Psych 253 - Lecture 4: Social Cognition and Heuristics pt. 2
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
schema
A schema is a mental model or representation that organizes the
important information about a thing, person, or event
Heuristic
A heuristic is a mental shortcut or rule
of thumb that reduces complex mental
problems to more simple rule-based
decisions.
Heuristics are necessary because
humans have bounded rationality:
people try to make rational choices but
are bounded by their cognitive
limitations (e.g., lack of information,
limited working memory, etc.)
Automatic & Controlled Processing
On Auto-pilot: Automatic Thinking
• We often size up a new situation very quickly
• Often these quick conclusions are correct
• E.g.—You can tell the difference between a college classroom
and a frat party without having to think about it
• E.g., You can tell if two people are a romantic couple or just
friends
• Imagine a different approach: slow and deliberate
thinking
• Imagine driving down the road and stopping repeatedly to
analyze every twist and turn.
• Imagine meeting a new person and excusing yourself for 15
minutes to analyze what you learned from them
• Schemas and heuristics are great examples of
automatic thinking; so, we know that automatic
thinking can often yield good judgments but not always
Accessibility and Priming
Accessibility is the extent to which schemas are at the
forefront of people’s minds and are therefore likely to be
used when we are making judgments about the social
world
Priming is the process by which recent experiences
increase the accessibility of a schema or concept
A schema or concept can be accessible for three main reasons:
Chronically accessible due to past experience (cocktail party - name)
Accessible because it is related to a current goal (eg. hungry)
Temporarily accessible because of our recent experience (priming)
A Note About Priming (challenges)
The kinds of priming studies that don’t replicate typically report
that some fairly minimal/subtle prime of a concept leads to a
behavioral or belief change
• The old age and walking speed study falls in this category
• Many “embodied cognition” findings, like the idea that holding a hot
drink increases warmth in social interactions
• Committing moral violations or reading about them (i.e., being primed)
leads people to physically cleanse themselves by washing hands or
using disinfectant
• Placing money in front of people makes them endorse capitalism and
the free market more
For the currency-related stimuli, it seems
that, as people tried to replicate these
results more and more often, also with
larger sample sizes and more rigorous
methods (in line with the Open Science
movement), the sizes of the effects
more-or-less shrank into nothingness
• It is not the case that this means that priming is “untrue” as an
entire concept!
• Priming concepts like gender and race absolutely changes more
modest DVs, like reaction times and error rates
• Priming can also change how people evaluate ambiguous stimuli
• Priming can influence how easily we are able to recall events
(memory effects)
• Anchoring and adjustment is highly robust and is a form of
priming
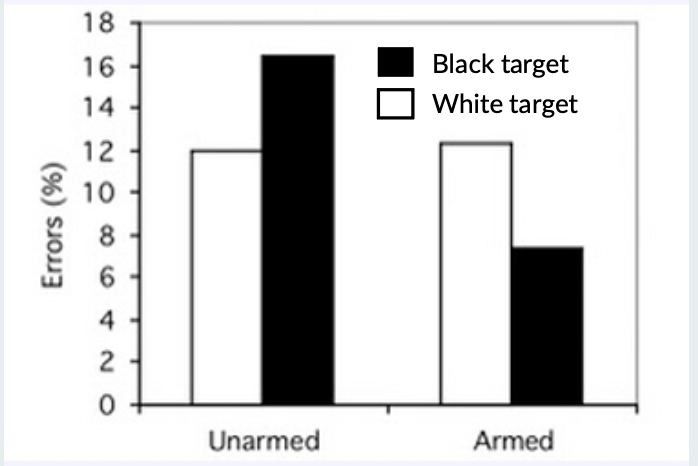
Priming Stereotypes - Shooter task
Participants brought into the lab to play a simple computer game
IV #1: If you seen an armed target (e.g., gun), choose to “shoot” as quickly as possible If you see an unarmed target (e.g., wallet), choose to “not shoot” as quickly as possible
IV #2: The people holding the objects were either Black or White
DVs: % of trials in which the answer is wrong;
IVs:
▪ Race of target: Black v. White
▪ Object: Weapon v. Neutral
▪ Ps asked to quickly decide whether to “shoot” or “not shoot”
▪ DVs: Reaction times and error rate
When applied to members of a
social group such as race, gender,
political parties, religious groups,
etc., schemas are commonly
referred to as stereotypes
Momentary v. Retrospective Measures (Gender stereotypes)
• Independent variables (IVs): IV* #1: Gender (Women vs. Men) - *Pseudo-IV (can’t assign)
• IV #2: Type of measure
Global
Momentary/Live
• DV: level of emotions reported
How would you react to all of these emotions throughout the day? - some given a survey (self report) , some asked to click a button when they feel it through day
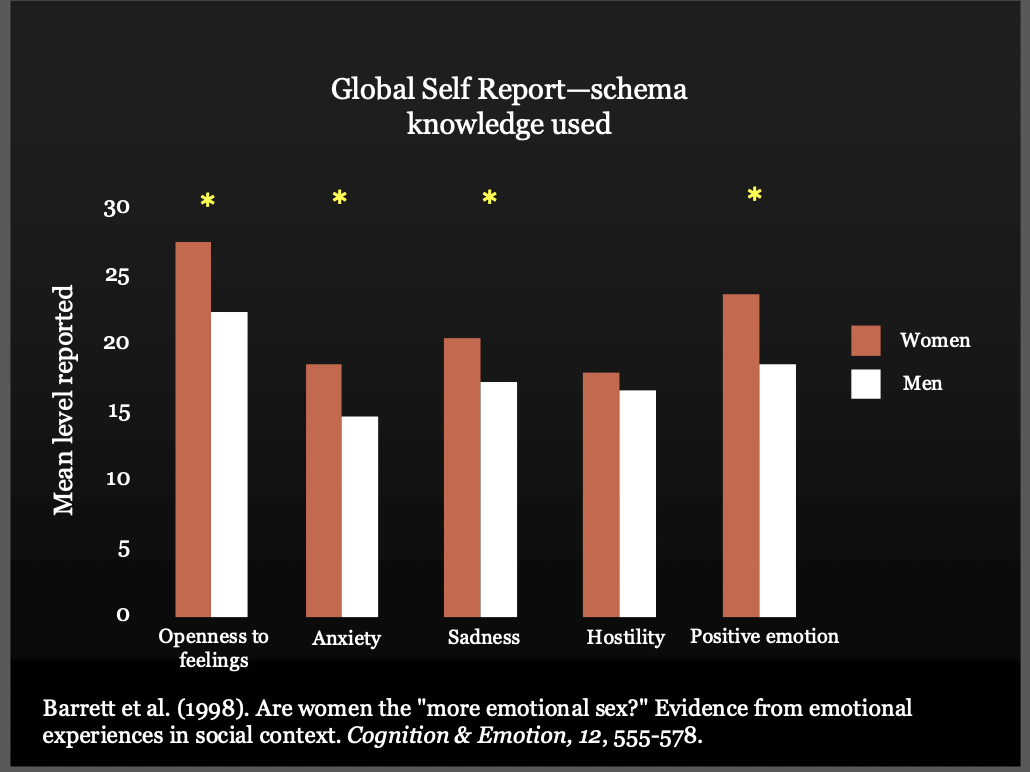
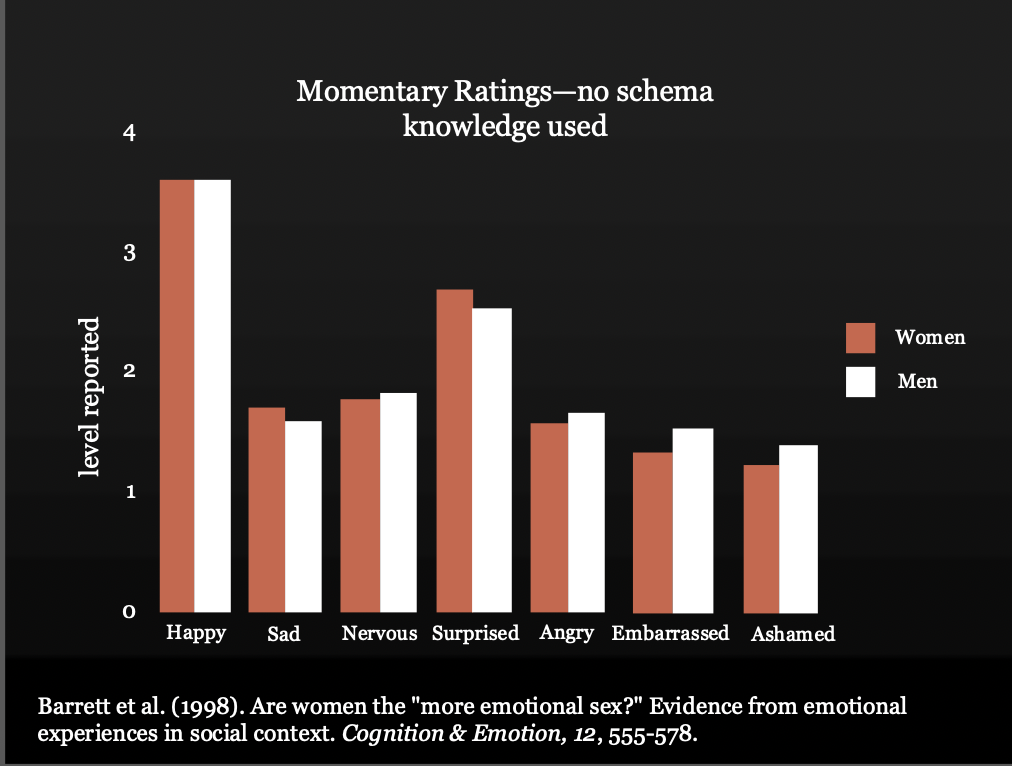
In the one when they are clicking button, no schema/bias involved, men and women were not that different.
Planning fallacy (how to mitigate) + Overconfidence definitions
• The planning fallacy describes how people underestimate the
amount of time a task is going to take
• Kind of a big deal when it comes to university!
• A useful strategy for counteracting the planning fallacy: break tasks
down into smaller portions/units and estimates will be more accurate
Overconfidence describes how people how people have greater
confidence in their judgments than is warranted by a controlled
or rational assessment
if you ask people if they would be able to explain how household appliances work, they prob say yes and then when you ask them to do it, they can’t do it.
Strategies for Improving Outcomes - Automatic thinking (opt-in/ opt out)
In domains in which it is very important, it can be possible to
identify that automatic thinking or heuristics are leading to bad
outcomes, then effortfully substitute more controlled decision-
making to reach better outcomes
Changing the environment (rather than trying to change people) can increase positive outcomes in aggregate
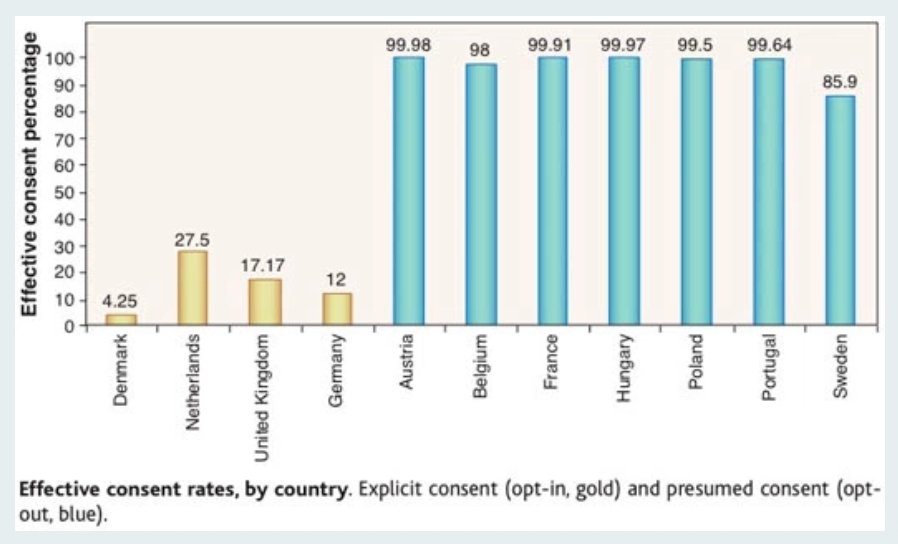
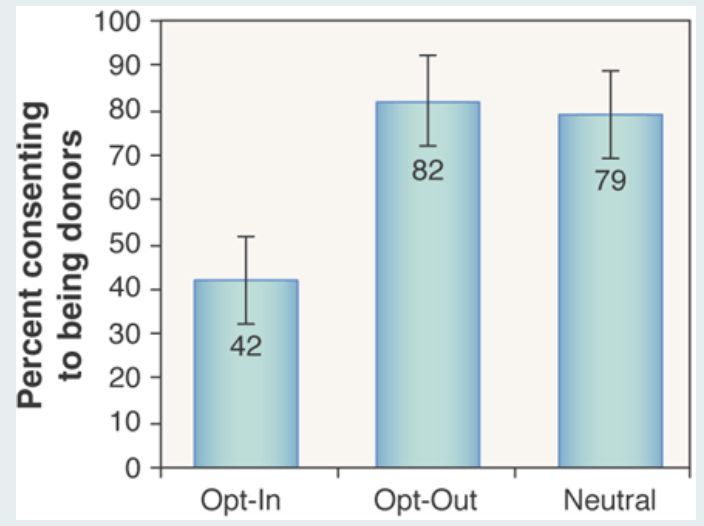
People tend to go with whatever is the default so better to have an Opt-out system than an Opt-in