PLTW Medical Interventions Midterm
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
what are the categories of medical interventions?
pharmacology, rehab, genetics, medical devices, diagnostics, surgery
What is bioinformatics?
the application of computational methods to the storage and analysis of biological data
How can DNA sequences be used to identify disease pathogens?
can determine specific segments of DNA that differ between different types of pathogens and analyze this segment by following a similar sequencing pattern
what are the basic steps for isolating and identifying bacterial DNA
1- isolate the DNA of the pathogen using PCR. Only copies DNA from the invader
2- cycle sequencing takes the copied DNA and creates DNA fragments of different lengths and separates them by size
3- organize fragments based on size. Florescent DNA goes through a laser
What is a serial dilution?
A stepwise dilution of a substance in solution
Explain the process of ELISA
step 1- sample is added to the wells. Proteins bind to the walls of the wells
step 2- detergent washes out unbound proteins and blocks surface proteins
step 3- primary antibody binds to a specific antibody
step 4- unbound primary antibody is washed away
step 5- secondary antibody that is linked with an enzyme is attached and added to walls and binds to the primary antibody
step 6- excess secondary antibody is washed away
step 7- substrate is added to the wells. The substrate binds to the enzyme bound to the secondary antibody and causes a color change
What is the mode of action of penicillin?
interferes with ability to synthesize cell. (attacks cells walls)
what is the mode of action of tetracycline?
binds to the ribosomes and halts protein production
what is the mode of action of floroquinoles?
messes up DNA replication
what is the mode of action of sulfonamides?
interferes with synthesis of folic acid
What is antibiotic resistance?
when the medicine no longer affects the bacteria because they are immune to it.
conjugation?
A pilius bridge forms. Plasmid duplicates and is transferred to another cell via the bridge
transformation?
naked DNA floats around and is picked up by other cells
Transduction?
phages infect bacteria bringing along genes of other cells that have resistance
What is sensorineural hearing loss?
hearing loss caused by damage to the cochlea's receptor cells or to the auditory nerves
What is conductive hearing loss?
hearing loss that is due to diminished sound reaching middle and inner ear.
Live attenuated vaccines
virus is weakened but still able to reproduce and cause an immune response in the body
Inactivated vaccines
dead bacteria injected into patient to build immunity
toxiod vaccine
vaccine is made from a toxin that is weakened so body can learn how to fight it off
DNA vaccines
create recombination by inserting microbial DNA into plasmid vector
subunit vaccines
use antigenic fragments to stimulate an immune response
How are vaccines produced?
Small weakened or dead viruses are injected into the body to produce antibodies, so they next time your body is attacked by the same virus your body fights it off without you even knowing that you contracted it.
What is DNA ligase?
connects the ends of molecules together
What are restriction enzymes?
They cut the DNA into specific parts
How can recombinant DNA be used to produce vaccines?
Bacteria carry DNA in plasmids. Plasmids work as vectors and have genes inserted into them. Recombinant DNA uses restriction enzymes to cut the plasmids and leave sticky ends. These ends can bond with any DNA cut by THE SAME restriction enzyme. The viral gene is inserted into the plasmid and glued together by DNA ligase. The new DNA can have resistance which makes it beneficial to vaccination
single gene recessive disorders
Must have 2 copies of the gene. (cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia)
Single gene - dominant disorder
disorder that is controlled by the inheritance of a single gene, must have at least 1 dominant allele
multifactorial disorders
conditions caused by interactions among one or more genes and the environment
chromosomal disorders
disorders caused by structural changes to a chromosome or deficiencies of entire genes located on chromosomes
Mitochondrial disorders
caused by mutations in non-chromosomal DNA which is passed from mother to child (LHON)
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)
In assisted reproductive technology, the determination of genetic abnormalities in the embryo before it is transferred to the uterus
fetal testing
Used to determine the possibility of a genetic disorder by taking a sample of fetal cells.
what are the ethical concerns of PDG and Fetal testing
throwing away life or trying to have the best child possible. In the future could lead to "designer babies"
How do genetic counselors use pedigrees?
show the history of the trait in the parents family and why they have what they have
why is there apprehensiveness to genetic testing?
might not want to know what you may have in the future such as Alzheimer's
what are the duties of genetic counselors
Analyze patient histories.
Provide genetic testing.
Perform genetic risk calculations.
Educate families about potential health risks.
Help patients to cope with a diagnosis
What is amniocentesis?
the sampling of amniotic fluid using a hollow needle inserted into the uterus, to screen for developmental abnormalities in a fetus.
what is CVS (chorionic villus sampling)
sampling of placenta to screen for abnormalities in a fetus
What is a karotype?
map of chromosomes; shows the sex and defects
How are karyotypes used in prenatal health
show sex of the baby and any chromosomal disorders
What is an ultrasound in pregnancy
a test that uses sound waves to make a video image of an unborn baby
What is an ultrasound?
medical test to show images from inside your body
What is gene therapy?
the transplantation of normal genes into cells in place of missing or defective ones in order to correct genetic disorders.
What is gene therapy used for?
Replace/Repair defected gene that is causing disease
Provide new or changed function to a cell
what are the advantages of using vectors in gene therapy?
deliver new gene by infecting cells without causing any real disease.
what are the disadvantages of using vectors in gene therapy?
Can cause immune responses
what factors must be considered when choosing a vector for gene therapy?
How many base pairs it can hold and which cells it will integrate to
What is PGD?
When a healthy embryo is selected from a group of embryos, and then implanted into a uterus.
What is IVF (in vitro fertilization)?
Procedure where oocytes are harvested and fertilization occurs outside the female body in a lab
What is cloning?
When an organism that is genetically identical to the organism from which it was produced.
what are the parts of the ear?
outer ear, middle ear, inner ear
what part of bacteria helps is stick to surfaces?
pilus
what part of bacteria helps it move?
flagella
what controls the cells activities?
cell membrane
what is the function of the ribosomes?
make proteins
whats the inside of the cell
cytoplasm
what is a plasmid?
small circular piece of DNA
bacterial cells
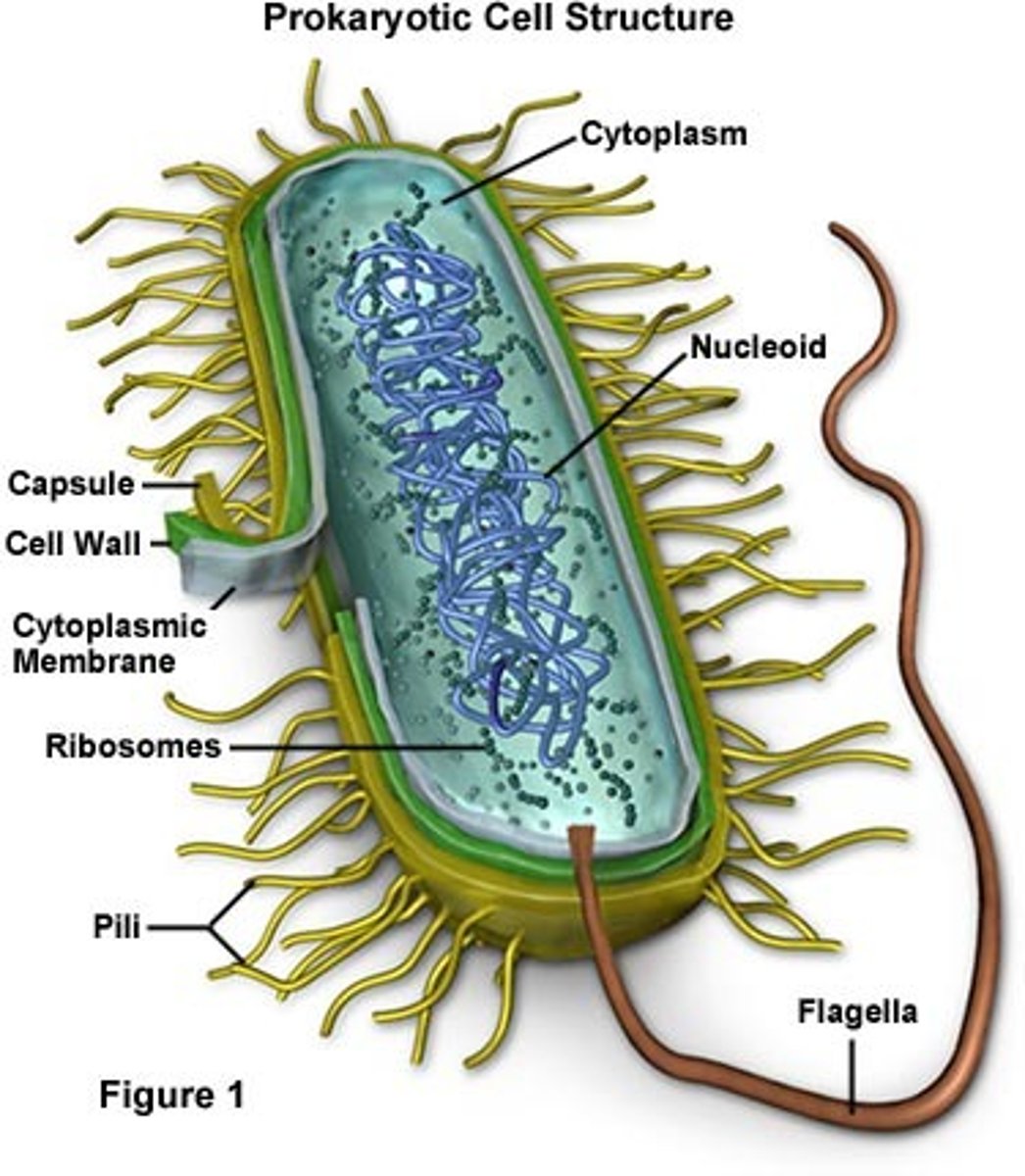
allows bacteria to attach to specific proteins?
capsule
Gram-positive bacteria
Bacteria that have a thick peptido glycan cell wall, and no outer membrane. They stain very darkly (purple) in Gram stain.
Gram-negative bacteria
type of bacteria that stain red with Gram stain and have a thin cell wall with an outer membrane
What is the nucleiod region?
where dna is stored
what is the key transmission of sound?
vibration
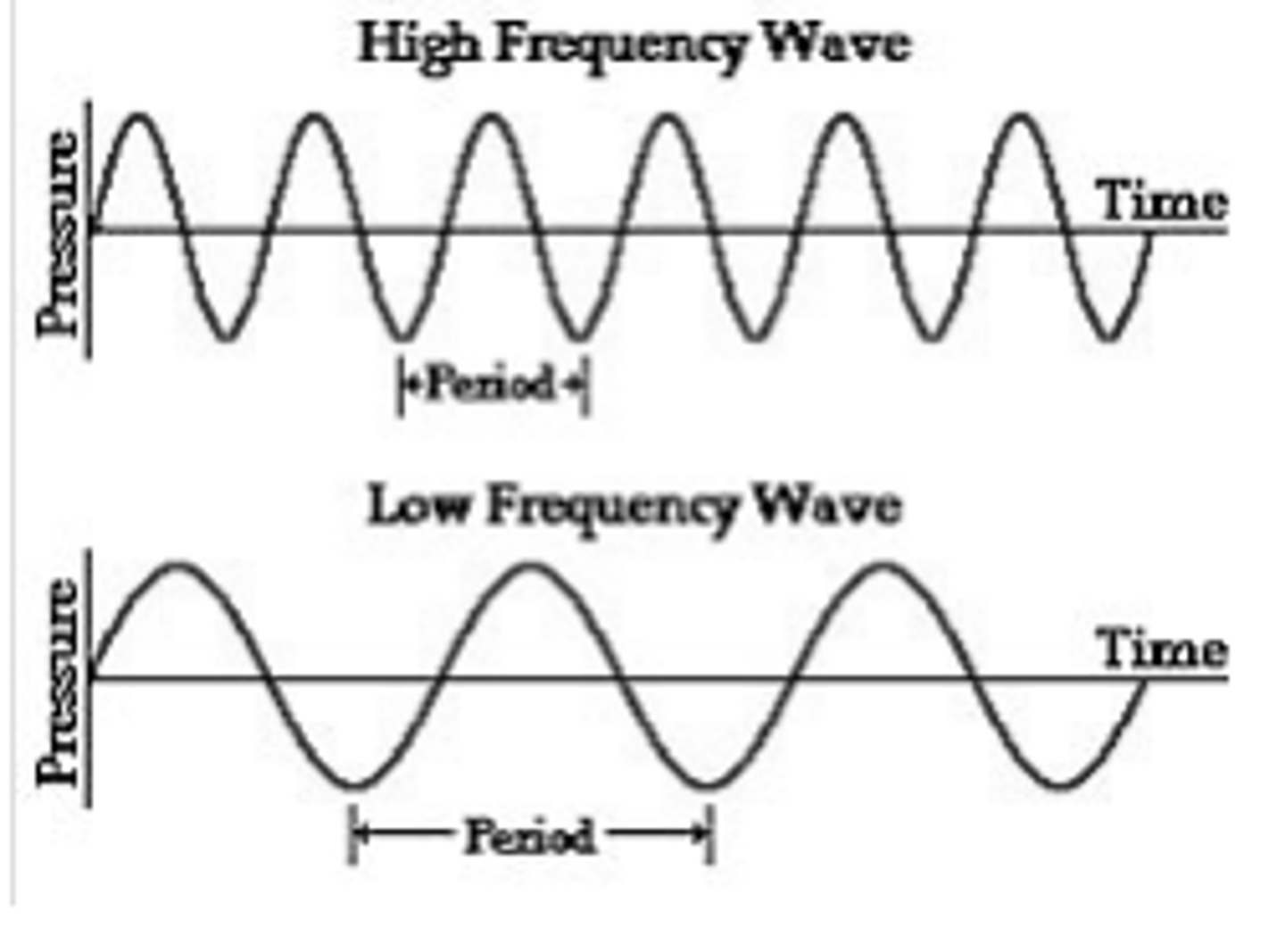
What is frequency?
number of waves per second, measured in hertz
What is high frequency?
fast short waves
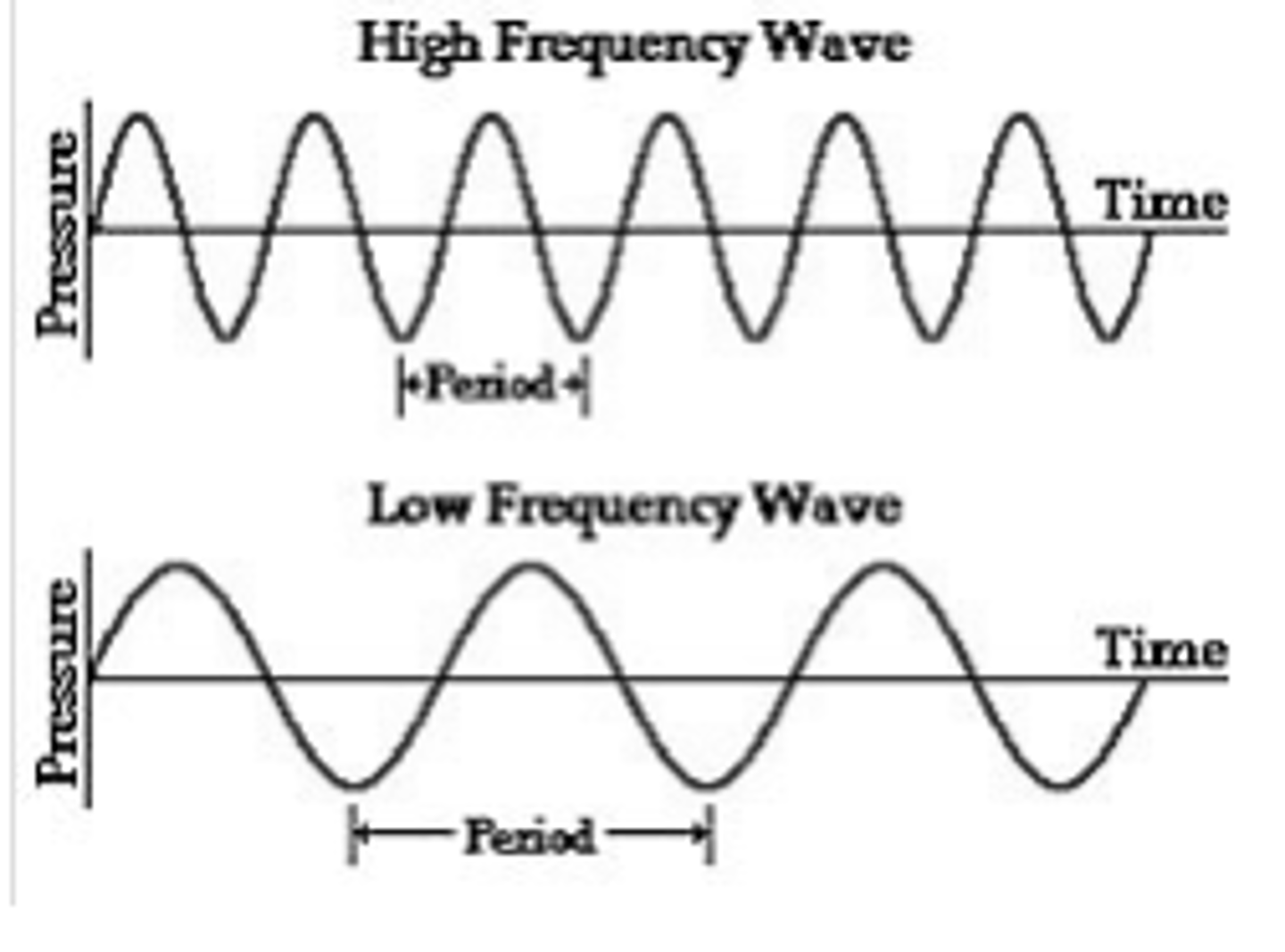
What is low frequency?
slow long waves
what is the inner ear?
the innermost part of the ear, containing the cochlea, semicircular canals, and vestibular sacs. Vestibular nerve helps with balance
What is the middle ear?
the small cavity(tympanic cavity) behind the tympanic membrane that contains 3 bones (the malleus, the incus, and the stapes). small cavity helps transmit vibrations
what is the outer ear?
pinna and auditory canal. funnels vibrations to auditory canal.
steps of hearing
1-sound waves enter the ear and cause vibrations in the ear drum
2-vibrations in the eardrum cause the bones in the middle ear to move back and forth
3- movement against the oval window causes movement in the fluid that fills the cochlea
4- movement of hairs in the cochlea stimulate an impulse among the auditory nerve to the brain.