Lecture 9 Gluconeogenesis
1/159
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Oh gosh wisheth me luck
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
160 Terms
What is gluconeogenesis?
The synthesis of glucose from non carbohydrate precursors
What are the phases of glucose use over time?
Absorptive phase, postabsorptive phase, early starvation, intermediate starvation, then prolonged starvation
The postabsorptive phase is when what pathway is activated?
Glycogenolysis (since the exogenous carbon source is depleted)
What pathway is activated at some point in the early starvation phase?
Gluconeogenesis (since glycogen levels are decreasing)
What pathways are activated in intermediate starvation?
Ketogenesis and beta oxidation of fats
Why is gluconeogenesis activated during starvation?
To keep critical organs functional by making glucose from alternate sources
What is the overall reaction for gluconeogenesis from pyruvate?
2 Pyruvate + 2 NADH + 4 ATP + 2 GTP + 6 H2O + 2H+ → Glucose + 2 NAD + 4 ADP + 2 GDP + 6 Pi
Does gluconeogenesis need more energy than the ATP directly produced by glycolysis?
YES
What process gives fuel for gluconeogenesis?
Beta oxidation of fats in the liver
Gluconeogenesis happens in situations where there is no?
Glucose
Any molecule that can be converted to pyruvate can be considered as?
Glucogenic
What are some non carbohydrate carbon sources that can be used for gluconeogenesis?
Pyruvate, lactic acid, oxaloacetate, glycerol, certain amino acids, so on
What are glucogenic molecules?
Molecules that can be used to make glucose (aka can feed into gluconeogenesis)
What enzymes catalyze reactions in gluconeogenesis and glycolysis?
Phosphoglucose isomerase, Aldolase, Triose phosphate isomerase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) dehydrogenase, Phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK), Phosphoglycerate mutase, and Enolase
What are the bypass steps in gluconeogenesis?
Pyruvate → Oxaloacetate (catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase)
Oxaloacetate → PEP (catalyzed by PEP carboxykinase)
F1,6-BP → F6P (catalyzed by fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase)
G6P → Glucose (catalyzed by glucose 6-phosphatase)
What are the enzymes involved in bypass steps in glycolysis?
Hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase
What are bypass steps?
Steps that are not reversible between two opposite pathways (ex. glycolysis and gluconeogenesis)
Not reversible, exergonic, unidirectional steps
What enzymes are most likely inhibited when glycolysis is favored over gluconeogenesis?
PEP carboxykinase and pyruvate carboxylase
What is the first bypass reaction in gluconeogenesis?
Pyruvate is converted to oxaloacetate by pyruvate carboxylase using biotin as a cofactor and ATP as an energy source
What step in gluconeogenesis is anaplerotic for the TCA cycle and what molecule does it replenish?
1st step (Pyruvate to OAA) replenishes OAA
What is the cofactor for pyruvate carboxylase?
Biotin
Pyruvate carboxylase is allosterically activated by what molecule?
Acetyl CoA
Where does the first step of gluconeogenesis take place?
In the mitochondrial matrix
Where does the second step of gluconeogenesis take place?
IN the cytosol
What does PEPCK stand for?
PEP carboxykinase
In fasting, the synthesis of what gluconeogenic enzyme increases?
PEPCK
What is step 2 of gluconeogenesis?
Oxaloacetate is phosphorylated and converted into PEP by phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) using a phosphate from either 1 ATP or 1 GTP
What is the source of phosphate groups for PEP carboxykinase?
ATP or GTP
Is the conversion of pyruvate into oxaloacetate during gluconeogenesis metabolically reversible?
NO it isn’t reversible
What is biotinylation?
The covalent attachment of biotin to an enzyme
Carbon is added to a substrate at what site in a carboxylase?
The C acceptor site
What are the steps of gluconeogenesis?
Pyruvate is reduced to OAA by Pyruvate carboxylase (using 1 ATP for energy and biotin as cofactor)
OAA is phosphorylated to get PEP by PEP carboxykinase (using 1 ATP or 1 GTP as phosphate source, releasing 1 CO2)
PEP undergoes hydration to get 2PG by Enolase
2PG is isomerized to 3PG by Phosphoglycerate mutase
3PG is phosphorylated to get 1,3BPG by Phosphoglycerate kinase
1,3BPG is reduced to G3P by G3P dehydrogenase
DHAP from glycerol processing is converted into G3P by Triose phosphate isomerase
2 molecules of G3P are rearranged into F1,6BP by Aldolase
F1,6BP is dephosphorylated to get F6P by Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
F6P is isomerized to G6P by phosphoglucose isomerase
G6P is dephosphorylated to get Glucose by glucose 6-phosphatase
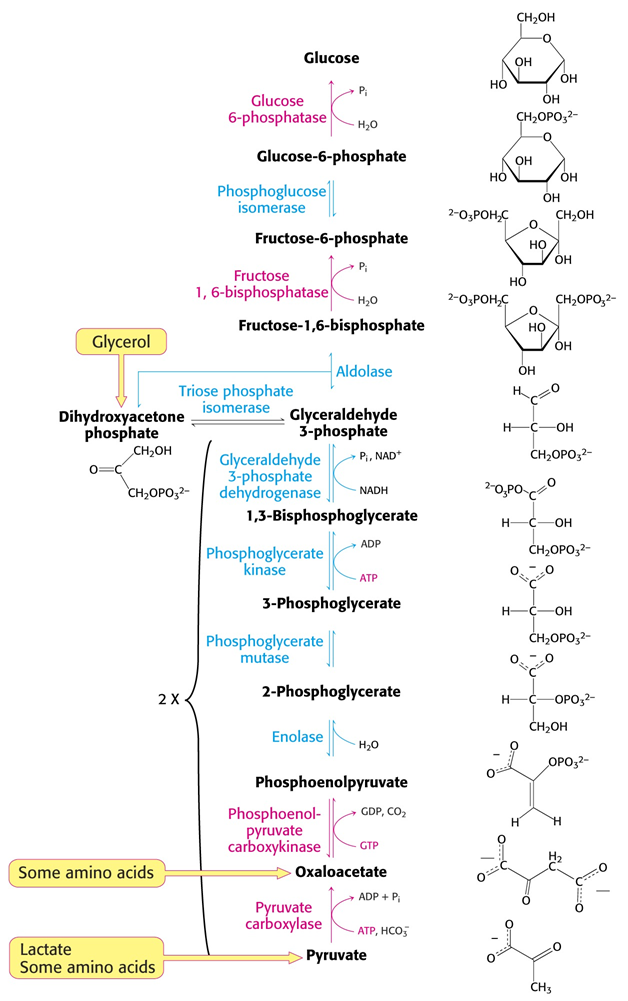
What is dephosphorylation?
The hydrolysis of a phosphate group to remove said phosphate group from a substrate (usually done by phosphatases)
What enzyme converts G6P to glucose?
Glucose-6-phosphatase
What enzyme converts F6P to G6P?
Phosphoglucose isomerase
What enzyme converts F1,6BP to F6P?
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
What enzyme converts G3P to F1,6BP?
Aldolase
What enzyme converts DHAP to G3P?
Triose phosphate isomerase
What enzyme converts 1,3BPG to G3P?
G3P dehydrogenase
What enzyme converts 3PG to 1,3BPG?
Phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK)
What enzyme converts 2PG to 3PG?
Phosphoglycerate mutase
What does PGK stand for?
Phosphoglycerate kinase
What molecule does pyruvate carboxylase use as an energy source?
ATP
What enzyme converts PEP to 2PG?
Enolase
What enzyme converts oxaloacetate to PEP?
PEPCK (PEP carboxykinase)
What enzyme converts pyruvate to oxaloacetate?
Pyruvate carboxylase
Name the major reactants, intermediates, and products of the gluconeogenesis of pyruvate?
Pyruvate + ATP + HCO3- or CO2 → Oxaloacetate + ADP + Pi
Oxaloacetate + ATP or GTP → PEP + ADP or GDP + CO2
PEP + H2O → 2PG
2PG → 3PG
3PG + ATP → 1,3BPG + ADP
1,3BPG + NADH → G3P + Pi + NAD+
DHAP → G3P
2x G3P → F1,6BP
F1,6BP + H2O → F6P + Pi
F6P → G6P
G6P + H2O → Glucose + Pi
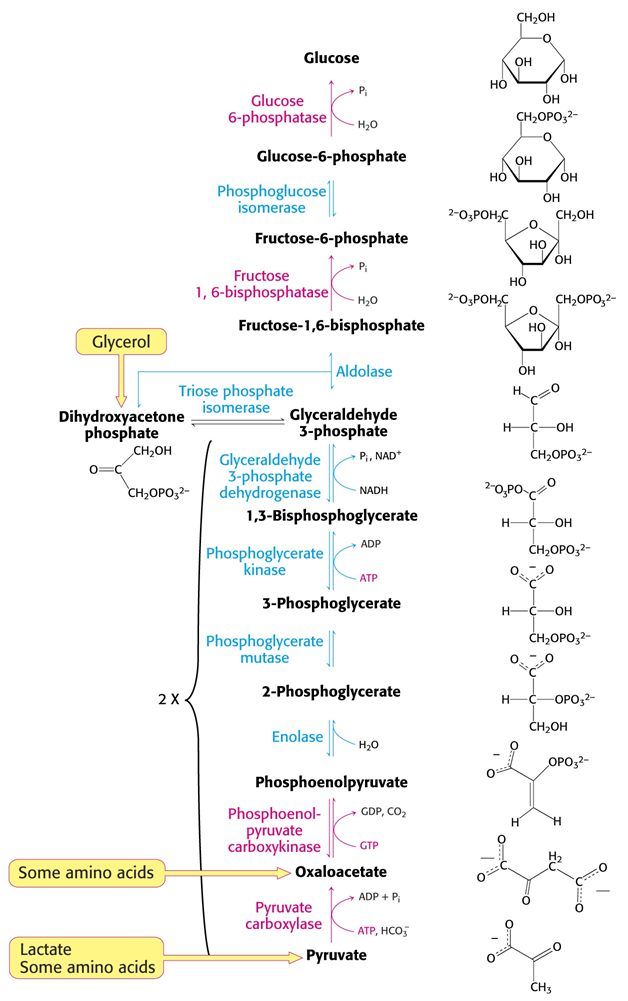
What step in gluconeogenesis releases 1 CO2?
2nd step: OAA to PEP catalyzed by PEPCK
Where does gluconeogenesis happen?
Trick question: it happens in the mitochondria (step 1) then the cytosol (rest of the steps)
Can oxaloacetate exit the mitochondria?
NO
Is the a mitochondrial oxaloacetate transporter?
NOPE
Oxaloacetate must be converted into what molecule to exit the mitochondria?
Malate
Is there a malate shuttle in the mitochondria?
YES
How does oxaloacetate exit the mitochondria during gluconeogenesis?
Oxaloacetate is reduced to malate by malate dehydrogenase
Malate leaves the mitochondria via a malate transporter
Malate is oxidized to oxaloacetate by malate dehydrogenase
Is oxaloacetate reduced or oxidized to malate?
REDUCED
What enzyme reduces oxaloacetate to malate?
Malate dehydrogenase (Malate DH)
What enzyme oxidizes malate to oxaloacetate?
Malate dehydrogenase
Malate dehydrogenase is found where in the cell?
Trick question: It’s in the cytosol and the mitochondria
Is the dephosphorylation of F1,6BP metabolically reversible?
NO!
What does F1,6BPase stand for?
Fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase
What molecules allosterically inhibit F1,6BPase?
AMP and F2,6BP
The third bypass reaction in gluconeogenesis is catalyzed by?
F1,6BPase
What gluconeogenic enzyme opposes the activity of PFK1?
F1,6BPase
What do phosphatases do to their substrate?
They dephosphorylate their substrate using water to hydrolyze the substrate phosphate group bond
If F1,6BPase is active, what enzyme must be inhibited?
PFK1
Is the hydrolysis of G6P to Glucose metabolically reversible?
NOPE
Glucose-6-phosphatase is only found in what organs?
Main ex: liver, kidney
Possible ex: pancreas, and small intestine
Tissues from what organs are the only ones that can convert G6P to glucose?
Mainly: Liver, kidney
Possibly: pancreas, and small intestine
What is the final bypass step in gluconeogenesis?
G6P → Glucose (hydrolysis by glucose-6-phosphatase)
What is G6P a precursor for?
Glycogen and glucose synthesis
Glucose-6-phosphatase is highly regulated in what organ?
Liver
Is gluconeogenesis endergonic or exergonic?
ENDERGONIC
Is an input of energy needed to synthesize glucose?
YES, an input of energy is needed
What are the 4 mechanisms controlling flux through glycolysis/gluconeogenesis?
Allosteric control
Covalent modifications
Substrate cycles aka Futile cycles
Genetic control via regulation of enzyme concentrations (control transcription/translation)
Flux through a pathway is controlled at what type of steps?
Rate limiting steps
In the liver, what two pathways are reciprocally regulated?
Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
What pathway does insulin stimulate in the liver?
Glycolysis
What pathway does glucagon stimulate in the liver?
Gluconeogenesis
High energy molecules generally stimulate what pathway in the liver?
Gluconeogenesis
Low energy state indicators generally inhibit what pathway in the liver?
Gluconeogenesis
What molecules are indicators of a high energy state in the liver?
TCA cycle intermediates (ex. citrate, acetyl CoA), high ATP concentrations
What molecules are indicators of a low energy state in the liver?
AMP, ADP, F2,6BP
What is a futile cycle?
Two opposing steps in two pathways (that, if both pathways are running, result in a cyclic process between the two opposing steps)
What are the enzymes in the futile cycle example for glycolysis and gluconeogenesis?
PFK1 and FBPase-1
What does a 1 after the enzyme name (ex. enzyme-1) stand for?
That the enzyme catalyzes a metabolic step
What does a 2 after the enzyme name (ex. enzyme-2) stand for?
That the enzyme regulates the metabolic enzymes
What is the isomeric form of F1,6BP?
F2,6BP
Is F2,6BP a metabolically intermediate in glycolysis or gluconeogenesis?
NONE, it ain’t in either pathway
What pathway is favored if F2,6BP levels are high?
Glycolysis
What enzyme does F2,6BP activate?
PFK1
What enzyme does F2,6BP inhibit?
FBPase-1
F2,6BP is what type of regulator?
Allosteric regulator
What enzymes regulate F2,6BP levels?
PFK2 and FBPase2
What effect does PFK2 have on F2,6BP levels?
Favors forming more F2,6BP so increases F2,6BP levels?
What effect does PFK2 have on PFK1 and FBPase1?
Increases F2,6BP levels, which promotes PFK1 activation and inhibition of FBPase1
Does PFK2 favor glycolysis or gluconeogenesis?
Glycolysis
What effect does FBPase2 have on F2,6BP levels?
FBPase2 reduces F2,6BP levels by dephosphorylating F2,6BP
What effect does FBPase2 have on FBPase1 and PFK1?
Decreases F2,6BP levels by dephosphorylating F2,6BP to make F6P, which decreases promotion of PFK1 activity and decreases inhibition of FBPase1
Does FBPase2 favor glycolysis or gluconeogenesis?
Gluconeogenesis
What enzyme phosphorylates FBPase2 and PFK2?
PKA