Reactive oxygen species
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Where are reactive oxygen species produced?
Mainly mitochondria
Lipoxygenases (LOX)
Cyclooxygenases (COX)
oxygen reduction chain into free radicals from the electron transport chain
Oxygen O2 +e-
superoxide radical O2• + e-
Superoxide dismultase (SOD)
Hydrogen peroxide H2O2 + e-
Catalase
Hydroxyl radical •OH + e-
Water H2O
What is a free radicals?
Unpaired e- → highly reactive
What other ways can •OH be produced and why are they bad?
ionising radiation
UV
X rays/ gamma rays
Cause haemolytic in red blood cells + damage DNA
cannot be eliminated by an enzyme system
How does the body neutralise free radicals?
Antioxidants (endogenous and exogenous)
Name the endogenous antioxidants
Enzymatic : SOD, catalase, PRDX, GPX
Non-animatic: glutathione (water soluble) coenzyme Q10 (lipid soluble)
Small molecule: glutathione + PRDX
Large molecule: SOD, catalase, GPX
Exogenous antioxidants
Vit C (peppers, strawberry, broccoli etc)
Vit E (nuts, seed, veg oil)
Carotenoids (carrot, tomato, spinach)
What is the structure of glutathione and how does it act as an antioxidant?
Gly-Cys-Glu
Thiol (SH) group donates an e- to R.O.S + reacts with another glutathione forming a disulphide bond with the enzyme glutathione peroxidase
How are R.O.S helpful?
Phagocytes synthesise and store free radicals to use against pathogens
Gene transcription
Skin cell differentiation
Induction of mutagenic response
What is oxidative stress?
Unbalance between the production and accumulation of R.O.S in cells and the ability of the body to detoxify it
What can oxidative stress lead to?
Lipid peroxidatjon → damage cell engraves
DNA damage → mutation
Protein modification
What happens in oxidative burst?
NADPH oxidase rapidly release superoxide and hydrogen peroxide from cells (usually leukocytes like neutrophils and monocytes)
Rapid release kills pathogens locally
How is chronic granulotamous disease caused?
Mutation → defective phagocyte NADPH oxidase → cannot do oxidative burst
** x- linked disorder
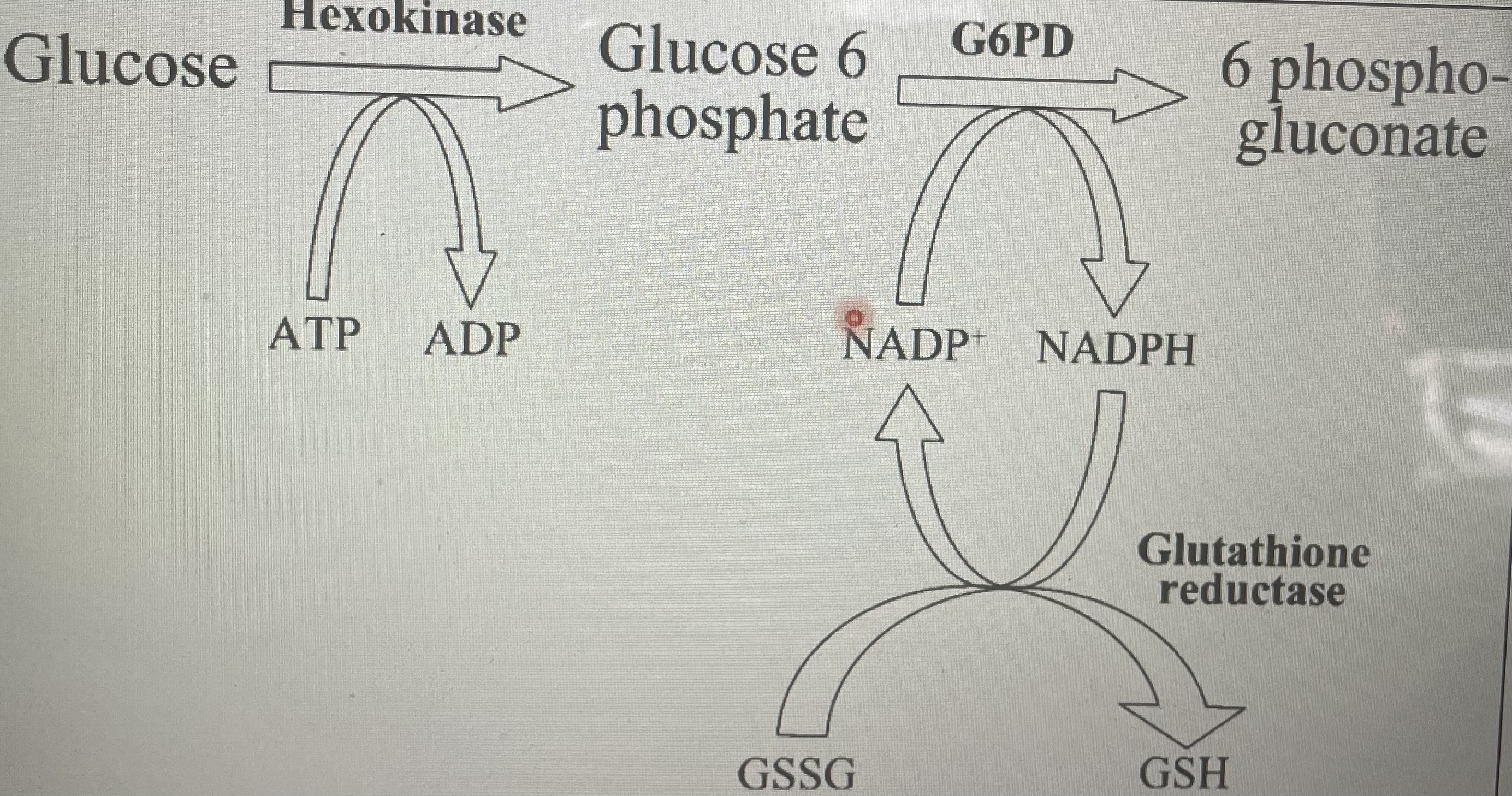
G6PDH deficiency
x-linked
Reduced production of NADPH
Reduced ability to recycle oxidised glutathione back to reduced glutathione
Form Heinz bodies
Triggers: bacterial/ viral infections, antibiotics/anti-malaria, fava beans(broad beans)
How does an paracetamol (acetaminophen) cause death + what is a treatment option for its overdose?
Accumulation in NAPQI → uses up glutathione → oxidative stress
Treatment: acetylcysteine