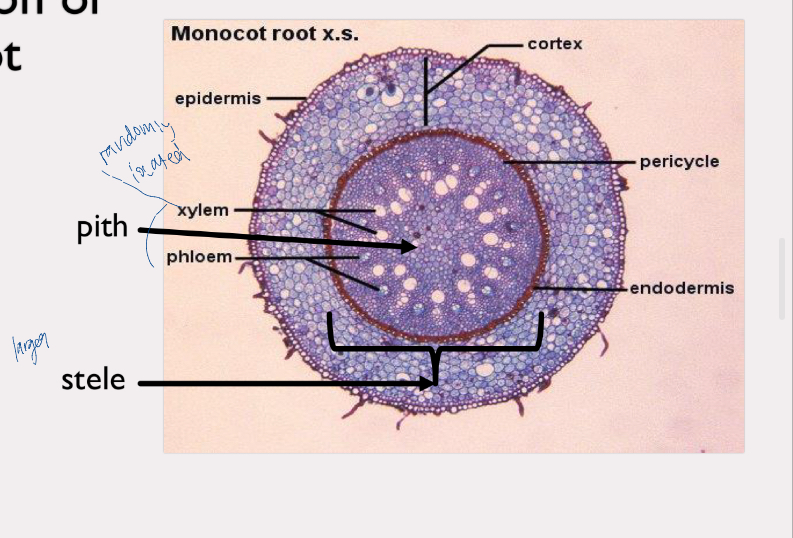
zea root
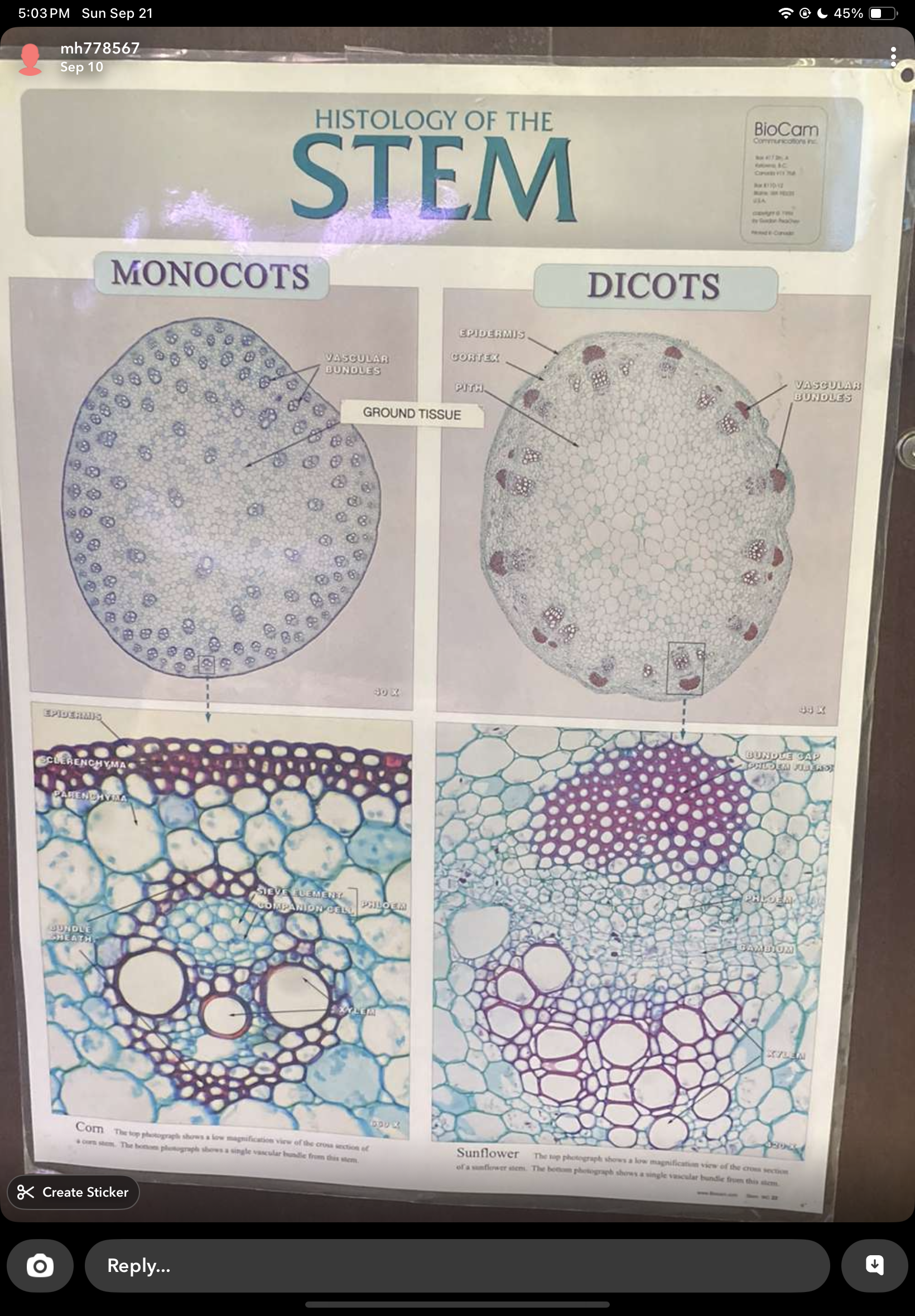
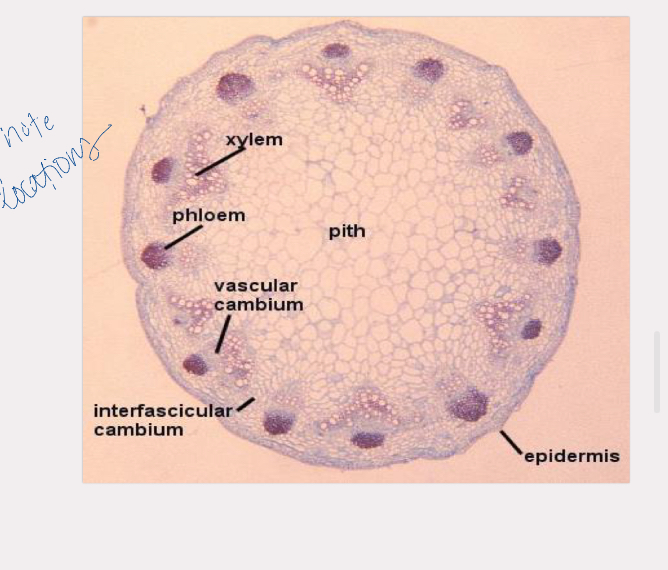
helianthus tem
epidermis, cortex, vascular bundles, pith
xylem is closer to pith, phloem to epidermis
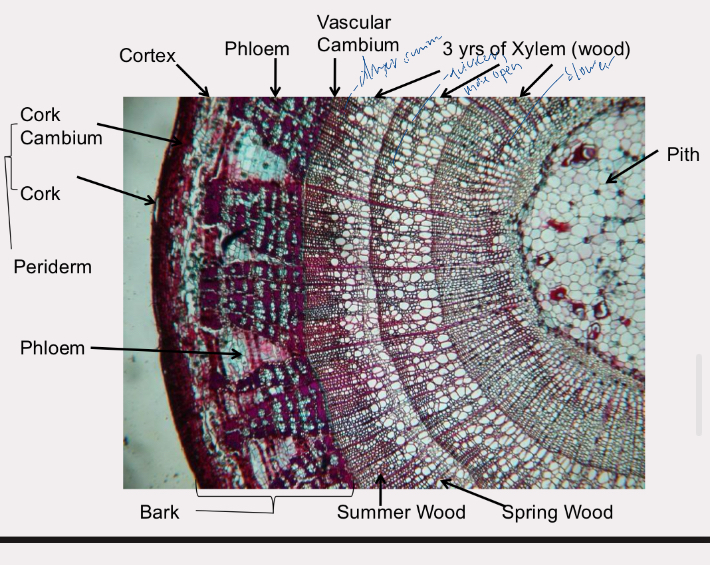
tilia woody stem
older xylem forms non func heartwood
newer xylem forms func sapwood
xylem added seasonally - rings
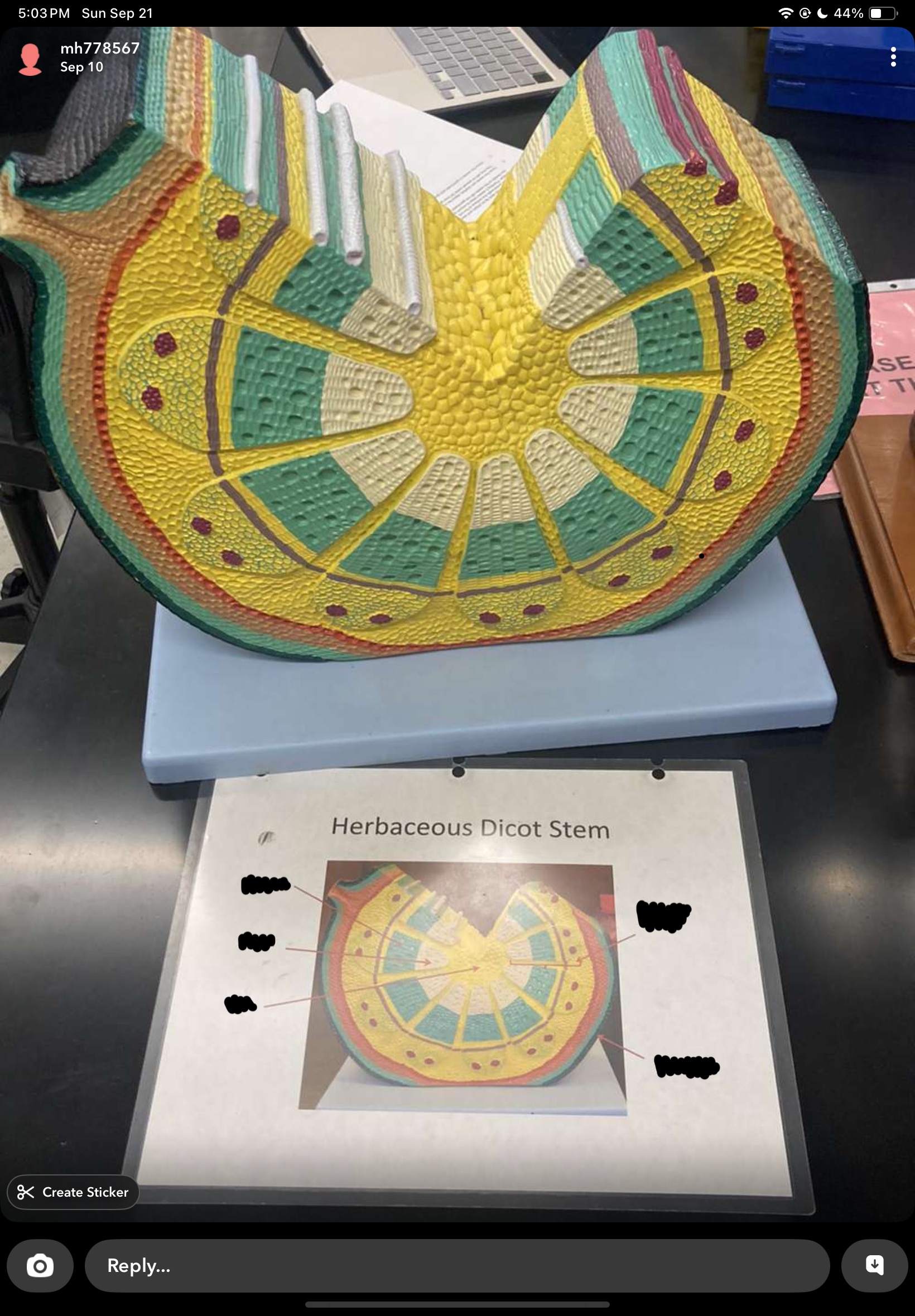
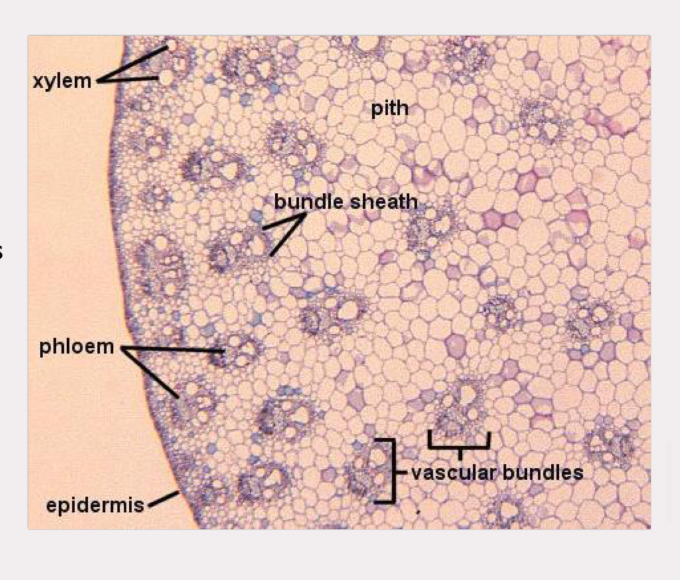
zea mays stem
epidermis, ground tissue, vascular bundles
vascular are scattered
phloem always external to xylem
annuals
a year or less for germination to death
biennials
live two years, one for vegetative growth and next for flowering
pernnials
live many years before dying of disease or injury
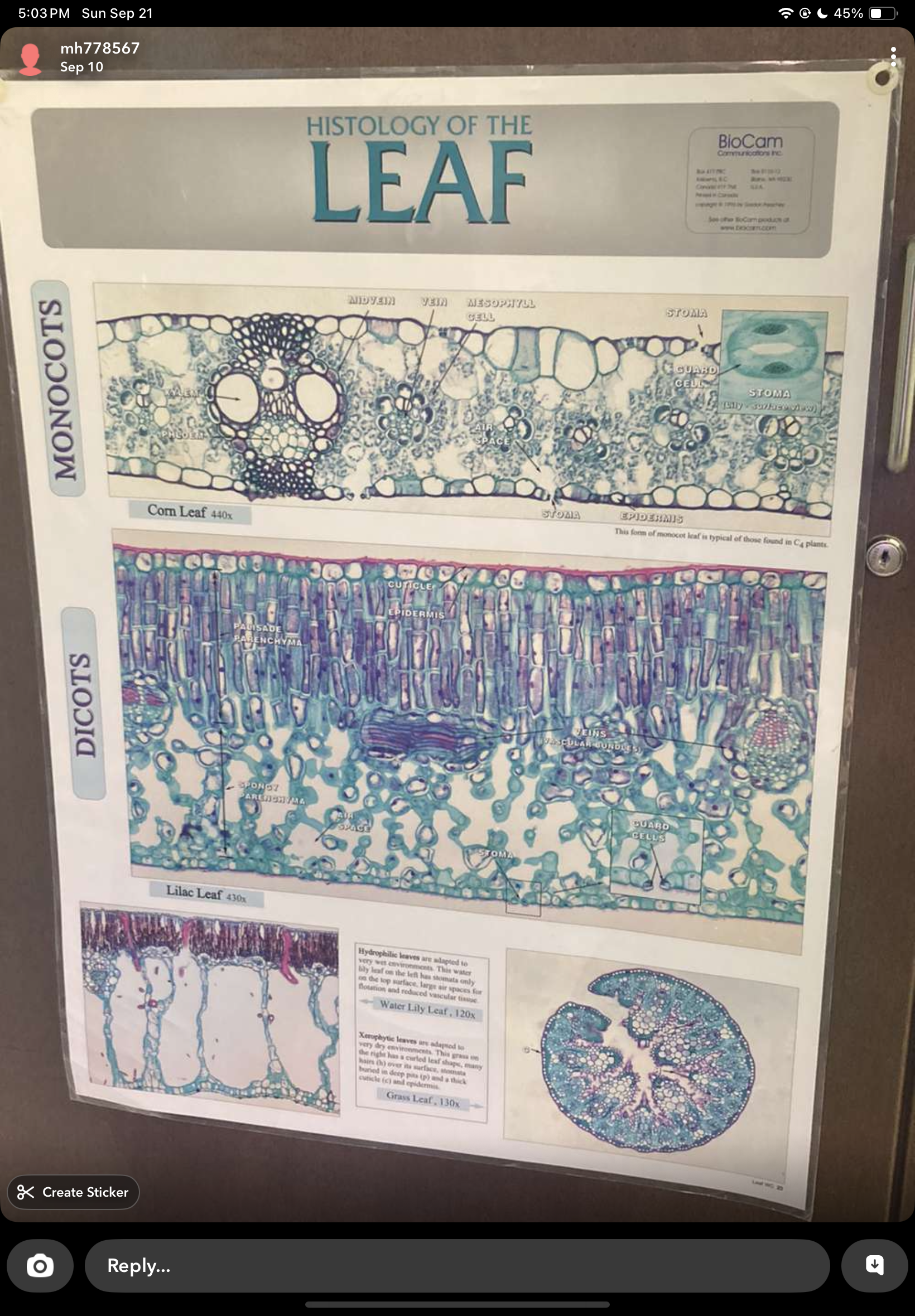
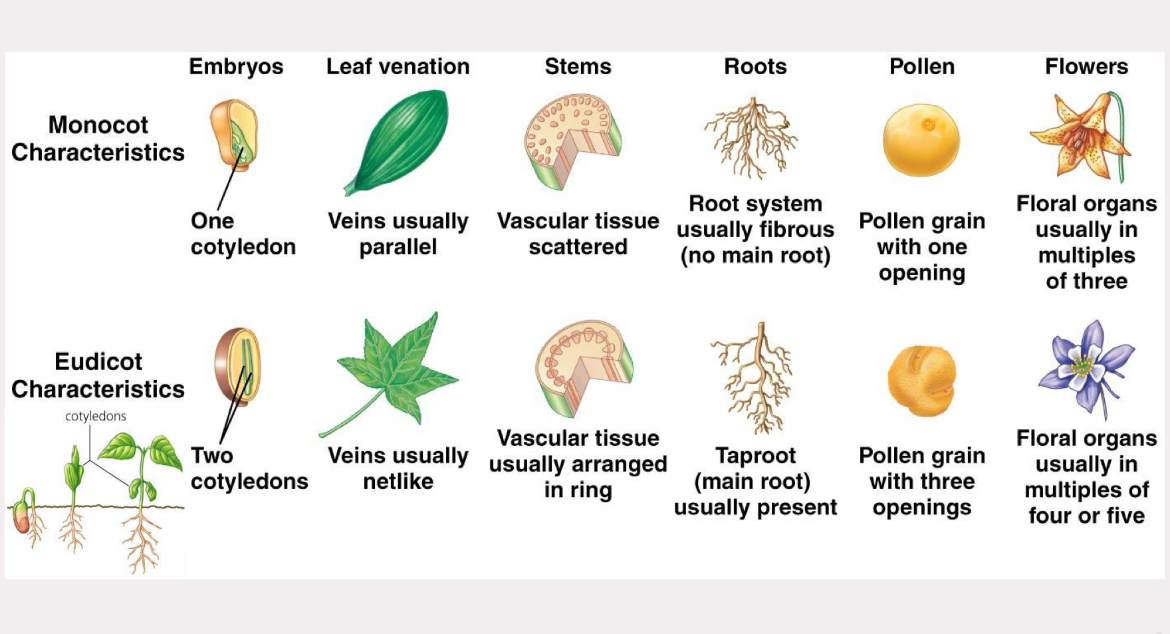
monocots vs dicots
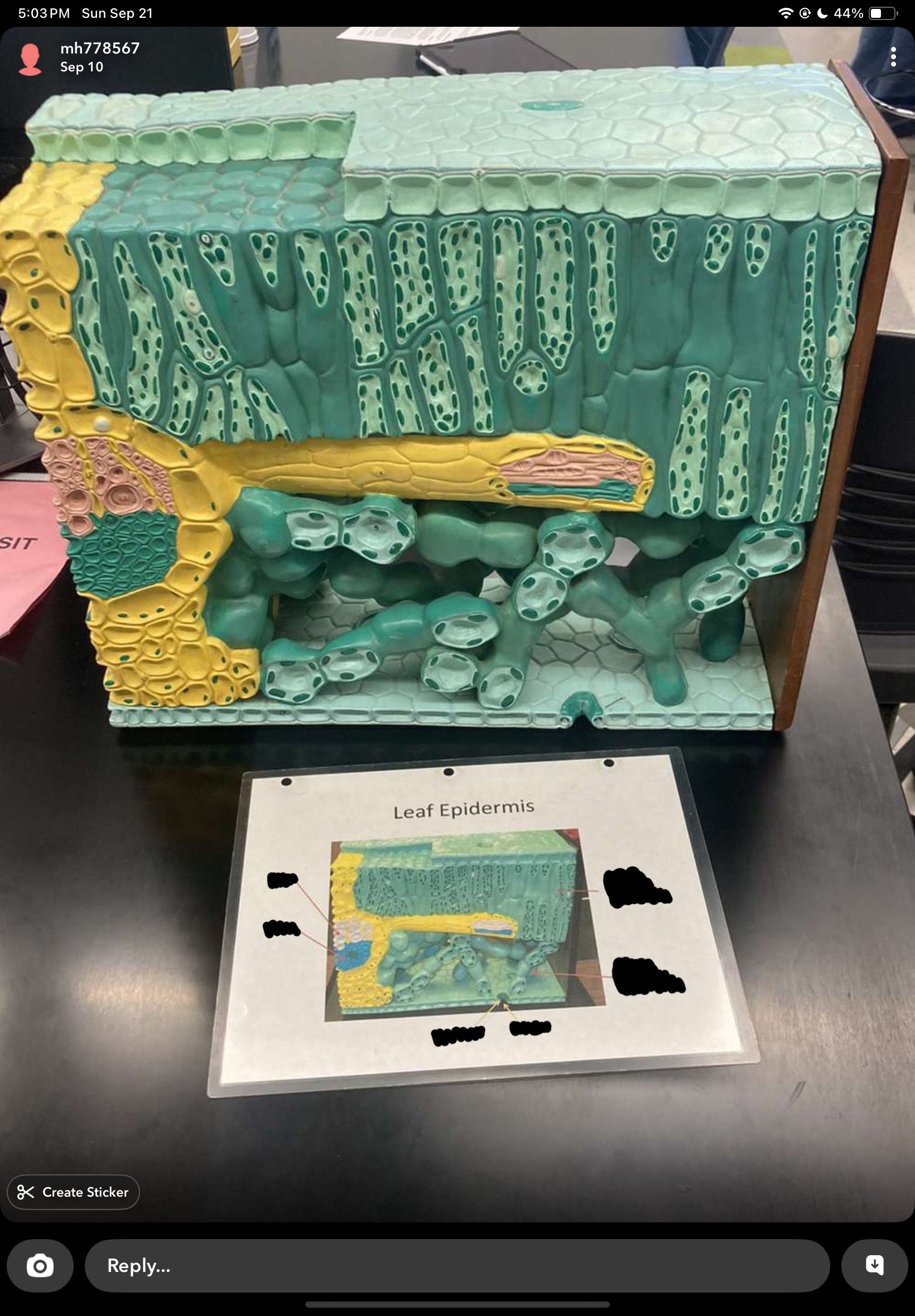
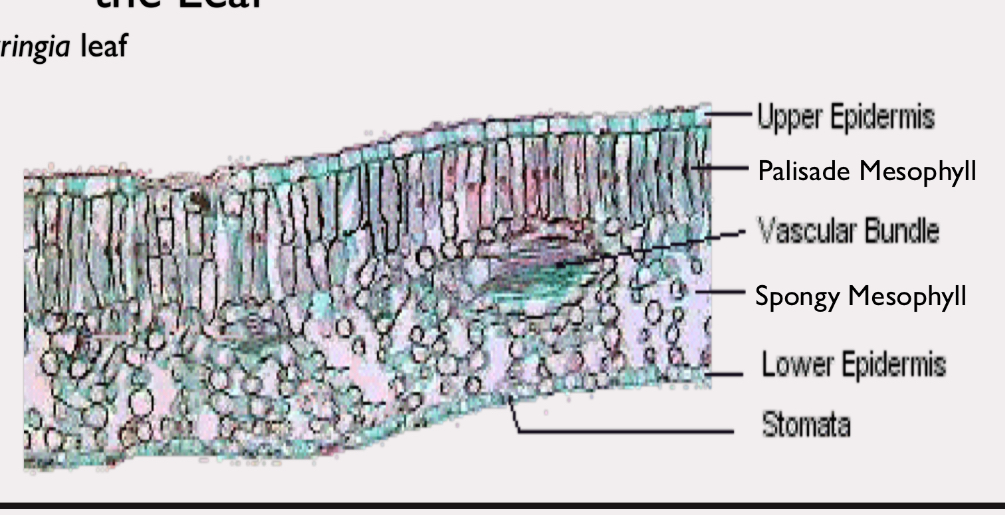
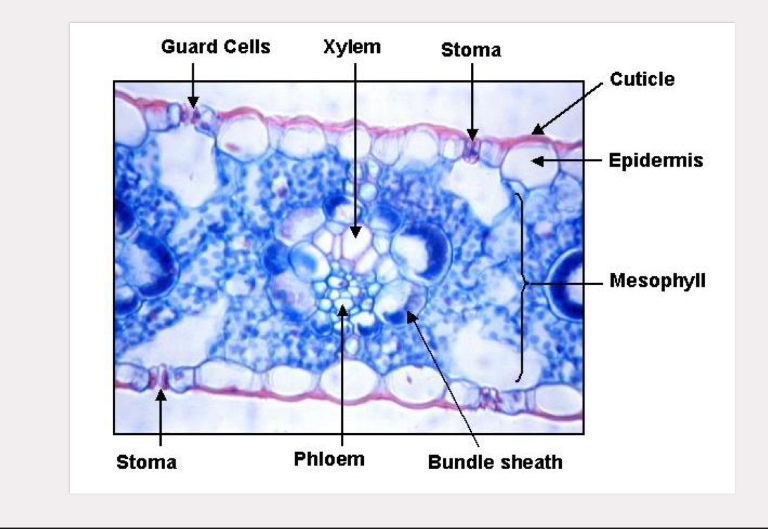
leaf epidermis
trichomes, guard cells, stomata
syringia leaf
leaf model
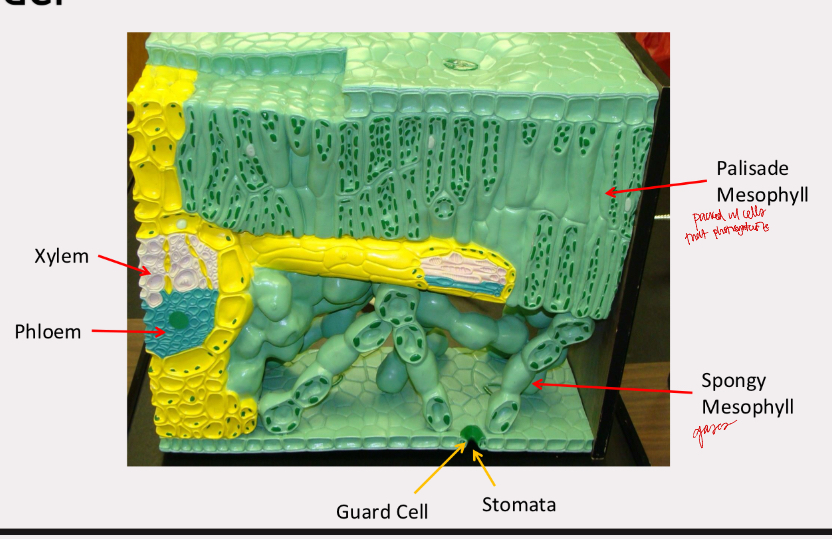
zea leaf
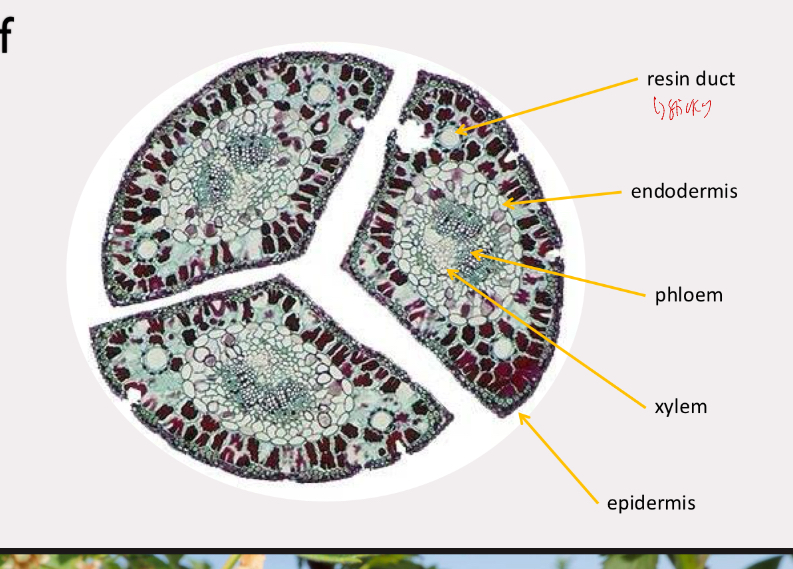
pinus leaf
monoecious plants
stamen and carpel
dioecious plants
either stem or carpel, one plant could have flowers with both
perfect flowers
stamens and carpel
imperfect flowers
either stemsn or carpel
complete flowers
sepals, petals, stamens, and carpel
incomplete flowers
missing sepal, petal, stamen, and/or carpel
aggregate
rasp and blackberry
multiple
pineapple, mulberry, fig
pome
apple, pear
drupe
cherry, peach, almond, olive
legume
beans, peas, soybeans, peanut
hesperidium
orange, lemons, grapefruitp
pepo
squash, cucumber, watermelon
berry
grape, tomato, peppers
grain
wheat, corn, rice
achene
sunflower
accessory
strawberry
nut
oat, hickory
sumara
ash, maple, elm
capsule
okra