bio112 exam 1
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
blood temperature
100.4 F
average blood volume (liters)
5 L
blood ph
7.35-7.45
blood functions
distribution, regulation, protection
components of blood
plasma (55%) (fluid portion of blood)
buffy coat (1%) (WBC, platelets)
erythrocytes (45%) (RBC)
formed elements of blood (cellular components)
buffy coat & erythrocytes
hematocrit
o2 carrying capacity of blood (percentage of whole blood made of RBCs)
average hematocrit (percentage)
45%
plasma composition
91.5% water (solvent)
7% protiens (albumin, globulin, clotting proteins, other proteins)
1.5% other (nitrogenous waste, nutrients, ions, gases)
albumin
transport protein, more than half of all proteins in plasma (most abundant protein in plasma)
globulins
round proteins (alpha & beta for transport, gamma for antibodies) (2nd most abundant in plasma)
clotting proteins
11 different proteins, most abundant being fibrinogen (3rd most abundant in plasma)
synthesis site for all plasma proteins except hormones and antibodies
liver
1.5% nitrogenous waste components
urea (protein waste
uric acid (dna/rna waste)
creatinine (musc metabolism waste)
bilirubin ( result of breakdown of RBCs)
homeopoiesis
blood cell formation in red bone marrow
Erythropoiesis
RBC produciton, stimulated by erythoprotein (hormone made in the kidney)
Thrombopoiesis
platelet production, stimulated by thromboprotein (hormone made in liver)
Leukopoiesis
WBC production, stimulated by interleukins, colony stimulating factors
erythropoiesis timeline
1.starter cell(hematopoietic stem cell)
2.myeloid stem cell (fills with hemoglobin, ejects nucleus & most organelles)
3.reticulocyte (young RBC, enters blood, lasts 2 days max)
4.erythrocyte( RBC, no nucleus or organelle, circulates 100-120 days)
RBC's per microliter of whole blood
4-6 million
average reticulocyte count
1-2%
jaundice
liver unable to process bilirubin, body turns yellow
RBC life cycle
1.erythropoeisis (in red bone marrow)
2.reticulocyte (young RBC, 1-2 days)
3.mature RBC (100-120 days, no organelles)
4.spleen disassembles hemoglobin
WBC facts
<1% of whole blood
5-10k WBCs per microliter of whole blood
funx: immunity, resistance to disease
chars: emigration, chemotaxis, most use phagocytosis
5 WBCs (NLMEB)
Neutrophils (60-70%, most abundant WBC)
Lymphocytes (20-25%, blue nucleus, pale blue ring)
Monocytes (3-8%, kidney nucleus, pale cytoplasm )
Eosinophils (2-4%, red)
Basophils (.5-1%, blue and purple)
differential WBC count
relative abundance of different kinds of WBCs in blood
monoctyes become __________ after emigration
macrophages
platelets
cell fragments
150k-400k per microliter of whole blood
Funx: protection from blood loss
thrombopoiesis steps
1.hematopoietic stem cell
2.myeloid stem cell
3.megakaryocyte
4.platelets
hemostasis (definiton and steps)
sequence to stop bleeding
1.vascular spasm
2.platelet plug forms
3.coagulation
clotting factors
11 proteins made by liver
2 non protein factors: calcium & tissue factor
tissue factor
chemical made by damaged tissue to trigger clotting
intrinsic clotting pathway
many reactions
makes prothrombinase
slow (several minutes)
needs calcium ions
extrinsic clotting pathway
fewer steps, faster (seconds)
makes prothrombinase
needs tissue factor
needs calcium ions
common clotting pathway
after prothrombinase
prothrombin+ prothrombinase = thrombin (active)
thrombin + fibrinogen = fibrin
fibrin mesh + trapped blood cells =
blood clot
TPA
tissue plasminogen activator
(breaks down blot clots)
plasmin function
breaks down clots
thrombus
clot in vessel wall
embolus
clot circulating in blood
embolism
clot blocks flow in vessel
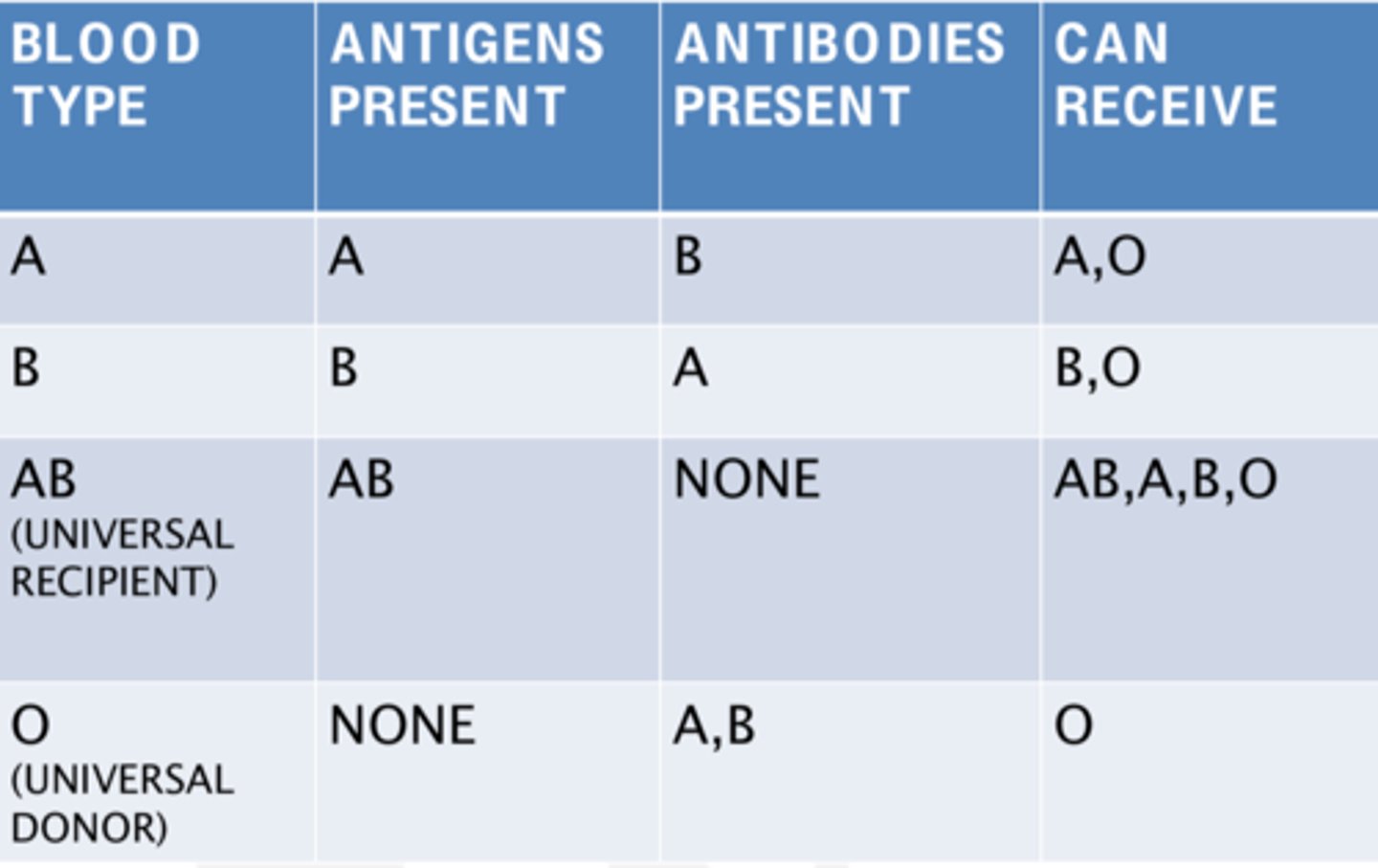
Agglutination
Clumping of RBCs due to antigen-antibody reaction.
Blood groups
A, B, AB, O, & RH factors
universal donor blood type
O-
universal recipient blood type
AB+
hemolytic disease of the newborn
RH+ fetus attacked by antibodies from RH- mom
Anemia
low o2 carrying capacity
HIV
destroys T cells
lymphatic system funx
drains excess interstitial fluid
transports dietary lipids
carries out immune responses
lymph
interstitial fluid leaked from capillaries
lymph flow
Lymphatic Capillaries --> Lymphatic Vessels --> Lymphatic Trunks --> Lymphatic Ducts --> Subclavian Veins (blood stream)
right lymphatic duct
drains right upper arm and right side of head and upper chest
thoracic duct
drains lymph from the left side of the head, neck, chest, abdomen, left arm, and lower extremities
MALT
Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue
- tonsils
- peyers patches
- appendix
other malt
-respiratory tract
-urinary tract
-reproductive tract
primary lymphatic organs
where lymphocytes become immunocompetent
red bone marrow and thymus (B & T cells)
secondary lymphatic organs
where immune response happens
lymph nodes, spleen
thymus
only lymphatic organ made of epithelial tissue (T cell training site)
spleen
largest lymphatic organ
fetus RBC production
reticular connective tissue
innate immune system
non specific
general purpose
born with it
Adaptive Immune System
targets specific pathogens
only B & T cells
long term protection
B cells
humoral immunity, protects body fluid
T cells
cell-mediated immunity, targets specific infected cells
1st line of defense (physical barriers)
skin and mucous membranes
2nd line of defense (internal)
phagocytes
non phagocytes
anti microbial proteins
inflammatory response
fever
phagocytes
a type of cell within the body capable of engulfing and absorbing bacteria and other small cells and particles
neutrophils
monocytes
macrophage
non phagocytes
eosinophils and natural killer cells
natural killer cells (NK)
cells that kill foreign or infected cells without antigen-antibody interaction
releases perforins, causing attacked cell to become leaky ending in lysis
lysis
cell leaks out contents
compliment proteins
group of at least 20 plasma proteins circulating in the blood in an inactive state, produced by liver. they assemble into a tube that penetrates cell membrane
stimulates histamine release
interferons
interferes with viral and bacterial reproduction
can be made by infected cells spreading to neighboring cells
Inflammatory Response
nonspecific defense reaction to tissue damage caused by injury or infection
signs: redness, heat, swelling, pain
fever
triggered by pyrogens released by WBCs during fight
pyrogens go to hypothalamus increasing temperature
higher body temp makes chemical reactions quicker and increases iron retention away from pathogens
3rd line of defense
B cells and T cells, can produce memory cells for long term protection against known pathogens
self tolerant
ability to respect healthy body cells
t cell adhesion proteins
cd8: cytotoxic, cell killers t cell
cd4: helper t cell
humoral immunity
specific immunity produced by B cells that produce antibodies that circulate in body fluids, lymph nodes, spleen, or malt
activation of B cell
Antigen receptor binds to foreign antigen in body fluid, takes several days
Proliferation of B cell
Rapid cell division of activated b cell
Differentiation of B Cell
develops into two roles
1.most become plasma cells, making specific antibodies
2.few become memory b cells for long term protection
Primary response
first time the immune system combats a particular foreign substance (No memory B cells at start, activation step required)
Secondary response
later interactions with the same foreign substance; faster and more effective due to memory b cells already present, makes more plasma than primary
antibody consists of
-4 polypeptide
-"V" region binds to the specific foreign antigen
-"C" region determines antibody class
immunoglobulins (MADGE)
IgM (pentamer, largest and first to be made, anti A/B, many antigen binding sites, causes agglutination)
IgA (15%, 2nd most abundant, secreted by mucous membranes in saliva, sweat, milk)
IgD( not very abundant, antigen receptors on B cell)
IgG (80% of antibodies, activates compliment proteins, small in size can cross placenta think RH)
IgE (least abundant, triggers inflammation, binds to basophils/mast cells to release histamine)
mechanisms of antibody action (PLAN)
Precipitation -settles out of solution due to cross linking of antibodies
Lysis- activates compliment proteins, results in destruction
Agglutination- IgMs cause clumping
Neutralization- toxin is surrounded
passive humoral immunity
antibodies not made by own body providing temporary immunity
Ex: antivenom, IgGs from mother to fetus, IgAs in milk from mother to baby
active humoral immunity
own b cells make antibodies and memory cells for longer term immunity
Ex: infection, vaccination
cell-mediated immunity
immune response from t cells
MHC antigens
self-antigens that allow the immune system to recognize own body cells
class 1: on surface of all nucleated body cells
class 2: on surface of antigen presenting cells
APCs
antigen presenting cells
-macrophages, dendritic cells, B cells
-helps activate T cells by presenting antigen on cell surfaces
effector cytotoxic t cells secrete _________
perforins- makes cell leaky, causes lysis
granzymes- chemical that causes body cell to self destruct
polycythemia
excess RBCs that increase blood viscosity
Thrombocytopenia
low platelet count, reduces clotting ability
sickle cell anemia
a genetic disorder in which erythroctyes take on an abnormal curved or "sickle" shape
immunodeficiences
Immune systems that are inadequate or inefficient, congenital and aquired conditions that cause immune cells, phagocytes, or complement to behave abnormally (AIDS, SCID)
autoimmune disorders
Immune system attacks body's own tissues
multiple sclerosis (MS)
type 1 diabetes
rheumatoid arthritis
Hypersensitivities
inappropriate or overactive immune response resulting in host damage
asthma
anaphylactic shock
blood group incompatibilities
transfusion reaction, hemolytic disease of the newborn