lung and colorectal
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
NSCLC Staging and general treatment
Stage I: no lymph node involvement
Surgery +/- radiation
Stage II: lymph node involvement
Surgery + adjuvant chemotherapy +/- radiation
Stage IIIA: early-stage
surgery, radiation, and pharmacotherapy
Stage IIIB: Advanced disease, usually unresectable
Chemoradiation + adjuvant chemotherapy +/- targeted agents
Stage IV: Advanced disease, unresectable tumor
Chemotherapy and radiation
Metastatic or recurrent disease (treatment failure) is based on biomarkers
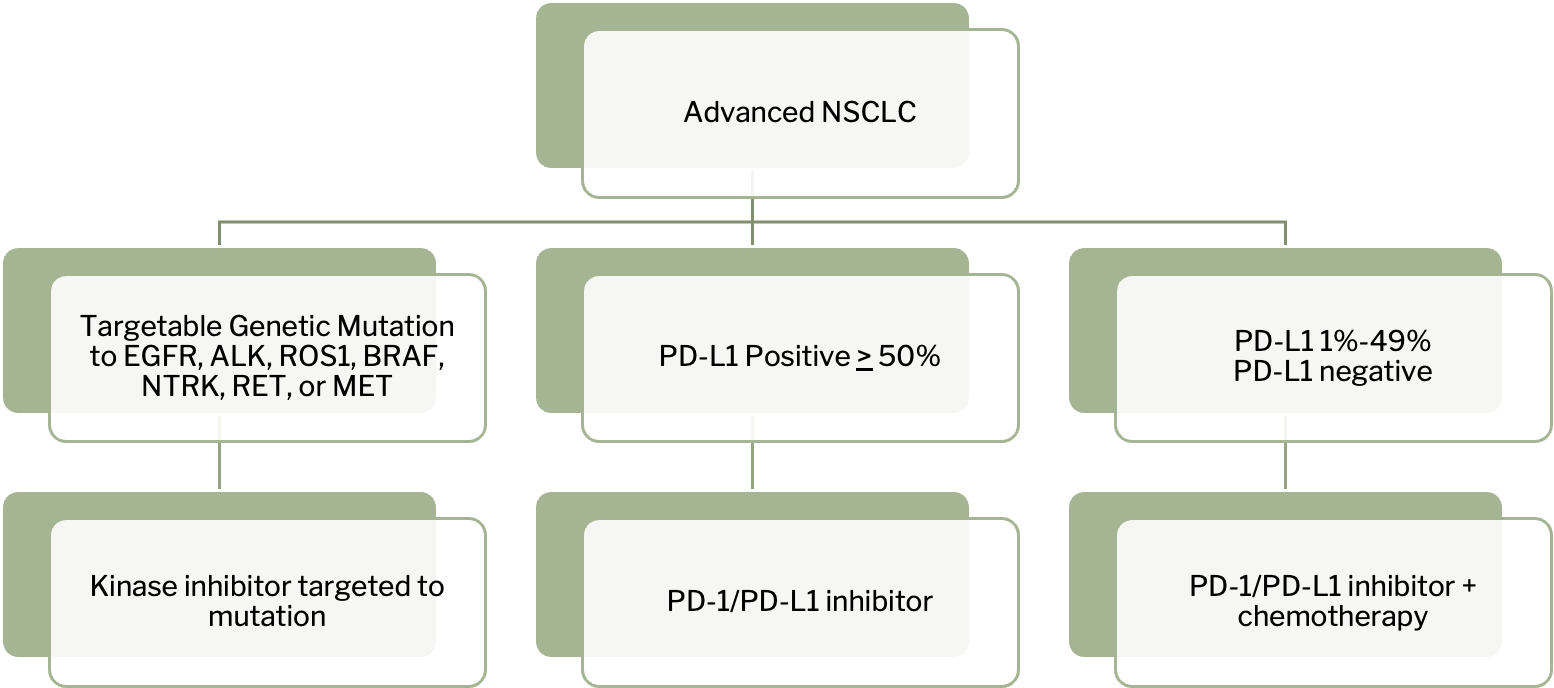
EGFR TKIs
osimertinib, erlotinib
EGFR TKI ADE
•Common: acneiform rash, diarrhea, anorexia, fatigue
•Rare/Severe: Interstitial lung disease
Erlotinib clinical pearls
•take on empty stomach (with food increases absorption/toxicity risk)
•DDI with warfarin- increased bleeding risk
ALK TKIs
alectinib, crizotinib (both orally administered)
ALK TKI ADE
•Common: leukopenia, fatigue, hepatotoxicity
•Rare/Severe: Interstitial lung disease
PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors
pembrolizumab, ipilimumab, nivolumab, atezolizumab, durvalumab
PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors MOA
•cancer cells try to evade the immune system by overexpressing PD-L1. PD-1 or PD0L1 inhibitors allows the T cells to remain active and destroy cancer cells.
PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors ADE
•Immune related toxicities: colitis, hepatitis, pulmonary toxicity (pneumonitis), nephrotoxicity, thyroid disorders, myocarditis, encephalitis, endocrinopathies (hyperglycemia), fatigue
•Immune related toxicities may require interruption or permanent discontinuation of treatment, also treated with steroids
Common lung cancer chemotherapy regimens
•cisplatin plus gemcitabine x 4-6 cycles
•(cisplatin or carboplatin) plus etoposide × 4-6 cycles
•(cisplatin or carboplatin) plus pemetrexed +/- pembrolizumab x 4 cycles
•(cisplatin or carboplatin) plus paclitaxel +/- pembrolizumab x 4 cycles
SCLC Treatment
Initially very sensitive to chemotherapy and radiation, response rate up to 90%
Cisplatin-etoposide with concurrent radiation best clinical data for limited stage
Patients with extensive disease should have immunotherapy (atezolizumab or durvalumab) added to chemotherapy
Carboplatin or cisplatin + etoposide + durvalumab x 4-6 cycles
Carboplatin or cisplatin + etoposide + atezolizumab x 4-6 cycles
If the patient achieves a complete remission from concurrent chest radiation and chemotherapy, prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) is recommended because the development of brain metastases is greater than 30% for SCLC.
colorectal cancer screening
Age: begin at 45 years old for average risk people
Methods:
Stool test: fecal immunochemical testing (FIT)
Looks for presence of blood in stool
Structural examination: Colonoscopy
Requires extensive bowel preparation and procedural sedation
Examines entire colon and rectum, can remove adenomatous polyps during procedure
Frequency:
FIT test: annually
Colonoscopy: every 10 years (can be more often if increased risk
CRC Treatment Overview
•Stage I: surgery
•Stage II: surgery +/- adjuvant chemotherapy
•Stage III: surgery + adjuvant chemotherapy
•Stage IV:
+/- neoadjuvant chemotherapy + surgery
chemotherapy
Common CRC chemotherapy regimens
•CAPEOX: capecitabine, oxaliplatin
•FOLFOX: leucovorin, oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil
•FOLFIRI: leucovorin, fluorouracil, irinotecan
•FOLFIRINOX: leucovorin, fluorouracil, irinotecan, oxaliplatin
Leucovorin roles
•Leucovorin is folinic acid (‘FOL’ in regimens)
•Leucovorin reduces toxicity for high dose methotrexate
•Reduces toxicity by providing a source of folic acid to healthy cells
•Started 24 hours after last dose of methotrexate
•Low dose: 15mg IV/PO Q6 hours x 3 days
•Leucovorin enhances cytotoxicity for fluorouracil
•Given alone, fluorouracil has short half life, adding leucovorin improves the binding of 5FU to an enzyme within cancer cell and increases half life
•Also increases ADEs (mucositis, hand/foot syndrome/diarrhea)
•High dose: 400mg/m2 given concurrently with 5-FU over 2-hour infusion
VEGF mAbs
bevacizumab
bevacizumab MOA
inhibits angiogenesis, an important step in tumor growth
bevacizumab ADE
infusion related reactions, hypertension, bleeding, thromboembolism, impaired wound healing, proteinuria, GI perforation
bevacizumab pearl
Wait until at least 4-6 weeks after surgery to initiate (to allow wound healing)
EGFR mAbs
cetuximab, panitumumab
EGFR mAb MOA
inhibits of cell growth, induces of apoptosis
EGFR mAbs ADE
infusion related reactions, acneiform rash, electrolyte abnormalities
EGFR mAb PGx
test for EGFR and KRAS gene expression, must be KRAS wild type to use
Rectal Cancer
Similar therapies as colon cancer (surgery and chemotherapy) except for emphasis on radiation or chemoradiation (chemotherapy + radiation) as standard modality in treatment