Organic Reactions and Conditions
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Reduction of an alkyne to a Z-alkene:
Lindlar’s catalyst, H2
Reduction of an alkyne to an E-alkene:
Na, NH3(l)
Oxymercuration or hydroboration of an alkene affords an …
alcohol
Oxymercuration affords the … substituted alcohol
more
Hydroboration affords the … substituted alcohol
less
Oxymercuration of an alkene:
Hg(OAc)2, H2O in THF
NaBH4
Hydroboration of an alkene:
H-BR2
H2O2, NaOH
cis-dihydroxylation of an alkene:
OsO4, NMO, H2O
acetone or tert-butanol
Epoxidation of an alkene:
mCPBA
Opening of an epoxide:
H2O and H+
OR
H2O and OH-
trans-dihydroxylation of an alkene:
mCPBA
H2O with either OH- or H+
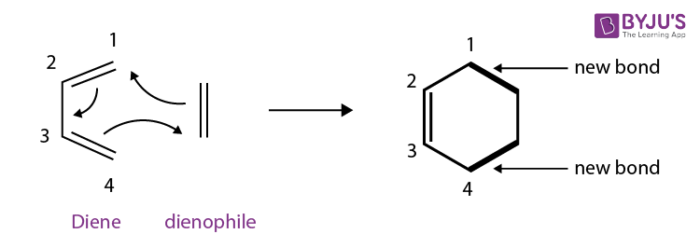
Diels-Alder reaction mechanism:
diene
dienophile
heat
Oxymercuration or hydroboration of an alkyne affords an …
enol
The enol formed from oxymercuration or hydroboration of an alkyne … to form either an … or a …
tautomerises, aldehyde, ketone
Wittig reaction:
phosphorus ylid reacts with carbonyl compound, affords an alkene
room temperature or gently heat
Elimination of an alkene to form an alkyne:
strong base (e.g. LDA)
Ozonolysis of an alkene to form an aldehyde or ketone:
O3, CH2Cl2
Zn, HCl or Ph3P or Me2S
-78°C
Ozonolysis of an alkene to form a carboxylic acid:
O3, CH2Cl2
H2O2
-78°C